New Insights into Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment
Share This Topical Collection
Editors
 Dr. Matteo Basilio Suter
Dr. Matteo Basilio Suter
 Dr. Matteo Basilio Suter
Dr. Matteo Basilio Suter
E-Mail
Collection Editor
SC Oncologia, ASST Sette Laghi, Varese, Italy
Interests: transitional oncology; liquid biopsy; breast cancer; lung cancer; phase I
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Breast cancer is the most prevalent cancer among women worldwide. In recent decades, there substantial advances in screening methods, early diagnosis, and breakthroughs in treatments have increased survival rates among women with breast cancer. Particularly, advances in medical imaging and genetic knowledge and introduction of artificial intelligence technology in radiological practice have paved the way to true personalized medicine through an implementation of radiomics, radiogenomics, and liquid biopsy. Similarly, progress in molecular biology and pharmacology has aided toward a better understanding of breast cancer, enabling the design of smarter therapeutics able to target cancer and respond to its microenvironment efficiently.
In this Special Issues, we aim to collect original studies, meta-analysis, reviews, pictorial review, and letters investigating the new frontiers of diagnosis and novel treatment strategies for breast cancer.
Dr. Filippo Pesapane
Dr. Matteo Basilio Suter
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Current Oncology is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2200 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- breast cancer
- oncology
- personalized medicine
- radiomics
- radiogenomics
- breast imaging
- artificial intelligence
- transitional oncology
Published Papers (27 papers)
Open AccessReview
Prevention and Treatment of Postmastectomy Lymphedema: A Physiotherapy Perspective
by
Rosalba León-Díaz and Andrea Medina-Otero
Viewed by 1104
Abstract
Lymphedema is a frequent complication associated with breast cancer treatment. It is estimated that up to 30% of patients undergoing mastectomy develop this condition within 12 to 24 months post-surgery. In Mexico, the limited emphasis placed on lymphedema prevention in breast cancer patients
[...] Read more.
Lymphedema is a frequent complication associated with breast cancer treatment. It is estimated that up to 30% of patients undergoing mastectomy develop this condition within 12 to 24 months post-surgery. In Mexico, the limited emphasis placed on lymphedema prevention in breast cancer patients is reflected in the insufficient coverage of this issue within official medical guidelines. In this review, research articles, systematic reviews, and official treatment guidelines were retrieved from PubMed, Google Scholar, Elsevier, SciELO, and Redalyc databases, to examine studies about the application and effectiveness of physiotherapy techniques for the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of postmastectomy lymphedema. Our findings indicate that complex decongestive therapy (CDT) is considered the first-line treatment for lymphedema. Among its components, compression therapy shows the strongest individual evidence base. Nevertheless, studies consistently demonstrate that the combined use of all four components of CDT (manual lymphatic drainage, compression, skin care, and exercise) results in superior patient outcomes. Despite this, CDT is not routinely implemented as a standard of care for patients following mastectomy and/or lymphadenectomy in Mexico. Therefore, there is a pressing need to promote the inclusion of physiotherapy strategies, particularly CDT, in the prevention and management of postmastectomy lymphedema within national healthcare protocols.
Full article
Open AccessCase Report
A Rare Case of Breast Metastasis from a Primary Lung Tumor: Case Report
by
Raquel Diaz, Federica Murelli, Letizia Cuniolo, Chiara Cornacchia, Francesca Depaoli, Cecilia Margarino, Chiara Boccardo, Marco Gipponi, Simonetta Franchelli, Marianna Pesce, Barbara Massa, Silvia Bozzano, Valentina Barbero, Franco De Cian and Piero Fregatti
Viewed by 1965
Abstract
Breast metastasis originating from a primary lung tumor is exceedingly rare and can present challenges in distinguishing it from primary breast cancer. This case report discusses the management of a 64-year-old woman who initially presented with a nodule in her left breast. A
[...] Read more.
Breast metastasis originating from a primary lung tumor is exceedingly rare and can present challenges in distinguishing it from primary breast cancer. This case report discusses the management of a 64-year-old woman who initially presented with a nodule in her left breast. A biopsy revealed an infiltrating ductal carcinoma. Despite negative BRCA genetic testing, her significant family history of cancer and the presence of a newly detected right breast lesion led to a bilateral mastectomy. Post-operative imaging identified multiple hypodense nodules and a spiculated pulmonary nodule, necessitating further investigation. An endoscopic lung biopsy confirmed a primary pulmonary carcinoma with histological features similar to the breast carcinoma, suggesting the lung as the primary source. This case highlights the complexity of differentiating breast metastasis originating from a lung tumor and primary breast cancer. It underscores the importance of comprehensive diagnostic evaluations and the consideration of extramammary origins in metastatic cases. The findings emphasize the role of multidisciplinary teams in managing such rare and challenging cases and highlight the necessity for thorough and repeated assessments in atypical breast cancer presentations.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
New Insight for Axillary De-Escalation in Breast Cancer Surgery: “SoFT Study” Retrospective Analysis
by
Gianluca Vanni, Marco Materazzo, Floriana Paduano, Marco Pellicciaro, Giordana Di Mauro, Enrica Toscano, Federico Tacconi, Benedetto Longo, Valerio Cervelli, Massimiliano Berretta and Oreste Claudio Buonomo
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 2515
Abstract
Background: The SOUND study demonstrated that an axillary de-escalation may be sufficient in locoregional and distant disease control in selected early breast cancer (EBC) patients. To establish any preoperative variables that may drive sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) omission, a study named
[...] Read more.
Background: The SOUND study demonstrated that an axillary de-escalation may be sufficient in locoregional and distant disease control in selected early breast cancer (EBC) patients. To establish any preoperative variables that may drive sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) omission, a study named sentinel omission risk factor (SOFT) 1.23 was planned.
Methods: A single-center retrospective study from a prospectively maintained database was designed, aiming at underlying preoperative prognostic factors involved in sentinel lymph node (SLN) metastasis (lymph node involvement (LN+) vs. negative lymph node (LN−) group). Secondary outcomes included surgical room occupancy analysis for SLNB in patients fulfilling the SOUND study inclusion criteria. The institutional ethical committee Area Territoriale Lazio 2 approved the study (n° 122/23).
Results: Between 1 January 2022 and 30 June 2023, 160 patients were included in the study and 26 (%) were included in the LN+ group. Multifocality, higher cT stage, and larger tumor diameter were reported in the LN+ group (
p = 0.020,
p = 0.014, and 0.016, respectively). Tumor biology, including estrogen and progesterone receptors, and molecular subtypes showed association with the LN+ group (
p < 0.001;
p = 0.001; and
p = 0.001, respectively). A total of 117 (73.6%) patients were eligible for the SOUND study and the potential operating room time saved was 2696.81 min.
Conclusions: De-escalating strategies may rationalize healthcare activities. Multifactorial risk stratification may further refine the selection of patients who could benefit from SLNB omission.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessCase Report
Multidisciplinary and Tailored Treatment of Locally Advanced Breast Cancer in Progression during Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: Case Report
by
Letizia Cuniolo, Marco Gipponi, Federica Murelli, Francesca Depaoli, Chiara Cornacchia, Simonetta Franchelli, Marianna Pesce, Elena Ronda, Stefano Picardi, Raquel Diaz, Francesca Poggio, Daniele Friedman, Franco De Cian and Piero Fregatti
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 4336
Abstract
Locally advanced breast cancer (LABC) is a complex disease that requires a multidisciplinary approach. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) is usually performed in order to achieve loco-regional radical resection; although its importance in the multidisciplinary approach to LABC is well recognized, a small number of
[...] Read more.
