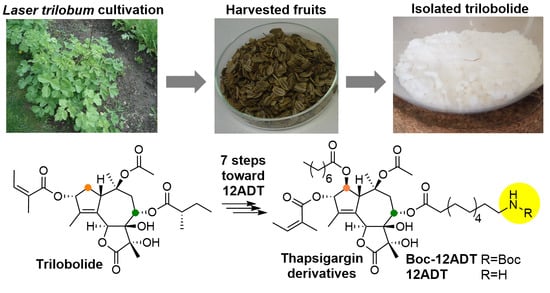
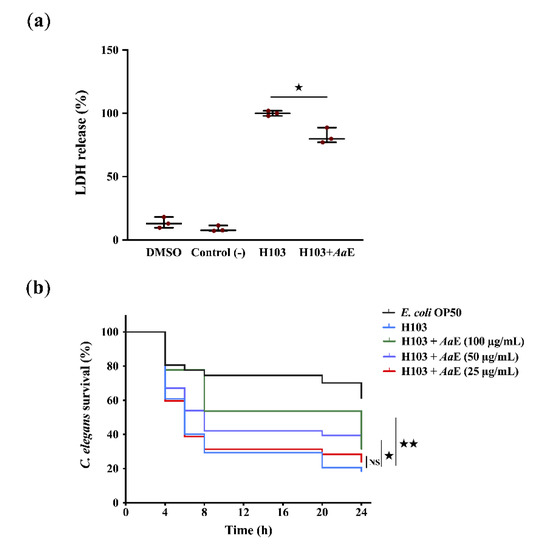
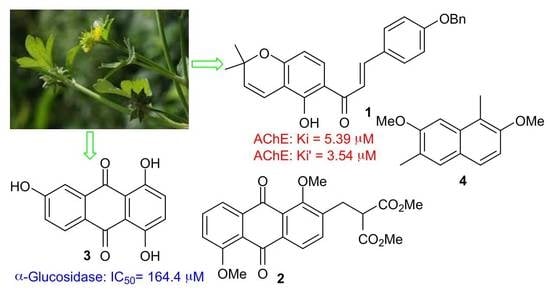
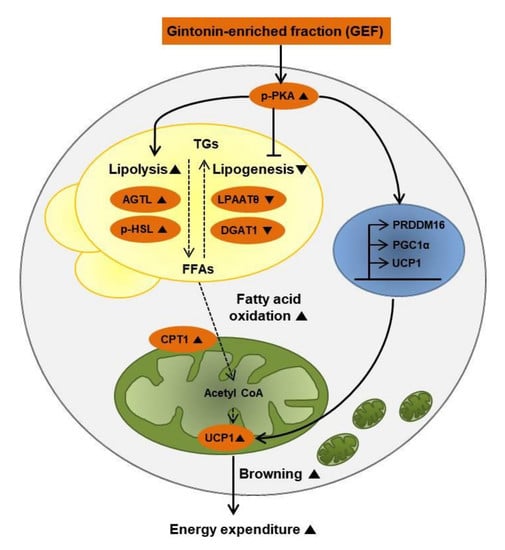
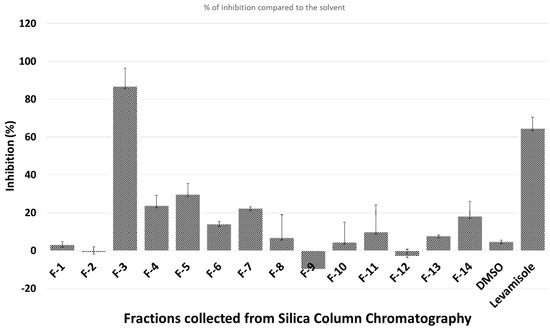
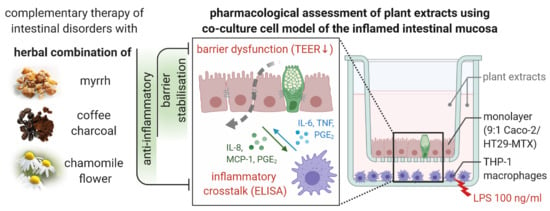
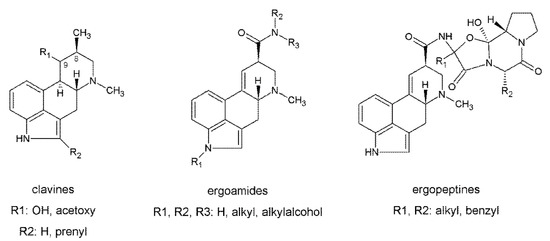
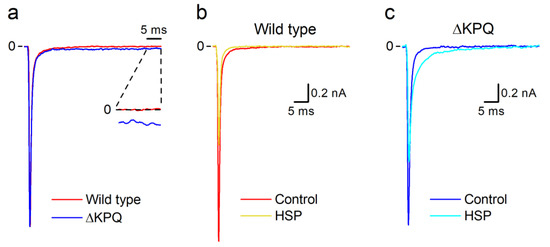
