Prognostic Significance of Complete Blood Count-Derived Inflammatory Biomarkers in Patients with Small Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Cervix
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Cox Regression and Survival Analysis
2.4. Nomogram Model Construction and Validation
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Survival Analysis
3.2.1. Univariate and Multivariate Cox Regression Analysis of PFS in SCNEC Patients
3.2.2. Univariate and Multivariate Cox Regression Analysis of OS in SCNEC Patients
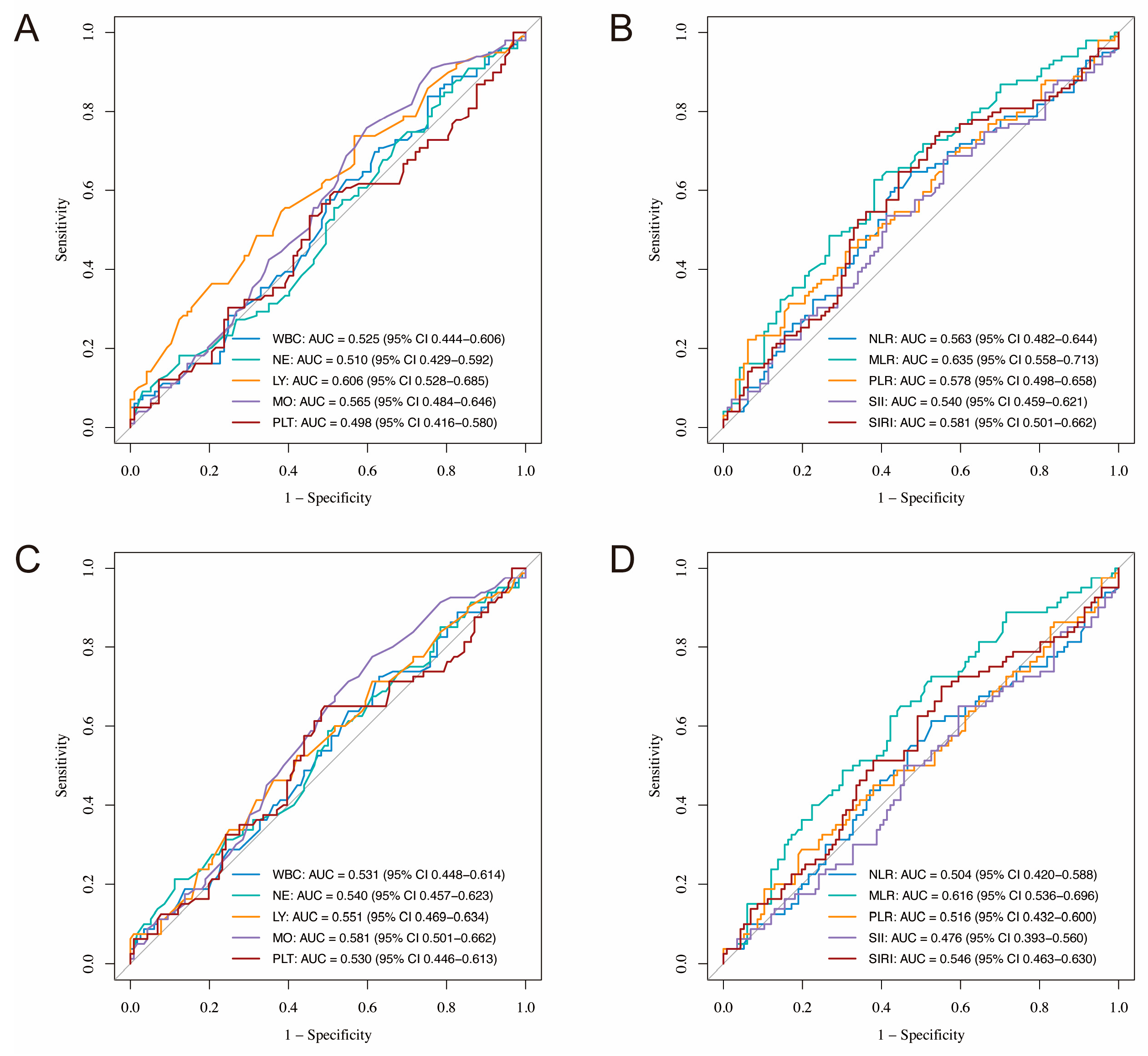
3.2.3. Predictive Performance of Inflammatory Markers
3.2.4. Relationship Between Inflammatory Biomarker Levels and PFS
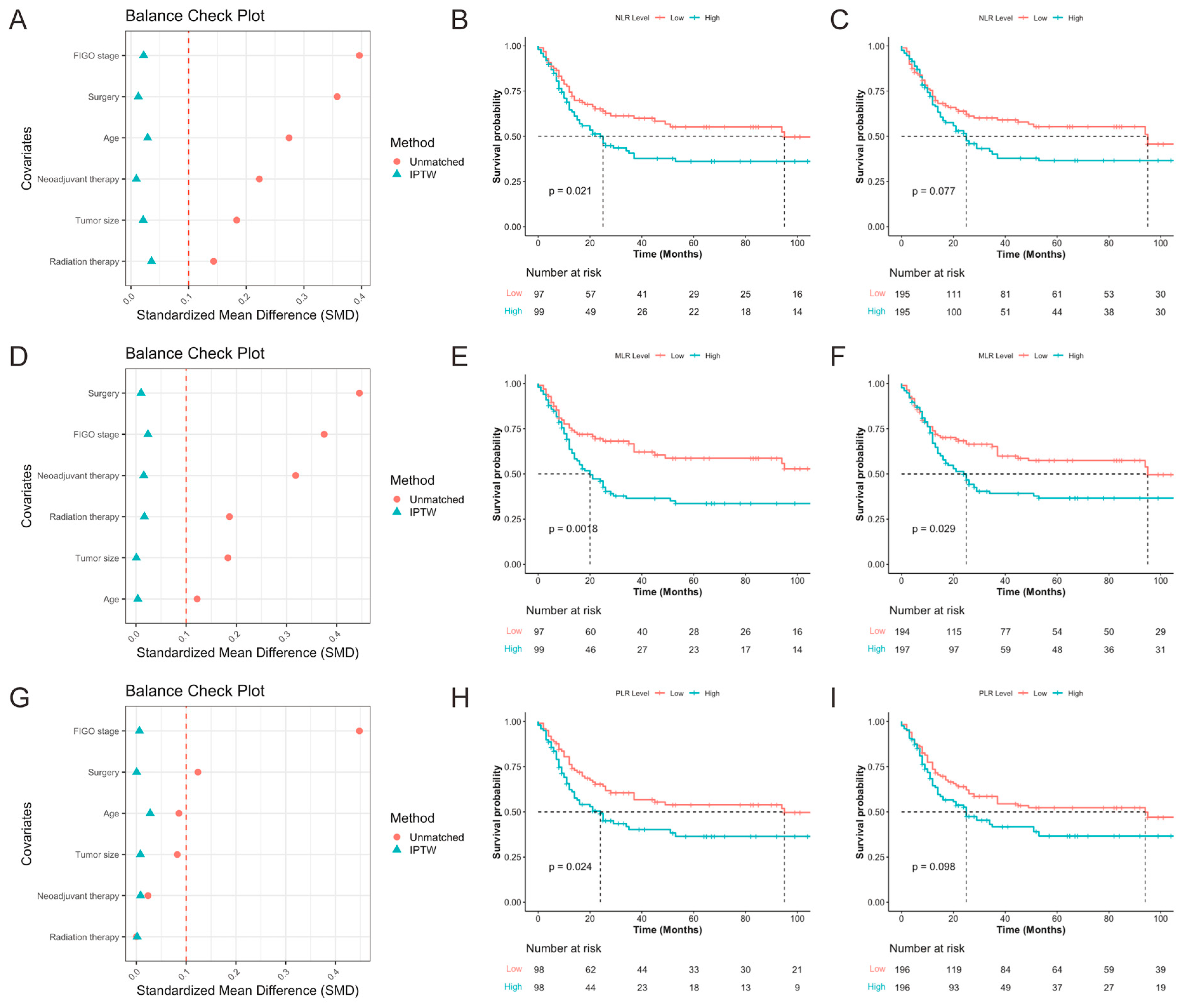
3.2.5. Subgroup Analysis
3.3. Construction and Validation of Nomogram
3.3.1. Patient Cohort Division
3.3.2. Feature Selection
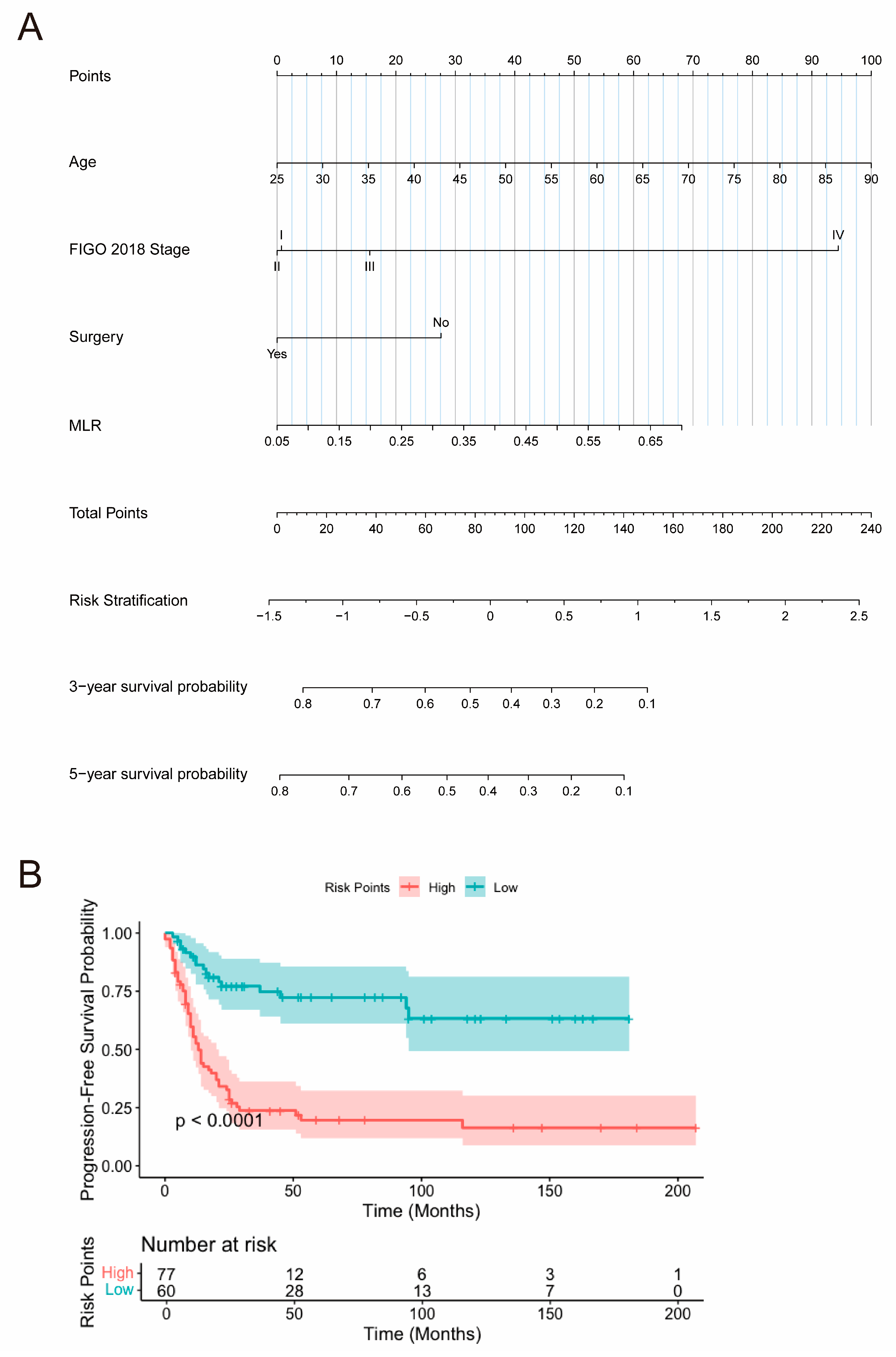
3.3.3. Nomogram Construction
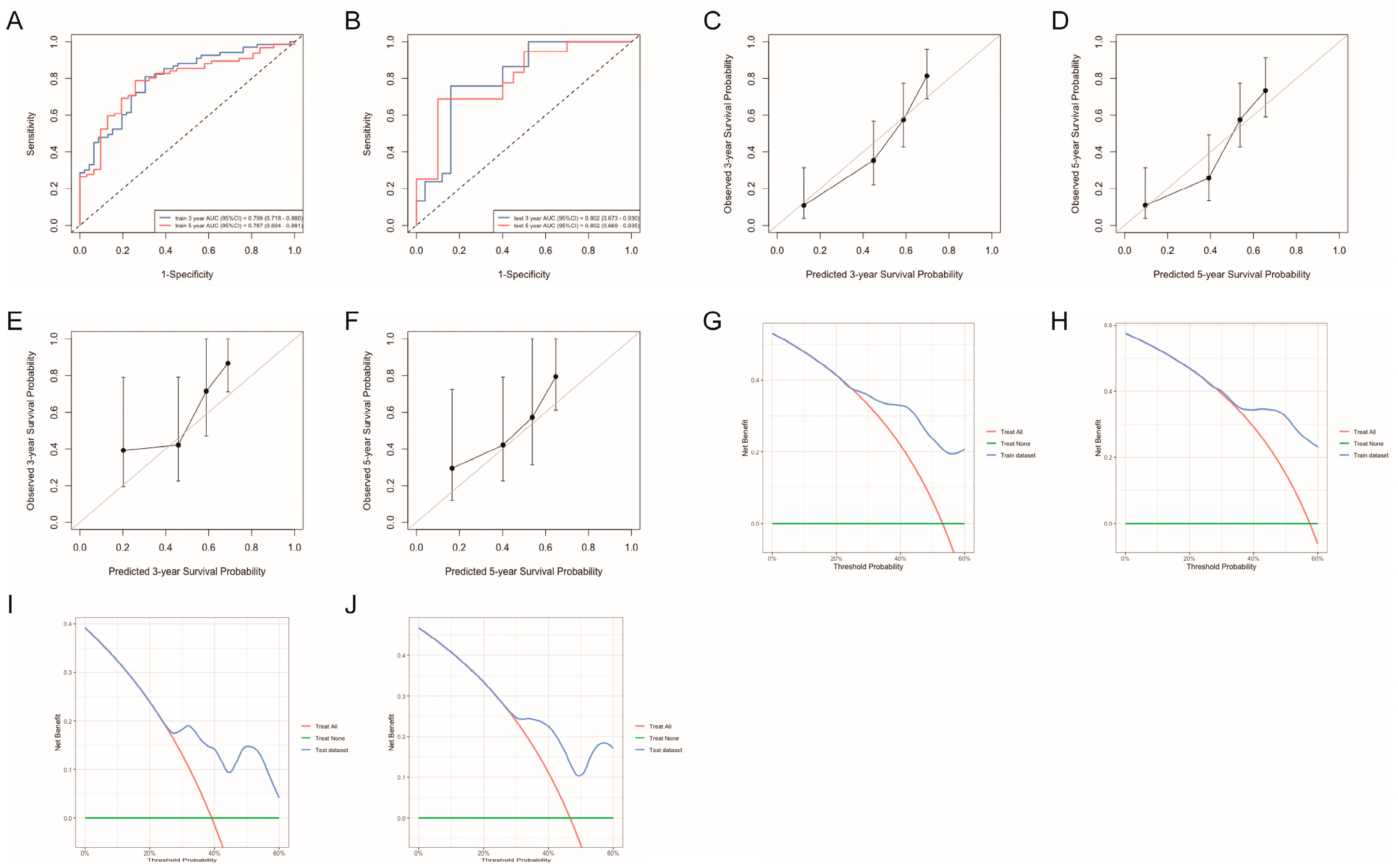
3.3.4. Nomogram Validation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crowder, S.; Tuller, E. Small Cell Carcinoma of the Female Genital Tract. Semin. Oncol. 2007, 34, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, A.; Wu, R.-C.; Lin, C.-Y.; Chang, T.-C.; Lai, C.-H. Small Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Cervix: From Molecular Basis to Therapeutic Advances. Biomed. J. 2023, 46, 100633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCusker, M.E.; Coté, T.R.; Clegg, L.X.; Tavassoli, F.J. Endocrine Tumors of the Uterine Cervix: Incidence, Demographics, and Survival with Comparison to Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Gynecol. Oncol. 2003, 88, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.J.; Soslow, R.A. Neoplastic Lesions of the Cervix. In Gynecologic Pathology, 2nd ed.; Nucci, M.R., Parra-Herran, C., Eds.; Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2020; pp. 227–293. ISBN 978-0-323-35909-2. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J.G.; Kapp, D.S.; Shin, J.Y.; Urban, R.; Sherman, A.E.; Chen, L.; Osann, K.; Chan, J.K. Small Cell Carcinoma of the Cervix: Treatment and Survival Outcomes of 188 Patients. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2010, 203, 347.e1–347.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Intaraphet, S.; Kasatpibal, N.; Siriaunkgul, S.; Chandacham, A.; Sukpan, K.; Patumanond, J. Prognostic Factors for Small Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Uterine Cervix: An Institutional Experience. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2014, 24, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, W.-H.; Schultheiss, T.E.; Wong, J.Y.; Wakabayashi, M.T.; Chen, Y.-J. Surgery versus Radiation Treatment for High-Grade Neuroendocrine Cancer of Uterine Cervix: A Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results Database Analysis. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2018, 28, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winer, I.; Kim, C.; Gehrig, P. Neuroendocrine Tumors of the Gynecologic Tract Update. Gynecol. Oncol. 2021, 162, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tempfer, C.B.; Tischoff, I.; Dogan, A.; Hilal, Z.; Schultheis, B.; Kern, P.; Rezniczek, G.A. Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Cervix: A Systematic Review of the Literature. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xiong, Y.; Ye, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, L. Influence of Clinicopathological Characteristics and Comprehensive Treatment Models on the Prognosis of Small Cell Carcinoma of the Cervix: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Gan, Q.; Cheng, J. Prognostic Factors and Local Treatment Modalities of Small-Cell Carcinoma of the Cervix: An Analysis According to the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics Stage. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 3445–3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, T.; Meng, Y.; Wu, P.; Li, Z.; Wen, H.; Ren, F.; Zou, D.; Lu, H.; Wu, L.; Zhou, S.; et al. The Prognosis of Patients with Small Cell Carcinoma of the Cervix: A Retrospective Study of the SEER Database and a Chinese Multicentre Registry. Lancet Oncol. 2023, 24, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon-Cabrera, S.; Schwertfeger, K.L.; Terrazas, L.I. Inflammation as a Target in Cancer Therapy. Mediat. Inflamm. 2019, 2019, 1971698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greten, F.R.; Grivennikov, S.I. Inflammation and Cancer: Triggers, Mechanisms, and Consequences. Immunity 2019, 51, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.-Z.; Zhong, J.-M.; Jiang, W.-P.; Liao, Z.-S.; Huang, S.-H.; Sun, Y.-W.; Lin, Y.; Ye, D.-X.; Pan, C.; Jiang, W.-Z. Preoperative Combination Score of Neutrophils, Monocytes, and Lymphocytes as a Predictor for Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2022, 37, 1097–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.; Ruan, G.; Wei, L.; Deng, L.; Zhang, Q.; Ge, Y.; Song, M.; Zhang, X.; Lin, S.; Liu, X.; et al. The Inflammatory Burden Index Is a Superior Systemic Inflammation Biomarker for the Prognosis of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2023, 14, 869–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, N.; Zhang, J.-X.; Zhang, J.-J.; Huang, Z.; Mao, L.-C.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Jin, W.-D. The Prognostic Value of the Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR) and Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (PLR) in Colorectal Cancer and Colorectal Anastomotic Leakage Patients: A Retrospective Study. BMC Surg. 2025, 25, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, A.; Yamaguchi, K.; Ishida, K.; Horikawa, N.; Kawai, E.; Kotani, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Kishimoto, N.; Tatsumi, K.; Okudate, M.; et al. Prognostic Significance of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio, Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio, and Monocyte-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Uterine Carcinosarcoma. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 30, 570–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Allavena, P.; Sica, A.; Balkwill, F. Cancer-Related Inflammation. Nature 2008, 454, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffelt, S.B.; de Visser, K.E. Cancer: Inflammation Lights the Way to Metastasis. Nature 2014, 507, 48–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, H.; Katai, H. Systemic Inflammatory Response in Gastric Cancer. World J. Surg. 2010, 34, 2399–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criscitiello, C.; Esposito, A.; Trapani, D.; Curigliano, G. Prognostic and Predictive Value of Tumor Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Early Breast Cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2016, 50, 205–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollinedo, F. Neutrophil Degranulation, Plasticity, and Cancer Metastasis. Trends Immunol. 2019, 40, 228–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Jurasz, P. The Role of Platelets in the Tumor Microenvironment: From Solid Tumors to Leukemia. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1863, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-X.; Chang, J.-Y.; He, M.-Y.; Wang, H.-R.; Luo, D.-Q.; Li, F.-H.; Li, J.-H.; Ran, L. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR) and Monocyte-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (MLR) Predict Clinical Outcome in Patients with Stage IIB Cervical Cancer. J. Oncol. 2021, 2021, 2939162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domenici, L.; Tonacci, A.; Aretini, P.; Garibaldi, S.; Perutelli, A.; Bottone, P.; Muzii, L.; Benedetti Panici, P. Inflammatory Biomarkers as Promising Predictors of Prognosis in Cervical Cancer Patients. Oncology 2021, 99, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Cao, D.; Huang, Y.; Xiong, Q.; Tan, D.; Liu, L.; Lin, T.; Wei, Q. The Prognostic and Clinicopathological Significance of Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index in Bladder Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 865643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Yu, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, W.; Xiao, R.; Wang, N.; Zhu, L.; Li, P.; Chen, T. The Value of Peripheral Blood Inflammation Markers in Risk Assessment and Prediction of Lung Cancer. Future Sci. OA 2025, 11, 2476870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Liu, R.; Li, X.; Yu, J.; Wang, W. Significant Association between Systemic Inflammation Response Index and Prognosis in Patients with Urological Malignancies. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1518647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, L.Y.; Cockshell, M.P.; Moore, E.; Myo Min, K.K.; Ortiz, M.; Johan, M.Z.; Ebert, B.; Ruszkiewicz, A.; Brown, M.P.; Ebert, L.M.; et al. Vasculogenic Mimicry Structures in Melanoma Support the Recruitment of Monocytes. Oncoimmunology 2022, 11, 2043673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, L.-C.; Fischer, U.; Raptis, G.; Bilek, K.; Hentschel, B. Tumor Size Is of Prognostic Value in Surgically Treated FIGO Stage II Cervical Cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2007, 107, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, N.; Yu, H.; Lin, J.; Deng, S.; Liu, L.; Sun, Y. A Nomogram for Predicting Prognosis for Young Cervical Neuroendocrine Carcinoma: A SEER-Based Study and External Validation. Front. Oncol. 2025, 15, 1463422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristic | N = 196 1 |
|---|---|
| Age | 48.00 (42.00, 54.00) |
| Tumor size | |
| 4 cm | 88 (45%) |
| 4 cm | 108 (55%) |
| FIGO 2018 stage | |
| I | 30 (15%) |
| II | 71 (36%) |
| III | 70 (36%) |
| IV | 25 (13%) |
| Neoadjuvant therapy | |