Locally advanced breast cancer (LABC) is a complex disease that requires a multidisciplinary approach. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) is usually performed in order to achieve loco-regional radical resection; although its importance in the multidisciplinary approach to LABC is well recognized, a small number of patients show Progressive Disease (PD). No standard salvage treatment (ST) has been defined and different strategies can be adopted, such as second-line systemic therapies, radiation therapy, and surgery. Herein, a case of LABC in PD during NAC is reported with a literature review, with the aim of highlighting the importance of a tailored multidisciplinary treatment for each patient.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Determining the Need for Metastatic Staging in Patients with Bilateral Breast Cancers
by
Veronica Siton Alcantara, Sut Mo Zachary Chan, Fuh Yong Wong, John Carson Allen and Geok Hoon Lim
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 1916
Abstract
Introduction: Bilateral breast cancers (BBC) diagnosed at an interval apart are uncommon. While metastatic staging guidelines are established in patients with unilateral breast cancer, its role in BBC diagnosed at an interval apart is unclear. We aim to identify the subgroup who would
[...] Read more.
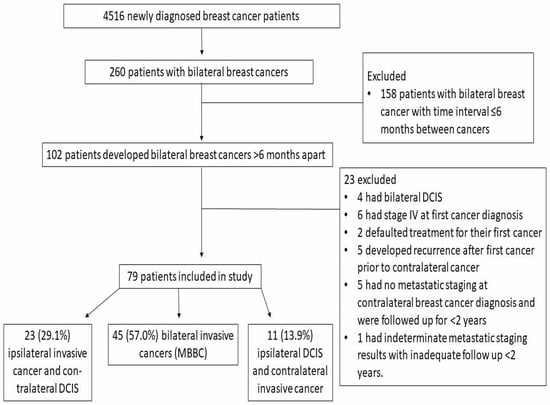
Introduction: Bilateral breast cancers (BBC) diagnosed at an interval apart are uncommon. While metastatic staging guidelines are established in patients with unilateral breast cancer, its role in BBC diagnosed at an interval apart is unclear. We aim to identify the subgroup who would benefit from metastatic staging at contralateral cancer diagnosis.
Methods: Eligible patients were divided into three categories: (A) ipsilateral invasive cancer and contralateral ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), (B) bilateral invasive cancers and (C) ipsilateral DCIS and contralateral invasive cancer and reviewed retrospectively. We excluded patients with bilateral DCIS, synchronous BBC diagnosed within 6 months from first cancer, patients who were stage IV at first cancer diagnosis and patients with recurrence prior to contralateral cancer.
Results: Of 4516 newly diagnosed breast cancer patients, 79 patients were included. Systemic metastasis occurred in 15.6% of patients in Group B. Having nodal positivity of either cancer which were diagnosed ≤30 months apart and nodal positivity of only the contralateral cancer when diagnosed >30 months apart was significantly associated with systemic metastasis (
p = 0.0322).
Conclusions: Both the nodal status and a 30 months cut-off time interval between the two cancers can be used to identify patients who will benefit from metastatic staging. This finding requires validation in larger studies.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Comparative Effectiveness and Safety of Trastuzumab Biosimilars to Herceptin for Adjuvant Treatment of HER2+ Breast Cancer
by
Caroline Muñoz, Xiaochen Tai, Jessica Arias, Andrea Eisen, Munaza Chaudhry, Scott Gavura and Kelvin K. W. Chan
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 3292
Abstract
Background: Ontario publicly funds reference trastuzumab (Herceptin) and four biosimilar trastuzumab products for adjuvant treatment of HER2+ breast cancer. We assessed the real-world safety and effectiveness of biosimilar trastuzumab compared to Herceptin for adjuvant treatment of patients with HER2+ breast cancer.
Methods: This
[...] Read more.
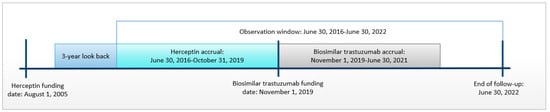
Background: Ontario publicly funds reference trastuzumab (Herceptin) and four biosimilar trastuzumab products for adjuvant treatment of HER2+ breast cancer. We assessed the real-world safety and effectiveness of biosimilar trastuzumab compared to Herceptin for adjuvant treatment of patients with HER2+ breast cancer.
Methods: This was a population-based, retrospective study comparing the safety and effectiveness of biosimilar trastuzumab and Herceptin for neoadjuvant/adjuvant treatment of HER2+ breast cancer from 2016 to 2021. Treatment patients started biosimilar trastuzumab from November 2019 to June 2021; historical comparator patients started Herceptin from June 2016 to October 2019. Safety outcomes death within 30 days of last dose of trastuzumab, direct hospitalization, emergency department visit leading to hospitalization, early treatment discontinuation, and in-patient admission for congestive heart failure were measured using logistic/negative binomial regression. Overall survival (OS) was measured using Kaplan–Meier methods and Cox proportional hazards regression. Propensity score matching was applied.
Results: From June 2016 to 2021, 5071 patients with breast cancer were treated with neoadjuvant/adjuvant trastuzumab. The rate of direct hospitalization (RR: 0.85, 95% CI: 0.74–0.98,
p-value: 0.032) was significantly lower in biosimilar compared to Herceptin patients. OS (log-rank test
p = 0.98) and risk of mortality (HR: 1.29, 95% CI: 0.72–2.30,
p-value = 0.39) did not significantly differ between treatment groups.
Conclusions: Biosimilar trastuzumab demonstrated similar safety and effectiveness to Herceptin. The findings can help improve confidence in and use of biosimilars and demonstrate the value of real-world evidence generation for supporting biosimilar implementations and reassessments.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Cavity Shave Margins in Breast Conservative Surgery a Strategy to Reduce Positive Margins and Surgical Time
by
Gianluca Vanni, Marco Pellicciaro, Giulia Renelli, Marco Materazzo, Amir Sadri, Valentina Enrica Marsella, Federico Tacconi, Sebastiano Angelo Bastone, Benedetto Longo, Giordana Di Mauro, Valerio Cervelli, Massimiliano Berretta and Oreste Claudio Buonomo
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 3261
Abstract
Background: Resection of additional tissue circumferentially around the cavity left by lumpectomy (cavity shave) was suggested to reduce rates of positive margins and re-excision.
Methods: A single center retrospective study which analyzed margins status, re-excision, and surgical time in patients who underwent breast
[...] Read more.
Background: Resection of additional tissue circumferentially around the cavity left by lumpectomy (cavity shave) was suggested to reduce rates of positive margins and re-excision.
Methods: A single center retrospective study which analyzed margins status, re-excision, and surgical time in patients who underwent breast conserving surgery and cavity shave or intraoperative evaluation of resection margins.
Results: Between 2021 and 2023, 594 patients were enrolled in the study. In patients subjected to cavity shave, a significant reduction in positive, focally positive, or closer margins was reported 8.9% vs. 18.5% (
p = 0.003). No difference was reported in terms of surgical re-excision (
p < 0.846) (5% vs. 5.5%). Surgical time was lower in patients subjected to cavity shave (<0.001). The multivariate analysis intraoperative evaluation of sentinel lymph node OR 1.816 and cavity shave OR 2.909 were predictive factors for a shorter surgical time. Excluding patients subjected to intraoperative evaluation of sentinel lymph node and patients with ductal carcinoma in situ, patients that underwent the cavity shave presented a reduced surgical time (67.9 + 3.8 min vs. 81.6 + 2.8 min) (
p = 0.006).