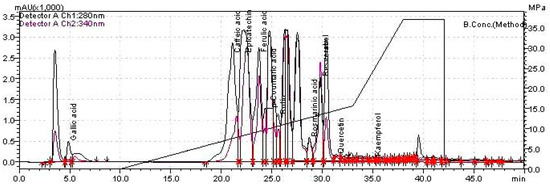
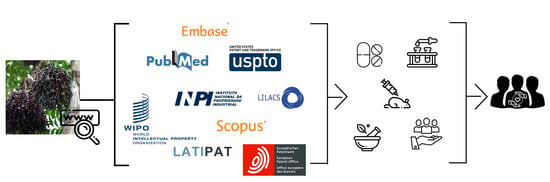
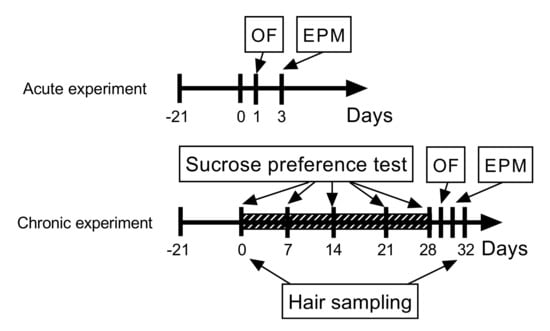
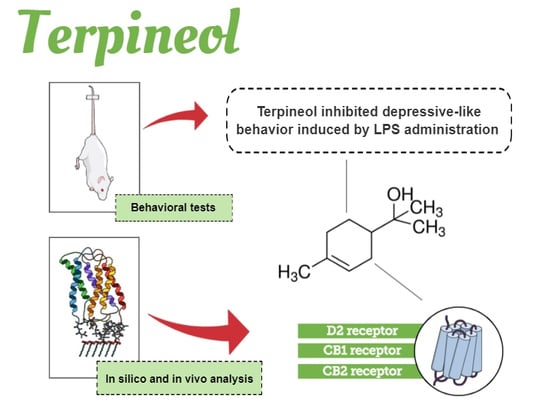
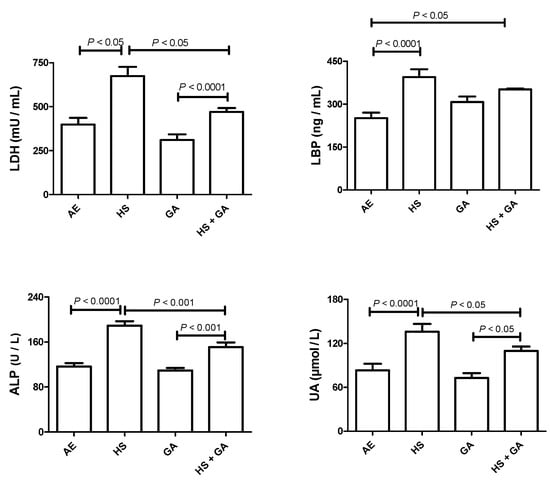
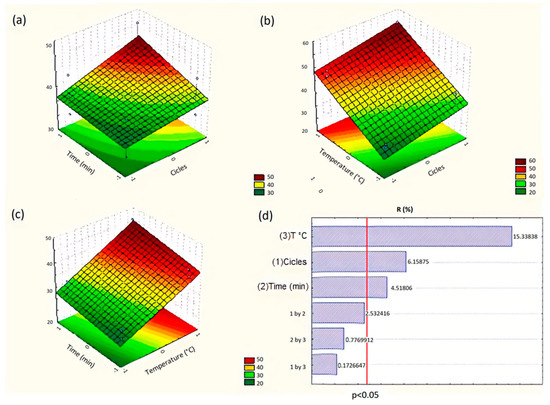
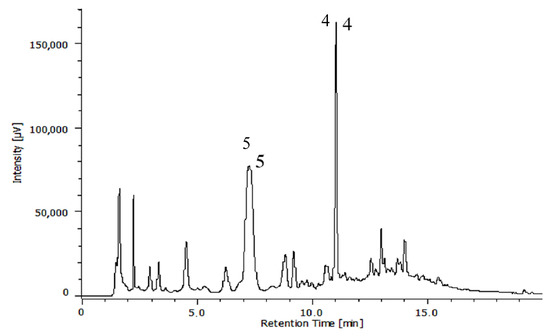