| No | 145 (74%) |
| Yes | 51 (26%) |
| Surgery | |
| No | 86 (44%) |
| Yes | 110 (56%) |
| Radiation therapy | |
| No | 70 (36%) |
| Yes | 126 (64%) |
| CBC count, 103/uL | |
| White blood cell | 6.34 (5.39, 8.00) |
| Neutrophils | 3.91 (3.10, 5.20) |
| Lymphocyte | 1.90 (1.50, 2.25) |
| Monocyte | 0.39 (0.29, 0.50) |
| Platelet | 276.50 (227.00, 334.00) |
| CBC-derived indicators | |
| NLR | 2.11 (1.61, 2.83) |
| MLR | 0.20 (0.15, 0.28) |
| PLR | 145.77 (113.80, 190.32) |
| SII | 582.03 (398.63, 840.62) |
| SIRI | 0.76 (0.51, 1.24) |
| PFS (Univariate Analysis) | PFS (Multivariate Analysis) | OS (Univariate Analysis) | OS (Multivariate Analysis) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristic | HR | 95% CI | p-Value | HR | 95% CI | p-Value | HR | 95% CI | p-Value | HR | 95% CI | p-Value |
| Age | 1.03 | 1.01, 1.05 | 0.003 | 1.03 | 1.01, 1.05 | 0.004 | 1.04 | 1.02, 1.06 | <0.001 | 1.04 | 1.01, 1.06 | 0.001 |
| Tumor size | 0.081 | 0.16 | ||||||||||
| 4 cm | — | — | — | — | ||||||||
| 4 cm | 1.43 | 0.95, 2.14 | 1.37 | 0.88, 2.15 | ||||||||
| FIGO 2018 stage | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.004 | ||||||||
| I | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||
| II | 1.94 | 0.86, 4.37 | 1.47 | 0.63, 3.45 | 2.93 | 1.03, 8.31 | 2.07 | 0.70, 6.13 | ||||
| III | 2.68 | 1.19, 6.03 | 1.87 | 0.80, 4.39 | 3.31 | 1.16, 9.47 | 2.16 | 0.72, 6.47 | ||||
| IV | 11.6 | 4.88, 27.5 | 5.98 | 2.22, 16.1 | 16.2 | 5.45, 48.0 | 6.12 | 1.84, 20.3 | ||||
| Neoadjuvant therapy | 0.084 | 0.13 | ||||||||||
| No | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||
| Yes | 0.67 | 0.41, 1.07 | 0.68 | 0.41, 1.14 | ||||||||
| Surgery | <0.001 | 0.020 | <0.001 | 0.014 | ||||||||
| No | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||
| Yes | 0.36 | 0.24, 0.53 | 0.56 | 0.35, 0.91 | 0.30 | 0.19, 0.47 | 0.51 | 0.30, 0.87 | ||||
| Radiation therapy | 0.47 | 0.59 | ||||||||||
| No | — | — | — | — | ||||||||