Conclusions: Cavity shaving after lumpectomy reduced the rate of positive margins and it was associated with a significant reduction in surgical time compared to intraoperative evaluation of resection margins.
Full article
Open AccessReview
The Role of Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy in Breast Cancer Patients Who Become Clinically Node-Negative Following Neo-Adjuvant Chemotherapy: A Literature Review
by
Giulia Ferrarazzo, Alberto Nieri, Emma Firpo, Andrea Rattaro, Alessandro Mignone, Flavio Guasone, Augusto Manzara, Giuseppe Perniciaro and Stefano Spinaci
Cited by 15 | Viewed by 6168
Abstract
Background: In clinically node-positive (cN+) breast cancer (BC) patients who become clinically node-negative (cN0) following neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT), sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) after lymphatic mapping with lymphoscintigraphy is not widely accepted; therefore, it has become a topic of international debate. Objective: Our
[...] Read more.
Background: In clinically node-positive (cN+) breast cancer (BC) patients who become clinically node-negative (cN0) following neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT), sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) after lymphatic mapping with lymphoscintigraphy is not widely accepted; therefore, it has become a topic of international debate. Objective: Our literature review aims to evaluate the current use of this surgical practice in a clinical setting and focuses on several studies published in the last six years which have contributed to the assessment of the feasibility and accuracy of this practice, highlighting its importance and oncological safety. We have considered the advantages and disadvantages of this technique compared to other suggested methods and strategies. We also evaluated the role of local irradiation therapy after SLNB and state-of-the-art SLN mapping in patients subjected to NACT. Methods: A comprehensive search of PubMed and Cochrane was conducted. All studies published in English from 2018 to August 2023 were evaluated. Results: Breast units are moving towards a de-escalation of axillary surgery, even in the NACT setting. The effects of these procedures on local irradiation are not very clear. Several studies have evaluated the oncological outcome of SLNB procedures. However, none of the alternative techniques proposed to lower the false negative rate (FNR) of SLNB are significant in terms of prognosis. Conclusions: Based on these results, we can state that lymphatic mapping with SLNB in cN+ BC patients who become clinically node-negative (ycN0) following NACT is a safe procedure, with a good prognosis and low axillary failure rates.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessOpinion
Clinical Considerations for the Integration of Adjuvant Olaparib into Practice for Early Breast Cancer: A Canadian Perspective
by
Jan-Willem Henning, Jean-François Boileau, Larissa Peck and Tom McFarlane
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 7345
Abstract
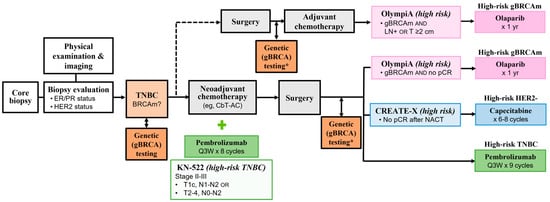
With the recent Health Canada approval of olaparib for high-risk, HER2-negative early breast cancer, physicians are now facing the practical challenges of integrating olaparib into current management of triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) and HR-positive, HER2-negative (HR+/HER2−) early breast cancer. This review provides perspectives
[...] Read more.
With the recent Health Canada approval of olaparib for high-risk, HER2-negative early breast cancer, physicians are now facing the practical challenges of integrating olaparib into current management of triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) and HR-positive, HER2-negative (HR+/HER2−) early breast cancer. This review provides perspectives on some of the challenges related to identification of olaparib candidates, with a focus on the latest guidance for germline BRCA testing and considerations regarding high-risk disease definitions. Updated treatment pathways are explored for both disease states, including other adjuvant treatment options such as pembrolizumab, capecitabine, and abemaciclib. Gaps in the current literature regarding the sequential or combined use of these adjuvant therapies are noted and future, potentially informative, studies are briefly examined.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceArticle
COVID-19 and Breast Cancer: Analysis of Surgical Management of a Large Referral Center during the 2020–2021 Pandemic Period
by
Fulvio Borella, Luca Bertero, Fabrizia Di Giovanni, Gianluca Witel, Giulia Orlando, Alessia Andrea Ricci, Alessandra Pittaro, Isabella Castellano and Paola Cassoni
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 3124
Abstract
Background: Coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19) has spread worldwide since December 2019 and was officially declared a pandemic in March 2020. Due to the rapid transmission and the high fatality rate, drastic emergency restrictions were issued, with a negative impact on routine clinical activities. In
[...] Read more.
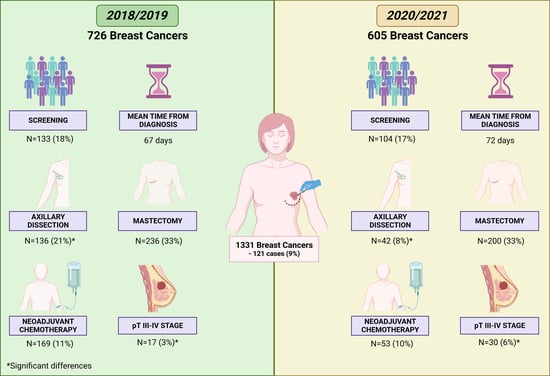
Background: Coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19) has spread worldwide since December 2019 and was officially declared a pandemic in March 2020. Due to the rapid transmission and the high fatality rate, drastic emergency restrictions were issued, with a negative impact on routine clinical activities. In particular, in Italy, many authors have reported a reduction in the number of breast cancer diagnoses and critical problems in the management of patients who accessed the breast units during the dramatic first months of the pandemic. Our study aims to analyze the global impact of COVID-19 in the two years of the pandemic (2020–2021) on the surgical management of breast cancer by comparing them with the previous two years. Methods: In our retrospective study, we analyzed all cases of breast cancer diagnosed and surgically treated at the breast unit of “Città della Salute e della Scienza” in Turin, Italy, making a comparison between the 2018–2019 pre-pandemic period and the 2020–2021 pandemic period. Results: We included in our analysis 1331 breast cancer cases surgically treated from January 2018 to December 2021. A total of 726 patients were treated in the pre-pandemic years and 605 in the pandemic period (−121 cases, 9%). No significant differences were observed regarding diagnosis (screening vs. no screening) and timing between radiological diagnosis and surgery for both in situ and invasive tumors. There were no variations in the breast surgical approach (mastectomy vs. conservative surgery), while a reduction in axillary dissection compared to the sentinel lymph node in the pandemic period was observed (
p-value < 0.001). Regarding the biological characteristics of breast cancers, we observed a greater number of grades 2–3 (
p-value = 0.007), pT stage 3–4 breast cancer surgically treated without previous neoadjuvant chemotherapy (
p-value = 0.03), and a reduction in luminal B tumors (
p-value = 0.007). Conclusions: Overall, we report a limited reduction in surgical activity for breast cancer treatment considering the entire pandemic period (2020–2021). These results suggest a prompt resumption of surgical activity similar to the pre-pandemic period.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Prognosis after Local Recurrence in Patients with Early-Stage Breast Cancer Treated without Chemotherapy
by
Victoria Sopik, David Lim, Ping Sun and Steven A. Narod
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 6336
Abstract
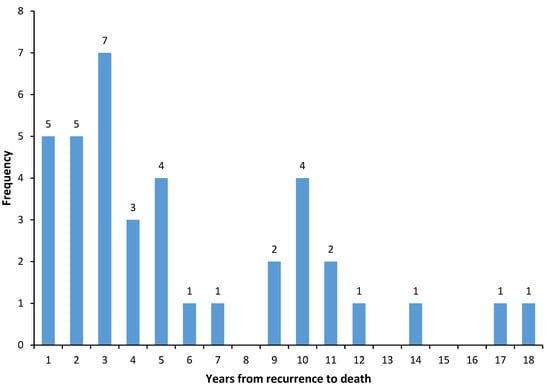
Background: Many women with early-stage breast cancer are predicted to be at sufficiently low risk for recurrence that they may forego chemotherapy. Nevertheless, some low-risk women will experience a local recurrence, and for them the risk of death increases significantly thereafter. The utility
[...] Read more.
