Journal Description
Scientia Pharmaceutica
Scientia Pharmaceutica
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal related to the pharmaceutical sciences, published quarterly online. It is the official journal of the Austrian Pharmaceutical Society (ÖPhG). Society members receive discounts on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, ESCI (Web of Science), Embase, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: CiteScore - Q2 (Pharmaceutical Science)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 22.8 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 3.1 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Journal Clusters-Pharmaceutical Science: Scientia Pharmaceutica, Marine Drugs, Pharmaceuticals, Pharmaceutics, Pharmacy, Future Pharmacology, Pharmacoepidemiology, Drugs and Drug Candidates and Journal of Pharmaceutical and BioTech Industry.
Impact Factor:
2.5 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
3.3 (2024)
Latest Articles
Standardized Hericium erinaceus Extract Powder Improves Scopolamine-Induced Cognitive Deficits via BDNF-Mediated Neuroplasticity
Sci. Pharm. 2026, 94(1), 12; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm94010012 - 23 Jan 2026
Abstract
Alzheimer’s disease and related neurodegenerative disorders are associated with progressive cognitive decline, primarily driven by cholinergic dysfunction and impaired synaptic signaling. Hericium erinaceus, also known as lion’s mane mushroom, has been reported to promote neuronal differentiation and synaptic plasticity. In this study,
[...] Read more.
Alzheimer’s disease and related neurodegenerative disorders are associated with progressive cognitive decline, primarily driven by cholinergic dysfunction and impaired synaptic signaling. Hericium erinaceus, also known as lion’s mane mushroom, has been reported to promote neuronal differentiation and synaptic plasticity. In this study, a standardized H. erinaceus extract powder (HEP) was prepared from fruiting bodies and quantified using hericene A as a marker compound. The neuroprotective effects of HEP were then evaluated in both cellular and animal models of scopolamine-induced cognitive dysfunction. Pretreatment of SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells with HEP (5–25 μg/mL) significantly improved cell viability and reduced scopolamine-induced apoptosis, while enhancing the activation of neuroplasticity-related signaling proteins, including brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB), and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK). In vivo, oral administration of HEP (300 mg/kg) to scopolamine-treated ICR mice markedly improved cognitive performance, increasing the recognition index to 63.8% compared with 41.6% in the scopolamine group, and enhancing spontaneous alternation in the Y-maze test to 59.6%. These cognitive improvements were accompanied by preserved hippocampal neuronal structure and increased BDNF immunoreactivity. Additionally, HEP improved cholinergic function by restoring serum acetylcholine levels and reducing acetylcholinesterase activity. Collectively, these findings suggest that standardized HEP exerts neuroprotective and cognition-enhancing effects via modulation of cholinergic markers and activation of BDNF-mediated neuroplasticity, highlighting its potential as a functional food ingredient or nutraceutical for preventing cognitive decline related to cholinergic dysfunction.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Functional Foods and Nutraceuticals in Health and Disease)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Synthesis, Antimicrobial and Antiproliferative Activity of 1-Trifluoromethylphenyl-3-(4-arylthiazol-2-yl)thioureas
by
Sreenivas Avula, Satish Koppireddi, Micky D. Tortorella and Cleopatra Neagoie
Sci. Pharm. 2026, 94(1), 11; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm94010011 - 19 Jan 2026
Abstract
This study reports the exclusive and rapid synthesis of twenty-four derivatives of 1-((mono/bis)trifluoromethyl)phenyl-3-(4-arylthiazol-2-yl)thioureas (series 7, 9 and 11), along with their antimicrobial activities against Candida albicans, Mycobacterium smegmatis and seven additional bacterial strains. The anticancer potential of these compounds was
[...] Read more.
This study reports the exclusive and rapid synthesis of twenty-four derivatives of 1-((mono/bis)trifluoromethyl)phenyl-3-(4-arylthiazol-2-yl)thioureas (series 7, 9 and 11), along with their antimicrobial activities against Candida albicans, Mycobacterium smegmatis and seven additional bacterial strains. The anticancer potential of these compounds was evaluated against various human cancer cell lines, including A549 (lung adenocarcinoma), HeLa (cervical carcinoma), IMR32 (neuroblastoma), MCF-7 (breast adenocarcinoma), HCT116 (colon cancer) and DU145 (prostate cancer). Among these, 1-(3,5-bistrifluoromethylphenyl)-3-(thiazol-2-yl)thiourea (7i) and 1-(4-trifluoromethylphenyl)-3-(4-(3-chlorophenyl)thiazol-2-yl)thiourea (11h) demonstrated significant antimicrobial activity against M. luteus, S. aureus, S. aureus 1 and C. albicans. Additionally, 1-(4-(3-chlorophenyl)thiazol-2-yl)-3-(3-trifluoromethylphenyl)thiourea (9g) and 1-(4-trifluoromethylphenyl)-3-(4-(2-fluorophenyl)thiazol-2-yl)thiourea (11g) showed activity against Mycobacterium smegmatis. The bioassay tests indicated that many of the thiourea derivatives exhibited moderate activity against the A549, HeLa, MCF-7 and HCT116 cancer cell lines.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Pharmaceutical Applications of Heterocyclic Compounds)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Phytomedicines for Mental Disorders in Hungary—Questionnaire and Phytochemical Analysis of Herbal OTC Products
by
Tibor Rák, Edit Ormai and Györgyi Horváth
Sci. Pharm. 2026, 94(1), 10; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm94010010 - 15 Jan 2026
Abstract
Mental health disorders, particularly anxiety and insomnia, are increasingly prevalent worldwide, prompting interest in herbal-based complementary therapies. This study surveyed 168 Hungarian healthcare professionals to evaluate their knowledge and recommendations regarding herbal sedatives and analyzed seven commonly suggested OTC products available in Hungary,
[...] Read more.