| Yes | 0.86 | 0.57, 1.29 | 0.88 | 0.56, 1.39 | ||||||||
| NLR | 1.19 | 1.05, 1.34 | 0.016 | 0.68 | 0.45, 1.01 | 0.050 | 1.15 | 0.98, 1.36 | 0.11 | |||
| MLR | 19.6 | 3.95, 97.2 | <0.001 | 1.01 | 1.00, 1.01 | 0.005 | 12.5 | 2.08, 75.3 | 0.009 | 1.68 | 0.07, 42.0 | 0.75 |
| PLR | 1.00 | 1.00, 1.01 | <0.001 | 3.04 | 0.12, 79.1 | 0.51 | 1.00 | 1.00, 1.01 | 0.050 | 1.00 | 1.00, 1.01 | 0.13 |
| SII | 1.00 | 1.00, 1.00 | 0.016 | 1.00 | 1.00, 1.00 | 0.89 | 1.00 | 1.00, 1.00 | 0.071 | |||
| SIRI | 1.27 | 1.09, 1.49 | 0.008 | 1.47 | 0.94, 2.30 | 0.12 | 1.30 | 1.08, 1.57 | 0.014 | 1.06 | 0.75, 1.52 | 0.74 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, M.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Lu, H.; Xu, Q. Prognostic Significance of Complete Blood Count-Derived Inflammatory Biomarkers in Patients with Small Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Cervix. Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32, 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32120654
Zhu M, Liu J, Wang Y, Lu H, Xu Q. Prognostic Significance of Complete Blood Count-Derived Inflammatory Biomarkers in Patients with Small Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Cervix. Current Oncology. 2025; 32(12):654. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32120654
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Mingxuan, Jing Liu, Yuqin Wang, Huaiwu Lu, and Qin Xu. 2025. "Prognostic Significance of Complete Blood Count-Derived Inflammatory Biomarkers in Patients with Small Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Cervix" Current Oncology 32, no. 12: 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32120654
APA StyleZhu, M., Liu, J., Wang, Y., Lu, H., & Xu, Q. (2025). Prognostic Significance of Complete Blood Count-Derived Inflammatory Biomarkers in Patients with Small Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Cervix. Current Oncology, 32(12), 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32120654




