Isopimaric Acid Derivatives as Potential Dual PPARα/γ Agonists in the Treatment of Metabolic Syndrome
Abstract
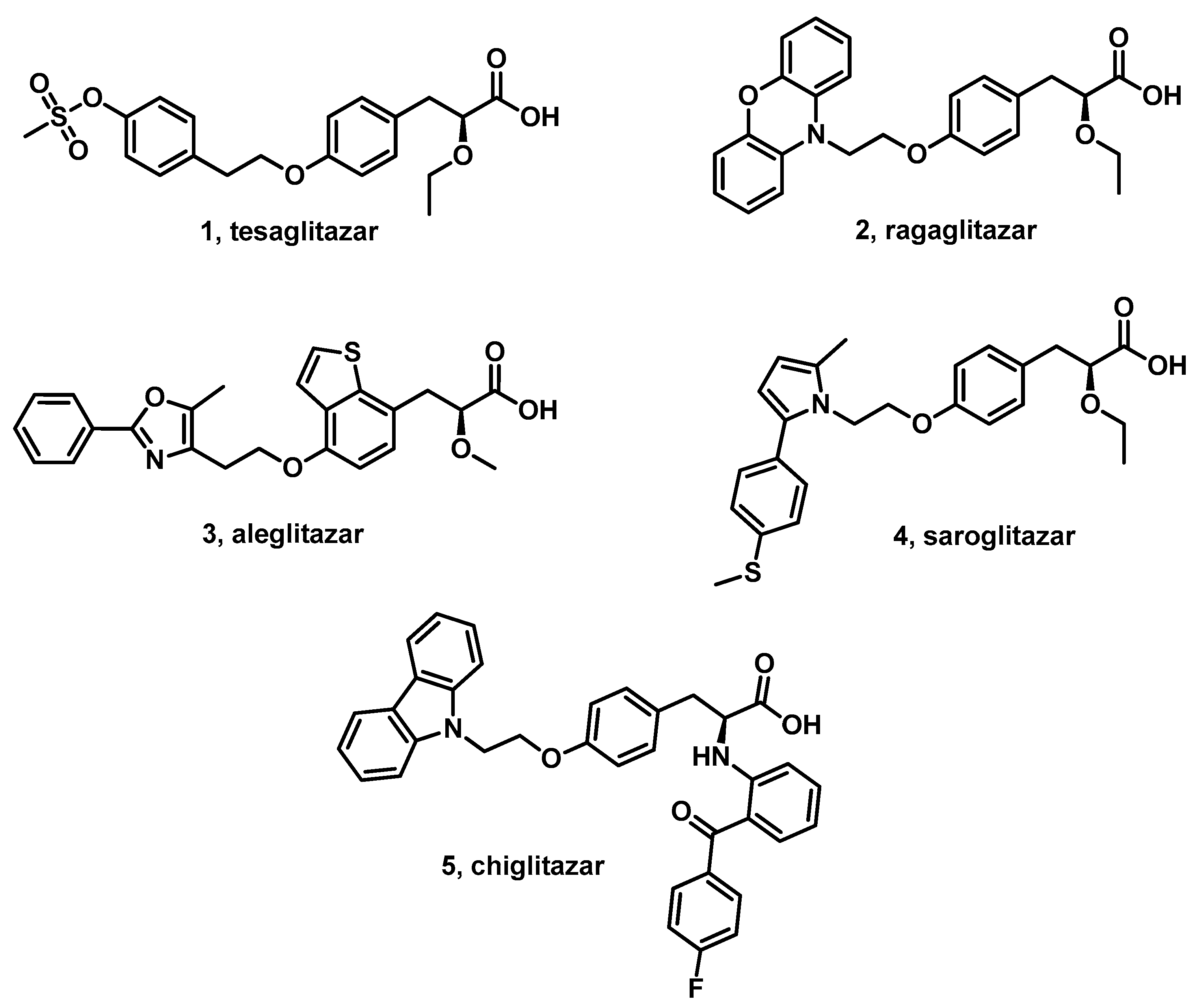
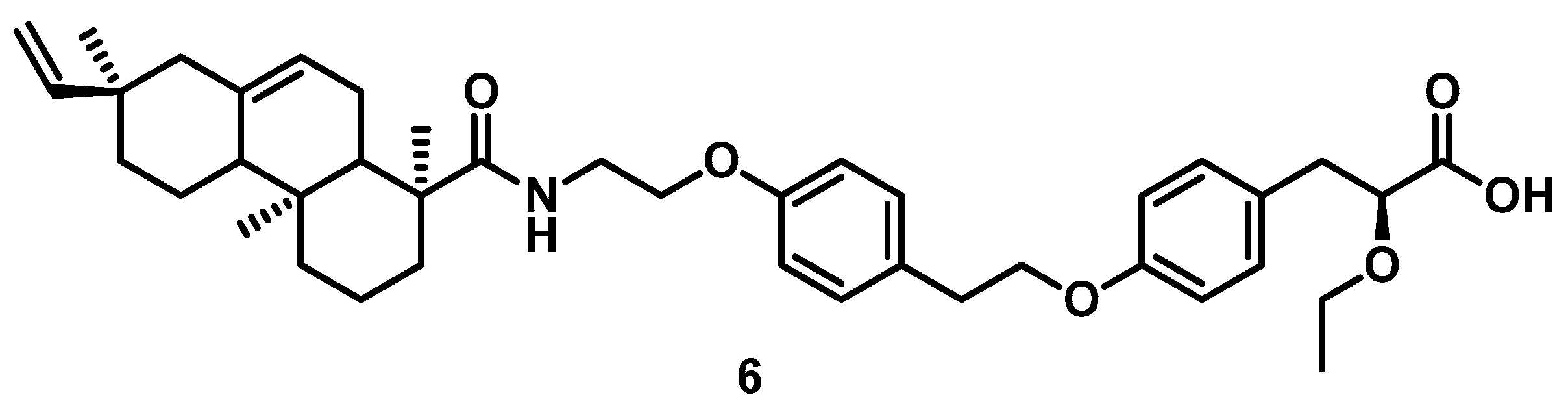
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
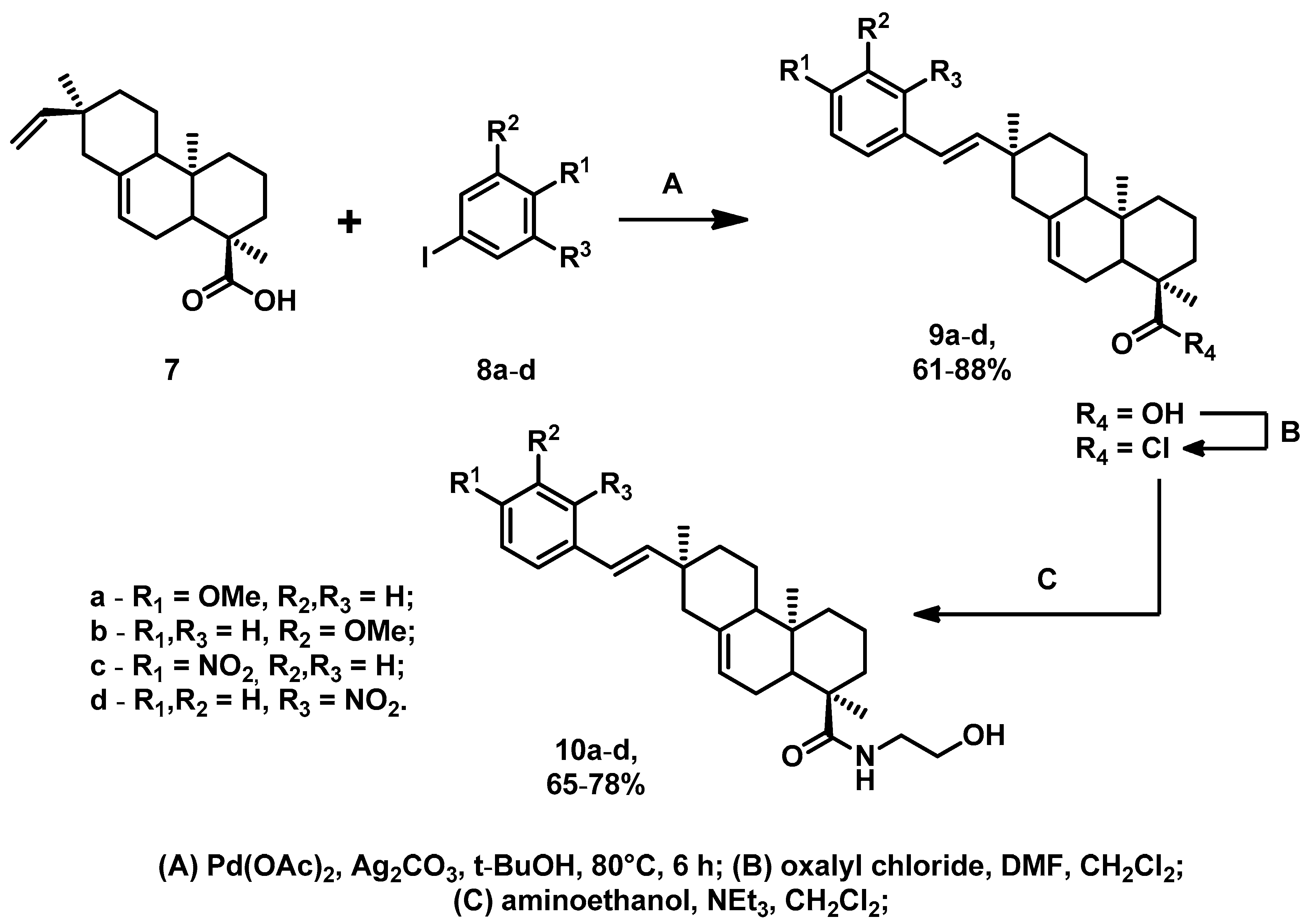
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Biology
2.2.1. Animals
2.2.2. The OGTT
2.2.3. The ITT
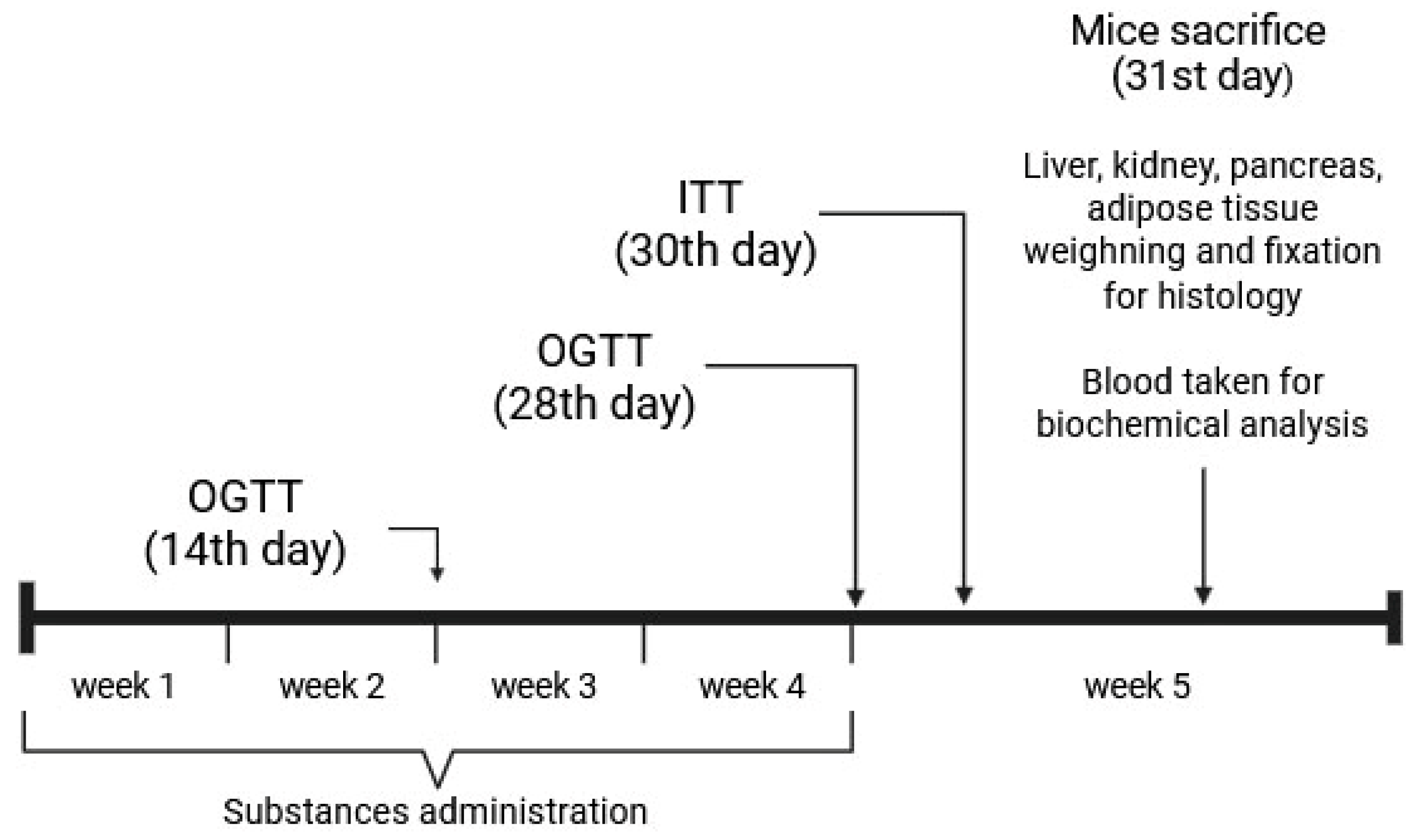
2.2.4. The AY Mice Experiment Design
2.2.5. Biochemical Assays
2.2.6. Histological Examination
2.2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
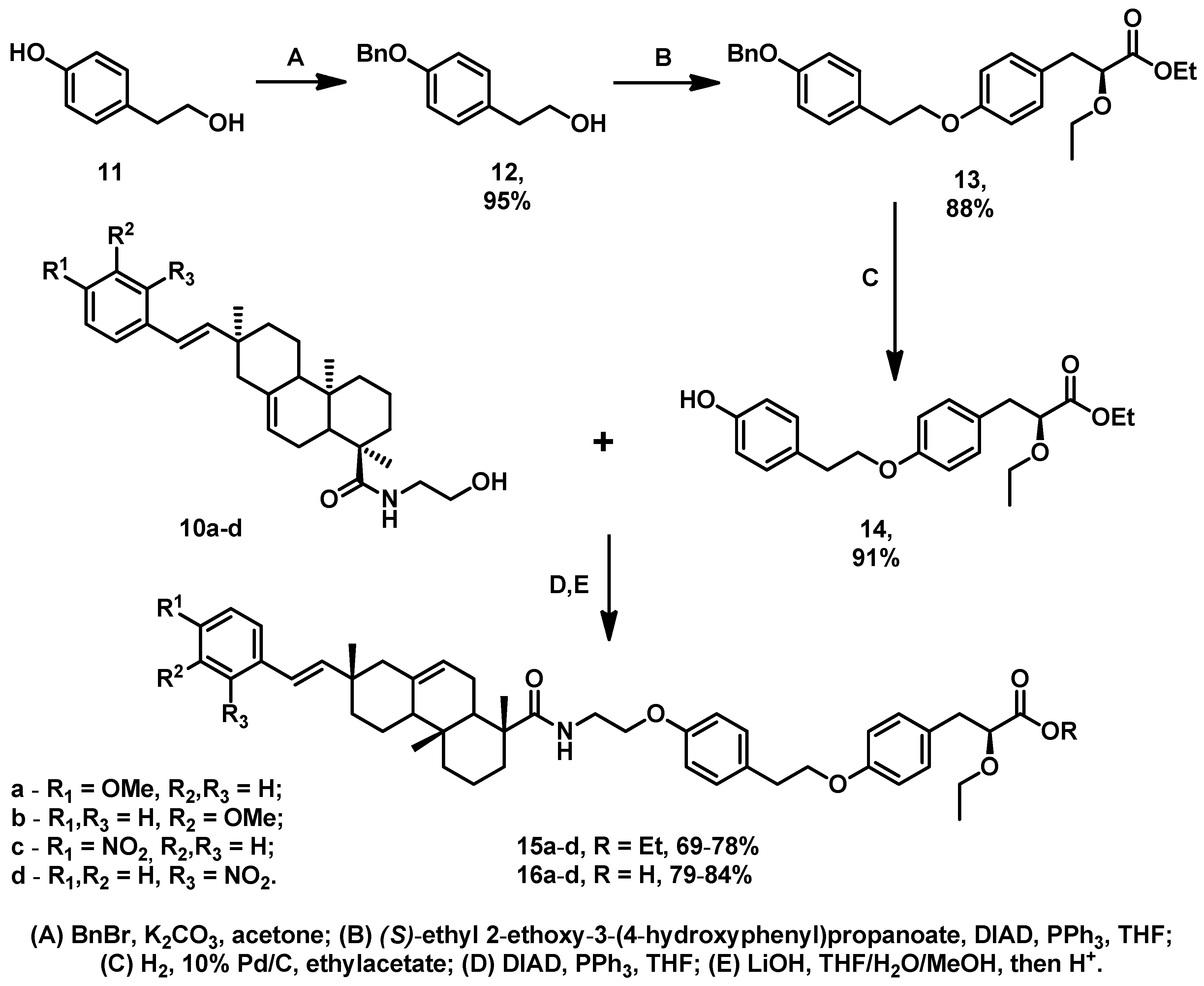
3.1. Chemistry
3.2. Biology
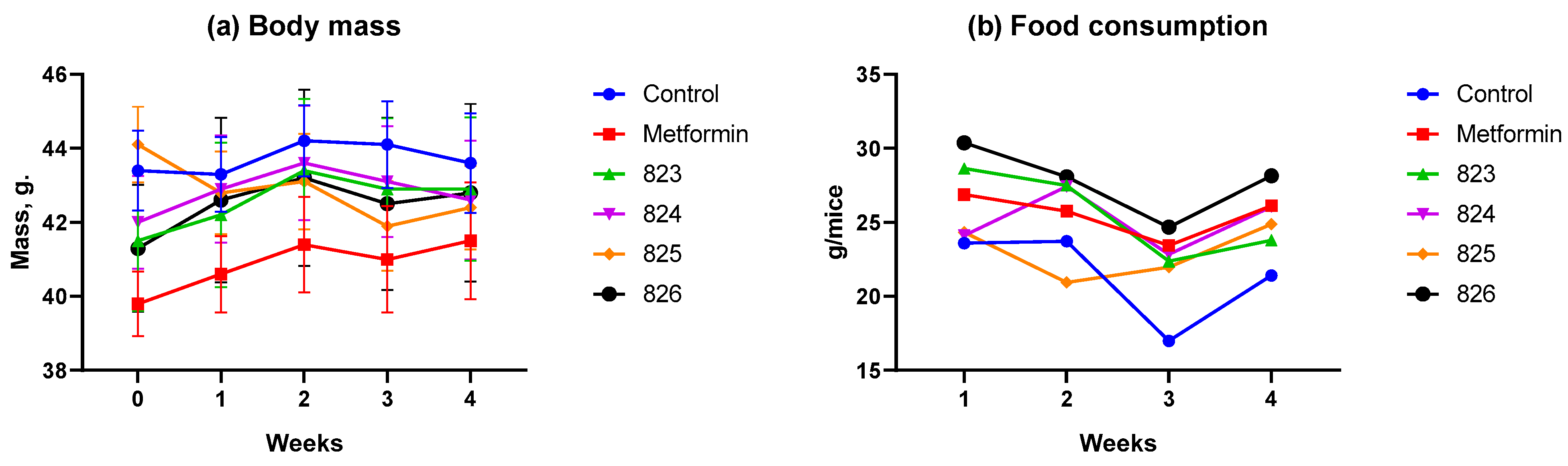
3.2.1. Body Weight and Food Consumption Dynamics
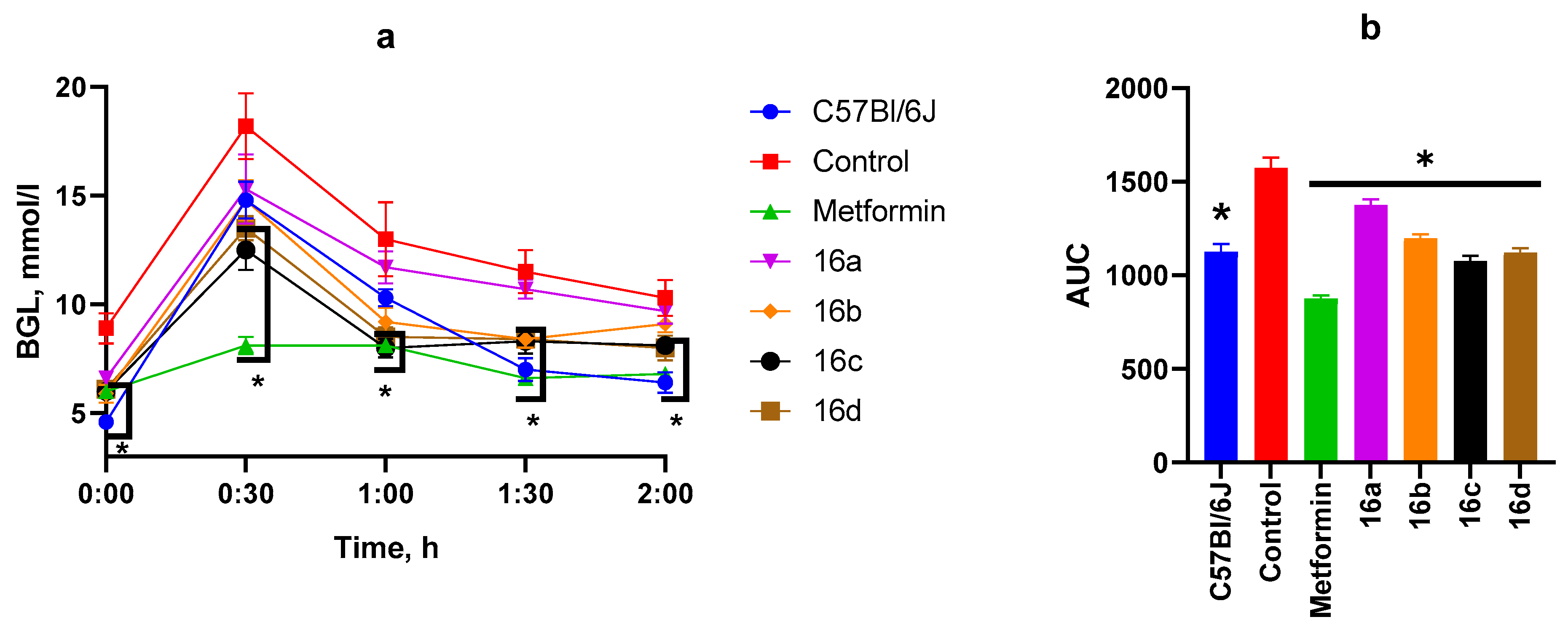
3.2.2. OGTT After Two Weeks of Substance Administration
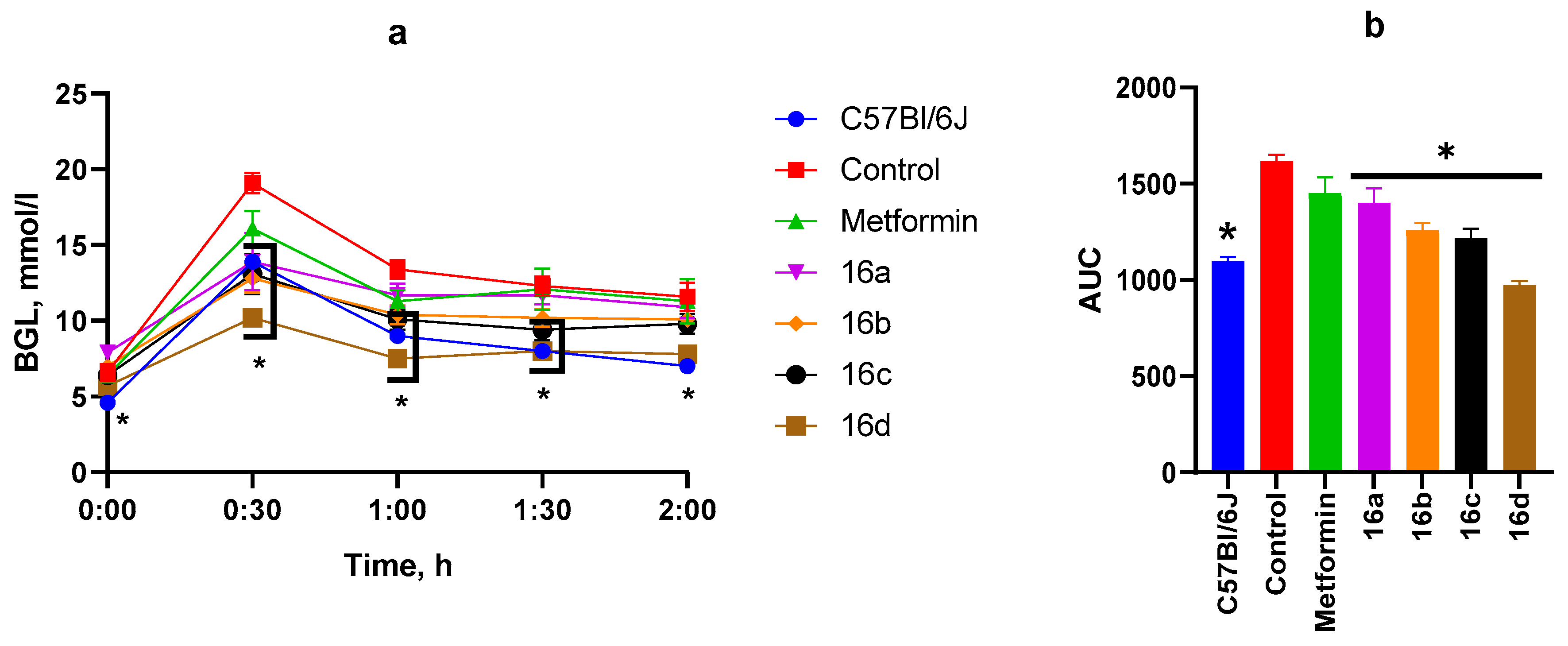
3.2.3. OGTT After Four Weeks of Substance Administration
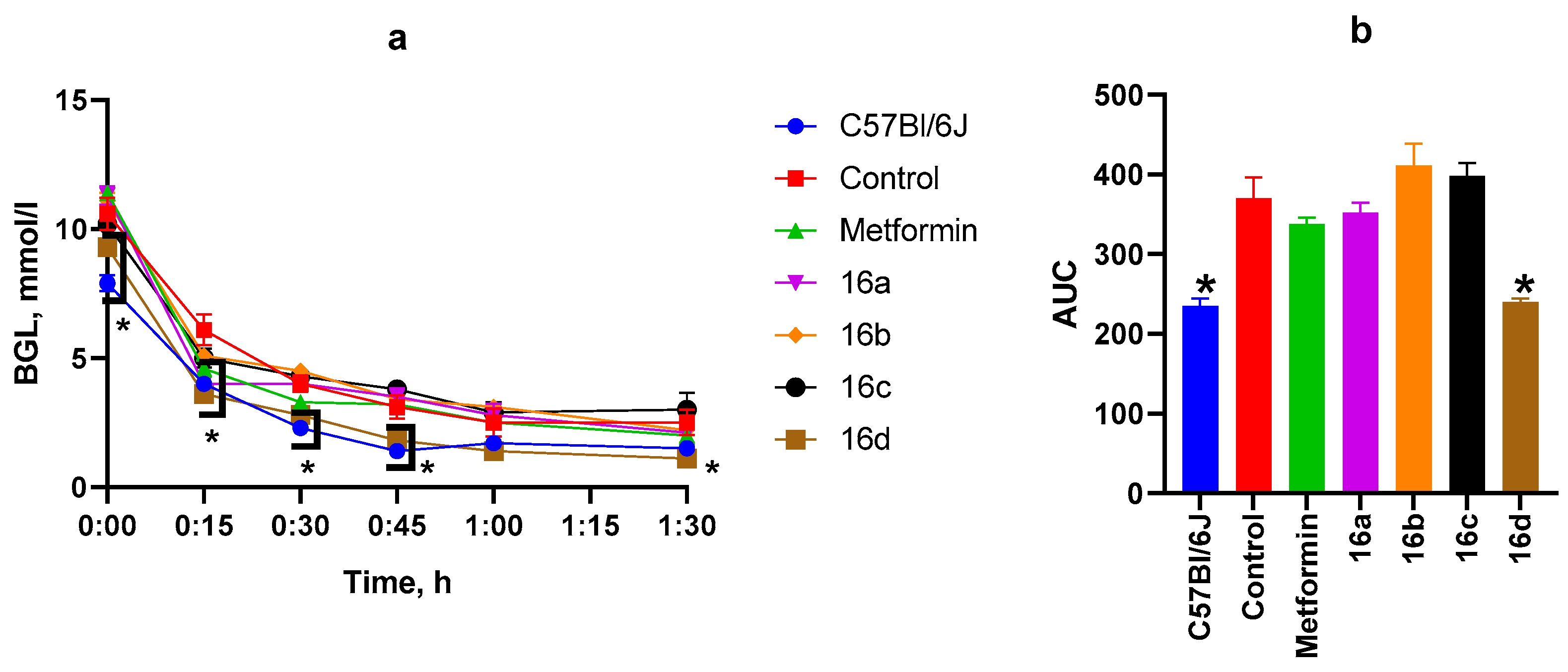
3.2.4. ITT
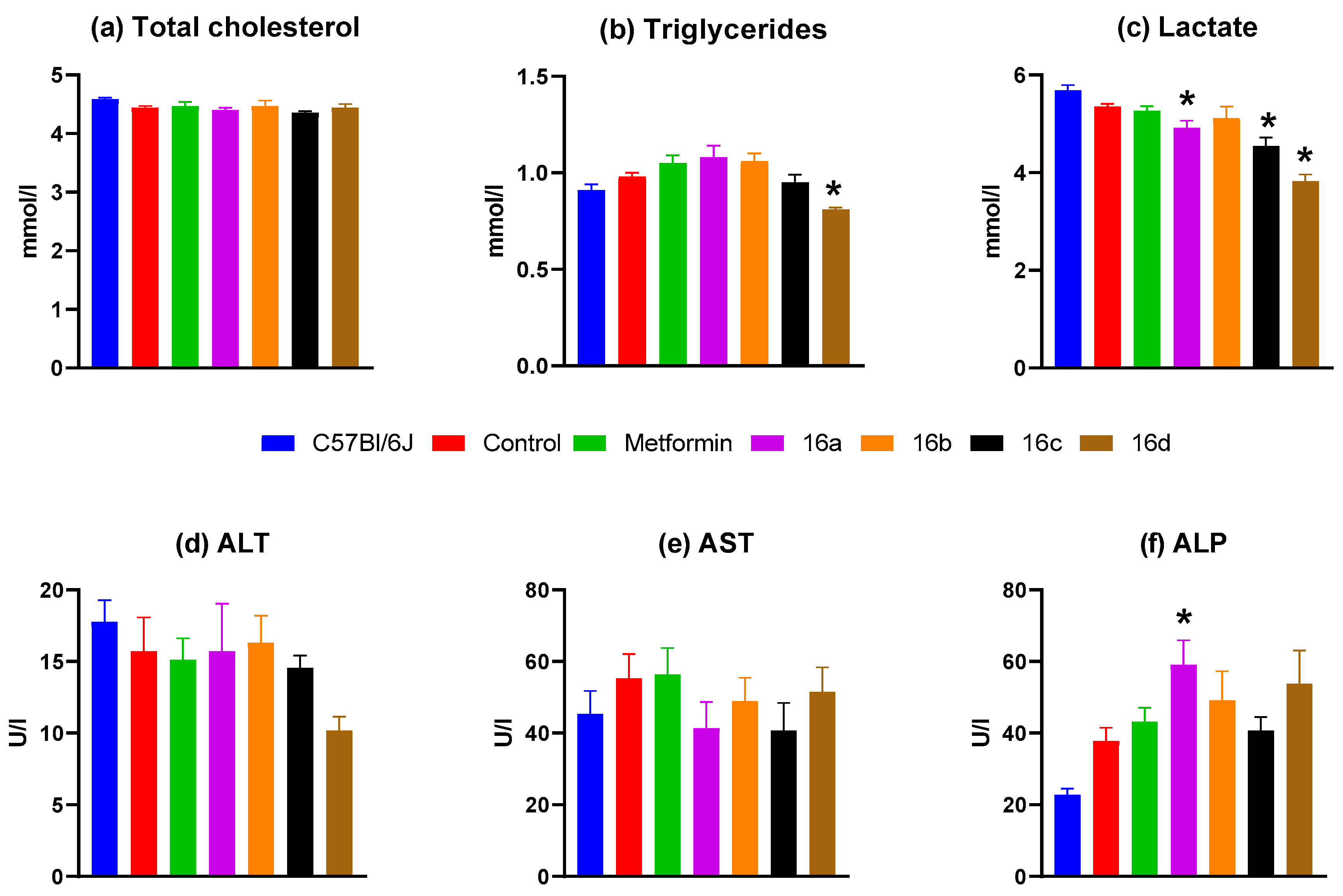
3.2.5. Biochemical Blood Analysis
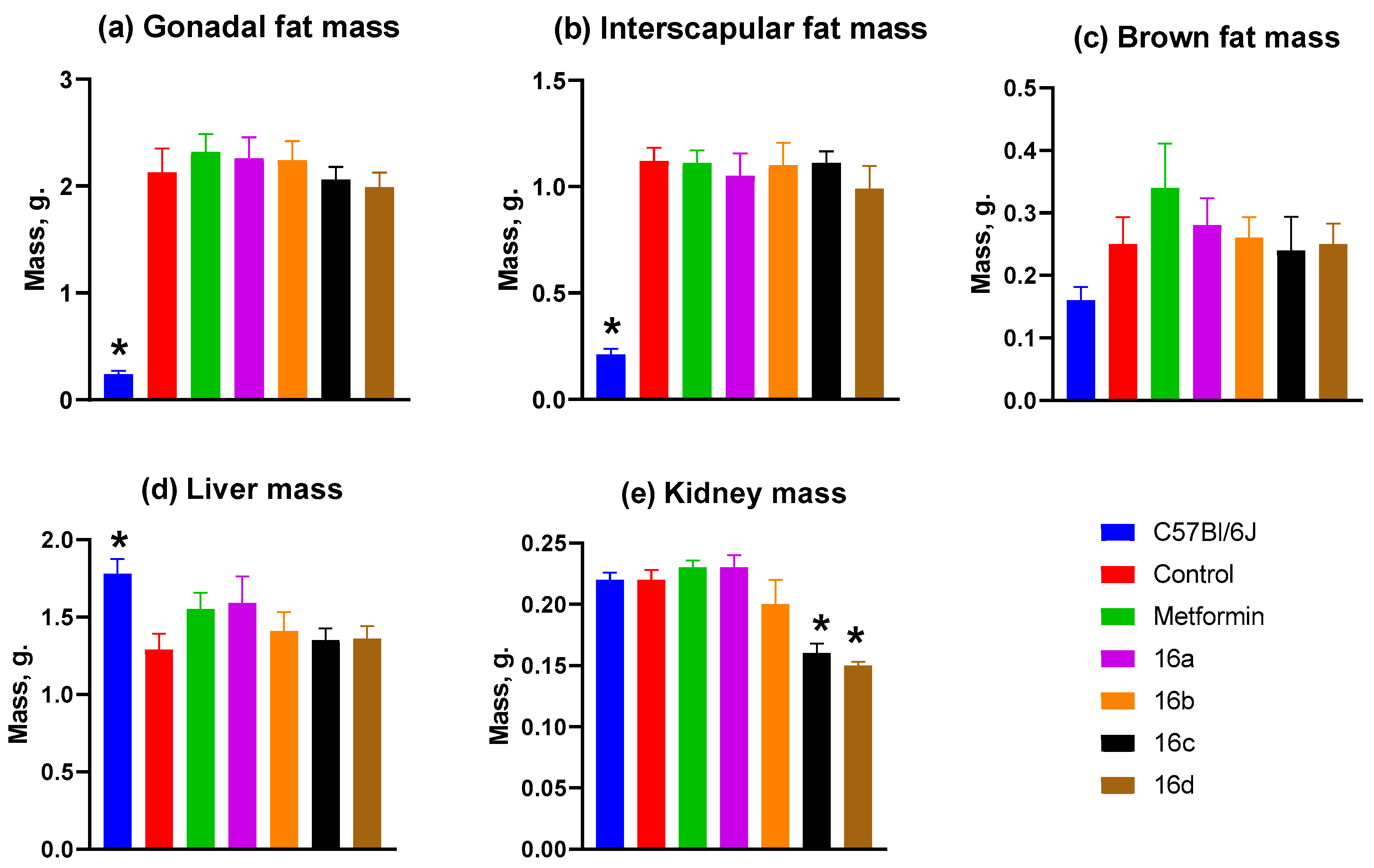
3.2.6. Mass of Animal Organs and Tissues
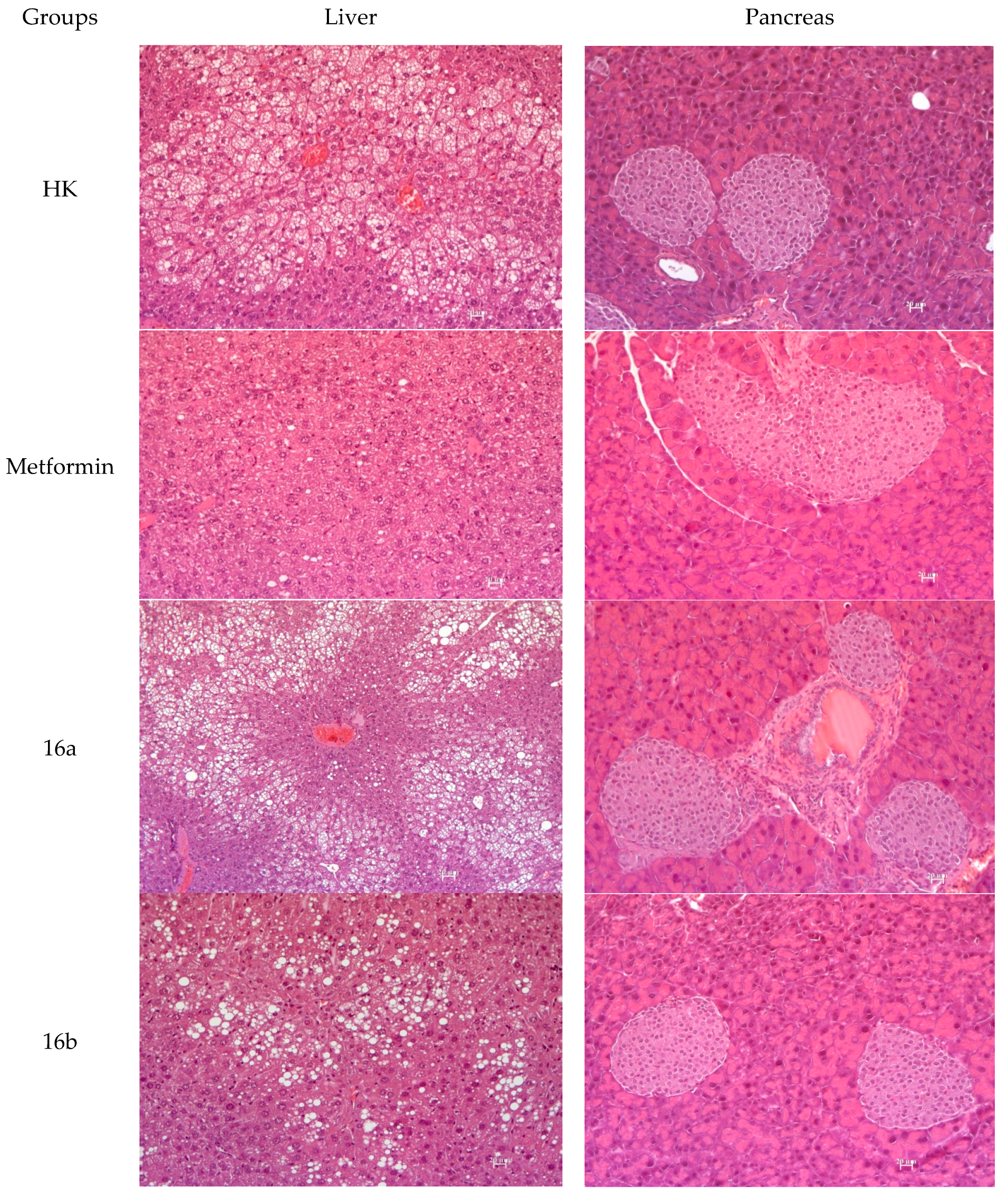
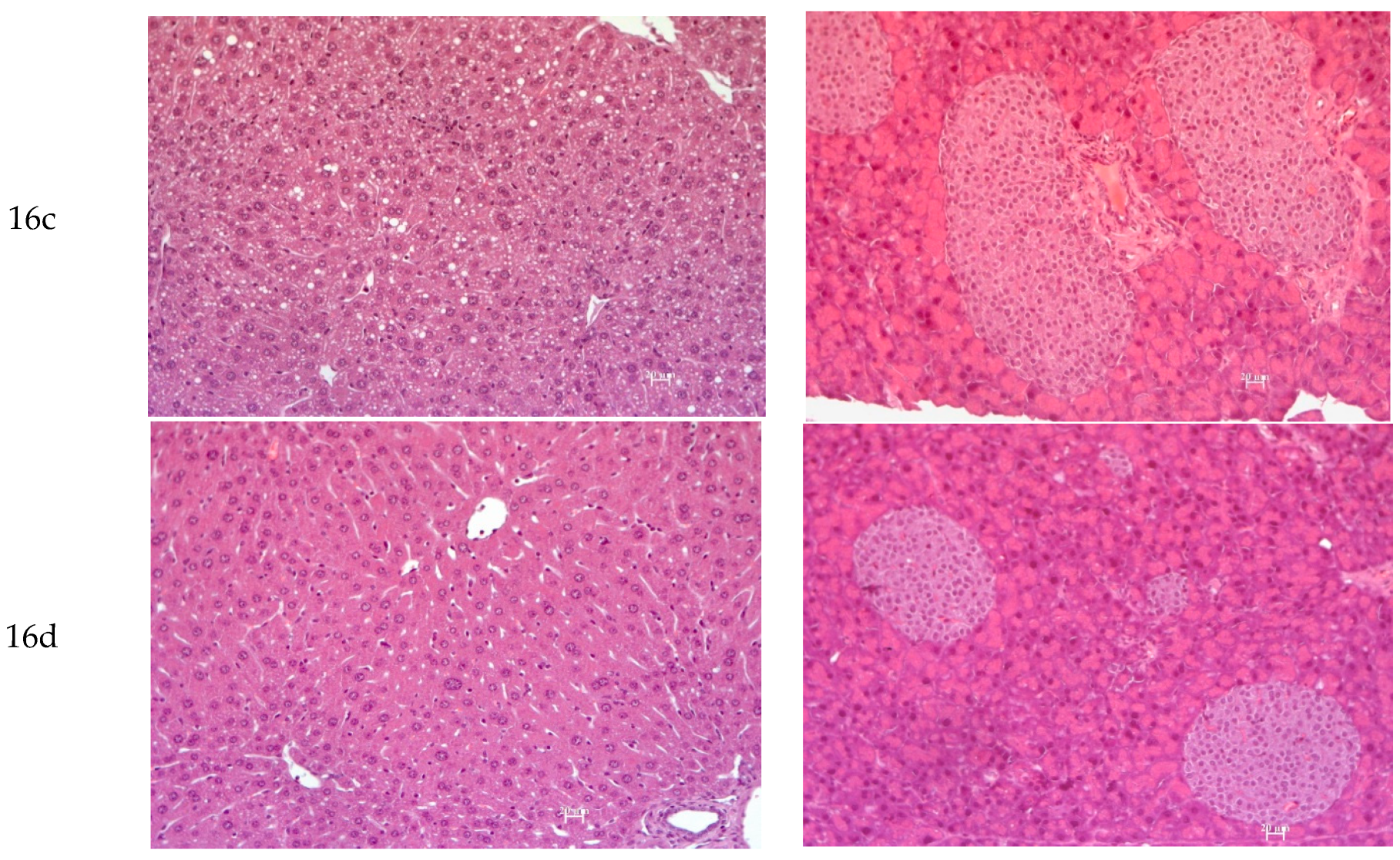
3.2.7. Histology
4. Discussion
4.1. Chemistry
4.2. Biology
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NAFLD | Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease |
| T2DM | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus |
| MS | Metabolic Syndrome |
| PPAR | Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors |
| DIAD | Diisopropyl Azodicarboxylate |
| THF | Tetrahydrofuran |
| HPLC | High-Performance Liquid Chromatography |
| NMR | Nuclear magnetic resonance |
| OGTT | Oral Glucose Tolerance Test |
| AUC | Areas Under the Curve |
| ITT | Insulin Tolerance Test |
| ALT | Alanine Aminotransferase |
| AST | Aspartate Aminotransferase |
| ALP | Alkaline Phosphatase |
References
- Mohamed, S.; Shalaby, M.A.; El-Shiekh, R.A.; Emam, S.R.; Bakr, A.F. Metabolic syndrome: Risk factors, diagnosis, pathogenesis, and management with natural approaches. Food Chem. Adv. 2023, 3, 100335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuschnir, M.C.; Bloch, K.V.; Szklo, M.; Klein, C.H.; Barufaldi, L.A.; Abreu Gde, A.; Schaan, A.; da Veiga, G.V.; da Silva, T.L.N.; de Vasconcellos, M.T.L.; et al. ERICA: Prevalence of metabolic syndrome in Brazilian adolescents. Rev. Saude Publica 2016, 50 (Suppl. 1), 11s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Duan, X.; Fan, Z.; Wang, S.; Liu, S.; Liu, L.; Wang, F.; Yu, L.; Zhou, F.; et al. Metabolic syndrome, and particularly the hypertriglyceridemic-waist phenotype, increases breast cancer risk, and adiponectin is a potential mechanism: A case–control study in chinese women. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 10, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, K.S.; Kim, H.; Jeong, H.; Choi, M.J.; Yoo, H.W.; Han, T.-H.; Lee, H. The relationship between metabolic syndrome and the incidence of colorectal cancer. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2020, 25, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grgurevic, I.; Podrug, K.; Mikolasevic, I.; Kukla, M.; Madir, A.; Tsochatzis, E.A. Natural history of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Implications for clinical practice and an individualized approach. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 2020, 9181368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Tu, R.; Yuan, H.; Shen, L.; Hou, J.; Liu, X.; Niu, M.; Zhai, Z.; Pan, M.; Wang, C. Associations of unhealthy lifestyles with metabolic syndrome in Chinese rural aged females. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association. 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2017, 40 (Suppl. 1), S11–S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazıcı, D.; Sezer, H. Insulin Resistance, Obesity and Lipotoxicity. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 960, 277–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erion, D.M.; Park, H.J.; Lee, H.Y. The role of lipids in the pathogenesis and treatment of type 2 diabetes and associated co-morbidities. BMB Rep. 2016, 49, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Shah, R.B.; Singhal, S.; Dutta, S.B.; Bansal, S.; Sinha, S.; Haque, M. Metformin: A review of potential mechanism and therapeutic utility beyond diabetes. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2023, 17, 1907–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, J.J.; Nauck, M.A. Risk of pancreatitis in patients treated with incretin-based therapies. Diabetologia 2014, 57, 1320–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcox, G. Insulin and insulin resistance. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2005, 26, 19–39. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ruscica, M.; Ferri, N.; Banach, M.; Sirtori, C.R.; Corsini, A. Side effects of statins: From pathophysiology and epidemiology to diagnostic and therapeutic implications. Cardiovasc. Res. 2023, 118, 3288–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zadelaar, A.S.; Boesten, L.S.; Jukema, J.W.; van Vlijmen, B.J.; Kooistra, T.; Emeis, J.J.; Lundholm, E.; Camejo, G.; Havekes, L.M. Dual PPARalpha/gamma agonist tesaglitazar reduces atherosclerosis in insulin-resistant and hypercholesterolemic ApoE*3Leiden mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2006, 26, 2560–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, R. The first approved agent in the Glitazar’s Class: Saroglitazar. Curr. Drug Targets 2014, 15, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.P.; Shan, S.; Chen, Y.T.; Ning, Z.Q.; Sun, S.J.; Liu, Q.; Lu, X.; Xie, M.; Shen, Z. The