Background: Many women with early-stage breast cancer are predicted to be at sufficiently low risk for recurrence that they may forego chemotherapy. Nevertheless, some low-risk women will experience a local recurrence, and for them the risk of death increases significantly thereafter. The utility of initiating chemotherapy at the time of local recurrence has not been adequately addressed. The purpose of this study is to identify, in a hospital-based series of patients with early-stage breast cancer who were not treated with chemotherapy, those factors which predict death post local recurrence. Methods: We identified 135 women who were diagnosed with early-stage breast cancer (node-negative, <5 cm) and who did not receive chemotherapy at diagnosis and who developed a local recurrence. They were diagnosed between 1987 and 2000 and treated at Women’s College Hospital. For each patient, we abstracted information on the initial cancer (age at diagnosis, tumour size, tumour grade, ER status, PR status, HER2 status, lympho-vascular invasion, type of surgery, use of radiotherapy, tamoxifen and chemotherapy), the time from initial diagnosis to local recurrence and treatment at recurrence. The Kaplan–Meier method was used to estimate the ten-year actuarial risk of breast cancer death post recurrence. A Cox proportional hazards model was used to estimate multivariate hazard ratios for the various factors. Results: Among the 135 women in the cohort, the mean time from initial diagnosis to local recurrence was 7.8 years (range: 0.3 to 22.6 years). A total of 38 of the 135 women (28.1%) died of breast cancer a mean of 5.3 years after experiencing the local recurrence (range: 0.3 to 17 years). The ten-year breast cancer survival post local recurrence was 71% and the 15-year survival was 65%. In a multivariate analysis, it was found that factors that were significantly associated with death after local recurrence were (1) PR-negative status, (2) young age at diagnosis (<40 years) and (3) time to local recurrence less than 2 years. Nine percent of women received chemotherapy at the time of local recurrence. Conclusions: For breast cancer patients with a low baseline risk of mortality, the risk of death after an isolated local recurrence is substantial. Systemic treatment at the time of local recurrence needs further study.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Factors Influencing Lymph Node Positivity in HER2/neu+ Breast Cancer Patients
by
Katherine Englander, Neha Chintapally, Julia Gallagher, Kelly Elleson, Weihong Sun, Junmin Whiting, Christine Laronga and Marie Catherine Lee
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 3432
Abstract
Axillary lymph node metastases are a key prognostic factor in breast cancer treatment. Our aim was to evaluate how tumor size, tumor location, and imaging results correlate to axillary lymph node diseases for patients with stage I-III HER2/neu+ breast cancer. This is a
[...] Read more.
Axillary lymph node metastases are a key prognostic factor in breast cancer treatment. Our aim was to evaluate how tumor size, tumor location, and imaging results correlate to axillary lymph node diseases for patients with stage I-III HER2/neu+ breast cancer. This is a single-institution retrospective chart review of female breast cancer patients diagnosed with primary invasive Her2/neu+ breast cancer who were treated with upfront surgical resection from 2000–2021. Of 75 cases, 44/75 (58.7%) had nodal metastasis, and there was a significant association of larger tumor size to nodal metastases (
p ≤ 0.001). Patients with negative nodes had a smaller mean tumor size (
n = 30; 15.10 mm) than patients with positive nodes (
n = 45; 23.9 mm) (
p = 0.002). Preoperative imaging detected suspicious nodes in 36 patients, and ultrasound detected the most positive nodes (14/18;
p = 0.027). Our data confirms that tumor size at diagnosis is correlated with a higher likelihood of axillary involvement in patients with Her2/neu+ breast cancer; notably, a large proportion of Her2/neu+ breast cancers have metastatic involvement of axillary lymph nodes even with small primary lesions.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Molecular Profile and Matched Targeted Therapy for Advanced Breast Cancer Patients
by
Rosa Falcone, Pasquale Lombardi, Marco Filetti, Alessandra Fabi, Valeria Altamura, Giovanni Scambia and Gennaro Daniele
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 4328
Abstract
(1) Background: Precision oncology is opening new treatment opportunities for patients suffering from solid tumors. In the last two decades, the advent of CDK4/6 inhibitors, immunotherapy, and antibody–drug conjugates (ADC) improved survival outcomes for advanced or metastatic breast cancers (BC). Nevertheless, some patients
[...] Read more.
(1) Background: Precision oncology is opening new treatment opportunities for patients suffering from solid tumors. In the last two decades, the advent of CDK4/6 inhibitors, immunotherapy, and antibody–drug conjugates (ADC) improved survival outcomes for advanced or metastatic breast cancers (BC). Nevertheless, some patients progress to approved therapies and still maintain good clinical conditions. (2) Methods: With the aim to estimate the accrual rate to experimental precision oncology treatments, we collected molecular and clinical characteristics of BC patients evaluated at Phase 1 Unit of Fondazione Policlinico Gemelli. Clinical data were retrieved from hospital records. Molecular analysis was performed using Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) FoundationOne CDx on tissue or blood. (3) Results: Among the 38 BC patients referred to our unit, 35 completed the genomic analysis. All patients were female with advanced (mean number of metastatic sites: 3, range 1–6) BC. Median age at our evaluation was 52 (IQR, 48–59). ECOG PS was good in 97% of the study population, although heavily pre-treated (median number of systemic treatments: 5, IQR 3–7). Half of referred patients were HR
+/HER2
− BC, with 39% triple negative breast cancer (TNBC). NGS testing was performed on relapsed disease among most (71%) participants, in particular lymph nodes and soft tissue. Liquid biopsy was requested in 23% of cases. The median time from sample collection to NGS testing was 1 month and from diagnosis 54 months. The median value of mutations, VUS, and TMB were 6, 11, and 5, respectively.
TP53,
PIK3CA,
BRCA2,
ESR1, and
RAD21 were the genes with the highest number of molecular alterations. In 5 patients (14%), the molecular analysis was helpful to assign targeted therapy in the context of clinical trials with a median progression-free survival of 5 months. (4) Conclusions: HR
+/HER2
− and TNBC were the most frequent subtypes referred for NGS testing. Tissue biopsy of relapsed disease was feasible in 71% of cases. The molecular analysis offered a new treatment opportunity in 14% of patients. The real benefit of these treatments remains to be evaluated in larger cohorts.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessCommunication
Are Radiation Target Volumes for Postmastectomy Radiation Therapy Too Large? Initial Report of the Complication Avoidance of Reconstruction Implant Radiation Therapy (CARIT) Study
by
Aruni Jayatilaka, Ashira Lokhandwala, Kimya Manouchehri, Muriel Brackstone and Michael Lock
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 2961
Abstract
Following mastectomy for breast cancer, women may choose implant-based reconstruction for many reasons, such as cosmesis, self-identity, and the ability to wear particular items of clothing. However, postmastectomy radiation therapy (PMRT) can compromise these cosmetic goals, including as much as a 40% loss
[...] Read more.