Mental health disorders, particularly anxiety and insomnia, are increasingly prevalent worldwide, prompting interest in herbal-based complementary therapies. This study surveyed 168 Hungarian healthcare professionals to evaluate their knowledge and recommendations regarding herbal sedatives and analyzed seven commonly suggested OTC products available in Hungary, using thin-layer chromatography (TLC) and UV–Vis spectrophotometry according to the European Pharmacopoeia. The survey revealed that 86.9% of respondents recommend herbal products for nervous system complaints, with Valeriana officinalis and Melissa officinalis being the preferred ingredients. Herbal teas and traditional herbal medicines were the most frequently suggested product categories. Laboratory analysis confirmed the presence of marker compounds in all tested products; however, significant variability in active ingredient concentrations was observed. One homeopathic product contained an unidentified alkaloid-like compound, raising safety concerns. Essential oil yields from tea mixtures also varied markedly, and some products did not meet pharmacopoeial standards for hypericin content. These findings highlight the popularity of phytotherapy among healthcare professionals and the need for stricter quality control of OTC herbal sedatives. Future research should include multi-batch analyses and clinical trials to establish robust evidence for efficacy and safety.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Natural Products and Drug Discovery—2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Computational Workflow for Chemical Compound Analysis: From Structure Generation to Molecular Docking
by
Jesus Magdiel García-Díaz, Asbiel Felipe Garibaldi-Ríos, Martha Patricia Gallegos-Arreola, Filiberto Gutiérrez-Gutiérrez, Jorge Iván Delgado-Saucedo, Moisés Martínez-Velázquez and Ana María Puebla-Pérez
Sci. Pharm. 2026, 94(1), 9; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm94010009 - 13 Jan 2026
Abstract
Drug discovery is a complex and expensive process in which only a small proportion of candidate molecules reach clinical approval. Computational methods, particularly computer-aided drug design (CADD), have become fundamental to accelerate and optimize early stages of discovery by integrating chemical, biological, and
[...] Read more.
Drug discovery is a complex and expensive process in which only a small proportion of candidate molecules reach clinical approval. Computational methods, particularly computer-aided drug design (CADD), have become fundamental to accelerate and optimize early stages of discovery by integrating chemical, biological, and pharmacokinetic information into predictive models. This review outlines a complete computational workflow for chemical compound analysis, covering molecular structure generation, database selection, evaluation of absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion and toxicity (ADMET), target prediction, and molecular docking. It focuses on freely accessible and web-based tools that enable reproducible, cost-effective, and scalable in silico studies. Key platforms such as PubChem, ChEMBL, RDKit, SwissADME, TargetNet, and SwissDock are highlighted as examples of how different resources can be integrated to support rational compound design and prioritization. The article also discusses essential methodological principles, data curation strategies, and common limitations in virtual screening and docking analyses. Finally, it explores future directions in computational drug discovery, including the incorporation of artificial intelligence, multi-omics integration, and quantum simulations, to enhance predictive accuracy and translational relevance.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Bioinformatics in Drug Design and Discovery—2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Astaxanthin as a Natural Photoprotective Agent: In Vitro and In Silico Approach to Explore a Multi-Targeted Compound
by
Aida Lahmar, Balkis Abdelaziz, Nahla Gouader, Abir Salek, Imen Waer and Leila Chekir Ghedira
Sci. Pharm. 2026, 94(1), 8; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm94010008 - 13 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Ultraviolet B radiation is a major cause of skin aging, cellular senescence, and inflammaging, mediated by the excessive production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and induction of apoptosis. This study evaluated the photo-protective effects of astaxanthin, one of the strongest natural antioxidants, in
[...] Read more.
Ultraviolet B radiation is a major cause of skin aging, cellular senescence, and inflammaging, mediated by the excessive production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and induction of apoptosis. This study evaluated the photo-protective effects of astaxanthin, one of the strongest natural antioxidants, in UVB-treated keratinocytes. The antioxidant capacity of astaxanthin was evaluated using ABTS, DPPH, and NBT/riboflavin/SOD assays. HaCaT cells were exposed to 30 mJ/cm2 of UVB radiation. Photoprotective effects and accumulated ROS were evaluated in UVB-irradiated HaCaT cells by MTT and DCFH-DA assays. Nitric oxide levels were quantified using the Griess reagent. Apoptosis was assessed by dual staining using acridine orange/ethidium bromide, lysosomal integrity by acridine orange uptake, and cell migration by scratch assay. Cell adhesion was assessed on ECM-coated Nunc plates. Finally, we formulated a 0.5% astaxanthin-enriched cream. Astaxanthin mitigated UVB-induced damage by reducing intracellular ROS levels by 3.7-fold, decreasing nitric oxide production to 29.8 ± 7.7% at the highest concentration, and maintaining lysosomal integrity. The carotenoid significantly enhanced cell viability, increasing it from 60.64 ± 8.3% in UV-treated cells to 102.1 ± 3.22% at 40 µM. Moreover, treated cells showed a significant reduction (p < 0.001) in the apoptotic rate (37.7 ± 3.1 vs. 87.7 ± 3.8 in UVB-irradiated cells, as evidenced by reduced chromatin condensation and nuclear fragmentation. Astaxanthin also enhanced tissue repair, as evidenced by increased cell migration and adhesion to several extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins (poly-L-lysine, laminin, fibrinogen, vitronectin and collagen I). In silico molecular docking predicted strong binding affinities between astaxanthin and key cellular targets, including JAK2 (−9.9 kcal/mol, highest affinity), STAT3, FAK, COX-2, NF-k-B, MMP2, and MMP9. The formulated cream demonstrated an in vitro SPF of 7.2 ± 2.5. Astaxanthin acts as a multifunctional photoprotective compound, providing a strong rationale for its incorporation into cosmetic and dermatological formulations, as further supported by the successful formulation and in vitro SPF estimation of an astaxanthin-enriched cream.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Pineapple-Derived Sodium Carboxymethylcellulose: Physicochemical Basis for Hydrogel Formulation
by
Mateo Pérez-R, G. Orozco, A. González-Ruiz and Miriam V. Flores-Merino
Sci. Pharm. 2026, 94(1), 7; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm94010007 - 8 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The synthesis of sodium carboxymethylcellulose (NaCMC) from lignocellulosic pineapple stubble provides a renewable alternative to conventional cellulose sources for pharmaceutical applications. This study aimed to obtain NaCMC from pineapple biomass, characterize it according to pharmacopoeial specifications, and formulate hydrogels as a physicochemical proof-of-concept
[...] Read more.
