Deciphering Drug Repurposing Strategies: Antiviral Properties of Candidate Agents Against the Mpox Virus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mpox Virus Biology and Pathogenesis
2.1. Genomic Characteristics and the Viral Lifecycle
2.2. Key Molecular Targets for Therapeutic Intervention
2.3. Host–Pathogen Interactions
3. The Rationale for Drug Repurposing in Mpox Management
3.1. Advantages of Repurposed Drugs in Addressing MPXV
3.2. Historical Success of Drug Repurposing in Viral Outbreaks
3.3. Criteria for Selecting Candidate Drugs
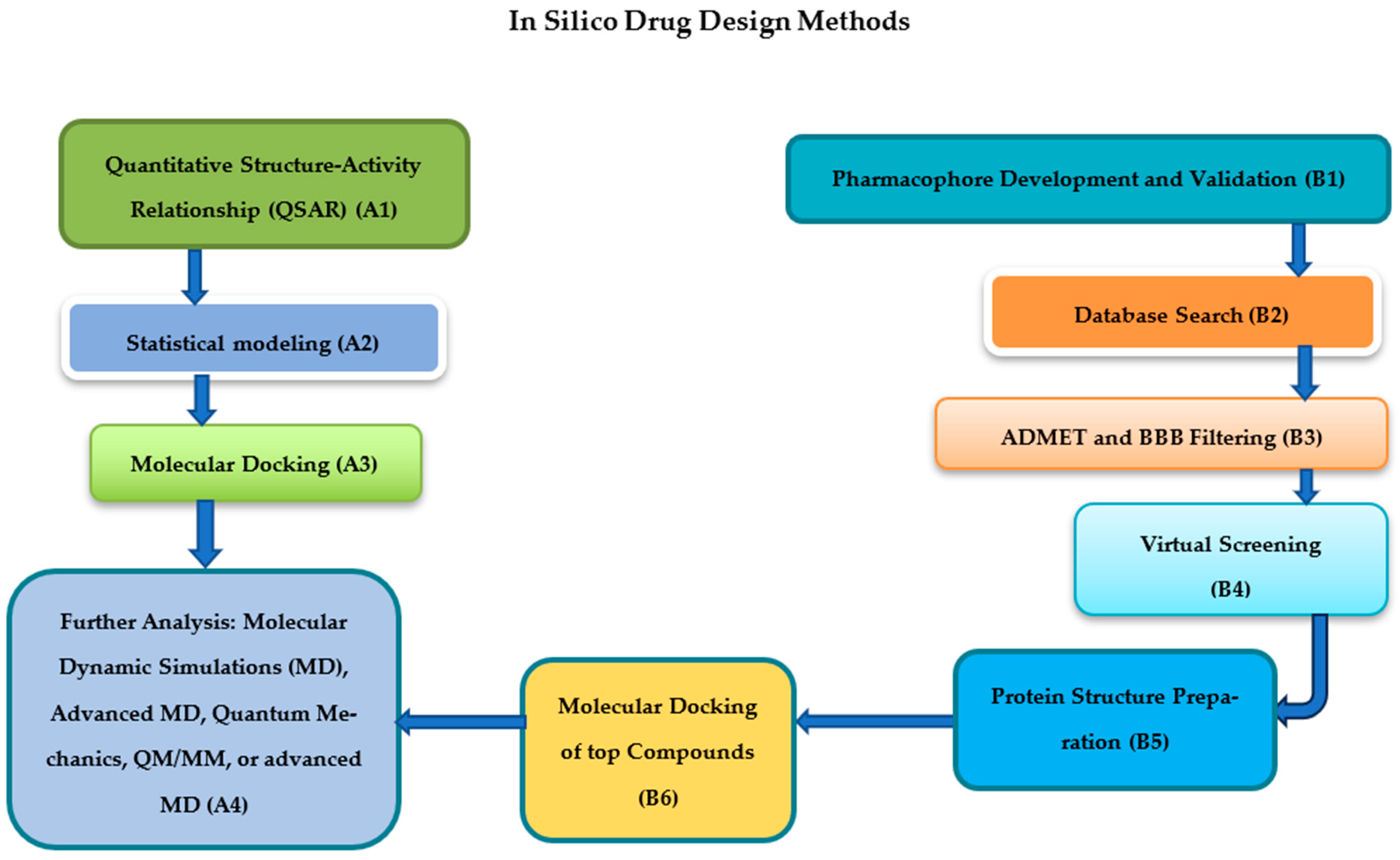
4. Computational Approaches in Drug Repurposing
4.1. Molecular Docking and Dynamics Simulations
4.2. Virtual Screening for Antiviral Candidates
4.3. Phenotypical Drug Repurposing Approaches
4.4. Systems Biology and Network Pharmacology in Drug Discovery
5. Repurposed Drug Candidates for Mpox Virus
5.1. Antiviral Agents with Potential Efficacy Against Mpox
5.2. Immunomodulatory Drugs for Symptom Management
5.3. Drugs Targeting Mpox-Specific Molecular Pathways
6. Preclinical and Clinical Evaluation of Repurposed Drugs
6.1. In Vitro and In Vivo Studies on Drug Efficacy
6.2. Insights from Case Studies and Small-Scale Clinical Trials
6.3. Challenges in Scaling Drug Trials for Emerging Viruses
7. Limitations and Challenges in Repurposing Drugs for Mpox
7.1. Drug–Drug Interactions and Safety Concerns
7.2. Addressing Obstacles and Viral Resistance to Repurposed Agents
7.3. Regulatory and Ethical Considerations
8. Future Directions in Mpox Therapeutics
8.1. Integrating Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Drug Repurposing
8.2. Advancing Combination Therapies and Technologies for Enhanced Efficacy
8.3. Establishing Global Networks for Collaborative Research
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marzo, R.R. Bridging borders: The collective fight against monkeypox outbreaks. In The Scientific Basis of Mpox (Monkeypox); Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2025; pp. 75–100. [Google Scholar]
- Atceken, N.; Bayaki, I.; Can, B.; Yigci, D.; Tasoglu, S. Mpox disease, diagnosis, and point of care platforms. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2025, 10, e10733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, W.E. Global One Health and Infectious Diseases: An Interdisciplinary Practitioner’s Guide; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Scarpa, F.; Azzena, I.; Ciccozzi, A.; Branda, F.; Locci, C.; Perra, M.; Pascale, N.; Romano, C.; Ceccarelli, G.; Terrazzano, G.; et al. Update of the genetic variability of monkeypox virus clade IIb Lineage B.1. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunleye, S.C.; Akinsulie, O.C.; Aborode, A.T.; Olorunshola, M.M.; Gbore, D.; Oladoye, M.; Adesola, R.O.; Gbadegoye, J.O.; Olatoye, B.J.; Lawal, M.A.; et al. The re-emergence and transmission of Monkeypox virus in Nigeria the role of one health. Front. Public Health 2024, 11, 1334238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushebenge, A.G.-A.; Mphuthi, D.D. Emerging Insights into Monkeypox: Clinical Features, Epidemiology, Molecular Insights, and Advancements in Management. BioMed 2025, 5, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabanillas, B.; Murdaca, G.; Guemari, A.; Torres, M.J.; Azkur, A.K.; Aksoy, E.; Vitte, J.; Fernández-Santamaria, R.; Karavelia, A.; Castagnoli, R.; et al. Monkeypox 2024 outbreak: Fifty essential questions and answers. Allergy 2024, 79, 3285–3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protopapas, K.; Dimopoulou, D.; Kalesis, N.; Akinosoglou, K.; Moschopoulos, C.D. Mpox and Lessons Learned in the Light of the Recent Outbreak: A Narrative Review. Viruses 2024, 16, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafaati, M.; Forghani, S.; Davoudi, A.S.; Samiee, R.; Mohammadi, K.; Akbarpour, S.; Seifi, A.; Salehi, M.; Zare, M. Current advances and challenges in mpox vaccine development a global landscape. Ther. Adv. Vaccines Immunother. 2025, 13, 25151355251314339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halwani, M.A. Endemic cross-transmission of Mpox within health-care settings: A comprehensive review. Hail J. Health Sci. 2024, 6, 9–18. [Google Scholar]
- Ganesan, A.; Arunagiri, T.; Mani, S.; Kumaran, V.R.; Sk, G.; Elumalai, S.; Kannaiah, K.P.; Chanduluru, H.K. Mpox treatment evolution past milestones, present advances, and future directions. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2024, 398, 1057–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.-Y.; Zheng, X.-L.; Coghi, P.S.; Chen, J.-H.; Dong, B.-J.; Fan, X.-X. Revolutionizing adjuvant development: Harnessing AI for next-generation cancer vaccines. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1438030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambaza, E.M. A review of the molecular understanding of the Mpox virus (MPXV) genomics, immune evasion, and therapeutic targets. Zoonotic Dis. 2025, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witwit, H.; Cubitt, B.; Khafaji, R.; Castro, E.M.; Goicoechea, M.; Lorenzo, M.M.; Blasco, R.; Martinez-Sobrido, L.; de la Torre, J.C. Repurposing Drugs for Synergistic Combination Therapies to Counteract Monkeypox Virus Tecovirimat Resistance. Viruses 2025, 17, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamim, M.A.; Satapathy, P.; Padhi, B.K.; Veeramachaneni, S.D.; Akhtar, N.; Pradhan, A.; Agrawal, A.; Dwivedi, P.; Mohanty, A.; Pradhan, K.B.; et al. Pharmacological treatment and vaccines in monkeypox virus: A narrative review and bibliometric analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1149909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Clercq, E.; Jiang, Y.; Li, G. Therapeutic strategies for human poxvirus infections: Monkeypox (mpox), smallpox, molluscipox, and orf. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2023, 52, 102528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nederlof, R.A.; Sainmaa, S.; Wissink-Argilaga, N.; Koo, B.-S.; Bakker, J. Preventative Vaccination of Nonhuman Primates. J. Zool. Bot. Gard. 2025, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Xu, A.; Guan, L.; Tang, Y.; Chai, G.; Feng, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, C.; Liu, X.; et al. A review of Mpox: Biological characteristics, epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention strategies. Exploration 2024, 5, 20230112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, B.; Seifert, S.N.; Lawson, C.; Koehler, H. Exploring the genomic basis of Mpox virus-host transmission and pathogenesis. MSphere 2024, 9, e0057624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, S. An overview of the progress made in research into the Mpox virus. Med. Res. Rev. 2025, 45, 788–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslamkhah, S.; Aslan, E.S.; Yavas, C.; Akcalı, N.; Batur, L.K.; Abuaisha, A.; Yildirim, E.E.; Solak, M.; White, K.N. Mpox virus (MPXV) comprehensive analysis of pandemic risks, pathophysiology, treatments, and mRNA vaccine development. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2025, 398, 6143–6163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, V.; Lucky, L.; Sable, H.; Bhalla, N. Interdisciplinary Approach to Monkeypox Prevention: Integrating Nanobiosensors, Nanovaccines, Artificial Intelligence, Visual Arts, and Social Sciences. Small Struct. 2025, 6, 2400647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, A.; Gaur, M.; Mahanandia, N.C.; Subudhi, E.; Swain, R.P.; Subudhi, B.B. Identification of core therapeutic targets for Monkeypox virus and repurposing potential of drugs against them: An in silico approach. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 161, 106971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Xing, H.; Wang, C.; Tang, M.; Wu, C.; Ye, F.; Yin, L.; Yang, Y.; Tan, W.; Shen, L. Mpox (formerly monkeypox) pathogenesis, prevention and treatment. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, M.; Mandal, S. Metadynamics approach elucidating the free energy landscape and binding modes of vomicine with virulence factor towards anti-mpox drug discovery. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2024, 846, 141355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Sun, Q.; Xu, Y.; Niu, Y.; Yang, F.; Feng, S. Novel drug targets for monkeypox: From viral to host proteins. Infect. Med. 2025, 4, 100165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Zhu, F.; Pan, P.; Wu, A.; Li, C. Development of multi-epitope vaccines against the monkeypox virus based on envelope proteins using immunoinformatics approaches. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1112816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathi, D.; Sahu, L.; Minj, A.; Satapathy, T. Post Invasional Host Interaction Consequences of Monkey Pox Virus and Its Advanced Treatment: A Mechanism Based Review. Curr. Res. Altern Complement Integr. Med. 2024, 1, 26–33. [Google Scholar]
- Malik, S.; Ahmed, A.; Ahsan, O.; Muhammad, K.; Waheed, Y. Monkeypox Virus: A Comprehensive Overview of Viral Pathology, Immune Response, and Antiviral Strategies. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer zu Natrup, C.; Clever, S.; Schünemann, L.M.; Tuchel, T.; Ohrnberger, S.; Volz, A. Strong and early monkeypox virus-specific immunity associated with mild disease after intradermal clade-IIb-infection in CAST/EiJ-mice. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Zhao, J.; Chen, J.; Liang, J.; Hu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, H.; Sun, G. Urogenital Manifestations in Mpox (Monkeypox) Infection: A Comprehensive Review of Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Therapeutic Approaches. Infect. Drug Resist. 2025, 18, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, B.; Fricke, I.; Imarogbe, C.; González, A.A.P.; Batista, O.A.; Mensah, P.; Chacon-Cruz, E. Immunopathogenesis of Orthopoxviridae: Insights into immunology from smallpox to monkeypox (mpox). Explor. Immunol. 2023, 3, 525–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, A.; Arunagiri, T.; Mani, S.; Kumaran, V.R.; Kannaiah, K.P.; Chanduluru, H.K. From pox to protection: Understanding Monkeypox pathophysiology and immune resilience. Trop. Med. Health 2025, 53, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imani, S.; Aminnezhad, S.; Alikarami, M.; Abedi, Z.; Mosleh, I.S.; Maghsoudloo, M.; Taheri, Z. Exploration of drug repurposing for Mpox outbreaks targeting gene signatures and host-pathogen interactions. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 29436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, H.; Gould, S.; Hine, P.; Snell, L.B.; Wong, W.; Houlihan, C.F.; Osborne, J.C.; Rampling, T.; Beadsworth, M.B.; Duncan, C.J.; et al. Clinical features and management of human monkeypox: A retrospective observational study in the UK. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 1153–1162, Correction in Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, E177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, Y.; Dai, X.; Xu, Y.; Xing, G.; Liu, H.; Lu, T.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y. Drug repositioning: Progress and challenges in drug discovery for various diseases. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 234, 114239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, D.; Saha, S.; Basu, S.; Chakraborti, T. Computational analysis of pathogen-host interactome for fast and low-risk in-silico drug repurposing in emerging viral threats like Mpox. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 18736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabaan, A.A.; Alfaresi, M.; Alrasheed, H.A.; Al Kaabi, N.A.; Abduljabbar, W.A.; Al Fares, M.A.; Al-Subaie, M.F.; Alissa, M. Network-Based Drug Repurposing and Genomic Analysis to Unveil Potential Therapeutics for Monkeypox Virus. Chem. Biodivers. 2024, 21, e202400895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamed, M.A.; Politza, A.J.; Liu, T.; Khalid, M.A.U.; Zhang, H.; Guan, W. CRISPR-based strategies for sample-to-answer monkeypox detection: Current status and emerging opportunities. Nanotechnology 2024, 36, 042001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Wu, N.; Liu, Y.; Tang, Y.; Quan, Q.; Luo, Y.; Jin, C. Mpox: Global epidemic situation and countermeasures. Virulence 2025, 16, 2457958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalil, A.C.; Patterson, T.F.; Mehta, A.K.; Tomashek, K.M.; Wolfe, C.R.; Ghazaryan, V.; Marconi, V.C.; Ruiz-Palacios, G.M.; Hsieh, L.; Kline, S.; et al. Baricitinib plus remdesivir for hospitalized adults with Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 795–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejinold, N.S.; Jin, G.; Choy, J. Harnessing Nanohybridized Niclosamide for Precision Mpox Therapeutics. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2025, 14, 2404818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadesa Tesema, M. Mitigation approaches of monkeypox outbreaks in developing countries. Discov. Viruses 2025, 2, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushpakom, S.; Iorio, F.; Eyers, P.A.; Escott, K.J.; Hopper, S.; Wells, A.; Doig, A.; Guilliams, T.; Latimer, J.; Mcnamee, C.; et al. Drug repurposing: Progress, challenges and recommendations. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousaf, M.A.; Michel, M.; Khan, A.T.-A.; Noreen, M.; Bano, S. Repurposing doxycycline for the inhibition of monkeypox virus DNA polymerase: A comprehensive computational study. Silico Pharmacol. 2025, 13, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, A.; Canard, B. Nucleotide analogues and mpox: Repurposing the repurposable. Antivir. Res. 2024, 234, 106057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunge, E.M.; Hoet, B.; Chen, L.; Lienert, F.; Weidenthaler, H.; Baer, L.R.; Steffen, R. The changing epidemiology of human monkeypox—A potential threat? A systematic review. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlov, M. Monkeypox in Africa: The science the world ignored. Nature 2022, 607, 17–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girometti, N.; Byrne, R.; Bracchi, M.; Heskin, J.; McOwan, A.; Tittle, V.; Gedela, K.; Scott, C.; Patel, S.; Gohil, J.; et al. Demographic and clinical characteristics of confirmed human monkeypox virus cases in individuals attending a sexual health centre in London, UK: An observational analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 1321–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabaan, A.A.; Halwani, M.A.; Alshehri, A.A.; Al-Subaie, M.F.; Almansour, Z.H.; AlShehail, B.M.; Alotaibi, N.; Khamis, F.; Al Kaabi, N.A.; Alsomali, G.; et al. Bioprospecting of Meliaceae family phytomolecules for the treatment of monkeypox virus infection: A QSAR modeling and MD simulation approach. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2025, 43, 2277–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.-Y.; Zhang, H.-X.; Mezei, M.; Cui, M. Molecular docking: A powerful approach for structure-based drug discovery. Curr. Comput. Aided Drug Des. 2011, 7, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mushebenge, A.G.; Ugbaja, S.C.; Mtambo, S.E.; Ntombela, T.; Metu, J.I.; Babayemi, O.; Chima, J.I.; Appiah-Kubi, P.; Odugbemi, A.I.; Ntuli, M.L.; et al. Unveiling the Inhibitory Potentials of Peptidomimetic Azanitriles and Pyridyl Esters towards SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease: A Molecular Modelling Investigation. Molecules 2023, 28, 2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollingsworth, S.A.; Dror, R.O. Molecular dynamics simulation for all. Neuron 2018, 99, 1129–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugbaja, S.C.; Mushebenge, A.G.-A.; Kumalo, H.; Ngcobo, M.; Gqaleni, N. Potential Benefits of In Silico Methods: A Promising Alternative in Natural Compound’s Drug Discovery and Repurposing for HBV Therapy. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushebenge, A.G.-A.; Ugbaja, S.C.; Magwaza, N.N.; Mbatha, N.A.; Muzumbukilwa, T.W.; Kadima, M.G.; Tata, F.Y.; Nxumalo, M.B.; Manimani, R.G.; Ndage, N.; et al. Mechanistic Insights into the Mutational Landscape of the Main Protease/3CLPro and Its Impact on Long-Term COVID-19/SARS-CoV-2 Management. Future Pharmacol. 2024, 4, 825–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alandijany, T.A.; El-Daly, M.M.; Tolah, A.M.; Bajrai, L.H.; Khateb, A.M.; Kumar, G.S.; Dubey, A.; Dwivedi, V.D.; Azhar, E.I. A multi-targeted computational drug discovery approach for repurposing tetracyclines against monkeypox virus. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 14570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajmal, A.; Mahmood, A.; Hayat, C.; Hakami, M.A.; Alotaibi, B.S.; Umair, M.; Abdalla, A.N.; Li, P.; He, P.; Wadood, A.; et al. Computer-assisted drug repurposing for thymidylate kinase drug target in monkeypox virus. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1159389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, R.; Bhattarai, A.; Karn, R.; Tamang, B. Computational investigations of potential inhibitors of monkeypox virus envelope protein E8 through molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulations. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 19585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhapola, R.; Kumari, S.; Sharma, P.; KumarKushawaha, P.; HariKrishnaReddy, D. Update on monkeypox virus infection: Focusing current treatment and prevention approaches. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2024, 38, 465–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurya, V.K.; Kumar, S.; Maurya, S.; Ansari, S.; Paweska, J.T.; Abdel-Moneim, A.S.; Saxena, S.K. Structure-based drug designing for potential antiviral activity of selected natural product against Monkeypox (Mpox) virus and its host targets. VirusDisease 2024, 35, 589–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, C.N.; Mall, R.; Bensmail, H. AI-driven drug repurposing and binding pose meta dynamics identifies novel targets for monkeypox virus. J. Infect. Public Health 2023, 16, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezat, A.A.; Abduljalil, J.M.; Elghareib, A.M.; Samir, A.; Elfiky, A.A. The discovery of novel antivirals for the treatment of mpox: Is drug repurposing the answer? Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2023, 18, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Huang, B.; Zhang, J.; Peng, C.; Kong, W.; Tan, W.; Li, S. Molecular architecture of monkeypox mature virus. Cell Discov. 2024, 10, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanisevic, T.; Sewduth, R.N. Multi-Omics Integration for the Design of Novel Therapies and the Identification of Novel Biomarkers. Proteomes 2023, 11, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perdomo-Quinteiro, P.; Wolstencroft, K.; Roos, M.; Queralt-Rosinach, N. Knowledge graphs and explainable ai for drug repurposing on rare diseases. bioRxiv 2024. bioRxiv:10.17.618804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-kenawy, E.-S.M. Leveraging Advanced Machine Learning for Pioneering Monkeypox Diagnosis: A New Paradigm in Infectious Disease Detection. Metaheuristic Optim. Rev. 2024, 1, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Q.; Li, P. Human skin organoids are valid models of mpox virus infection. Nature 2023, 8, 1950–1951. [Google Scholar]
- Rosa, R.B.; Ferreira de Castro, E.; Vieira da Silva, M.; Paiva Ferreira, D.C.; Jardim, A.C.G.; Santos, I.A.; Marinho, M.D.S.; Ferreira França, F.B.; Pena, L.J. In vitro and in vivo models for monkeypox. iScience 2023, 26, 105702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, F.M.A.; Bappy, N.I.; Robin, T.B.; Ahmad, I.; Patel, H.; Jahan, N.; Rabbi, G.R.; Roy, A.; Chowdhury, W.; Ahmed, N.; et al. A review on computational studies and bioinformatics analysis of potential drugs against monkeypox virus. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2024, 42, 6091–6107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loganathan, T.; Fletcher, J.; Abraham, P.; Kannangai, R.; Chakraborty, C.; El Allali, A.; Alsamman, A.M.; Zayed, H.; C, G.P.D. Expression analysis and mapping of Viral-Host Protein interactions of Poxviridae suggests a lead candidate molecule targeting Mpox. BMC Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdizadeh, T. Identification of novel potential inhibitors of monkeypox virus thymidine kinase using molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulation and MM/PBSA methods. Mol. Divers. 2024, 28, 2513–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, A.K.; Augusthian, P.D.; Muralitharan, I.; Vivek-Ananth, R.P.; Kumar, K.; Kumar, G.; Ranganathan, G.; Samal, A. In silico identification of potential inhibitors of vital monkeypox virus proteins from FDA approved drugs. Mol. Divers. 2023, 27, 2169–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Sharma, A.; Kaur, H.; Singh, M.; Devi, B.; Raj, A.R.N.; Sood, V.; Pandey, A.; Gartia, J.; Kumar, R.; et al. Screening of potential inhibitors against structural proteins from Monkeypox and related viruses of Poxviridae family via docking and molecular dynamics simulation. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2024, 42, 10978–10993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchoslav, V.; Boura, E. Structure of monkeypox virus poxin implications for drug design. Arch. Virol. 2023, 168, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arasu, M.; Vijayaragavan, P.; Purushothaman, S.; Rathi, M.; Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Gopalakrishnan, V.; Choi, K.C.; Ilavenil, S. Molecular docking of monkeypox (mpox) virus proteinase with FDA approved lead molecules. J. Infect. Public Health 2023, 16, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, L.B.; Bergeron, G.; Cadieux, G.; Charest, H.; Fafard, J.; Levade, I.; Blais, A.C.; Huchet, E.; Trottier, B.; Vlad, D.; et al. Monkeypox in Montréal: Epidemiology, phylogenomics, and public health response to a large North American outbreak. Ann. Intern. Med. 2023, 176, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, E.; Li, W.; Lv, R.; Lin, Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, J.; Lai, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Lin, S.; et al. Advances and challenges of mpox detection technology. Biosaf. Health 2024, 6, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnard, D.L.; Day, C.W.; Bailey, K.; Heiner, M.; Montgomery, R.; Lauridsen, L.; Winslow, S.; Hoopes, J.; Li, J.K.-K.; Lee, J.; et al. Enhancement of the infectivity of SARS-CoV in BALB/c mice by IMP dehydrogenase inhibitors, including ribavirin. Antivir. Res. 2006, 71, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenchula, S.; Atal, S.; Ghanta, M.K.; Uppugunduri, C.R.; Karunakaran, S.; Amerneni, K.C.; Sarma, P.; Prakash, S.; Amerneni, L.S.; Padmavathi, R.; et al. Emerging variants of Mpox virus and tecovirimat resistance: Genomic insights and implications for treatment strategies. Virology 2025, 608, 110532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rietdijk, J.; Tampere, M.; Pettke, A.; Georgiev, P.; Lapins, M.; Warpman-Berglund, U.; Spjuth, O.; Puumalainen, M.-R.; Carreras-Puigvert, J. A phenomics approach for antiviral drug discovery. BMC Biol. 2021, 19, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, F.; Nueda, A.; Lee, J.; Schenone, M.; Prunotto, M.; Mercola, M. Phenotypic drug discovery: Recent successes, lessons learned and new directions. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 899–914, Erratum in Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.; Sun, Q.; Zeng, J.; Tang, J.; Cheng, P.; Qiu, Z.; Long, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wei, J.; et al. Network-based approach for drug repurposing against mpox. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 270, 132468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Zhang, G.; Wan, X. Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Analysis Reveal Insights into the Molecular Mechanism of Shengma-Gegen Decoction on Monkeypox. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, W.-Y.; Shen, Z.-H.; Chen, Y.; Chen, T.-H.; Lu, X.; Fu, Y.-S. Therapeutic implications of quercetin and its derived-products in COVID-19 protection and prophylactic. Heliyon 2024, 10, e30080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.R.; Lv, Q.-L.; Peng, H.-W.; Liu, X.-Y.; Hu, W.-L.; Hu, J.-F. Drug screening against F13 protein, the target of tecovirimat, as potential therapies for monkeypox virus. J. Infect. 2023, 86, 154–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Aneja, S.; Biswal, B.K. Approved and experimental antivirals for mpox. In The Scientific Basis of Mpox (Monkeypox); Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2025; pp. 401–420. [Google Scholar]
- Siegrist, E.A.; Sassine, J. Antivirals with activity against mpox: A clinically oriented review. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2023, 76, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akazawa, D.; Ohashi, H.; Hishiki, T.; Morita, T.; Iwanami, S.; Kim, K.S.; Jeong, Y.D.; Park, E.-S.; Kataoka, M.; Shionoya, K.; et al. Potential anti-mpox virus activity of atovaquone, mefloquine, and molnupiravir, and their potential use as treatments. J. Infect. Dis. 2023, 228, 591–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, D.A. Computational repurposing of drugs for viral diseases and current and future pandemics. J. Math. Chem. 2024, 62, 2844–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Mahmud, S.A.; Chen, A.; Li, K.; Tan, H.; Joyce, R. An overview of antivirals against monkeypox virus and other orthopoxviruses. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 4468–4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, E.B.; Neto, R.F.O.; Santos, V.C.; Ferreira, A.L.S. Deep Reinforcement Learning and Structure-Based Approaches in the de novo Design of a New Potential Inhibitor of F13 Protein from Monkeypox Virus. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2025, 36, e-20250022. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, B.M.; Modi, P. Breaking Barriers: Current Advances and Future Directions in Mpox Therapy. Curr. Drug Targets 2024, 25, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutt, M.; Kumar, A.; Rout, M.; Dehury, B.; Martinez, G.; Ndishimye, P.; Kelvin, A.A.; Kelvin, D.J. Drug repurposing for Mpox: Discovery of small molecules as potential inhibitors against DNA-dependent RNA polymerase using molecular modeling approach. J. Cell. Biochem. 2023, 124, 701–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grajales, D.B.; Kar, S. Exploring Monkeypox: Prospects for therapeutics through computational-aided drug discovery. Mol. Divers. 2023, 28, 3497–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, H.; Ilyas, A.; Upadhyay, S.; Rai, P.K.; Borkotoky, S. Computational screening of FDA-approved and natural compounds against Mpox Dual specificity protein phosphatase (H1). Indian J. Biochem. Biophys. 2025, 62, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.; Ahmad, T.; Ahsan, O.; Muhammad, K.; Waheed, Y. Recent Developments in Mpox Prevention and Treatment Options. Vaccines 2023, 11, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojkova, D.; Zöller, N.; Tietgen, M.; Steinhorst, K.; Bechtel, M.; Rothenburger, T.; Kandler, J.D.; Schneider, J.; Corman, V.M.; Ciesek, S.; et al. Repurposing of the antibiotic nitroxoline for the treatment of mpox. J. Med. Virol. 2023, 95, e28652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Guruparan, D.; Karuppanan, K.; Kumar, K.J.S. Comprehensive Insights into Monkeypox (mpox): Recent Advances in Epidemiology, Diagnostic Approaches and Therapeutic Strategies. Pathogens 2025, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernuccio, R.; León, A.M.; Poojari, C.S.; Buchrieser, J.; Selverian, C.; Jaleta, Y.; Meola, A.; Guivel-Benhassine, F.; Porrot, F.; Haouz, A.; et al. Mechanisms of tecovirimat antiviral activity and poxvirus resistance. Res. Sq. 2024. preprint. [Google Scholar]
- Hashemi, M.; Zabihian, A.; Hajsaeedi, M.; Hooshmand, M. Antivirals for monkeypox virus: Proposing an effective machine/deep learning framework. PloS ONE 2024, 19, e0299342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizk, Y.; Lippi, G.; Henry, B.M.; Notarte, K.I.; Rizk, J.G. Update on mpox management: Epidemiology, vaccines and therapeutics, and regulatory changes. Drugs 2025, 85, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.I.; Salama, A. Natural Immunomodulatory Agents as a Complementary Therapy for Poxviruses. Poxviruses 2024, 2024, 337–354. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, D.; Liu, Y.; Dou, D.; Su, B. The unique immune evasion mechanisms of the mpox virus and their implication for developing new vaccines and immunotherapies. Virol. Sin. 2024, 39, 709–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Z.H.; Yang, C.-H.; Qiu, Y.; Ge, X.-Y. Evolutionary Analysis and Antiviral Drug Prediction of Mpox Virus. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Z. Subcellular Investigation of Poxvirus Coinfections and the Impact on the Evolution of Cidofovir Resistance. Master’s Thesis, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, W.; Kim, Y.-J.; Lee, S.J.; Ahn, D.-G.; Kim, S.-J. Current Status of Epidemiology, Diagnosis, Therapeutics, and Vaccines for the Re-Emerging Human Monkeypox Virus. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 33, 981–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prichard, M.N.; Kern, E.R. Orthopoxvirus targets for the development of new antiviral agents. Antivir. Res. 2012, 94, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Bergant, V.; Grass, V.; Emslander, Q.; Hamad, M.S.; Hubel, P.; Mergner, J.; Piras, A.; Krey, K.; Henrici, A.; et al. Multi-omics characterization of the monkeypox virus infection. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Shi, Q.; Yue, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Ou, Z.; Liang, L.; Hu, J.; et al. Identification of core therapeutic targets for Monkeypox virus and repurposing potential of drugs: A WEB prediction approach. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0303501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohapatra, R.K.; Mahal, A.; Mohapatra, P.K.; Sarangi, A.K.; Mishra, S.; Alsuwat, M.A.; Alshehri, N.N.; Abdelkhalig, S.M.; Garout, M.; Aljeldah, M.; et al. Structure-based discovery of F. religiosa phytochemicals as potential inhibitors against Monkeypox (mpox) viral protein. J. Biosaf. Biosecur. 2024, 6, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, H.Y.I.; Guan, J.S.; Mu, Y. In silico repurposed drugs against monkeypox virus. Molecules 2022, 27, 5277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanto, S.; Faiyazuddin; Gholap, A.D.; Darshan, J.C.; Bhunia, A.; Subbaram, K.; Ahmed, M.G.; Nag, S.; Akhtar, M.S.; Bonilla-Aldana, D.K.; et al. Addressing the resurgence of global monkeypox (Mpox) through advanced drug delivery platforms. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2023, 56, 102636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warner, B.M.; Klassen, L.; Sloan, A.; Deschambault, Y.; Soule, G.; Banadyga, L.; Cao, J.; Strong, J.E.; Kobasa, D.; Safronetz, D. In vitro and in vivo efficacy of tecovirimat against a recently emerged 2022 monkeypox virus isolate. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eade7646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Sharazly, B.M.; Ahmed, A.; Elsheikha, H.M.; Carter, W.G. An In Silico and In Vitro Assessment of the Neurotoxicity of Mefloquine. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leela, S.L.; Srisawat, C.; Sreekanth, G.P.; Noisakran, S.; Yenchitsomanus, P.-T.; Limjindaporn, T. Drug repurposing of minocycline against dengue virus infection. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 478, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, R.; Hellgren, U.; Greenwood, B.; Menéndez, C. Mefloquine safety and tolerability in pregnancy: A systematic literature review. Malar. J. 2014, 13, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrei, G.; Snoeck, R. Cidofovir Activity against Poxvirus Infections. Viruses 2010, 2, 2803–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikyam, H.K.; Patil, S.B.; Hussain, N.; Vallal, R.E.E.; Sharma, S.; Patil, A.R. High-Throughput Insilico Drug Screen against Mpox Targeted Proteins in Comparison with Repurposed Antiviral Drugs against Natural Compounds. J. Pharm. Res. Int. 2024, 36, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, J.; Stoeckle, K.; Huang, S.; Berardi, J.; Gray, B.; Glesby, M.J.; Zucker, J. Tecovirimat Treatment of People With HIV During the 2022 Mpox Outbreak: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2023, 176, 642–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLaurentis, C.E.; Kiser, J.; Zucker, J. New Perspectives on Antimicrobial Agents: Tecovirimat for Treatment of Human Monkeypox Virus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2022, 66, e0122622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabil, M.; Khatib, M.N.; Ballal, S.; Bansal, P.; Tomar, B.S.; Ashraf, A.; Kumar, M.R.; Sinha, A.; Rawat, P.; Gaidhane, A.M.; et al. Effectiveness of Tecovirimat in Mpox Cases: A Systematic Review of Current Evidence. J. Med. Virol. 2024, 96, e70122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghajani, J.; Farnia, P.; Farnia, P.; Ghanavi, J.; Velayati, A.A. Molecular Dynamic Simulations and Molecular Docking as a Potential Way for Designed New Inhibitor Drug without Resistance. Tanaffos 2022, 21, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Prévost, J.; Sloan, A.; Deschambault, Y.; Tailor, N.; Tierney, K.; Azaransky, K.; Kammanadiminti, S.; Barker, D.; Kodihalli, S.; Safronetz, D. Treatment efficacy of cidofovir and brincidofovir against clade II Monkeypox virus isolates. Antivir. Res. 2024, 231, 105995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, N.C.; Shishido, A.; Fulco, P.P.; Sastry, S. Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome due to monkeypox in two patients with AIDS. AIDS 2023, 37, 1187–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Sridhar, S.B.; Shareef, J.; Talath, S.; Mohapatra, P.; Khatib, M.N.; Ballal, S.; Kaur, M.; Nathiya, D.; Sharma, S.; et al. The resurgence of monkeypox: Epidemiology, clinical features, and public health implications in the post-smallpox eradication era. New Microbes New Infect. 2024, 62, 101487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alorfi, N.M.; Alshehri, F.S.; Haseeb, A. Characterization of interventional clinical trials for monkeypox; systematic review of ClinicalTrials.gov database. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1144325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roper, R.L.; Garzino-Demo, A.; Del Rio, C.; Bréchot, C.; Gallo, R.; Hall, W.; Esparza, J.; Reitz, M.; Schinazi, R.F.; Parrington, M.; et al. Monkeypox (Mpox) requires continued surveillance, vaccines, therapeutics and mitigating strategies. Vaccine 2023, 41, 3171–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajudeen, Y.A.; Oladipo, H.J.; Muili, A.O.; Ikebuaso, J.G. Monkeypox: A review of a zoonotic disease of global public health concern. Health Promot. Perspect. 2023, 13, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olawade, D.B.; Wada, O.Z.; Fidelis, S.C.; Oluwole, O.S.; Alisi, C.S.; Orimabuyaku, N.F.; David-Olawade, A.C. Strengthening Africa’s response to Mpox (monkeypox): Insights from historical outbreaks and the present global spread. Sci. One Health 2024, 3, 100085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Junior, M.A.; Andrade, B.S.; Guevara-Vega, M.; de Melo, I.S.; Cunha, T.M.; Jardim, A.C.G.; Sabino-Silva, R. Oral Infection, Oral Pathology and Salivary Diagnostics of Mpox Disease: Relevance in Dentistry and OMICs Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, G.R.d.S.; Ribeiro, C.J.N.; Santos Júnior, J.F.C.d.; Almeida, V.S.; Nascimento, R.d.C.D.; Barreto, N.M.P.V.; Sousa, A.R.d.; Bezerra-Santos, M.; Cepas, L.A.; Fernandes, A.P.M.; et al. Mpox Vaccine Hesitancy Among Brazilian Men Who Have Sex with Men: A National Cross-Sectional Study. Vaccines 2024, 12, 1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourner, J.; Garcia-Gallo, E.; Mbrenga, F.; Boum, Y.; Nakouné, E.; Paterson, A.; Jones, B.; Olliaro, P.; Rojek, A. Challenges in clinical diagnosis of Clade I Mpox: Highlighting the need for enhanced diagnostic approaches. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2024, 18, e0012087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdoul-Latif, F.M.; Ainane, A.; Mohamed, H.; Ali, A.M.; Aboubaker, I.H.; Jutur, P.P.; Ainane, T. Mpox Resurgence: A Multifaceted Analysis for Global Preparedness. Viruses 2024, 16, 1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Škvára, P. Structural Analysis of 2′-O-methyltransferase VP39 Derived from Mpox Virus. Ph.D. Thesis, Charles University, Prague, Czech Republic, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Idisi, I.O.; Oshinubi, K.; Sewanu, V.B.; Yahaya, M.M.; Olagbami, O.S.; Edogbanya, H.O. Investigating Mpox Strain Dynamics Using Computational and Data-Driven Approaches. Viruses 2025, 17, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.; Kwon, S. The Effects of Intellectual Property Rights on Access to Medicines and Catastrophic Expenditure. Int. J. Health Serv. 2015, 45, 507–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenni, B.; Moir, H.V.J.; Townsend, B.; Kilic, B.; Farrell, A.-M.; Keegel, T.; Gleeson, D. What is the impact of intellectual property rules on access to medicines? A systematic review. Glob. Health 2022, 18, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahiwala, A. Advancing drug delivery research: Sustainable strategies for innovation and translation. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2025, 15, 1513–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saldana, C.S.; Kelley, C.F.; Aldred, B.M.; Cantos, V.D. Mpox and HIV: A Narrative Review. Curr. HIV/AIDS Rep. 2023, 20, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.M.; Rakhmanina, N.Y.; Yang, Z.; Bukrinsky, M.I. Mpox (Monkeypox) Virus and Its Co-Infection with HIV, Sexually Transmitted Infections, or Bacterial Superinfections: Double Whammy or a New Prime Culprit? Viruses 2024, 16, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tempestilli, M.; Mondi, A.; D’AVolio, A.; Forini, O.; Pinnetti, C.; Mazzotta, V.; Gagliardini, R.; Beccacece, A.; De Nicolò, A.; Faccendini, P.; et al. Pharmacokinetics of tecovirimat in subjects with Mpox. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2024, 63, 107068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoy, S.M. Tecovirimat: First Global Approval. Drugs 2018, 78, 1377–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, A.T.; Grosenbach, D.W.; Chinsangaram, J.; Honeychurch, K.M.; Long, P.G.; Lovejoy, C.; Maiti, B.; Meara, I.; Hruby, D.E. An overview of tecovirimat for smallpox treatment and expanded anti-orthopoxvirus applications. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2021, 19, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.G.; Gigante, C.M.; Wynn, N.T.; Matheny, A.; Davidson, W.; Yang, Y.; Condori, R.E.; O’cOnnell, K.; Kovar, L.; Williams, T.L.; et al. Tecovirimat Resistance in Mpox Patients, United States, 2022–2023. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2023, 29, 2426–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucker, J.; Hazra, A.; Titanji, B.K. Mpox and HIV—Collision of two diseases. Curr. HIV/AIDS Rep. 2023, 20, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aden, D.; Zaheer, S.; Kumar, R.; Ranga, S. Monkeypox (Mpox) outbreak during COVID-19 pandemic—Past and the future. J. Med. Virol. 2023, 95, e28701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanoujia, J.; Tarannum, S.; Kaurav, M.; Raina, N.; Jain, K.; Gupta, M. Insight into Recent Updates on Vaccines Development and Immunology of Monkeypox Infection. Curr. Treat. Options Infect. Dis. 2024, 16, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danladi, N.P.; Agboola, P.; Olaniyi, P.; Eze, S.; Oladapo, O.; Obiwulu, D.; Akano, O.S.; Adeola, O.A.; Olawale, K.; Adiatu, A.I.; et al. Challenges in Global Distribution and Equitable Access to Monkeypox Vaccines. Viruses 2024, 16, 1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinnah, M.A.; Uddin, B.; Hasan, T.; Das, S.; Khatun, F.; Hasan, H.; Udonsom, R.; Rahman, M.; Ashour, H.M. The Re-Emergence of Mpox: Old Illness. Mod. Challenges. Biomed. 2024, 12, 1457. [Google Scholar]
- El Dine, F.B.; Gebreal, A.; Samhouri, D.; Estifanos, H.; Kourampi, I.; Abdelrhem, H.; Mostafa, H.A.; Elshaar, A.G.; Suvvari, T.K.; Ghazy, R.M. Ethical considerations during Mpox Outbreak: A scoping review. BMC Med. Ethics 2024, 25, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Laughlin, K. Clinical use of tecovirimat (Tpoxx) for treatment of monkeypox under an investigational new drug protocol—United States, May–August 2022. MMWR. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2022, 71, 1190–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prompetchara, E.; Ketloy, C.; Khawsang, C.; Palaga, T.; Ruxrungtham, K. Mpox global health emergency: Insights into the virus, immune responses, and advancements in vaccines PART II: Insights into the advancements in vaccines. Asian Pac. J. Allergy Immunol. 2024, 42, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musuka, G.; Moyo, E.; Tungwarara, N.; Mhango, M.; Pierre, G.; Saramba, E.; Iradukunda, P.G.; Dzinamarira, T. A critical review of mpox outbreaks, risk factors, and prevention efforts in Africa: Lessons learned and evolving practices. IJID Reg. 2024, 12, 100402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witzel, T.C.; Ghobrial, A.; Palich, R.; Charles, H.; Rodger, A.J.; Sabin, C.; Sparrowhawk, A.; Pool, E.R.; Prochazka, M.; Vivancos, R.; et al. Experiences of mpox illness and case management among cis and trans gay, bisexual and other men who have sex with men in England: A qualitative study. EclinicalMedicine 2024, 70, 102522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampogu, S. A review on the use of machine learning techniques in monkeypox disease prediction. Sci. One Health 2023, 2, 100040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamaqa, A.; Bahgat, W.M.; AbdulAzeem, Y.; Balaha, H.M.; Badawy, M.; Elhosseini, M.A. Early detection of monkeypox: Analysis and optimization of pretrained deep learning models using the Sparrow Search Algorithm. Results Eng. 2024, 24, 102985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, F.O.; Fallah, M.; Jain, U.; Richardson, E.T.; Ndembi, N.; Ngongo, N.; Kaseya, J. Challenges and Ongoing Actions to Address the Mpox Emergency in Africa. Ann. Glob. Health 2024, 90, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forni, D.; Cagliani, R.; Molteni, C.; Clerici, M.; Sironi, M. Monkeypox virus: The changing facets of a zoonotic pathogen. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2022, 105, 105372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, N.; Ramírez, A.L.; Muñoz, M.; Ballesteros, N.; Patiño, L.H.; Castañeda, S.A.; Bonilla-Aldana, D.K.; Paniz-Mondolfi, A.; Ramírez, J.D. Phylogenomic analysis of the monkeypox virus (MPXV) 2022 outbreak: Emergence of a novel viral lineage? Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2022, 49, 102402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, H.M.; Uthaman, A.; Thomas, S. Silver Nanoparticle as an Effective Antiviral Agent. In Polymer Nanocomposites Based on Silver Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization and Applications; Lal, H.M., Maria, H.J., Thomas, S., Li, T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 247–265. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, N.A.; Zupin, L.; Mazi, S.I.; Al-Khatib, H.A.; Crovella, S. Nanomedicine as a Potential Tool against Monkeypox. Vaccines 2023, 11, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, J.P.; Hossen, K.; Sayed, S.B.; Khandaker, S.; Dev, P.C.; Sarker, S.; Hossain, T. Identification of potential biomarkers for 2022 Mpox virus infection a transcriptomic network analysis and machine learning approach. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, R.; Hu, X.; Wang, X. The current status and future prospects of CRISPR-based detection of monkeypox virus: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2025, 1336, 343295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, S.; Kohl, A.; Pena, L.; Pardee, K. Clinical and laboratory diagnosis of monkeypox (mpox): Current status and future directions. iScience 2023, 26, 106759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingelhöfer, D.; Braun, M.; Groneberg, D.A.; Brüggmann, D. Global mpox research in the light of the current outbreak: Demands, drivers, and obstacles. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2023, 12, 2210696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Technological Approach | What It Does (Scope)/Typical Inputs | Primary Readouts/Outputs | Key Strengths/Principal Limitations | Validation/Next Steps | Example MPXV Applications | Best Used for/Pipeline Stage | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Structure-based in silico docking | Predicts ligand binding poses/affinities to viral or host targets/3D target structures (experimental or predicted), prepared ligand libraries | Docking scores, predicted poses, interaction maps | Fast, low cost; screens 104–106 compounds; hypothesis generation for SAR/Dependent for structure quality and protonation; ignores full dynamics/solvent; risk of false positives | Re-dock known ligands; MM/GBSA rescoring; move hits to MD, biophysics (isothermal titration calorimetry and surface plasmon resonance), and cell assays | Docking to MPXV enzymes (e.g., VP39 cap MTase, D1/D12 polymerase complex) and host JAK1; prioritization of nitroxoline, atovaquone, tilorone, ZINC leads | Early hit identification and triage | [60] |
| Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations | Tests the stability and dynamics of protein–ligand complexes; refines docking/protein–ligand complexes, force fields, explicit solvent/ions | Root Mean Square Deviation/Root Mean Square Fluctuation, H-bond occupancy, binding free energy (e.g., MM/PBSA), conformational ensembles | Captures flexibility, water networks; filters docking artifacts; supports binding hypotheses/Compute-intensive; sensitive to parameters/timescale; not a direct measure of potency | Orthogonal biophysics; mutagenesis; enzymatic half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50/EC50)/Ki; cell-based EC50 | Stability of candidate inhibitors in MPXV VP39 pocket; MD of host-targeted the Janus kinase-signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK/STAT) modulators | Post-docking refinement; pre-experimental risk reduction | [58] |
| AI-driven structure prediction (e.g., AlphaFold/ColabFold) | Predicts protein 3D structures and complexes; maps pockets/amino-acid sequences, multiple sequence alignments, co-evolution data | 3D models with confidence metrics (predicted local distance difference test, predicted aligned error), interface predictions | Enables targets lacking structures; rapid; broad proteome coverage/Accuracy varies for flexible regions/complexes; requires experimental validation | Cryo-EM/X-ray/Nuclear Magnetic Resonance confirmation; benchmarking via known domains | Models for MPXV proteins without PDB structures to enable docking/MD | Target Enablement and Pocket Discovery | [61] |
| High-throughput screening (HTS) | Empirical activity screening across large libraries/cell-based infection assays or enzymatic assays; 103–106 compounds | Hit rates, EC50/IC50, 50% cytotoxic concentration (CC50), selectivity index (SI) | Direct activity readout; unbiased mechanism of action (MoA) discovery; scalable robotics/costly infrastructure; false positives; assay interference; needs robust BSL-2/3 models | Hit confirmation, counter-screens, MoA deconvolution, medicinal chemistry | Cell-based screens of FDA libraries against orthopox/MPXV surrogates; identification of DNA synthesis and egress blockers | Primary empirical discovery; lead finding | [62] |
| Cryo-electron microscopy (Cryo-EM) | Determines the near-native structures of large assemblies/Purified proteins/complexes/virions, vitrification | 3–5 Å (or better) maps; atomic models; ligand density | Captures native states and complexes; ideal for large pox proteins/assemblies/high cost; expertise; not high throughput | Functional assays; docking/MD guided by EM maps; fragment campaigns | Structural analysis of poxvirus polymerase and capping machinery; guide structure-based design | Structure determination; hit-to-lead optimization | [63] |
| Phenotypic assays (infection-based) | Measure the antiviral effect in relevant biology without prior target/Live virus or pseudotyped systems; human cell lines/organoids | Viral load reduction (quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR)/plaques), CPE rescue, imaging, SI | Physiological relevance; reveals host-directed MoAs; detects polypharmacology/Target unknown; off-target/cytotoxicity risk; model dependence | Target deconvolution (proteomics/CRISPR), pharmacokinetic pharmacodynamic (PK/PD), in vivo | MPXV infection assays in primary keratinocytes and organoids; validation of tecovirimat alternatives | Hit validation, MoA discovery, prioritization | [13,34] |
| Multi-omics integration (genomics/proteomics/transcriptomics/metabolomics) | Maps virus–host networks; identifies targets/pathways and biomarkers/bulk/single-cell RNA-seq, proteomics, phospho-proteomics, metabolomics | Differential pathways, network hubs, drug–gene signatures | Systems-level insight; reveals host targets and combinations/Complex analysis; batch effects; causal inference is hard | Network pharmacology, CRISPR perturbations, small-molecule probing | Host interactome proximity analyses suggesting JAK/STAT and NF-κB modulators; signatures guiding baricitinib/infliximab hypotheses | Target nomination; combination strategy design | [64] |
| AI/ML-guided repurposing (knowledge graphs, signature matching) | Prioritizes candidates using literature, omics, and chemistry graphs/Curated corpora, drug–target networks, and disease signatures | Ranked candidates, mechanism hypotheses, polypharmacy suggestions | Leverages existing data; scalable; uncovers non-obvious links/Data bias; spurious correlations; requires wet-lab confirmation | Prospective validation in phenotypic assays and animal models | Prioritized immunomodulators (such as JAK inhibitors and anti-TNF agents) and DNA metabolism inhibitors for MPXV | Hypothesis generation; portfolio triage | [65,66] |
| Organoid/3D tissue models | Human-relevant platforms for efficacy/toxicity/skin/mucosal organoids, immune co-cultures | Viral replication kinetics, barrier integrity, cytokine profiling | Closer to human physiology; detects tissue-specific effects/Throughput lower than 2D; cost; standardization | Bridge to in vivo; PK/PD translation; safety pharmacology | MPXV replication and drug testing in skin organoids relevant to lesion tropism | Preclinical validation; safety/efficacy translation | [67] |
| Animal models (marmoset, prairie dog, and mouse with VACV/ectromelia models) | In vivo efficacy and safety assessment/infected animals; candidate dosing | Survival, lesion burden, viral load, PK/PD | Integrates immunity/ADME; regulatory credibility/species differences; ethics; BSL-3; cost | Dose optimization, tox studies; clinical trial design | Benchmarking tecovirimat; testing host-directed combinations | Late preclinical go/no-go | [68] |
| Drug Name | Original Indication | Target Protein in MPXV | Mechanism of Action | Computational Method Used | In Vitro/In Vivo Evidence | Potential Benefits | Limitations/Challenges | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adalimumab | Rheumatoid arthritis | TNF-α (host) | Reduces inflammation and viral pathogenesis | Network-based approach | Computational analysis suggests anti-inflammatory benefit | Well-studied immune modulator | May not directly inhibit viral replication | [38,89] |
| Atovaquone | Antimalarial | D13L capsid protein | Inhibits viral assembly by targeting structural proteins | Molecular docking, MD simulations | In vitro inhibition of poxvirus replication | FDA-approved, well-tolerated | Requires further clinical validation | [90] |
| Baricitinib | Rheumatoid arthritis | JAK1/JAK2 (host pathway) | Reduces hyperinflammatory response | Network-based pharmacology | Identified via AI; suppresses MPXV-driven inflammation | FDA-approved immunomodulator | Indirect antiviral activity; risk of immunosuppression | [38] |
| Batefenterol | Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) (β-agonist) | Unknown (Host target) | Modulates immune and inflammatory response | AI-based drug screening | Suggested in silico as host-modulatory agent | Potential host-targeted antiviral strategy | No experimental validation yet | [13] |
| Batefenterol | COPD | DNA-dependent RNA polymerase | Inhibits viral transcription machinery | Molecular docking, MD simulations | Potential activity suggested by computational studies | High specificity, existing safety profile | Lacks direct antiviral validation | [13] |
| Brincidofovir | Cytomegalovirus, Adenovirus | DNA Polymerase (D5R) | Inhibits viral DNA polymerization | Virtual screening, docking | In vivo studies show partial MPXV inhibition | Oral bioavailability; lipid-modified for uptake | Gastrointestinal toxicity; mixed clinical efficacy | [62] |
| Burixafor | Stem cell mobilizer | DNA-dependent RNA polymerase | Inhibits viral transcription | Molecular docking, MD simulations | Predicted inhibition in in silico models | Potential for rapid repurposing | No in vivo validation yet | [13] |
| Cidofovir | Antiviral (CMV) | Viral DNA polymerase | Inhibits viral DNA synthesis | Molecular docking, MD simulations | Effective against MPXV in vitro and in vivo | Established antiviral, broad-spectrum | High nephrotoxicity risk | [62,91] |
| Deoxyuridine Analogs | Herpesvirus infections | DNA Polymerase (D5R) | Inhibits viral DNA elongation | Pharmacophore modeling, MD simulations | Strong docking scores & molecular stability | Potential for combination therapy | No in vivo validation yet | [62] |
| Doxorubicin | Chemotherapy | Viral DNA polymerase | Inhibits viral DNA replication | Molecular docking, MD simulations | Shows inhibition in computational and preliminary in vitro studies | Existing FDA approval, known safety profile | High cytotoxicity limits therapeutic window | [92,93] |
| Eluxadoline | IBS treatment | DNA-dependent RNA polymerase | Blocks viral transcription | Molecular docking, MD simulations | Identified via computational screening | FDA-approved, potential oral formulation | Lacks clinical validation | [13,94] |
| Elvitegravir | HIV integrase inhibitor | VP39 / DNA replication complex (putative) | Binds nucleic-acid–processing pockets | Docking (AutoDock/Vina), ADMET filters | None for MPXV wet lab | Known human PK, safety | Off-target risk; needs efficacy data | [61] |
| Etanercept | Autoimmune disorders | TNF-α (host) | Prevents cytokine overproduction | Network-based approach | Identified as a potential adjunctive therapy | Could reduce MPXV disease severity | May impair immune response to infection | [38] |
| Fostamatinib | SYK inhibitor (ITP) | VP39 (mRNA cap 2-O-MTase); host SYK pathway | Interference with RNA capping; host immune modulation | Docking to VP39 (PDB 8CEQ), MD refinement | None specific to MPXV in cited papers | Oral, known safety profile | Off-target immunomodulation; needs MPXV validation | [34,37] |
| Infliximab | Autoimmune diseases (TNF-α inhibitor) | TNF-α (Host pathway) | Suppresses immune hyperactivation | Protein-ligand interaction networks | Reduces cytokine storm in MPXV cases | Prevents immune overactivation | Potential immunosuppressive side effects | [38] |
| Infliximab | Autoimmune disorders | TNF-α (host) | Modulates immune response, reducing viral pathogenesis | Network-based approach | Potential benefit in controlling cytokine storm in MPXV cases | Immunomodulatory effects | Risk of immune suppression | [38] |
| Mefloquine | Antimalarial | D13L capsid protein | Disrupts viral assembly and replication | Molecular docking, MD simulations | Effective against poxviruses in preclinical studies | Long half-life, immune-modulatory properties | CNS side effects limit broad use | [92,95] |
| Methisazone (Marboran) | Historical anti-pox | Host translation (eIF-2–dependent early protein synthesis) | Inhibits early viral protein synthesis | (historic pharmacology) | Historical prophylaxis/limited efficacy vs. variola/vaccinia in older reports; not used currently | Mechanistic precedent for pox antivirals | Poor efficacy/tolerability; obsolete | [96] |
| Minocycline | Antibiotic | DNA-dependent RNA polymerase | Inhibits viral transcription | Molecular docking, MD simulations | Computational predictions suggest strong inhibition | FDA-approved, broad antiviral potential | Requires further in vivo validation | [56] |
| Niclosamide | Anthelmintic | VP37/F13 (envelopment/egress) | Inhibits virion egress by binding F13 pocket (putative) | Structure-based docking to F13/VP37 | No MPXV wet-lab signal reported in cited work | Oral, generic, broad antiviral reports | Poor solubility; primarily computational evidence here | [34] |
| Nitroxoline | Urinary tract infections (UTI) | Thymidylate kinase (TMPK) | Blocks DNA synthesis and viral replication | AI-driven screening, QSAR | In vitro antiviral activity confirmed | FDA-approved; broad-spectrum activity | Requires systemic efficacy validation | [97] |
| Remdesivir | RdRp inhibitor (Ebola/COVID-19) | MPXV DNA polymerase complex (off-target) | Nucleoside analogue mismatch (unlikely optimal for DNA viruses) | Docking screens | Weak/variable activity vs. orthopox in vitro; no MPXV clinical signal | Known safety; IV | Limited mechanism fit for DNA poxviruses | [41,98] |
| Ribavirin | Broad-spectrum antiviral | IMPDH/guanosine pools; viral polymerases | Depletes GTP; error catastrophe (RNA-virus-centric) | (mechanistic repurposing) | Limited/variable anti-orthopox effects in vitro; toxicity at doses required | Oral option; cheap | Hemolysis; limited pox efficacy | [98] |
| Tecovirimat (ST-246) | Smallpox (Orthopoxviruses) | F13L (Envelope protein) | Inhibits viral egress and prevents virion maturation | Molecular docking, MD simulations | FDA-approved; in vitro MPXV efficacy confirmed | Specific to orthopoxviruses; FDA-approved | Resistance mutations (F13L escape variants) | [99] |
| Tigecycline/Omadacycline | Tetracycline antibiotic | Multi-target: thymidylate kinase, DNA topoisomerase I, F13 (p37) | Binds nucleotide/ATP pockets; blocks DNA synthesis/egress (putative) | Multi-target docking, MM-GBSA rescoring, MD | No MPXV wet lab in cited study | Multi-site binding; favorable docking energies | IV use; antibacterial AEs; translational gap | [56] |
| Tilorone | Antiviral (Influenza) | Viral helicase | Disrupts viral genome processing | Molecular docking, MD simulations | Computationally predicted to inhibit MPXV replication | Broad-spectrum antiviral, immune modulating | Requires further in vivo and clinical testing | [100] |
| ZINC22060520 | Not approved (In silico lead) | JAK1 | Targets host immune pathways | Pharmacophore modeling, MD simulations | Strong binding affinity in MD simulations | Novel candidate with high specificity | No clinical validation yet | [38] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Österreichische Pharmazeutische Gesellschaft. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mushebenge, A.G.-A.; Mphuthi, D.D. Deciphering Drug Repurposing Strategies: Antiviral Properties of Candidate Agents Against the Mpox Virus. Sci. Pharm. 2025, 93, 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93040051
Mushebenge AG-A, Mphuthi DD. Deciphering Drug Repurposing Strategies: Antiviral Properties of Candidate Agents Against the Mpox Virus. Scientia Pharmaceutica. 2025; 93(4):51. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93040051
Chicago/Turabian StyleMushebenge, Aganze Gloire-Aimé, and David Ditaba Mphuthi. 2025. "Deciphering Drug Repurposing Strategies: Antiviral Properties of Candidate Agents Against the Mpox Virus" Scientia Pharmaceutica 93, no. 4: 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93040051
APA StyleMushebenge, A. G.-A., & Mphuthi, D. D. (2025). Deciphering Drug Repurposing Strategies: Antiviral Properties of Candidate Agents Against the Mpox Virus. Scientia Pharmaceutica, 93(4), 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm93040051