Following mastectomy for breast cancer, women may choose implant-based reconstruction for many reasons, such as cosmesis, self-identity, and the ability to wear particular items of clothing. However, postmastectomy radiation therapy (PMRT) can compromise these cosmetic goals, including as much as a 40% loss of implant rate. To minimize the risk of radiation toxicity, it is important to consider how clinical target volumes (CTVs) can be optimized in PMRT to preserve the implant and reduce complications. Typically, guidelines from organizations such as the Radiation Oncology Group are used, which include regions previously encompassed by tangential fields. This includes all structures below the pectoralis muscle, such as the chest wall, where the risk of recurrence is negligible; this technique often requires incidental inclusion of portions of the lung and heart plus circumferential radiation of the implant. We present the preliminary single institution case series of a technique of complication avoidance of reconstruction implant radiation therapy, called CARIT, where the chest wall, and a large proportion of the implant, is not irradiated. In a retrospective review of 30 cases in which CARIT has been attempted, it was found that 24% of patients treated required a second surgery due to Baker grade III/IV capsular contracture. Using the Modified Harvard Harris Cosmetic Scale, 66.5% of patients had cosmetic outcomes rated as “good” or “excellent”. CARIT could offer a technique to reduce complications in postmastectomy implant-based reconstruction patients, with our next steps focusing on improving dosimetry, and formally comparing the cosmesis and tumor control aspects with commonly used techniques.
Full article
Open AccessReview
Lysine-Specific Demethylase 1 (LSD1)-Mediated Epigenetic Modification of Immunogenicity and Immunomodulatory Effects in Breast Cancers
by
Dong Yeul Lee, Talha Salahuddin and Jabed Iqbal
Cited by 14 | Viewed by 6924
Abstract
Tumor evolution to evade immune surveillance is a hallmark of carcinogenesis, and the modulation of tumor immunogenicity has been a challenge to present therapeutic responses in immunotherapies alone for numerous cancers. By altering the cell phenotype and reshaping the tumor microenvironment, epigenetic modifications
[...] Read more.
Tumor evolution to evade immune surveillance is a hallmark of carcinogenesis, and the modulation of tumor immunogenicity has been a challenge to present therapeutic responses in immunotherapies alone for numerous cancers. By altering the cell phenotype and reshaping the tumor microenvironment, epigenetic modifications enable tumor cells to overcome immune surveillance as a mechanism of cancer progression and immunotherapy resistance. Demethylase enzymatic activity of lysine-specific demethylase 1 (LSD1), a histone demethylase first identified in 2004, plays a pivotal role in the vast cellular processes of cancer. While FDA-approved indications for epigenetic therapies are limited to hematological malignancies, it is imperative to understand how epigenetic machinery can be targeted to prime immunotherapy responses in breast cancers. In this review, we discuss the potential roles of epigenetics and demethylating agent LSD1 as a potent new cancer management strategy to combat the current challenges of breast cancers, which have presented modest efficacy to immune checkpoint inhibitors till date. Additionally, we describe the combined use of LSD1-specific inhibitors and immune checkpoint inhibitors in existing breast cancer preclinical and clinical trials that elicits a robust immune response and benefit. Overall, the promising results observed in LSD1-targeting therapies signify the central role of epigenetics as a potential novel strategy to overcome resistance commonly seen in immunotherapies.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceArticle
Machine Learning Approaches with Textural Features to Calculate Breast Density on Mammography
by
Mario Sansone, Roberta Fusco, Francesca Grassi, Gianluca Gatta, Maria Paola Belfiore, Francesca Angelone, Carlo Ricciardi, Alfonso Maria Ponsiglione, Francesco Amato, Roberta Galdiero, Roberta Grassi, Vincenza Granata and Roberto Grassi
Cited by 23 | Viewed by 4106
Abstract
Background: breast cancer (BC) is the world’s most prevalent cancer in the female population, with 2.3 million new cases diagnosed worldwide in 2020. The great efforts made to set screening campaigns, early detection programs, and increasingly targeted treatments led to significant improvement in
[...] Read more.
Background: breast cancer (BC) is the world’s most prevalent cancer in the female population, with 2.3 million new cases diagnosed worldwide in 2020. The great efforts made to set screening campaigns, early detection programs, and increasingly targeted treatments led to significant improvement in patients’ survival. The Full-Field Digital Mammograph (FFDM) is considered the gold standard method for the early diagnosis of BC. From several previous studies, it has emerged that breast density (BD) is a risk factor in the development of BC, affecting the periodicity of screening plans present today at an international level. Objective: in this study, the focus is the development of mammographic image processing techniques that allow the extraction of indicators derived from textural patterns of the mammary parenchyma indicative of BD risk factors. Methods: a total of 168 patients were enrolled in the internal training and test set while a total of 51 patients were enrolled to compose the external validation cohort. Different Machine Learning (ML) techniques have been employed to classify breasts based on the values of the tissue density. Textural features were extracted only from breast parenchyma with which to train classifiers, thanks to the aid of ML algorithms. Results: the accuracy of different tested classifiers varied between 74.15% and 93.55%. The best results were reached by a Support Vector Machine (accuracy of 93.55% and a percentage of true positives and negatives equal to TPP = 94.44% and TNP = 92.31%). The best accuracy was not influenced by the choice of the features selection approach. Considering the external validation cohort, the SVM, as the best classifier with the 7 features selected by a wrapper method, showed an accuracy of 0.95, a sensitivity of 0.96, and a specificity of 0.90. Conclusions: our preliminary results showed that the Radiomics analysis and ML approach allow us to objectively identify BD.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
“It Will Lead You to Make Better Decisions about Your Health”—A Focus Group and Survey Study on Women’s Attitudes towards Risk-Based Breast Cancer Screening and Personalised Risk Assessments
by
Jonathan Jun Kit Liow, Zi Lin Lim, Tomiko Mei Ying Sim, Peh Joo Ho, Su-Ann Goh, Sheen Dian Choy, Ying Jia Chew, Benita Kiat-Tee Tan, Veronique Kiak Mien Tan, Mikael Hartman, Keri McCrickerd and Jingmei Li
Cited by 14 | Viewed by 4119
Abstract
Singapore launched a population-based organised mammography screening (MAM) programme in 2002. However, uptake is low. A better understanding of breast cancer (BC) risk factors has generated interest in shifting from a one-size-fits-all to a risk-based screening approach. However, public acceptability of the change
[...] Read more.