The synthesis of sodium carboxymethylcellulose (NaCMC) from lignocellulosic pineapple stubble provides a renewable alternative to conventional cellulose sources for pharmaceutical applications. This study aimed to obtain NaCMC from pineapple biomass, characterize it according to pharmacopoeial specifications, and formulate hydrogels as a physicochemical proof-of-concept for future drug delivery and tissue regeneration applications. NaCMC was successfully synthesized and met the requirements of the Mexican Pharmacopoeia. Hydrogels were prepared by blending NaCMC with gelatin and crosslinking with citric acid. Spectroscopic, morphological, and thermal analyses confirmed the structural equivalence between pineapple-derived NaCMC (NaCMC-Pi) and commercial NaCMC (NaCMC-Co). Swelling and gel fraction studies showed that NaCMC-Pi hydrogels exhibited a higher gel fraction, indicating a more crosslinked network, which corresponded to lower swelling capacity but higher thermal stability compared to NaCMC-Co hydrogels. Overall, these results demonstrate that pineapple stubble is a viable source of pharmaceutical-grade NaCMC and that the resulting hydrogels provide a robust physicochemical basis for future biomedical validation. The use of agro-industrial residues additionally offers a complementary sustainability benefit without compromising pharmaceutical performance.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessOpinion
Crocin Modified Drugs for Neuronal Trans-Differentiation: A Future Regenerative Approach
by
Pratikshya Paudel and Prabir Kumar Gharai
Sci. Pharm. 2026, 94(1), 6; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm94010006 - 8 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Neurodegeneration—driven by oxidative stress, chronic inflammation, and protein aggregation—underlies disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease, and stroke. Current pharmacological treatments are largely symptomatic and do not restore lost neural circuitry, motivating regenerative approaches. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) provide neurotrophic and
[...] Read more.
Neurodegeneration—driven by oxidative stress, chronic inflammation, and protein aggregation—underlies disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease, and stroke. Current pharmacological treatments are largely symptomatic and do not restore lost neural circuitry, motivating regenerative approaches. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) provide neurotrophic and immunomodulatory benefits and can support synaptic repair, yet robust conversion into mature, electrophysiologically functional neurons remain challenging and often depends on complex inducer cocktails with translational limitations. Crocin, a saffron-derived carotenoid, is reported to enhance neurogenesis and neuroprotection in preclinical models through pathways including Wnt/β-catenin, Notch1, CREB/BDNF, and modulation of GSK-3β, while reducing apoptosis and inflammatory signaling. Here, we synthesize evidence supporting crocin’s neuroprotective and proneurogenic activity and propose a testable hypothesis that crocin-based or crocin-modified formulations could be evaluated as adjuncts to guide MSC neuronal lineage commitment. Importantly, direct evidence that crocin alone can drive MSC trans-differentiation into fully functional neurons is currently insufficient; future work should define functional benchmarks (electrophysiology, synaptogenesis, and phenotypic stability) and rigorously validate safety, dosing, and delivery strategies for neuroregenerative translation.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Development and Validation of HPLC Methods for the Quantitative Determination and Related Impurities of Naftifine Hydrochloride in Solution and Cream Dosage Forms
by
Oleksandra Havrylenko, Yuliya Kondratova, Kateryna Typlynska and Liliya Logoyda
Sci. Pharm. 2026, 94(1), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm94010005 - 31 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The main goal of this study was to develop methods for quality control of naftifine hydrochloride in solution and cream forms, focusing on “Quantitative Determination” and “Related Impurities.” New, precise, accurate, and environmentally friendly high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) methods were developed for
[...] Read more.
