- Article
Real-World Outcomes of Axicabtagene Ciloleucel for Treatment of Relapsed or Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma in Canada
- Christopher Lemieux,
- John Kuruvilla and
- Kevin Hay
- + 13 authors
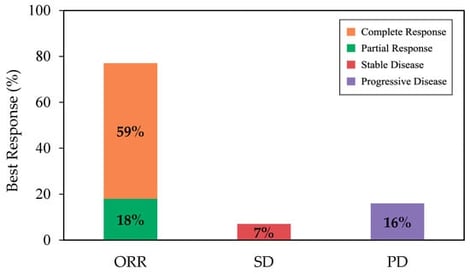
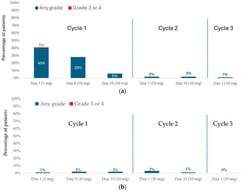
CD19 CAR T-cell therapy has significantly improved the survival of patients with relapsed or refractory large B cell lymphoma (R/R LBCL) and is considered standard of care for eligible patients in Canada. Axicabtagene ciloleucel (axi-cel) is an autologous CAR T-cell therapy, initially approved by Health Canada for adults with R/R LBCL after 2 or more lines of therapy. This multi-centre analysis, with registry data collected from CIBMTR, aims to present a Canadian perspective on the real-world experience of axi-cel in patients with R/R LBCL. With a median follow-up of 12.4 months, the best objective response rate (ORR) and complete response (CR) rate among all patients were 77% and 59%, respectively. At 12 months, estimated progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were 49% and 59%, respectively. Notably, the incidence and severity of adverse events were lower in this cohort compared to ZUMA-1 and other real-world reports, with CRS occurring in 77% (grade ≥ 3, 3%) and ICANS occurring in 38% (grade ≥ 3, 10%) of patients. Outcomes remained largely consistent across patient and disease characteristics. These findings demonstrate effectiveness and safety profiles comparable to international real-world studies and the ZUMA-1 trial, supporting the use of axi-cel as an effective treatment across broad Canadian populations.
31 January 2026