Singapore launched a population-based organised mammography screening (MAM) programme in 2002. However, uptake is low. A better understanding of breast cancer (BC) risk factors has generated interest in shifting from a one-size-fits-all to a risk-based screening approach. However, public acceptability of the change is lacking. Focus group discussions (FGD) were conducted with 54 women (median age 37.5 years) with no BC history. Eight online sessions were transcribed, coded, and thematically analysed. Additionally, we surveyed 993 participants in a risk-based MAM study on how they felt in anticipation of receiving their risk profiles. Attitudes towards MAM (e.g., fear, low perceived risk) have remained unchanged for ~25 years. However, FGD participants reported that they would be more likely to attend routine mammography after having their BC risks assessed, despite uncertainty and concerns about risk-based screening. This insight was reinforced by the survey participants reporting more positive than negative feelings before receiving their risk reports. There is enthusiasm in knowing personal disease risk but concerns about the level of support for individuals learning they are at higher risk for breast cancer. Our results support the empowering of Singaporean women with personal health information to improve MAM uptake.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperEditor’s ChoiceReview
Applying Deep Learning for Breast Cancer Detection in Radiology
by
Ella Mahoro and Moulay A. Akhloufi
Cited by 47 | Viewed by 16574
Abstract
Recent advances in deep learning have enhanced medical imaging research. Breast cancer is the most prevalent cancer among women, and many applications have been developed to improve its early detection. The purpose of this review is to examine how various deep learning methods
[...] Read more.
Recent advances in deep learning have enhanced medical imaging research. Breast cancer is the most prevalent cancer among women, and many applications have been developed to improve its early detection. The purpose of this review is to examine how various deep learning methods can be applied to breast cancer screening workflows. We summarize deep learning methods, data availability and different screening methods for breast cancer including mammography, thermography, ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging. In this review, we will explore deep learning in diagnostic breast imaging and describe the literature review. As a conclusion, we discuss some of the limitations and opportunities of integrating artificial intelligence into breast cancer clinical practice.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessSystematic Review
Expression and Signaling Pathways of Nerve Growth Factor (NGF) and Pro-NGF in Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review
by
Francesco Bruno, Domenico Arcuri, Francesca Vozzo, Antonio Malvaso, Alberto Montesanto and Raffaele Maletta
Cited by 19 | Viewed by 6241
Abstract
Breast cancer represents the most common type of cancer and is the leading cause of death due to cancer among women. Thus, the prevention and early diagnosis of breast cancer is of primary urgency, as well as the development of new treatments able
[...] Read more.
Breast cancer represents the most common type of cancer and is the leading cause of death due to cancer among women. Thus, the prevention and early diagnosis of breast cancer is of primary urgency, as well as the development of new treatments able to improve its prognosis. Nerve Growth Factor (NGF) is a neurotrophic factor involved in the regulation of neuronal functions through the binding of the Tropomyosin receptor kinase A (TrkA) and the Nerve Growth Factor receptor or Pan-Neurotrophin Receptor 75 (NGFR/p75NTR). In addition, its precursor (pro-NGF) can extert biological activity by forming a trimeric complex with NGFR/p75NTR and sortilin, or by binding to TrkA receptors with low affinity. Several examples of in vitro and in vivo evidence show that NGF is both synthesized and released by breast cancer cells, and has mitogen, antiapoptotic and angiogenic effects on these cells through the activation of different signaling cascades that involve TrkA and NGFR/p75NTR receptors. Conversely, pro-NGF signaling has been related to breast cancer invasion and metastasis. Other studies suggested that NGF and its receptors could represent a good diagnostic and prognostic tool, as well as promising therapeutic targets for breast cancer. In this paper, we comprehensively summarize and systematically review the current experimental evidence on this topic. INPLASY ID: INPLASY2022100017.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Real-World Clinical Outcomes of Ribociclib in Combination with a Non-Steroidal Aromatase Inhibitor and a Luteinizing Hormone-Releasing Hormone Agonist in Premenopausal HR+/HER2− Advanced Breast Cancer Patients: An Italian Managed Access Program
by
Nicoletta Staropoli, Elena Geuna, Gaetana Rinaldi, Giancarlo Bisagni, Vieri Scotti, Giovanni Faggioni, Laura Vannini, Carlo Arcara, Gabriella Moretti, Marco Gunnellini, Luigi Coltelli, Francesco Verderame, Lorenzo Livi, Giuseppina Sanna, Donatella Grasso, Giulia Abbinante and Francesca Ragni
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 4168
Abstract
Ribociclib plus an aromatase inhibitor and ovarian function suppression is the preferred first-line option for pre-/perimenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor-2-negative advanced or metastatic breast cancer. We opened an italian managed access program (MAP) that permitted access to ribociclib to
[...] Read more.
Ribociclib plus an aromatase inhibitor and ovarian function suppression is the preferred first-line option for pre-/perimenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor-2-negative advanced or metastatic breast cancer. We opened an italian managed access program (MAP) that permitted access to ribociclib to selected patients and allowed to collect informative results on the clinical impact of the therapy. The MAP (April 2018–May 2020) included 64 premenopausal patients, with characteristics similar to those of the MONALEESA-7 trial. Of 57 patients with a known response, 48 (84.2%) achieved a clinical benefit (i.e., complete response, N = 7 (12.3%); partial response, N = 17 (29.8%); stable disease, N = 24 (42.1%)), while 9 (15.8%) experienced tumor progression. Some patients (N = 15–23.4%) needed ribociclib dose reduction because of adverse events. Thereafter, the treatment was well tolerated, and no new safety signals emerged. Our study is the first reported Italian real-world evidence of ribociclib effectiveness in premenopausal HR+/HER2− advanced breast cancer patients. Response and clinical benefit rates were particularly encouraging compared with those of the ribociclib group of MONALEESA-7. Our work confirms that ribociclib in combination with endocrine therapy is highly effective in the treatment of premenopausal HR+/HER2− advanced breast cancer patients with an expected safety profile.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Impact of Body Composition on Postoperative Outcomes in Patients Undergoing Robotic Nipple-Sparing Mastectomy with Immediate Breast Reconstruction
by
Jiae Moon, Jeea Lee, Dong Won Lee, Hye Jung Shin, Sumin Lee, Yhenseung Kang, Na Young Kim and Hyung Seok Park
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 3634
Abstract
Nipple-areolar complex (NAC)-related complications are common during nipple-sparing mastectomy (NSM), with obesity as a risk factor. Although the incidence of NAC-related complications after robotic NSM (RNSM) with immediate breast reconstruction (IBR) is lower than that after conventional NSM, it remains one of the
[...] Read more.