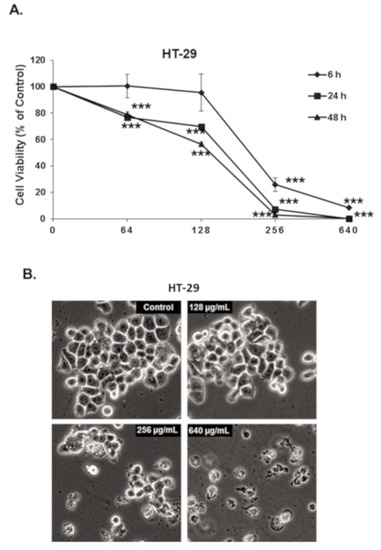
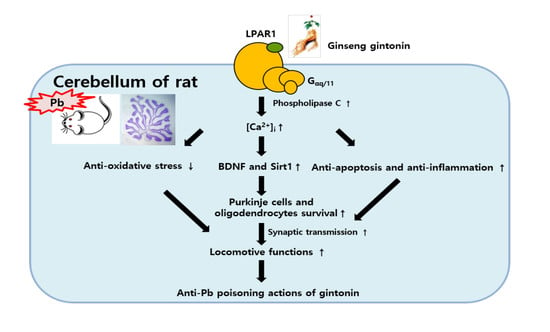
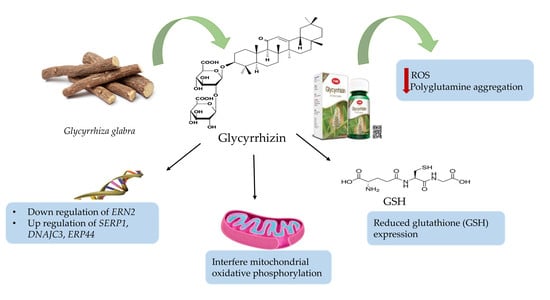
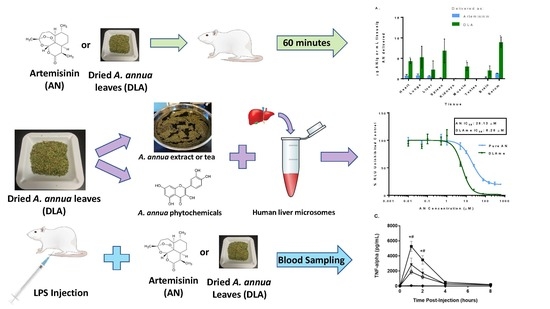
Pharmacology of Medicinal Plants
A topical collection in Biomolecules (ISSN 2218-273X). This collection belongs to the section "Natural and Bio-derived Molecules".
