Characterization and Valorization of the Microalgal Co-Product Spirugrass®: Protein Profile, Iron Speciation, and Potential Use as a Supplement for Honeybees
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of Spirugrass® and Comparison with Algal Biomass
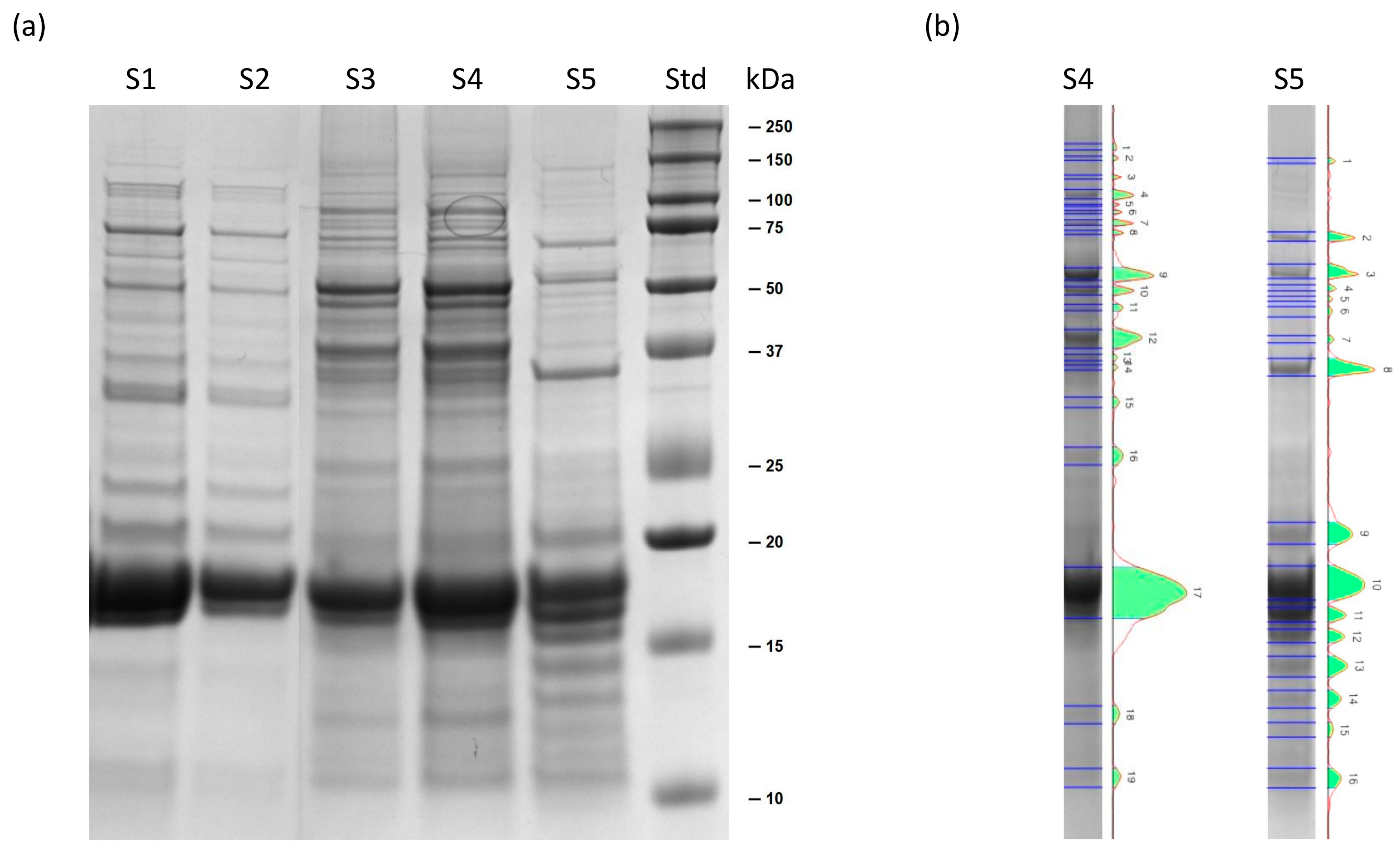
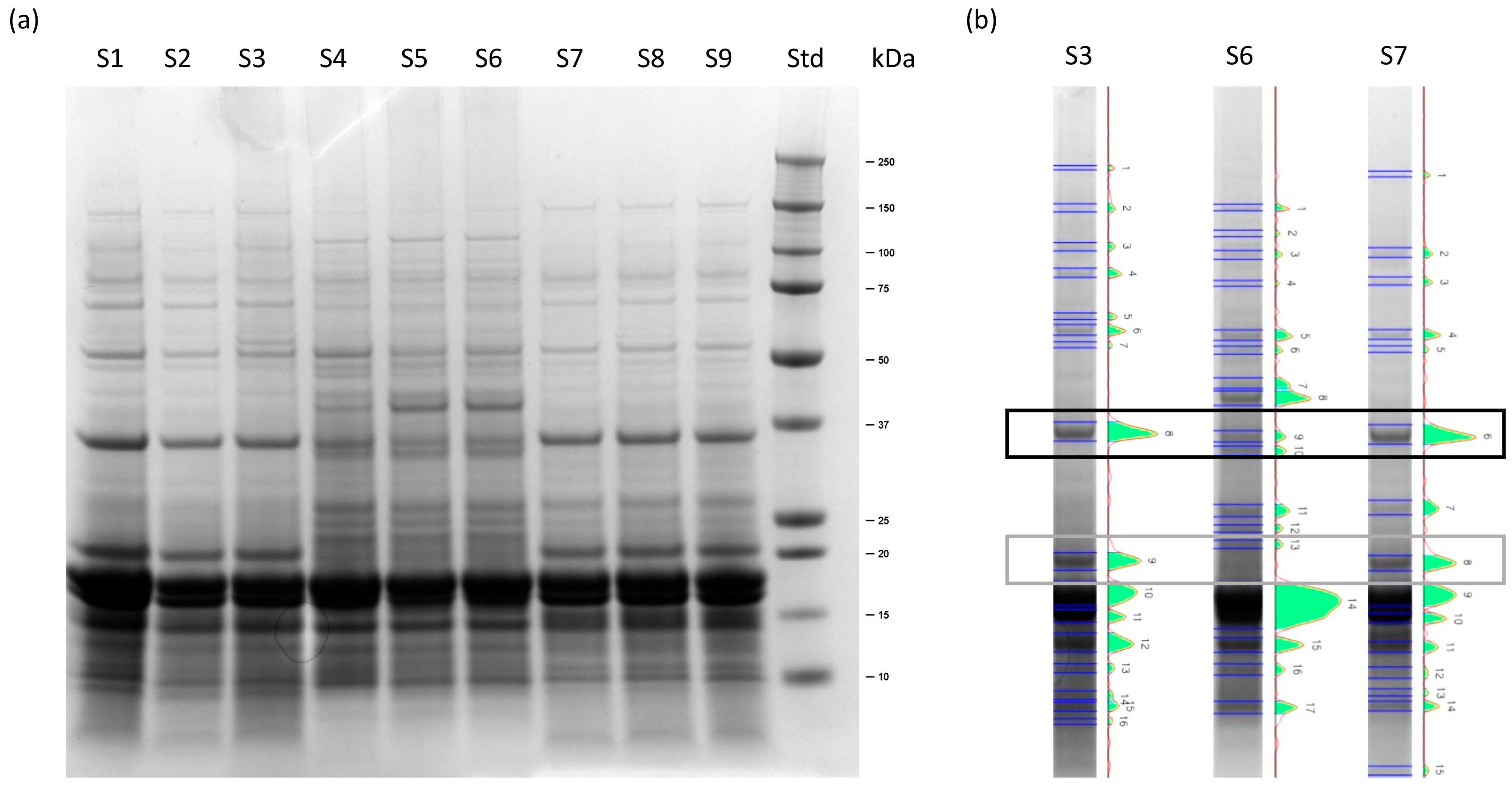
2.1.1. SDS-PAGE of Soluble Extracts
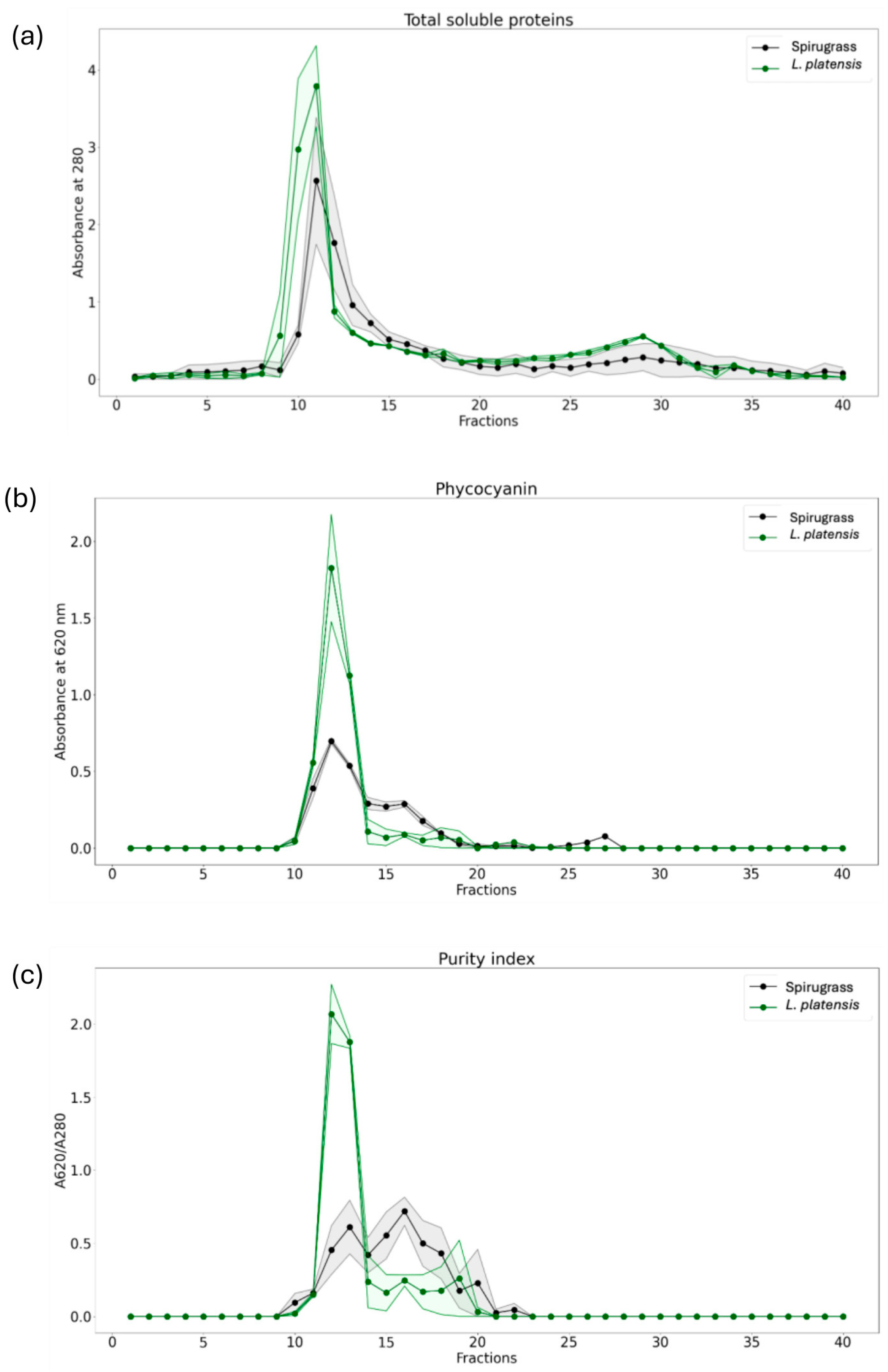
2.1.2. Size Exclusion Chromatography
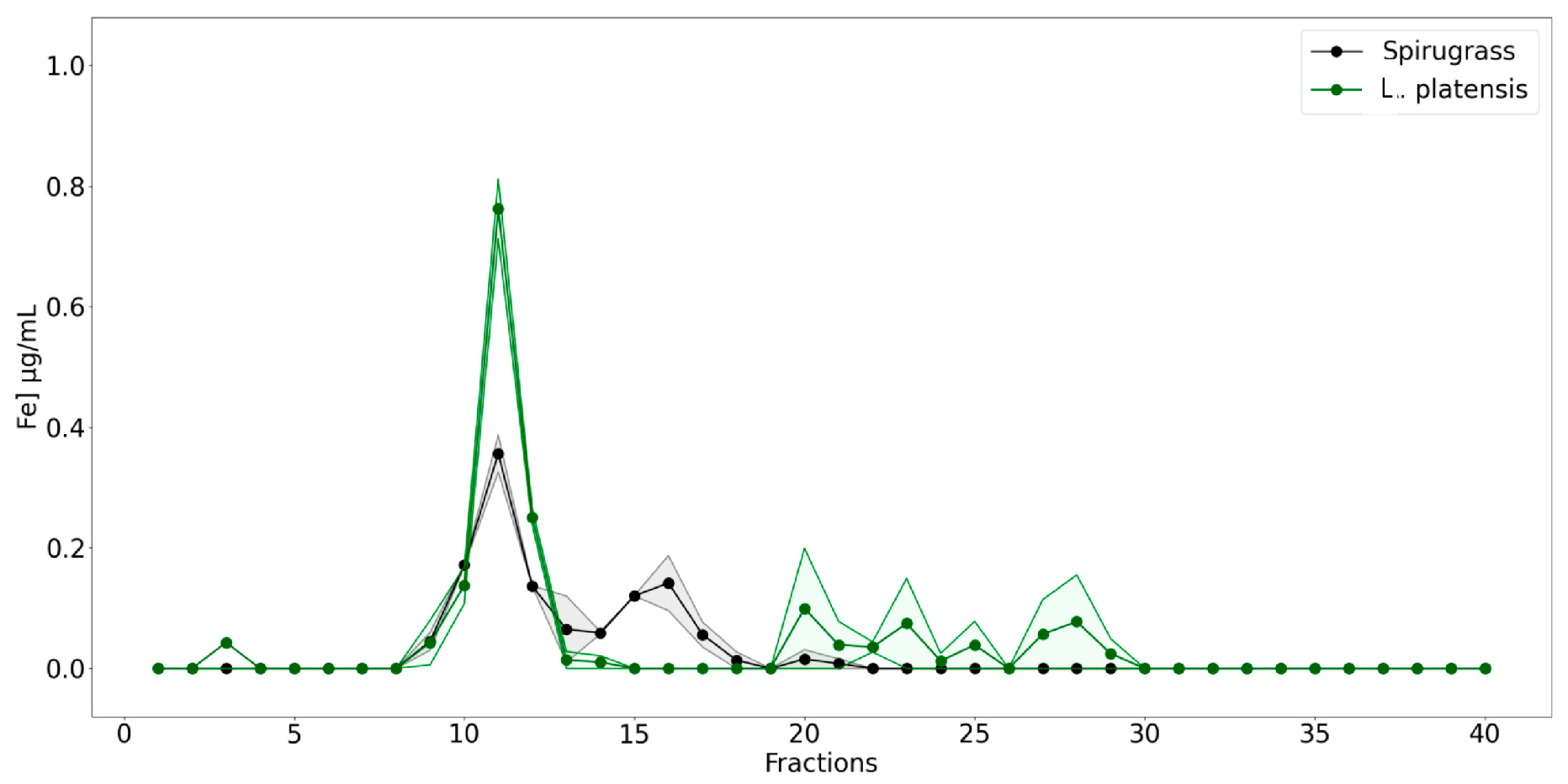
2.1.3. Iron Content and Speciation
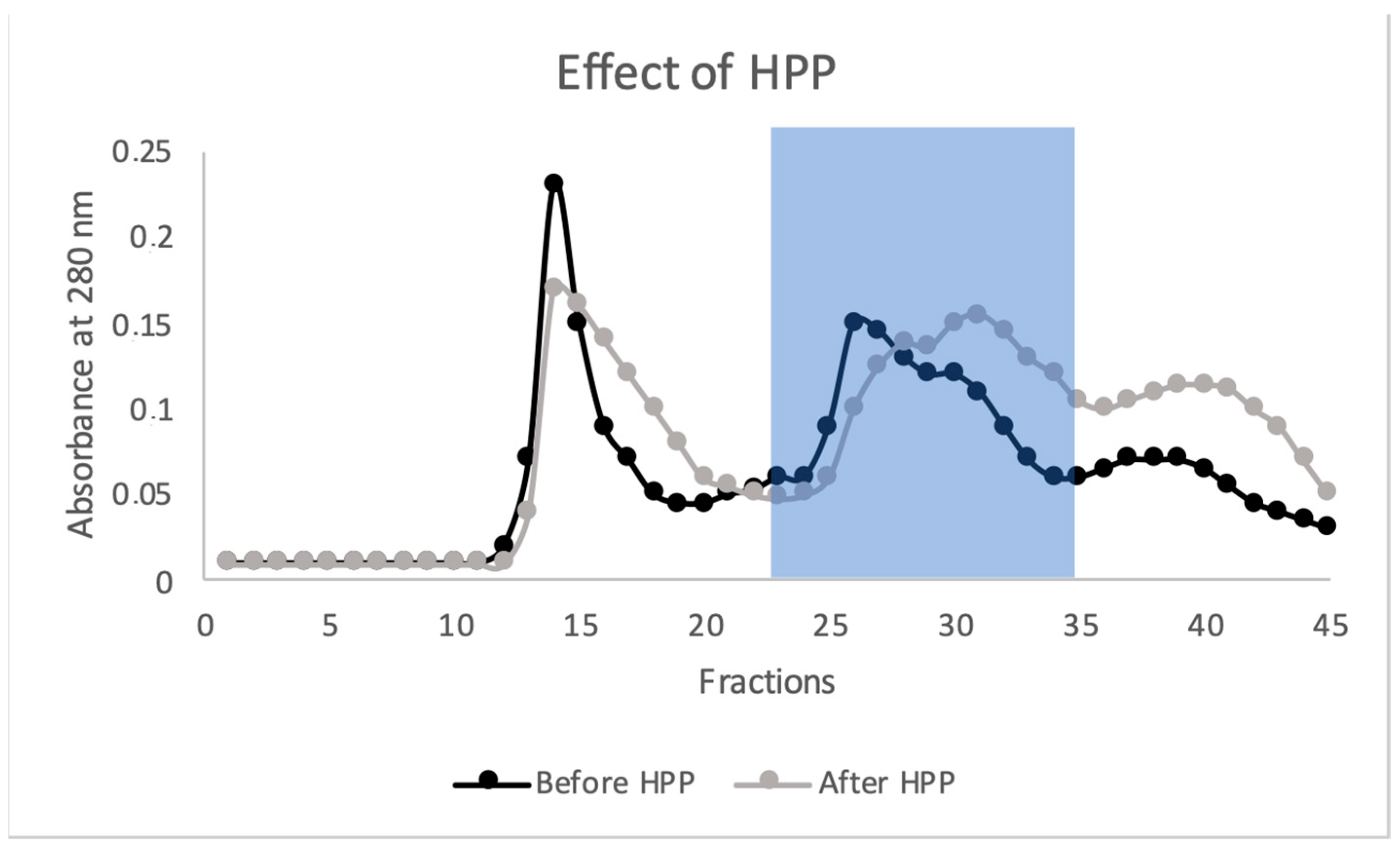
2.2. Effect of HPP on Spirugrass® Proteins
2.3. Possible Application of Spirugrass® as a Nutritional Supplement for Honeybee Health
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Characterization of Spirugrass® and Comparison with the Algal Biomass
3.2. Soluble Protein Extraction from Algal Samples and Iron Quantification
3.2.1. SDS-PAGE of Protein Extracts
3.2.2. Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC)
3.2.3. Iron Analysis Using Atomic Absorption Spectrometry
3.3. HPP Treatment
3.4. Effect of HPP on Spirugrass® Proteins
3.5. Honeybees and Experimental Feeding Trial
3.5.1. Hemolymph Total Protein Determination
3.5.2. SDS-PAGE of Proteins in Honeybee Hemolymph
3.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Habib, M.A.B.; Parvin, M.; Huntington, T.C.; Hasan, M.R. A Review on Culture, Production and Use of Spirulina as Food for Humans and Feeds for Domestic Animalsand Fish. FAO Fish. Aquac. Circ. 2008, 1034, 33. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva Vaz, B.; Moreira, J.B.; de Morais, M.G.; Costa, J.A.V. Microalgae as a New Source of Bioactive Compounds in Food Supplements. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2016, 7, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spínola, M.P.; Mendes, A.R.; Prates, J.A.M. Chemical Composition, Bioactivities, and Applications of Spirulina (Limnospira Platensis) in Food, Feed, and Medicine. Foods 2024, 13, 3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira de Oliveira, A.P.; Bragotto, A.P.A. Microalgae-Based Products: Food and Public Health. Futur. Foods 2022, 6, 100157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadaoui, I.; Rasheed, R.; Aguilar, A.; Cherif, M.; Al Jabri, H.; Sayadi, S.; Manning, S.R. Microalgal-Based Feed: Promising Alternative Feedstocks for Livestock and Poultry Production. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 12, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, B.J.; Ricigliano, V.A. Uses and Benefits of Algae as a Nutritional Supplement for Honey Bees. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2022, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, C.M.M.; Bastos, T.S.; Santos, M.C. dos Microalgae Use in Animal Nutrition. Res. Soc. Dev. 2021, 10, e53101622986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmonte, T.; Vecchiato, C.G.; Biagi, G.; Fabbri, M.; Andreani, G.; Isani, G. Iron Bioaccessibility and Speciation in Microalgae Used as a Dog Nutrition Supplement. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isani, G.; Ferlizza, E.; Bertocchi, M.; Dalmonte, T.; Menotta, S.; Fedrizzi, G.; Andreani, G. Iron Content, Iron Speciation and Phycocyanin in Commercial Samples of Arthrospira Spp. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union. Commission Regulation (EC) No 2073/2005 of 15 November 2005 on Microbiological Criteria for Foodstuffs. Off. J. Eur. Union 2005, 338, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Nikbakht Nasrabadi, M.; Sedaghat Doost, A.; Mezzenga, R. Modification Approaches of Plant-Based Proteins to Improve Their Techno-Functionality and Use in Food Products. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 118, 106789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasrebi-de Kom, I.A.R.; Biesmeijer, J.C.; Aguirre-Gutiérrez, J. Risk of Potential Pesticide Use to Honeybee and Bumblebee Survival and Distribution: A Country-Wide Analysis for The Netherlands. Divers. Distrib. 