Nipple-areolar complex (NAC)-related complications are common during nipple-sparing mastectomy (NSM), with obesity as a risk factor. Although the incidence of NAC-related complications after robotic NSM (RNSM) with immediate breast reconstruction (IBR) is lower than that after conventional NSM, it remains one of the most unwanted complications. We aimed to evaluate body composition-based risk factors for NAC-related complications after RNSM with IBR. Data of 92 patients with breast cancer who underwent RNSM with IBR using direct-to-implant or tissue expander from November 2017 to September 2020 were analyzed retrospectively. Risk factors for NAC-related complications were identified with a focus on body composition using preoperative transverse computed tomography at the third lumbar vertebra level. Postoperative complications were assessed for 6 months. The most common complication was NAC ischemia, occurring in 15 patients (16%). Multivariate analysis revealed a low skeletal muscle index/total adipose tissue index (SMI/TATI) ratio as an independent NAC ischemia risk factor. An increase in the SMI/TATI ratio by one decreased the incidence of NAC ischemia by 0.940-fold (
p = 0.030). A low SMI/TATI ratio is a risk factor for postoperative NAC ischemia in patients undergoing RNSM with IBR for breast cancer. Preoperative body composition-focused evaluation is more valuable than simple body mass index assessment.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Potential Role of CCN Proteins in Breast Cancer: Therapeutic Advances and Perspectives
by
Kazi Ahsan Ahmed, Tasnin Al Hasib, Shamrat Kumar Paul, Md. Saddam, Afsana Mimi, Abu Saim Mohammad Saikat, Hasan Al Faruque, Md. Ataur Rahman, Md. Jamal Uddin and Bonglee Kim
Cited by 18 | Viewed by 5712
Abstract
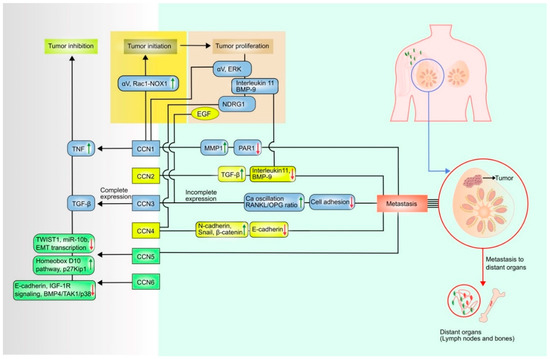
CCNs are a specific type of matricellular protein, which are essential signaling molecules, and play multiple roles in multicellular eukaryotes. This family of proteins consists of six separate members, which exist only in vertebrates. The architecture of CCN proteins is multi-modular comprising four
[...] Read more.
CCNs are a specific type of matricellular protein, which are essential signaling molecules, and play multiple roles in multicellular eukaryotes. This family of proteins consists of six separate members, which exist only in vertebrates. The architecture of CCN proteins is multi-modular comprising four distinct modules. CCN Proteins achieve their primary functional activities by binding with several integrin7 receptors. The CCN family has been linked to cell adhesion, chemotaxis and migration, mitogenesis, cell survival, angiogenesis, differentiation, tumorigenesis, chondrogenesis, and wound healing, among other biological interactions. Breast cancer is the most commonly diagnosed cancer worldwide and CCN regulated breast cancer stands at the top. A favorable or unfavorable association between various CCNs has been reported in patients with breast carcinomas. The pro-tumorigenic CCN1, CCN2, CCN3, and CCN4 may lead to human breast cancer, although the anti-tumorigenic actions of CCN5 and CCN6 are also present. Several studies have been conducted on CCN proteins and cancer in recent years. CCN1 and CCN3 have been shown to exhibit a dual nature of tumor inhibition and tumor suppression to some extent in quiet recent time. Pharmacological advances in treating breast cancer by targeting CCN proteins are also reported. In our study, we intend to provide an overview of these research works while keeping breast cancer in focus. This information may facilitate early diagnosis, early prognosis and the development of new therapeutic strategies.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Advances in Breast Cancer Management and Extracellular Vesicle Research, a Bibliometric Analysis
by
Ramon Handerson Gomes Teles, Rafael Sussumu Yano, Nicolas Jones Villarinho, Ana Sayuri Yamagata, Ruy Gastaldoni Jaeger, Patrick Meybohm, Malgorzata Burek and Vanessa Morais Freitas
Cited by 31 | Viewed by 6264
Abstract
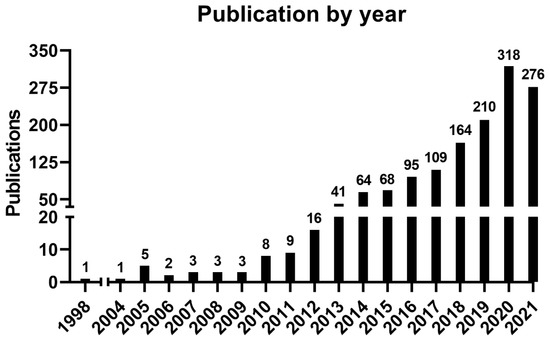
Extracellular vesicles transport variable content and have crucial functions in cell–cell communication. The role of extracellular vesicles in cancer is a current hot topic, and no bibliometric study has ever analyzed research production regarding their role in breast cancer and indicated the trends
[...] Read more.
Extracellular vesicles transport variable content and have crucial functions in cell–cell communication. The role of extracellular vesicles in cancer is a current hot topic, and no bibliometric study has ever analyzed research production regarding their role in breast cancer and indicated the trends in the field. In this way, we aimed to investigate the trends in breast cancer management involved with extracellular vesicle research. Articles were retrieved from Scopus, including all the documents published concerning breast cancer and extracellular vesicles. We analyzed authors, journals, citations, affiliations, and keywords, besides other bibliometric analyses, using R Studio version 3.6.2. and VOSviewer version 1.6.0. A total of 1151 articles were retrieved, and as the main result, our analysis revealed trending topics on biomarkers of liquid biopsy, drug delivery, chemotherapy, autophagy, and microRNA. Additionally, research related to extracellular vesicles in breast cancer has been focused on diagnosis, treatment, and mechanisms of action of breast tumor-derived vesicles. Future studies are expected to explore the role of extracellular vesicles on autophagy and microRNA, besides investigating the application of extracellular vesicles from liquid biopsies for biomarkers and drug delivery, enabling the development and validation of therapeutic strategies for specific cancers.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperReview
Breast Cancer Surgery: New Issues
by
Francesca Magnoni, Sofia Alessandrini, Luca Alberti, Andrea Polizzi, Anna Rotili, Paolo Veronesi and Giovanni Corso
Cited by 16 | Viewed by 7423
Abstract
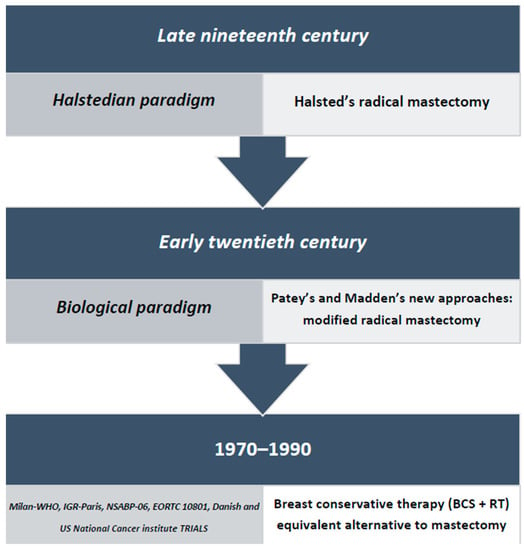
Since ancient times, breast cancer treatment has crucially relied on surgeons and clinicians making great efforts to find increasingly conservative approaches to cure the tumor. In the Halstedian era (mid-late 19th century), the predominant practice consisted of the radical and disfiguring removal of
[...] Read more.