Submission Status: Closed | Viewed by 410036Editor
Interests: pharmacology; natural products; neurotransmission; behavioral pharmacology; experimental pharmacology; preclinical pharmacology; CB1 receptor; PPARs; cannabinoids; endocannabinoids; CB2 receptor
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
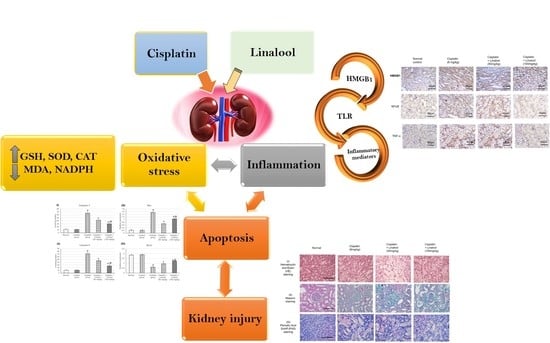
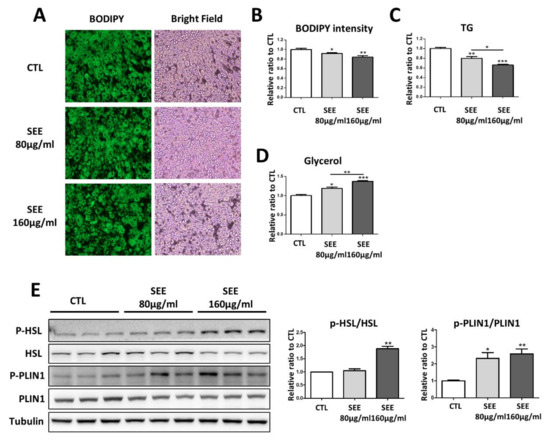
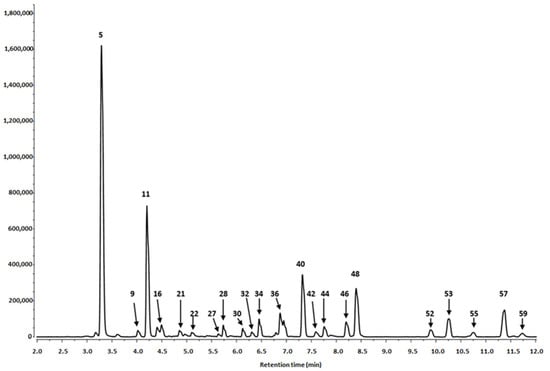
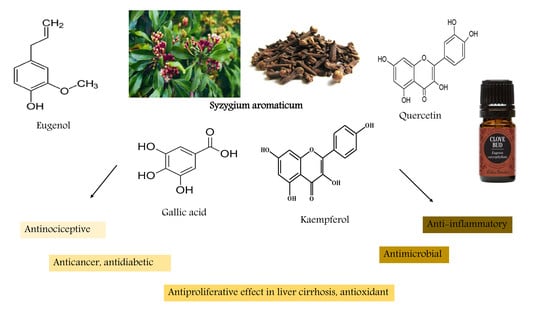
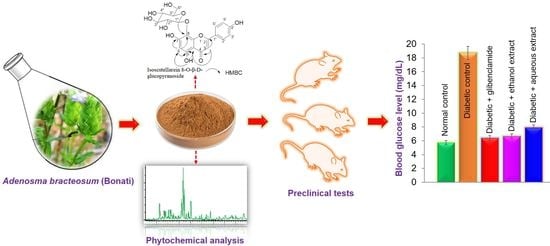
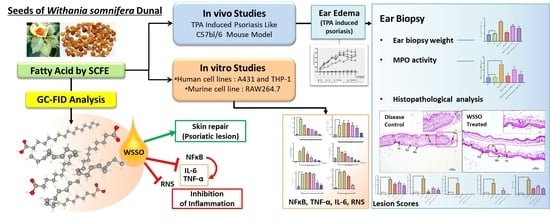
The end of the last century witnessed a vigorous resurgence in the interest in, and use of, medicinal plant products. Medicinal plants play an important role in the discovery of new drugs and innovative mechanisms of action.
Medicinal plants contain multiple compounds that, either individually or together, are responsible for the biological effects of these natural products. Although many plant-derived natural products have already been isolated and characterized, the molecular mechanisms underlying their therapeutic effects remain unexplored. This Special Issue aims to comprehensively cover the newest discoveries in herbal medicinal products with an emphasis on their molecular targets and pharmacological activity. Therefore, I cordially invite authors to contribute original articles, as well as reviews, covering the most recent advances in the use of medicinal plants.
Prof. Dr. Raffaele Capasso
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 250 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for assessment.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Biomolecules is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- medicinal plants
- biological activity
- molecular mechanisms
- medical use
- plant side effects
- pharmacological interactions