The main goal of this study was to develop methods for quality control of naftifine hydrochloride in solution and cream forms, focusing on “Quantitative Determination” and “Related Impurities.” New, precise, accurate, and environmentally friendly high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) methods were developed for the determination of naftifine hydrochloride and its impurities. “Quantitative determination” was performed using a diode array detector at 254 nm with an isocratic mobile phase (1.154 g of ammonium acetate R dissolved in 300 mL of water R, followed by the addition of 0.2 mL of glacial acetic acid R, mixed well) and methanol (30:70). The chromatographic columns Gemini C18 and Luna C18 were used. “Related impurities” were separated at 270 nm using a gradient mobile phase consisting of 10 M sodium octanesulfonate, 0.4 g/L disodium hydrogen phosphate anhydrous solution (pH 6.5), acetonitrile, and the Synergi Hydro-RP chromatographic column. The developed method, validated according to ICH guidelines, showed run times of 55 min for impurity analysis and 6 min for active ingredient determination. The methods were successfully applied to the quality control of the solution and cream.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Evolution, Validation and Current Challenges in Bioanalytical Methods for Praziquantel: From Fluorometry to LC–MS/MS
by
Edwin Y. Valladares Chávez, Luis A. Moreno-Rocha, Lucia Ortega Cabello, Ponciano García-Gutiérrez and Jorge E. Miranda-Calderón
Sci. Pharm. 2026, 94(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm94010004 - 31 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The accurate determination and quantification of praziquantel are essential for optimizing its therapeutic effectiveness in treating schistosomiasis and neurocysticercosis, two significantly neglected tropical diseases. Its challenging physicochemical profile, extensive metabolism, and stereochemical complexity requires robust analytical methods for reliable quantification in clinical, veterinary,
[...] Read more.
The accurate determination and quantification of praziquantel are essential for optimizing its therapeutic effectiveness in treating schistosomiasis and neurocysticercosis, two significantly neglected tropical diseases. Its challenging physicochemical profile, extensive metabolism, and stereochemical complexity requires robust analytical methods for reliable quantification in clinical, veterinary, and pharmaceutical samples. This review provides a comprehensive and critical evaluation of analytical strategies used for PZQ determination, spanning fluorometric and radiometric assays, HPLC–UV, LC–MS, LC–MS/MS, and enantioselective chromatographic approaches. Particular emphasis is placed on the evolution toward highly sensitive LC–MS/MS methods and their alignment with contemporary regulatory expectations, including ICH M10 requirements. These advancements have significantly improved sensitivity, specificity, and reproducibility, which are crucial for pharmacokinetic, pharmacodynamic, and bioequivalence studies. Enantioselective methods for distinguishing PZQ enantiomers and metabolites are discussed. The aim of these innovations is to increase praziquantel bioavailability, improve patient adherence, and support its continued use in mass drug administration programs. Finally, the review highlights implementation challenges in resource-limited settings and proposes analytical models to expand global bioanalytical capacity. Together, these insights provide a structured foundation for selecting and developing high-quality, regulatory-compliant analytical methods for PZQ.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Nanotechnology for Metformin Release Systems: Nanostructures, Biopolymer Carriers, and Techniques—A Review
by
Eneida Azaret Montaño-Grijalva, Francisco Rodríguez-Félix, José Agustín Tapia-Hernández, Enrique Márquez-Ríos, Carmen Lizette Del-Toro-Sánchez, Dora Evelia Rodríguez-Félix, Ricardo Nalda-Molina, Elizabeth Carvajal-Millan, Carlos Gregorio Barreras-Urbina, Itzel Yanira López-Peña and Cielo Estefanía Figueroa-Enríquez
Sci. Pharm. 2026, 94(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm94010003 - 24 Dec 2025
Abstract
Currently, there are various approaches to the treatment of diabetes. Regarding type 2 diabetes (T2D), treatment focuses on blood glucose control. When changes in lifestyle do not achieve this glycemic control, the option is to start therapy with antidiabetic drugs such as metformin.
[...] Read more.
Currently, there are various approaches to the treatment of diabetes. Regarding type 2 diabetes (T2D), treatment focuses on blood glucose control. When changes in lifestyle do not achieve this glycemic control, the option is to start therapy with antidiabetic drugs such as metformin. However, long-term metformin use causes disturbances that may affect treatment approaches. This review examines recent advances in nanotechnology that have developed new forms of drug administration that can improve the efficacy of the treatment, where nanomaterials, nanostructures, and nanoparticle design are involved, so that they provide controlled and gradual release. The use of biopolymers (as drug delivery systems) has ensured biocompatibility, biodegradability, and low toxicity. There are several methods for obtaining a drug delivery system, including electrospinning, electrospraying, nanoprecipitation, etc. These systems improve drug delivery and can be used orally, transdermally, or intravenously, among means of administration. This review describes the new forms of the administration of metformin in the treatment of T2D, based on the encapsulation of metformin in polymeric matrices such as proteins, polysaccharides, and lipids, among others.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Complementary Strategies in Drug Delivery: From Particle Engineering to System Optimization)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
New Horizons in Quality Control of Enzyme Pharmaceuticals: Combining Dynamic Light Scattering, Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy, and Radiothermal Emission Analysis
by
Gleb Vladimirovich Petrov, Aleksandr Andreevich Nazarov, Alena Mikhailovna Koldina and Anton Vladimirovich Syroeshkin
Sci. Pharm. 2026, 94(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm94010002 - 22 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Hyaluronidase and its modified analogs are clinically significant enzyme-based pharmaceuticals used to treat fibrosis, increase tissue permeability, and improve drug diffusion. While pharmacopeial quality control methods are well defined, scientific literature provides limited information about the physicochemical evaluation of such enzyme pharmaceuticals, necessitating
[...] Read more.