2019, 25, 1709–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricigliano, V.A.; Mott, B.M.; Maes, P.W.; Floyd, A.S.; Fitz, W.; Copeland, D.C.; Meikle, W.G.; Anderson, K.E. Honey Bee Colony Performance and Health Are Enhanced by Apiary Proximity to US Conservation Reserve Program (CRP) Lands. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolezal, A.G.; St. Clair, A.L.; Zhang, G.; Toth, A.L.; O’Neal, M.E. Native Habitat Mitigates Feast–Famine Conditions Faced by Honey Bees in an Agricultural Landscape. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 25147–25155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacifici, M.; Foden, W.B.; Visconti, P.; Watson, J.E.M.; Butchart, S.H.M.; Kovacs, K.M.; Scheffers, B.R.; Hole, D.G.; Martin, T.G.; Akçakaya, H.R.; et al. Assessing Species Vulnerability to Climate Change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2015, 5, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.D.; Cameron, A.; Green, R.E.; Bakkenes, M.; Beaumont, L.J.; Collingham, Y.C.; Erasmus, B.F.N.; De Siqueira, M.F.; Grainger, A.; Hannah, L.; et al. Extinction Risk from Climate Change. Nature 2004, 427, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danihlík, J.; Škrabišová, M.; Lenobel, R.; Šebela, M.; Omar, E.; Petřivalský, M.; Crailsheim, K.; Brodschneider, R. Does the Pollen Diet Influence the Production and Expression of Antimicrobial Peptides in Individual Honey Bees? Insects 2018, 9, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alaux, C.; Ducloz, F.; Crauser, D.; Le Conte, Y. Diet Effects on Honeybee Immunocompetence. Biol. Lett. 2010, 6, 562–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geada, P.; Moreira, C.; Silva, M.; Nunes, R.; Madureira, L.; Rocha, C.M.R.; Pereira, R.N.; Vicente, A.A.; Teixeira, J.A. Algal Proteins: Production Strategies and Nutritional and Functional Properties. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 332, 125125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Htoo, N.Y.M.; Kraseasintra, O.; Buncharoen, W.; Kaewkod, T.; Pekkoh, J.; Tragoolpua, Y.; Khoo, K.S.; Chaipoot, S.; Srinuanpan, S.; Pumas, C. In Vitro Immunomodulation Activity of Protein Hydrolysate from Spirulina (Arthrospira Platensis): The Ingredient of Future Foods. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1303025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isani, G.; Niccolai, A.; Andreani, G.; Dalmonte, T.; Bellei, E.; Bertocchi, M.; Tredici, M.R.; Rodolfi, L. Iron Speciation and Iron Binding Proteins in Arthrospira Platensis Grown in Media Containing Different Iron Concentrations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello, G.; Li, Y.; Boschin, G.; Bollati, C.; Arnoldi, A.; Lammi, C. Chemical and Biological Characterization of Spirulina Protein Hydrolysates: Focus on ACE and DPP-IV Activities Modulation. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 63, 103592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.; Soltanzadeh, M.; Ebrahimi, A.R.; Hamishehkar, H. Spirulina Platensis Protein Hydrolysates: Techno-Functional, Nutritional and Antioxidant Properties. Algal Res. 2022, 65, 102739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pez Jaeschke, D.; Rocha Teixeira, I.; Damasceno Ferreira Marczak, L.; Domeneghini Mercali, G. Phycocyanin from Spirulina: A Review of Extraction Methods and Stability. Food Res. Int. 2021, 143, 110314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, R.; Campos, J.; Serra, M.; Fidalgo, J.; Almeida, H.; Casas, A.; Toubarro, D.; Barros, A.I.R.N.A. Exploring the Benefits of Phycocyanin: From Spirulina Cultivation to Its Widespread Applications. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, M.M.; El-Fakharany, E.M.; Hegazy, G.E. Purification and Fractionation of Phycobiliproteins from Arthrospira Platensis and Corallina Officinalis with Evaluating Their Biological Activities. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 14270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Principe, M.; Permigiani, I.; Vedova, M.; Petenatti, E.; Pacheco, P.; Gil, R.; Garrido, G. Bioaccessibility Studies of Fe, Cu and Zn from Spirulina Dietary Supplements with Different Excipient Composition and Dosage Form. J. Pharm. Pharmacogn. Res. 2020, 8, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masten Rutar, J.; Jagodic Hudobivnik, M.; Nečemer, M.; Vogel Mikuš, K.; Arčon, I.; Ogrinc, N. Nutritional Quality and Safety of the Spirulina Dietary Supplements Sold on the Slovenian Market. Foods 2022, 11, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fediaf, E. Nutritional Guidelines for Complete and Complementary Pet Food for Cats and Dogs; European Pet Food Industry: Brussels, Belgium, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, M.; Bhatia, S.; Bagchi, D.; Tak, Y.; Kaur, G.; Kaur, C.; Kaur, A.; Sharma, N. Enhancing Microalgal Proteins for Nutraceutical and Functional Food Applications. Futur. Foods 2025, 11, 100564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-W.; Chang, Y.B.; Park, C.W.; Han, S.H.; Suh, H.J.; Ahn, Y. Protein Hydrolysate from Spirulina Platensis Prevents Dexamethasone-Induced Muscle Atrophy via Akt/Foxo3 Signaling in C2C12 Myotubes. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarioğlu-Bozkurt, A.; Topal, E.; Güneş, N.; Üçeş, E.; Cornea-Cipcigan, M.; Coşkun, İ.; Cuibus, L.; Mărgăoan, R. Changes in Vitellogenin (Vg) and Stress Protein (HSP 70) in Honey Bee (Apis Mellifera Anatoliaca) Groups under Different Diets Linked with Physico-Chemical, Antioxidant and Fatty and Amino Acid Profiles. Insects 2022, 13, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudelli, C.; Galuppi, R.; Cabbri, R.; Dalmonte, T.; Fontanesi, L.; Andreani, G.; Isani, G. Field Application of an Innovative Approach to Assess Honeybee Health and Nutritional Status. Animals 2024, 14, 2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricigliano, V.A.; Simone-Finstrom, M. Nutritional and Prebiotic Efficacy of the Microalga Arthrospira Platensis (Spirulina) in Honey Bees. Apidologie 2020, 51, 898–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.A.; Ghramh, H.A. Nutritional Efficacy of Different Diets Supplemented with Microalga Arthrospira Platensis (Spirulina) in Honey Bees (Apis Mellifera). J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2022, 34, 101819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isani, G.; Bellei, E.; Rudelli, C.; Cabbri, R.; Ferlizza, E.; Andreani, G. SDS-PAGE-Based Quantitative Assay of Hemolymph Proteins in Honeybees: Progress and Prospects for Field Application. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunc, M.; Dobeš, P.; Hurychová, J.; Vojtek, L.; Poiani, S.; Danihlík, J.; Havlík, J.; Titěra, D.; Hyršl, P. The Year of the Honey Bee (Apis Mellifera L.) with Respect to Its Physiology and Immunity: A Search for Biochemical Markers of Longevity. Insects 2019, 10, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, Q.W.T.; Howes, C.G.; Foster, L.J. Quantitative Comparison of Caste Differences in Honeybee Hemolymph. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2006, 5, 2252–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabbri, R.; Ferlizza, E.; Nanetti, A.; Monari, E.; Andreani, G.; Galuppi, R.; Isani, G. Biomarkers of Nutritional Status in Honeybee Haemolymph: Effects of Different Biotechnical Approaches for Varroa Destructor Treatment and Wintering Phase. Apidologie 2018, 49, 606–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutz, W.; Lüscher, M. The Occurrence of Vitellogenin in Workers and Queens of Apis Mellifica and the Possibility of Its Transmission to the Queen. J. Insect Physiol. 1974, 20, 897–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, J.A.; Boyd, A.; House, M.; Cowin, G.; Baer, B. Multi-Modal Imaging and Analysis in the Search for Iron-Based Magnetoreceptors in the Honeybee Apis Mellifera. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018, 5, 181163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-García, C.; Heerman, M.C.; Cook, S.C.; Evans, J.D.; DeGrandi-Hoffman, G.; Banmeke, O.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, S.; Hamilton, M.; Chen, Y.P. Transferrin-Mediated Iron Sequestration Suggests a Novel Therapeutic Strategy for Controlling Nosema Disease in the Honey Bee, Apis Mellifera. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.-Q.; Gong, H.-R.; Huang, S.-K.; Sohr, A.; Hu, F.-L.; Chen, Y.P. Evidence of the Synergistic Interaction of Honey Bee Pathogens Nosema Ceranae and Deformed Wing Virus. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 177, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abalde, J.; Betancourt, L.; Torres, E.; Cid, A.; Barwell, C. Purification and Characterization of Phycocyanin from the Marine Cyanobacterium Synechococcus Sp. IO9201. Plant Sci. 1998, 136, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrés, V.; Mateo-Vivaracho, L.; Guillamón, E.; Villanueva, M.J.; Tenorio, M.D. High Hydrostatic Pressure Treatment and Storage of Soy-Smoothies: Colour, Bioactive Compounds and Antioxidant Capacity. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 69, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtado, A.; Picouet, P.; Jofré, A.; Guàrdia, M.D.; Ros, J.M.; Bañón, S. Application of High Pressure Processing for Obtaining “Fresh-Like” Fruit Smoothies. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2015, 8, 2470–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Biological Hazards (BIOHAZ Panel); Koutsoumanis, K.; Alvarez-Ordóñez, A.; Bolton, D.; Bover-Cid, S.; Chemaly, M.; Davies, R.; De Cesare, A.; Herman, L.; Hilbert, F.; et al. The Efficacy and Safety of High-Pressure Processing of Food. EFSA J. 2022, 20, e07128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniel, W.W.; Cross, C.L. Biostatistics: A Foundation for Analysis in the Health Sciences; Wiley Series in Probability and Statistics; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; ISBN 9781119282372. [Google Scholar]


| Experimental Conditions | Total Proteins (mg/mL) |
|---|---|
| NEG-CTR | 16.80 ± 4.41 |
| POS-CTR | 24.52 ± 10.15 |
| Spirugrass® | 18.94 ± 9.25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dalmonte, T.; Rudelli, C.; Alberoni, D.; Lembo, A.; Gifuni, I.; Andreani, G.; Castellari, M.; Isani, G. Characterization and Valorization of the Microalgal Co-Product Spirugrass®: Protein Profile, Iron Speciation, and Potential Use as a Supplement for Honeybees. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23110443
Dalmonte T, Rudelli C, Alberoni D, Lembo A, Gifuni I, Andreani G, Castellari M, Isani G. Characterization and Valorization of the Microalgal Co-Product Spirugrass®: Protein Profile, Iron Speciation, and Potential Use as a Supplement for Honeybees. Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(11):443. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23110443
Chicago/Turabian StyleDalmonte, Thomas, Cecilia Rudelli, Daniele Alberoni, Angelica Lembo, Imma Gifuni, Giulia Andreani, Massimo Castellari, and Gloria Isani. 2025. "Characterization and Valorization of the Microalgal Co-Product Spirugrass®: Protein Profile, Iron Speciation, and Potential Use as a Supplement for Honeybees" Marine Drugs 23, no. 11: 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23110443
APA StyleDalmonte, T., Rudelli, C., Alberoni, D., Lembo, A., Gifuni, I., Andreani, G., Castellari, M., & Isani, G. (2025). Characterization and Valorization of the Microalgal Co-Product Spirugrass®: Protein Profile, Iron Speciation, and Potential Use as a Supplement for Honeybees. Marine Drugs, 23(11), 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23110443