PPARalpha/gamma dual agonist chiglitazar improves insulin resistance and dyslipidemia in MSG obese rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 148, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural products as sources of new drugs from 1981 to 2014. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 629–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fomenko, V.; Blokhin, M.; Kuranov, S.; Khvostov, M.; Baev, D.; Borisova, M.S.; Luzina, O.; Tolstikova, T.G.; Salakhutdinov, N.F. Triterpenic acid amides as a promising agent for treatment of metabolic syndrome. Sci. Pharm. 2021, 89, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khvostov, M.V.; Blokhin, M.E.; Borisov, S.A.; Fomenko, V.V.; Meshkova, Y.V.; Zhukova, N.A.; Nikonova, S.V.; Pavlova, S.V.; Pogosova, M.A.; Medvedev, S.P.; et al. Antidiabetic effect of dihydrobetulonic acid derivatives as PPARα/γ agonists. Sci. Pharm. 2024, 92, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blokhin, M.E.; Kuranov, S.O.; Khvostov, M.V.; Fomenko, V.V.; Luzina, O.A.; Zhukova, N.A.; Elhajjar, C.; Tolstikova, T.G.; Salakhutdinov, N.F. Terpene-containing analogues of glitazars as potential therapeutic agents for metabolic syndrome. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 2230–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Feliciano, A.; Medarde, M.; Cabellero, E.; Tome, F.; Hebrero, B. β-Stereospecific hydroboration of 13-epi-pimar-8(14)-enes. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1 1992, Issue 13, 1665–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddick, J.A.; Bunger, W.B.; Sakano, T.K. Organic Solvents: Physical Properties and Methods of Purification, 4th ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1986; ISBN 9780471084679. [Google Scholar]
- Tai, M.M. A mathematical model for the determination of total area under glucose tolerance and other metabolic curves. Diabetes Care 1994, 17, 152–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohnert, T.; Prakash, C. ADME profiling in drug discovery and development: An overview. In Encyclopedia of Drug Metabolism and Interactions; Lyubimov, A.V., Ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gromova, M.A.; Kharitonov, Y.V.; Rybalova, T.V.; Shults, E.E. Synthetic studies on tricyclic diterpenoids: Convenient synthesis of 16-arylisopimaranes. Monatshefte Chem. 2020, 151, 1817–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantri, S.; Thakkar, A.; Vora, A.; Alavala, R.R. Towards a mechanistic understanding of atherosclerosis drug design. In Applications of Computational Tools in Drug Design and Development; Rao, G.S.K., Alavala, R.R., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2025; pp. 801–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.C.; Ye, W.R.; Zheng, Y.J.; Zhang, S.S. Oxamate enhances the anti-inflammatory and insulin-sensitizing effects of metformin in diabetic mice. Pharmacology 2017, 100, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nepali, K.; Lee, H.Y.; Liou, J.P. Nitro-Group-Containing Drugs. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 2851–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiodi, D.; Ishihara, Y. Methoxy group: A non-lipophilic “scout” for protein pocket finding. Future Med. Chem. 2025, 17, 983–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Singh, R.; Vasudeva, N.; Sharma, S. Acute and chronic animal models for the evaluation of anti-diabetic agents. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2012, 11, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foretz, M.; Guigas, B.; Viollet, B. Metformin: Update on mechanisms of action and repurposing potential. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2023, 19, 460–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, A.Z.; Althagafi, I.I.; Shamshad, H. Role of PPAR receptor in different diseases and their ligands: Physiological importance and clinical implications. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 166, 502–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Österreichische Pharmazeutische Gesellschaft. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Blokhin, M.E.; Borisov, S.A.; Gromova, M.A.; Meshkova, Y.V.; Zhukova, N.A.; Nikonova, S.V.; Zhurakovsky, I.P.; Luzina, O.A.; Khvostov, M.V.; Kudlay, D.A.; et al. Isopimaric Acid Derivatives as Potential Dual PPARα/γ Agonists in the Treatment of Metabolic Syndrome. Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93, 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93030044
Blokhin ME, Borisov SA, Gromova MA, Meshkova YV, Zhukova NA, Nikonova SV, Zhurakovsky IP, Luzina OA, Khvostov MV, Kudlay DA, et al. Isopimaric Acid Derivatives as Potential Dual PPARα/γ Agonists in the Treatment of Metabolic Syndrome. Scientia Pharmaceutica. 2025; 93(3):44. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93030044
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlokhin, Mikhail E., Sergey A. Borisov, Mariia A. Gromova, Yulia V. Meshkova, Nataliya A. Zhukova, Sophia V. Nikonova, Igor P. Zhurakovsky, Olga A. Luzina, Mikhail V. Khvostov, Dmitry A. Kudlay, and et al. 2025. "Isopimaric Acid Derivatives as Potential Dual PPARα/γ Agonists in the Treatment of Metabolic Syndrome" Scientia Pharmaceutica 93, no. 3: 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93030044
APA StyleBlokhin, M. E., Borisov, S. A., Gromova, M. A., Meshkova, Y. V., Zhukova, N. A., Nikonova, S. V., Zhurakovsky, I. P., Luzina, O. A., Khvostov, M. V., Kudlay, D. A., & Salakhutdinov, N. F. (2025). Isopimaric Acid Derivatives as Potential Dual PPARα/γ Agonists in the Treatment of Metabolic Syndrome. Scientia Pharmaceutica, 93(3), 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93030044