Hyaluronidase and its modified analogs are clinically significant enzyme-based pharmaceuticals used to treat fibrosis, increase tissue permeability, and improve drug diffusion. While pharmacopeial quality control methods are well defined, scientific literature provides limited information about the physicochemical evaluation of such enzyme pharmaceuticals, necessitating a more holistic analytical approach. Commercial pharmaceuticals of hyaluronidase and its modified analog were analyzed using a combination of dynamic light scattering, infrared spectroscopy, and detection of intrinsic radiothermal emission (RTE). Dimensional characteristics were studied using a Zetasizer Nano ZSP (ZetasizerNano ZSP, Malvern Instruments, Malvern, UK) confirmed theoretical diameters of 5–8 nm, consistent with experimental values (6–8 nm). Fourier-Transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) (Agilent Cary 630, Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) revealed characteristic transmission bands for the modified enzyme at 1464, 1448, 1326, 1158, and 1010 cm−1, confirming structural modification. RTE measurements using a TES-92 detector (TES Electrical Electronic Corp., Taipei, Taiwan) demonstrated a correlation between emission intensity and shelf life: 12.8 ± 0.8 µW/m2 for proper shelf-life samples, 8.3 ± 0.8 µW/m2 for six-month-expired, and 5.1 ± 1.0 µW/m2 for one-year-expired pharmaceuticals. The study offers a promising supplementary tool for pharmaceutical quality control of hyaluronidase-based drugs.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Crystallographic Modification of Rosuvastatin Calcium: Formulation, Characterization and Pharmacokinetic Evaluation for Enhanced Dissolution, Stability and Bioavailability
by
Deepak Kulkarni and Sanjay Pekamwar
Sci. Pharm. 2026, 94(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm94010001 - 19 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Rosuvastatin calcium is a promising lipid-lowering agent and the drug of choice in hyperlipidemia. Conventional solid oral delivery of rosuvastatin is limited by its poor solubility and ultimately poor bioavailability. An attempt was made to fabricate the cocrystals of RSC for enhancing solubility
[...] Read more.
Rosuvastatin calcium is a promising lipid-lowering agent and the drug of choice in hyperlipidemia. Conventional solid oral delivery of rosuvastatin is limited by its poor solubility and ultimately poor bioavailability. An attempt was made to fabricate the cocrystals of RSC for enhancing solubility and bioavailability. Cocrystals were prepared by a microwave synthesiser-assisted solvent evaporation technique with multiple cocrystal formers. Rosuvastatin-Ascorbic acid (RSC-AA) cocrystals showed the highest solubility (~5-fold increased) amongst all twenty drug-coformer combination (DCC). RSC-AA cocrystals (1:1 ratio) were further characterized by various analytical techniques like FTIR, DSC and XRD to confirm the formation of cocrystals. RSC-AA cocrystals also showed improved flow properties and compressibility in comparison with pure drug, and it was demonstrated using the SeDeM diagram. RSC-AA cocrystals were further formulated into an immediate-release tablet by implementing experimental optimization. Comparative dissolution study of the cocrystal and pure drug tablet revealed improved dissolution after cocrystallization. RSC-AA cocrystal tablet showed the % drug release of 95.61 ± 3.94 while RSC pure drug showed the drug release of 67.83 ± 3.29. In vivo pharmacokinetic analysis showed significant improvement in systemic availability and cumulative absorption of the drug. The peak plasma concentration (Cmax) for RSC pure drug was 13.924 ± 0.477 μg/mL, while RSC-AA cocrystals showed a peak plasma concentration of 22.464 ± 0.484 μg/mL. Area Under Curve (AUC) of RSC-AA cocrystal was also significantly greater compared to the pure drug. In the stability study analysis, the shelf life was calculated from a graphical method and was found to be around 34.58 months for RSC-AA cocrystal tablets and 19.87 months for RSC pure drug tablets, which indicates improved stability with cocrystallization. Overall, the cocrystallization resulted in significant improvement in dissolution and solubility of RSC.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Injectable Biostimulator in Adipose Tissue: An Update and Literature Review
by
Kar Wai Alvin Lee, Heesoo Kim, Jong Keun Song, Olena Sydorchuk, Wong Ka Fai, Isabella Rosellini, Hongseok Kim, Kian Hong Lau, Michael H. Gold and Kyuho Yi
Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93(4), 62; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93040062 - 24 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Injectable biostimulatory agents such as poly-L-lactic acid (PLLA), polycaprolactone (PCL), and calcium hydroxyapatite (CaHA) have emerged as key tools in regenerative aesthetics due to their ability to stimulate adipogenesis and adipocyte metabolic activity, enhance collagen production, and improve dermal quality. This review aimed
[...] Read more.
Injectable biostimulatory agents such as poly-L-lactic acid (PLLA), polycaprolactone (PCL), and calcium hydroxyapatite (CaHA) have emerged as key tools in regenerative aesthetics due to their ability to stimulate adipogenesis and adipocyte metabolic activity, enhance collagen production, and improve dermal quality. This review aimed to provide an updated synthesis of the role of these agents in adipocyte stimulation, focusing on their mechanisms of action, clinical efficacy, and therapeutic applications. A comprehensive search of the MEDLINE, PubMed, and Ovid databases was conducted for studies published from 2018 onward, including in vitro and in vivo experiments, randomized controlled trials, and observational studies, which were evaluated according to the Oxford Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine hierarchy. The findings demonstrated that PCL promotes adipose-derived stem cell differentiation and extracellular matrix remodeling, while PLLA exhibits dual effects on collagen synthesis and adipocyte stimulation, with clinical trials such as the SPLASH study confirming significant improvements in dermal thickness and adipogenesis. CaHA provided immediate volumizing benefits with long-term tissue regeneration, and innovative approaches including combination therapies and novel injection protocols expanded clinical applications. Overall, PLLA, PCL, and CaHA represent effective and versatile biostimulatory agents that support natural and durable outcomes in aesthetic practice. Nevertheless, the absence of large-scale trials and standardized protocols highlights the need for further research to optimize safety, efficacy, and long-term treatment strategies.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Integrating 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing into Personalized Medicine for Pharmaceuticals: Opportunities, Limitations, and Future Perspectives
by
Nithin Vidiyala, Pavani Sunkishala, Preethi Mandati, Prashanth Parupathi and Dinesh Nyavanandi
Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93(4), 61; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93040061 - 24 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Over the last decade, additive manufacturing (AM) has been widely investigated for developing on-demand, patient-centric, and personalized medications. Among various AM techniques, fused deposition modeling (FDM), semi-solid extrusion (SSE), inkjet printing, binder jet printing, stereolithography (SLA), and selective laser sintering (SLS) have been
[...] Read more.
Over the last decade, additive manufacturing (AM) has been widely investigated for developing on-demand, patient-centric, and personalized medications. Among various AM techniques, fused deposition modeling (FDM), semi-solid extrusion (SSE), inkjet printing, binder jet printing, stereolithography (SLA), and selective laser sintering (SLS) have been most widely studied for developing simple and complex pharmaceutical medications. Implementing the AM platform enables decentralized manufacturing of medications at the hospitals and clinical sites. The dose and release profiles of the dosage forms can be tailored based on patient needs, providing flexibility to the physician. In fact, streamlining the AM process into a continuous manufacturing process equipped with process analytical technology (PAT) tools will ensure the manufacturing and delivery of safe and efficacious medications to the patient population. Complex medications, such as polypills, which are complex and time-consuming to manufacture using traditional manufacturing techniques, can be printed quickly using the AM approach. The pediatric patient population can be attracted to medication by printing the dosage forms with a geometry of interest. The AM platform can be integrated with artificial intelligence (AI) and health records to accelerate drug development and tailor medications based on patient conditions. Despite the various advantages that the AM platform brings to the pharmaceutical field, a few limitations, such as scalability, material innovation, secondary processing, and regulatory evolution, need to be addressed. This review article compares the advantages and limitations of the existing AM techniques along with a note on the recent advancements and future perspectives.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Terminological and Grammatical Study of Essential and Fatty Oils of Plants from the Austrian, Hungarian, Spanish, and Belgian Pharmacopoeias (19th Century)
by
Zsuzsanna Takáts, Attila Almási, Judit Szalai-Szolcsányi, Tünde Ambrus and Nóra Papp
Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93(4), 60; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93040060 - 20 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In this study, a terminological and grammatical survey of essential and fatty oils of plant origin was performed in the selected Austrian, Hungarian, Spanish, and Belgian pharmacopoeias from the 18th to 19th centuries. The Latin-language prescriptions were analysed for their content, sections, and
[...] Read more.
In this study, a terminological and grammatical survey of essential and fatty oils of plant origin was performed in the selected Austrian, Hungarian, Spanish, and Belgian pharmacopoeias from the 18th to 19th centuries. The Latin-language prescriptions were analysed for their content, sections, and indications, and then translated from Latin into English, and supplemented with the source plants. Oil types were categorised based on their preparation and origin. Most oils belong to essential oils in Ph. Austriaca I–IV, Ph. Belgica, and Ph. Hungarica I (20 in each). Cooked oils are described as having the highest number in Ph. Hispanica (21), while pressed oils are also included in a high ratio in Ph. Hisp. (18) and Ph. Austriaca V (15). At the same time, those from minerals are described only in Ph. Belg. (2) and Ph. Hisp. (5). Latin terms are used in preparation methods, including the most concise descriptions in Ph. Austriaca V and Ph. Hg. I. This comprehensive study provides new linguistic data on the oils of herbs in the selected pharmacopoeias. Studies of essential oils have recently been progressing, and this analysis might help in understanding information from old pharmacopoeias.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessPerspective
Biopharmaceuticals—Current Information and New Challenges
by
Miroslav Radenković
Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93(4), 59; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93040059 - 19 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Biopharmaceuticals are medical drugs produced by means of biotechnology. In contrast with small-molecule (traditional) drugs, which are usually synthesized chemically, biopharmaceuticals are derived from biological sources, including tissues, cells, or microorganisms. Biopharmaceuticals comprise a wide extent of therapies, such as vaccines, monoclonal antibodies,
[...] Read more.
Biopharmaceuticals are medical drugs produced by means of biotechnology. In contrast with small-molecule (traditional) drugs, which are usually synthesized chemically, biopharmaceuticals are derived from biological sources, including tissues, cells, or microorganisms. Biopharmaceuticals comprise a wide extent of therapies, such as vaccines, monoclonal antibodies, cell therapies, recombinant proteins, and gene therapies, as well as biosimilars. These products are designed to become important treatment options for different diseases, including cancer, autoimmune pathological disorders, andinfectious diseases. The development of biopharmaceuticals often includes multifaceted processes, involving genetic engineering and cellular culture techniques, to guarantee efficacy and safety. Accordingly, biopharmaceuticals’ legislation is a key component for ensuring the highest quality of medical products, as well as protecting public health. As a rapidly developing area inside the pharmaceutical industry, biopharmaceuticals represent a significant advancing stage in modern medicine, offering targeted therapies that can improve patient outcomes. Accordingly, this paper seeks to provide current state-of-the-art didactic information, including better insight into various challenges related to biopharmaceuticals’ development, classification, medical use, legislation and ethics.
Full article
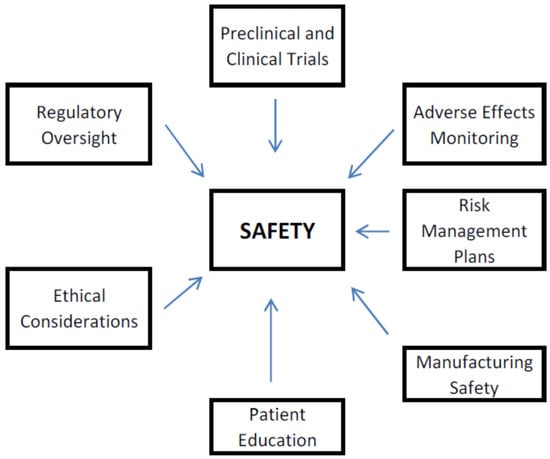
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Development and Optimisation of Docetaxel-Loaded Polymeric Nanoparticles for Oral Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer
by
Divya Wali, Shivakumar H. Nanjappa, Avichal Kumar and Rushikesh Shinde
Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93(4), 58; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93040058 - 14 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Docetaxel (DTX)-loaded polymeric nanoparticles composed of Eudragit RL and RS 100 were developed by solvent evaporation using D-α-tocopheryl polyethene glycol 1000 succinate as an emulsifier and optimised by Central Composite Design. The effects of homogenisation and sonication times on entrapment efficiency (%EE) and
[...] Read more.
Docetaxel (DTX)-loaded polymeric nanoparticles composed of Eudragit RL and RS 100 were developed by solvent evaporation using D-α-tocopheryl polyethene glycol 1000 succinate as an emulsifier and optimised by Central Composite Design. The effects of homogenisation and sonication times on entrapment efficiency (%EE) and drug release (%DR) were statistically analysed across nine batches. Particle size (PS) ranged from 302 ± 1.0 to 502 ± 2.0 nm, and zeta potential (ZP) from 25.8 ± 2.5 to 42.9 ± 1.7 mV. %EE and %DR (pH 1.2 for 2 h, then pH 7.4 for 22 h, 40 mL medium at 37 ± 0.5 °C) ranged from 69.32 ± 3.77 to 92.71 ± 0.16% and 19.24 ± 3.03 to 49.17 ± 1.98%, respectively. Optimised DTX nanoparticles (DNPs) showed EE of 78.18 ± 0.56%, DR of 46.21 ± 1.41% at 24 h, PS of 357.9 ± 2.4 nm, and ZP of 42.9 ± 3.7 mV. Scanning electron microscopy revealed ~300 nm cuboidal particles with smooth surfaces. X-Ray Diffraction and Differential Scanning Colorimetry confirmed reduced drug crystallinity in DNPs. In vitro haemolysis assays showed ~11.5-fold lower haemolytic potential (p < 0.0001) versus DTX, confirming improved safety. Fluorescence microscopy indicated enhanced cellular uptake of DNPs in MDA-MB-231 cells, while cytotoxicity assays of DNPs showed a lower IC50 (39.52 µM) compared to DTX (60.81 µM), demonstrating superior anticancer efficacy. Overall, DNPs represent a promising oral chemotherapy platform for breast cancer management.
Full article
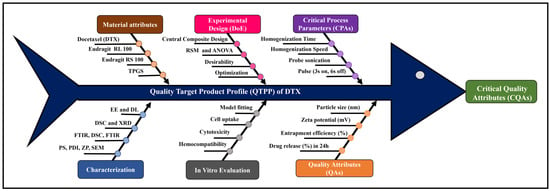
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Dysphania ambrosioides as a Source of Antioxidant Candidates for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) and Prostatitis: A Critical Review and In Silico Prioritisation
by
Enrique Jiménez-Ferrer, Tania Abarca-Salgado, Azamar Aarón Vargas-Radilla, José de Jesús Flores-Melgar and Rodolfo Abarca-Vargas
Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93(4), 57; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93040057 - 13 Nov 2025
Abstract
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and prostatitis are multifactorial urological disorders associated with chronic inflammation, oxidative stress, and androgenic imbalance. Dysphania ambrosioides (L.) Mosyakin & Clemants contains flavonoids and phenolic acids with well-recognised antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties; however, its potential activity against the molecular
[...] Read more.
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and prostatitis are multifactorial urological disorders associated with chronic inflammation, oxidative stress, and androgenic imbalance. Dysphania ambrosioides (L.) Mosyakin & Clemants contains flavonoids and phenolic acids with well-recognised antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties; however, its potential activity against the molecular targets of these prostatic disorders has not been systematically evaluated. A comparative quantitative analysis was performed using studies published between 2005 and 2025 that reported antioxidant activity (DPPH assay, IC50 in µg/mL) of D. ambrosioides extracts. Metabolites from extracts with IC50 values below the global mean (398.410 ± 81.810 µg/mL; n = 35) were selected for in silico prioritisation using OSIRIS, PASS, and ProTox 3.0, followed by molecular docking (CB-Dock2) against AR, 5AR2, COX-2, NLRP3, and α1A receptors. Luteolin and rosmarinic acid showed favourable binding energies (−9.5 to −7.7 kcal/mol) comparable in magnitude to reference drugs (finasteride −13.4, celecoxib −11.4, tamsulosin −7.3 kcal/mol). These metabolites, exhibited affinity for androgenic, inflammatory, and adrenergic targets, suggesting their potential to modulate key mechanisms underlying both BPH and prostatitis. This study integrates, for the first time, a quantitative assessment of antioxidant activity with a multitarget in silico analysis of D. ambrosioides, prioritising luteolin and rosmarinic acid as natural candidates with potential antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antiandrogenic properties relevant to prostatic health.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Antioxidant Activity of Natural Products—2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessCommunication
A Score-Based Rapid Screening and Network Visualization Method Based on Bioactive Ingredient-Induced Variations in Skin Cell Gene Expression
by
Mio Ogawa, Charles W. Crawford, Ayumu Ishigaki, Iri Sato-Baran, David D. Ordinario and Tadayoshi Miyashita
Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93(4), 56; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93040056 - 12 Nov 2025
Abstract
Bioactive ingredients are compounds, typically derived from natural sources, that provide specific health benefits or perform certain beneficial functions. Although they can play a role in maintaining good health, their effects can vary widely based on a person’s specific genotype and phenotype, leading
[...] Read more.
Bioactive ingredients are compounds, typically derived from natural sources, that provide specific health benefits or perform certain beneficial functions. Although they can play a role in maintaining good health, their effects can vary widely based on a person’s specific genotype and phenotype, leading to situations where certain ingredients induce beneficial responses for some individuals but not others. Herein, we report a method for the rapid discovery of relationships between genes, bioactive ingredients, and physiological effects. First, RNA-Seq was performed after applying 6 plant-derived ingredients to a three-dimensional skin model. After determining expression changes for each ingredient, these changes were ranked and visualized using score-based prediction models. Based on our analysis, we were able to quickly determine and visualize the effect (or lack thereof) of the ingredients on gene expression. Our findings demonstrate the utility of combining RNA-Seq with score-based models and visualizations for screening bioactive ingredients by gene expression, visualizing their impact based on ingredient or physiological effect, and the applicability of this method to any bioactive ingredient for rapid determination of potential ingredients relevant to maintaining health and wellness.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Bioinformatics in Drug Design and Discovery—2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Advancements in Encapsulation Technologies: The Potential of Polyphenols as an Antidiabetic Therapy
by
Rigoberto Cabanillas-Ponce de León, Feliznando Isidro Cardenas-Torres, Noe Ontiveros, Laura Aracely Contreras-Angulo, Cristina Alicia Elisande-Romero, Nayely Leyva-López, Manuel de Jesús Bernal-Millán, Jose Basilio Heredia and Erick Paul Gutiérrez-Grijalva
Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93(4), 55; https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93040055 - 28 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a disease that affects over 537 million people worldwide and results in 6.7 million deaths annually. Conventional treatment of this disease focuses on lifestyle changes and drug administration. However, very few people can adhere to a healthier lifestyle, and
[...] Read more.
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a disease that affects over 537 million people worldwide and results in 6.7 million deaths annually. Conventional treatment of this disease focuses on lifestyle changes and drug administration. However, very few people can adhere to a healthier lifestyle, and drugs are difficult to access, especially in low- and middle-income countries. An alternative as an adjuvant to the treatment of DM is the phenolic compounds from plants with reported anti-diabetic effects. However, the bioavailability of these compounds is very low since they are affected by the gastrointestinal tract and xenobiotic metabolism. To improve the availability of these compounds, an emerging technology such as encapsulation is being used since it has been reported that the encapsulation of phenolic compounds improves both their bioaccessibility and bioavailability, as well as their bioactivity. In this review, we will focus on compiling the most up-to-date information on the different encapsulation processes of phenolic compounds and the antidiabetic effect of encapsulated phenolic compounds using the databases PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar. We will discuss the mechanisms, pathways, and receptors involved in the modulation of DM, especially those related to inflammation, oxidative stress, and insulin resistance.
Full article
Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal MenuJournal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
27 January 2026
Meet Us at the 5th Molecules Medicinal Chemistry Symposium, 14–17 May 2026, Beijing, China
Meet Us at the 5th Molecules Medicinal Chemistry Symposium, 14–17 May 2026, Beijing, China

3 December 2025
Meet Us at the 5th Molecules Medicinal Chemistry Symposium, 14–17 May 2026, Beijing, China
Meet Us at the 5th Molecules Medicinal Chemistry Symposium, 14–17 May 2026, Beijing, China

Topics
Topic in
Cancers, IJMS, Pharmaceuticals, Pharmaceutics, Sci. Pharm., Current Oncology, Molecules
Recent Advances in Anticancer Strategies, 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Hassan Bousbaa, Zhiwei HuDeadline: 31 March 2026
Topic in
CIMB, Molecules, Pharmaceuticals, Pharmaceutics, Sci. Pharm.
Challenges and Opportunities in Drug Delivery Research, 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Lenuta Profire, Ioana Mirela VasincuDeadline: 30 June 2026
Topic in
Cancers, CIMB, Current Oncology, Sci. Pharm., Antibodies, IJMS, IJTM
Antibody-Mediated Therapy and Other Emerging Therapies in Cancer Treatment
Topic Editors: Won Sup Lee, Yaewon Yang, Seil GoDeadline: 31 July 2026
Topic in
Biomedicines, IJMS, Sci. Pharm., Molecules, Future Pharmacology, Biomolecules
Natural Products and Drug Discovery—2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Sonia Piacente, Marta MenegazziDeadline: 30 September 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Sci. Pharm.
Monoclonal Antibodies in the Treatment of Diseases: Focus on Stability, Storage, and Administration
Guest Editor: Stefano RugaDeadline: 31 May 2026
Special Issue in
Sci. Pharm.
Anticancer Potential of Natural Products
Guest Editor: Yulin RenDeadline: 31 May 2026
Special Issue in
Sci. Pharm.
Pharmaceutical Applications of Heterocyclic Compounds
Guest Editor: Thierry BessonDeadline: 31 May 2026
Special Issue in
Sci. Pharm.
Computer-Aided Drug Design and Molecular Synthesis
Guest Editors: Osvaldo Santos-Filho, Arthur Eugen KümmerleDeadline: 31 May 2026