Since ancient times, breast cancer treatment has crucially relied on surgeons and clinicians making great efforts to find increasingly conservative approaches to cure the tumor. In the Halstedian era (mid-late 19th century), the predominant practice consisted of the radical and disfiguring removal of the breast, much to the detriment of women’s psycho-physical well-being. Thanks to enlightened scientists such as Professor Umberto Veronesi, breast cancer surgery has since impressively progressed and adopted a much more conservative approach. Over the last three decades, a better understanding of tumor biology and of its significant biomarkers has made the assessment of genetic and molecular profiles increasingly important. At the same time, neo-adjuvant treatments have been introduced, and great improvements in genetics, imaging technologies and in both oncological and reconstructive surgical techniques have been made. The future of breast cancer management must now rest on an ever more precise and targeted type of surgery that, through an increasingly multidisciplinary and personalized approach, can ensure oncological radicality while offering the best possible quality of life.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
The Usefulness of Spectral Mammography in Surgical Planning of Breast Cancer Treatment—Analysis of 999 Patients with Primary Operable Breast Cancer
by
Andrzej Lorek, Katarzyna Steinhof-Radwańska, Anna Barczyk-Gutkowska, Wojciech Zarębski, Piotr Paleń, Karol Szyluk, Joanna Lorek, Anna Grażyńska, Paweł Niemiec and Iwona Gisterek
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 4224
Abstract
Contrast-enhanced spectral mammography (CESM) is a promising, digital breast imaging method for planning surgeries. The study aimed at comparing digital mammography (MG) with CESM as predictive factors in visualizing multifocal-multicentric cancers (MFMCC) before determining the surgery extent. We analyzed 999 patients after breast
[...] Read more.
Contrast-enhanced spectral mammography (CESM) is a promising, digital breast imaging method for planning surgeries. The study aimed at comparing digital mammography (MG) with CESM as predictive factors in visualizing multifocal-multicentric cancers (MFMCC) before determining the surgery extent. We analyzed 999 patients after breast cancer surgery to compare MG and CESM in terms of detecting MFMCC. Moreover, these procedures were assessed for their conformity with postoperative histopathology (HP), calculating their sensitivity and specificity. The question was which histopathological types of breast cancer were more frequently characterized by multifocality–multicentrality in comparable techniques as regards the general number of HP-identified cancers. The analysis involved the frequency of post-CESM changes in the extent of planned surgeries. In the present study, MG revealed 48 (4.80%) while CESM 170 (17.02%) MFMCC lesions, subsequently confirmed in HP. MG had MFMCC detecting sensitivity of 38.51%, specificity 99.01%, PPV (positive predictive value) 85.71%, and NPV (negative predictive value) 84.52%. The respective values for CESM were 87.63%, 94.90%, 80.57% and 96.95%. Moreover, no statistically significant differences were found between lobular and NST cancers (27.78% vs. 21.24%) regarding MFMCC. A treatment change was required by 20.00% of the patients from breast-conserving to mastectomy, upon visualizing MFMCC in CESM. In conclusion, mammography offers insufficient diagnostic sensitivity for detecting additional cancer foci. The high diagnostic sensitivity of CESM effectively assesses breast cancer multifocality/multicentrality and significantly changes the extent of planned surgeries. The multifocality/multicentrality concerned carcinoma, lobular and invasive carcinoma of no special type (NST) cancers with similar incidence rates, which requires further confirmation.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Recent Radiomics Advancements in Breast Cancer: Lessons and Pitfalls for the Next Future
by
Filippo Pesapane, Anna Rotili, Giorgio Maria Agazzi, Francesca Botta, Sara Raimondi, Silvia Penco, Valeria Dominelli, Marta Cremonesi, Barbara Alicja Jereczek-Fossa, Gianpaolo Carrafiello and Enrico Cassano
Cited by 60 | Viewed by 8652
Abstract
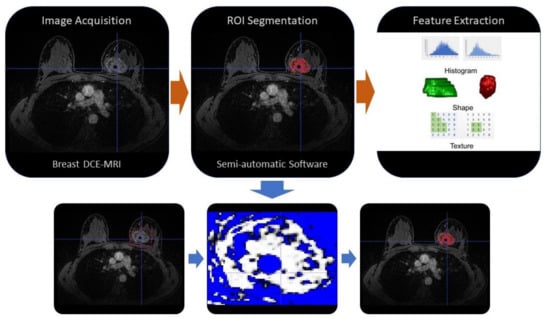
Radiomics is an emerging translational field of medicine based on the extraction of high-dimensional data from radiological images, with the purpose to reach reliable models to be applied into clinical practice for the purposes of diagnosis, prognosis and evaluation of disease response to
[...] Read more.
Radiomics is an emerging translational field of medicine based on the extraction of high-dimensional data from radiological images, with the purpose to reach reliable models to be applied into clinical practice for the purposes of diagnosis, prognosis and evaluation of disease response to treatment. We aim to provide the basic information on radiomics to radiologists and clinicians who are focused on breast cancer care, encouraging cooperation with scientists to mine data for a better application in clinical practice. We investigate the workflow and clinical application of radiomics in breast cancer care, as well as the outlook and challenges based on recent studies. Currently, radiomics has the potential ability to distinguish between benign and malignant breast lesions, to predict breast cancer’s molecular subtypes, the response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy and the lymph node metastases. Even though radiomics has been used in tumor diagnosis and prognosis, it is still in the research phase and some challenges need to be faced to obtain a clinical translation. In this review, we discuss the current limitations and promises of radiomics for improvement in further research.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
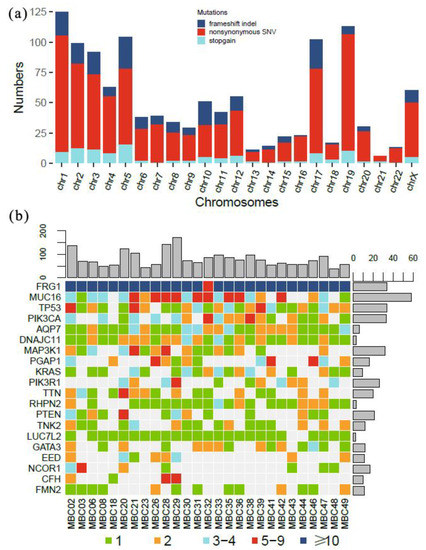
Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing of Circulating Tumor DNA Mutations among Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients
by
Min-Ying Sun, Fang-Qin Lin, Lu-Jia Chen, Hong Li, Wei-Quan Lin, Hong-Yan Du, Xue-Xi Yang and Ming Li
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 4121
Abstract
Liquid biopsy through the detection of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) has potential advantages in cancer monitoring and prediction. However, most previous studies in this area were performed with a few hotspot genes, single time point detection, or insufficient sequencing depth. In this study,
[...] Read more.
Liquid biopsy through the detection of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) has potential advantages in cancer monitoring and prediction. However, most previous studies in this area were performed with a few hotspot genes, single time point detection, or insufficient sequencing depth. In this study, we performed targeted next-generation sequencing (NGS) with a customized panel in metastatic breast cancer (MBC) patients. Fifty-four plasma samples were taken before chemotherapy and after the third course of treatment for detection and analysis. Paired lymphocytes were also included to eliminate clonal hematopoiesis (CH)-related alternatives. A total of 1182 nonsynonymous mutations in 419 genes were identified. More ctDNA mutations were detected in patients with tumors > 3 cm (
p = 0.035) and HER2(−) patients (
p = 0.029). For a single gene, the distribution of ctDNA mutations was also correlated with clinical characteristics. Multivariate regression analysis revealed that HER2 status was significantly associated with mutation burden (
OR 0.02, 95%
CI 0–0.62,
p = 0.025). The profiles of ctDNA mutations exhibited marked discrepancies between two time points, and baseline ctDNA was more sensitive and specific than that after chemotherapy. Finally, elevated ctDNA mutation level was positively correlated with poor survival (
p < 0.001). Mutations in ctDNA could serve as a potential biomarker for the evaluation, prediction, and clinical management guidance of MBC patients with chemotherapy.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures