Journal Description
Current Oncology
Current Oncology
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal published online by MDPI (from Volume 28 Issue 1-2021). Established in 1994, the journal represents a multidisciplinary medium for clinical oncologists to report and review progress in the management of this disease. The Canadian Association of Medical Oncologists (CAMO), the Canadian Association of Psychosocial Oncology (CAPO), the Canadian Association of General Practitioners in Oncology (CAGPO), the Cell Therapy Transplant Canada (CTTC), the Canadian Leukemia Study Group (CLSG) and others are affiliated with the journal and their members receive a discount on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, MEDLINE, PMC, Embase, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Oncology)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 21.5 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.5 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- Journal Clusters of Oncology: Cancers, Current Oncology, Onco and Targets.
Impact Factor:
3.4 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
3.3 (2024)
Latest Articles
Trastuzumab Deruxtecan-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease: Real-World Insights from a Tertiary Care Center
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(10), 575; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32100575 (registering DOI) - 16 Oct 2025
Abstract
Background: Trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd), a HER2-directed antibody-drug conjugate, has significantly advanced the management of HER2-expressing malignancies. However, interstitial lung disease (ILD) remains a clinically significant adverse effect. Despite increasing clinical use of T-DXd, real-world data on ILD incidence, characteristics, and outcomes—particularly in Middle
[...] Read more.
Background: Trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd), a HER2-directed antibody-drug conjugate, has significantly advanced the management of HER2-expressing malignancies. However, interstitial lung disease (ILD) remains a clinically significant adverse effect. Despite increasing clinical use of T-DXd, real-world data on ILD incidence, characteristics, and outcomes—particularly in Middle Eastern populations remain limited. Methods: This retrospective study analyzed medical records of patients who received trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd) at a tertiary care hospital. Data collected included demographics, tumor characteristics, prior treatments, and interstitial lung disease (ILD)-related outcomes. ILD events were identified and graded according to the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) version 5.0. Descriptive statistics were used to summarize baseline characteristics and ILD features. Univariate logistic regression was performed to assess potential risk factors associated with ILD development. Kaplan–Meier survival analysis was used to evaluate time-to-event outcomes, including time to ILD onset and resolution. Results: Among 65 patients with advanced stage IV cancer (90.8% with breast cancer), 16 (24.6%) developed ILD following T-DXd therapy. The median time to ILD onset was 125.5 days. The most common presenting symptoms were dyspnea and cough (50%). A history of ground-glass opacities was associated with increased odds of ILD (OR 2.7; p = 0.236), though not statistically significant. Patients with Grade ≥ 3 ILD had significantly lower oxygen saturation levels compared to those with milder grades (88.3% vs. 97.7%, p = 0.049). Median time to clinical resolution was 297 days (95% CI: 77.5–516). No significant associations were observed with smoking history, pulmonary metastases, or prior thoracic radiation. Conclusions: In this real-world cohort, ILD occurred in nearly one-quarter of patients receiving T-DXd, predominantly within the first six months of treatment. The findings highlight the importance of early respiratory symptom monitoring and pulse oximetry—particularly in patients with pre-existing pulmonary abnormalities. These results underscore the need for vigilant ILD surveillance strategies and further prospective studies to validate predictive risk factors and optimize management protocols.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Thoracic Oncology)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Use of Irreversible Electroporation in Pancreatic Cancer Patients: A Multi-Center Experience
by
Bart Hendrikx, Eline-Alice Brys, Alexandra Dili, Thomas Apers, Vera Hartman, Martin Brichard, Filip Gryspeerdt, Claude Bertrand, Geert Roeyen and Frederik Berrevoet
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(10), 574; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32100574 (registering DOI) - 16 Oct 2025
Abstract
Background: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) has a poor prognosis, with a 5-year survival rate of 10%. Irreversible electroporation (IRE), a non-thermal ablative technique, may improve outcomes in locally advanced (LAPC) and borderline resectable pancreatic cancer (BRPC). This multi-center retrospective study aims to evaluate
[...] Read more.
Background: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) has a poor prognosis, with a 5-year survival rate of 10%. Irreversible electroporation (IRE), a non-thermal ablative technique, may improve outcomes in locally advanced (LAPC) and borderline resectable pancreatic cancer (BRPC). This multi-center retrospective study aims to evaluate postoperative complications, 90-day mortality, and survival following IRE. Methods: 35 pancreatic cancer patients were treated with IRE between 2015 and 2023 across three Belgian hospitals. IRE was performed for tumor destruction in unresectable LAPC (n = 13) (IRE-LAPC) and for margin accentuation during resection in BRPC (n = 22) (IRE-MA). Primary endpoints were 90-day mortality, complications, and survival (only 33 patients included); secondary endpoints included metastases, local recurrence, and R0-resection rates. Results: Postoperative complications occurred in 23.1% (IRE-LAPC) and 68.2% (IRE-MA) of patients. Overall survival at 24 months was 27.3% (IRE-LAPC) and 27.3% (IRE-MA). Median survival time was 12.7 months (IRE-LAPC) and 13.3 months (IRE-MA). Six patients (17.1%) died within 90 days. Metastasis occurred in 51.5% of patients after a median time of 9.8 months. Local recurrence was seen in 24.2% of patients after a median time of 7.5 months. R0 resection was achieved in 63.6% (IRE-MA). Discussion: IRE for margin accentuation in BRPC is associated with relatively high morbidity and mortality rates and cannot be considered beneficial. In unresectable LAPC, IRE appears relatively safe for local disease control. Further research should clarify patient selection and optimize its therapeutic role.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Gastrointestinal Oncology)
►▼
Show Figures
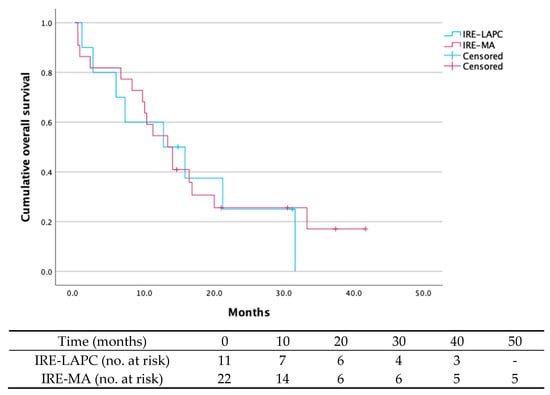
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Bevacizumab in Pediatric Neuro-Oncology
by
Jacob Silverman, Sayanthen Sathyakumar, Hallie Coltin, Sebastien Perreault, Nada Jabado, Eric Bouffet and Samuele Renzi
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(10), 573; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32100573 (registering DOI) - 16 Oct 2025
Abstract
Bevacizumab is often used off-label in pediatric neuro-oncology, and evidence for indications of bevacizumab use in pediatric neuro-oncology is often fragmented. Therefore, this review aims to provide an organized summary of efficacy across different types of tumors, highlight outcomes, and link findings to
[...] Read more.
Bevacizumab is often used off-label in pediatric neuro-oncology, and evidence for indications of bevacizumab use in pediatric neuro-oncology is often fragmented. Therefore, this review aims to provide an organized summary of efficacy across different types of tumors, highlight outcomes, and link findings to the underlying biology. Gaps in the literature were also identified to guide future research. We narratively synthesized various pediatric studies, and the following tumor categories were identified for discussion: low-grade glioma, high-grade glioma, diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma, schwannoma, medulloblastoma, radiation necrosis, and cerebral edema. Key outcomes considered included overall survival, event-free survival, progression-free survival, vision and/or hearing improvements, steroid use, quality of life, and toxicity. The greatest benefits were observed in cases such as recurrent medulloblastoma in combination with temozolomide and irinotecan, optic pathway glioma visual function, and diminished steroid use in radiation necrosis. Results were poorer in cases of newly diagnosed high-grade gliomas and diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas. The medication was overall well tolerated, with adverse events like hypertension, proteinuria, and epistaxis often being manageable with surveillance. In consideration of the results, bevacizumab should be considered based on the tumor profile, and its outcome measured along functional endpoints, besides radiological evolution. Continued investigations into outcome measures, as well as combination with targeted treatments and optimizing therapy, will contribute to improving outcomes in this vulnerable population.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Neuro-Oncology)
Open AccessReview
A Current Perspective of Two of the Most Aggressive Head and Neck Cancers: Pharyngeal and Laryngeal
by
Mihaela Iuliana Sîrbu (Ciortan), Maria Alina Marin, Doina Chioran, Iasmina-Alexandra Predescu, Nicolae Constantin Balica, Sergio Liga, Mircea Rivis, Ştefania Dinu and Şerban Talpoş
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(10), 572; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32100572 (registering DOI) - 15 Oct 2025
Abstract
Background: Head and neck cancers (HNCs) represent a substantial global health burden, with an estimated mortality rate exceeding 50% annually. Among the various subsites, pharyngeal and laryngeal carcinomas are recognized as two of the most aggressive and challenging forms, characterized by high incidence,
[...] Read more.
Background: Head and neck cancers (HNCs) represent a substantial global health burden, with an estimated mortality rate exceeding 50% annually. Among the various subsites, pharyngeal and laryngeal carcinomas are recognized as two of the most aggressive and challenging forms, characterized by high incidence, poor prognosis, and a strong association with advanced-stage diagnosis. Methods: A systematic literature review was performed using electronic literature databases (e.g., PubMed, Google Scholar). Search terms included “head and neck cancer”, “laryngeal cancer”, and “pharyngeal cancer”. Selected studies are published within the last two decades. Results: Laryngeal cancer constitutes approximately 40% of head and neck malignancies, with a clear male predominance, and pharyngeal cancer shows increased incidence in male populations from the Americas and Africa. Despite therapeutic advancements in radiotherapy, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy, overall survival rates remain unsatisfactory. Moreover, patients are at increased risk for second primary malignancies, particularly within the lungs and esophagus, due to the widespread carcinogenic exposure along the aerodigestive tract. Conclusions: To mitigate the morbidity and mortality associated with pharyngeal and laryngeal cancers, early detection, risk factor mitigation, and public health education are imperative. Enhancing screening among high-risk populations and adopting personalized, multidisciplinary treatment strategies may significantly improve clinical outcomes and long-term survival.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Head and Neck Oncology)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Automated Software Evaluation in Screening Mammography: A Scoping Review of Image Quality and Technique Assessment
by
Kelly M. Spuur, Clare L. Singh, Dana Al Mousa and Minh T. Chau
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(10), 571; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32100571 - 15 Oct 2025
Abstract
Background: Standardised breast positioning and optimal compression are critical components of effective breast cancer screening. This scoping review aims to report the current landscape of automated software tools developed for image quality assessment and mammographic technique evaluation, and to examine their reported impact.
[...] Read more.
Background: Standardised breast positioning and optimal compression are critical components of effective breast cancer screening. This scoping review aims to report the current landscape of automated software tools developed for image quality assessment and mammographic technique evaluation, and to examine their reported impact. Methods: A scoping review was undertaken across PubMed (MEDLINE), Scopus, and Emcare. Eligible studies were published between January 2014 and March 2025 and investigated the use of automated software or artificial intelligence-based tools to assess image quality, breast positioning, or compression in mammography or digital breast tomosynthesis. Results: Automated software was predominantly utilised in high-resource settings, where it provided benchmarked feedback, reduced the subjectivity inherent in traditional visual grading systems, and supported radiographer learning and skill development with measurable improvements. However, radiographer training in these systems, the impact of software on clinical workflow, and barriers to implementation, particularly in low-resource settings, were insufficiently addressed in the literature. Furthermore, no studies reported on the relationship between software-generated metrics and breast cancer screening outcomes. Conclusions: Automated software for image quality evaluation represents a significant advancement in breast screening, illustrating the potential of technology to strengthen the screening-to-treatment continuum in breast cancer care. Nonetheless, widespread adoption requires evidence that these tools directly contribute to improved cancer detection outcomes to justify their uptake.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue From Screening to Treatment: Technology’s Impact on Breast Cancer Care)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Exploring the Experiences of Individuals Diagnosed with Metastatic Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Qualitative Study
by
Sarah Scruton, Caroline Hovey, Cynthia Kendell and Robin Urquhart
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(10), 570; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32100570 - 15 Oct 2025
Abstract
Advancements in targeted therapies and immunotherapies have improved survival for individuals with metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (mNSCLC), creating a growing population of Canadians living long-term with the disease. These individuals face ongoing physical, emotional, and practical challenges, yet existing supportive care services are
[...] Read more.
Advancements in targeted therapies and immunotherapies have improved survival for individuals with metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (mNSCLC), creating a growing population of Canadians living long-term with the disease. These individuals face ongoing physical, emotional, and practical challenges, yet existing supportive care services are often designed for patients receiving curative intent treatment and may not adequately address the challenges of those undergoing continuous treatment. To explore these experiences and inform the development of supports tailored to their needs, eight participants with mNSCLC completed one-on-one virtual interviews. They described limited support for managing side effects and psychosocial concerns despite general satisfaction with oncology care. Fatigue and cognitive challenges impacted daily functioning, and emotional challenges (e.g., fear of progression, stigma, and difficulty finding meaning) impacted quality of life. Financial burden, including unexpected costs and loss of income, further affected their well-being. Existing supports, such as exercise programs, were viewed positively but were often difficult to access, were offered only short-term, and required patients to find them independently. Recommendations included improved coordination and communication across the healthcare system, alongside tailored interventions such as navigation services, resource directories, health promotion supports, and expanded peer support. Overall, people living long term with mNSCLC face distinct challenges and unmet supportive care needs, highlighting the importance of integrating supportive services into routine oncology care.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Small Extracellular Vesicles Derived from NF2-Associated Schwannoma Cells Modulate Tumor Progression and Immunity via HSP90
by
Ying Wang, Yuan Ren, Qi Zhang, Chao Zhang, Minjun Yan, Xin Ma, Bo Wang, Peng Li and Pinan Liu
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(10), 569; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32100569 - 13 Oct 2025
Abstract
In-depth exploration of tumor immune suppression mechanisms may provide new therapeutic options for NF2-associated tumors. In this study, we found that sEVs secreted by NF2-associated schwannomas (NF2-EVs) facilitate the conversion of CD14+ monocytes into an MDSC-like phenotype, showcasing MDSC-like inhibitory functions. Moreover,
[...] Read more.
In-depth exploration of tumor immune suppression mechanisms may provide new therapeutic options for NF2-associated tumors. In this study, we found that sEVs secreted by NF2-associated schwannomas (NF2-EVs) facilitate the conversion of CD14+ monocytes into an MDSC-like phenotype, showcasing MDSC-like inhibitory functions. Moreover, these NF2-EVs are capable of enhancing tumor cell proliferation. Through proteomic analysis and subsequent validation of the NF2-EVs, we identified elevated levels of HSP90. When we knocked down HSP90 expression in tumor cells, the sEVs secreted showed diminished capacity to convert monocytes into MDSCs and a reduced ability to promote tumor cell proliferation. Conversely, sEVs secreted by tumor cells that overexpress HSP90 displayed the opposite effects. Further mechanistic studies revealed that HSP90 could influence the expression of AKT/p-AKT and ERK/p-ERK. Our results suggest that NF2 tumor cells could regulate the AKT/p-AKT and ERK/p-ERK pathways to promote tumor cell proliferation and the formation of an immunosuppressive microenvironment by secreting sEVs’ HSP90, offering valuable insights into the involvement of HSP90 in exosome-mediated communication within the context of NF2-related schwannomatosis (NF2-SWN). This information has the potential to inform the design of effective immunotherapeutic protocols and offer new treatment options for NF2-SWN patients.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Neuro-Oncology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Retrospective Cohort Study of Intrapericardial Cisplatin for Risk Reduction of Malignant Pericardial Effusion Recurrence
by
Francisco Javier Muñoz-Carrillo, Roxana Maribel Reyes, David Pesántez, Gemma Carrera, Enric Cascos, Pedro Castro, Sara Fernández-Méndez, Carme Font, Laura González-Aguado, Ignacio Grafiá, Lucía Llavata, Inés Monge-Escartín, Joan Padrosa, Noemí Reguart, Adrián Téllez, Albert Tuca, Margarita Viladot, Carles Zamora-Martínez, Patrícia Amorós-Reboredo and Javier Marco-Hernández
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(10), 568; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32100568 - 11 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Malignant pericardial effusion (MPE) is a life-threatening condition in patients with cancer, with common recurrences after simple pericardiocentesis. Consequently, the intrapericardial instillation of sclerosing or cytotoxic agents has been explored, with limited evidence from small studies with different methodologies. We undertook an observational,
[...] Read more.
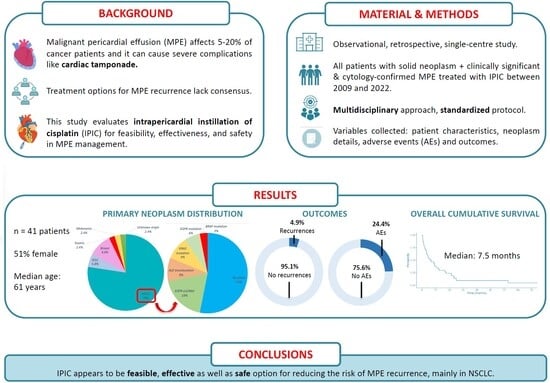
Malignant pericardial effusion (MPE) is a life-threatening condition in patients with cancer, with common recurrences after simple pericardiocentesis. Consequently, the intrapericardial instillation of sclerosing or cytotoxic agents has been explored, with limited evidence from small studies with different methodologies. We undertook an observational, retrospective, single-centre study, including all patients diagnosed with a solid neoplasm and clinically significant and/or recurrent, cytology-confirmed MPE, treated with Intrapericardial Instillation of Cisplatin (IPIC), between 2009 and 2022. Patients with hematological malignancies were excluded. The procedure followed a multidisciplinary approach and a standardized protocol. Variables collected included baseline patient characteristics, neoplasm details, MPE impact, adverse events (AEs) from procedures (pericardiocentesis and IPIC) and outcomes (time to MPE recurrence and survival). This study adhered to the STROBE guidelines. A total of 41 patients were included, 51% female, with a median age of 61 (51–69) years. Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) was the predominant primary tumour (78%) and in 44% of the cohort, MPE was identified at cancer diagnosis. Most patients (90.2%) presented symptoms related to MPE at diagnosis, and 88% had cardiac tamponade on echocardiography. IPIC was administered a median of four times. IPIC-related AEs occurred in 10 patients (24.4%), with transient atrial fibrillation (AF) being the most frequent one. Two patients (4.9%) experienced MPE recurrence within 30 days after IPIC. The median survival time from MPE diagnosis was 161 days (5.4 months; IQR 73–455 days). IPIC appears to be a feasible, effective and safe option for reducing the risk of MPE recurrence, mainly in NSCLC.
Full article
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Predictive Factors and Clinical Impact of Radioactive Seed Migration After Prostate Brachytherapy: A Retrospective Study
by
Shota Kikuchi, Takashi Fukagai, Jin Yamatoya, Kazuhiko Oshinomi, Masakazu Nagata, Masashi Morita, Kosuke Toyofuku, Atsuhito Sekimoto, Masako Kato, Madoka Morota and Yoshinori Ito
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(10), 567; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32100567 - 11 Oct 2025
Abstract
Radioactive seed migration after low-dose-rate brachytherapy (LDR-BT) for prostate cancer is a known phenomenon; however, its clinical impact remains unclear. We retrospectively analyzed 611 patients treated with LDR-BT using loose iodine-125 seeds. Post-treatment imaging was used to assess seed migration. Treatment efficacy was
[...] Read more.
Radioactive seed migration after low-dose-rate brachytherapy (LDR-BT) for prostate cancer is a known phenomenon; however, its clinical impact remains unclear. We retrospectively analyzed 611 patients treated with LDR-BT using loose iodine-125 seeds. Post-treatment imaging was used to assess seed migration. Treatment efficacy was evaluated using post-plan dosimetry (V100 and D90) and biochemical recurrence-free survival (bRFS). Seed migration was observed in 150 patients (24.5%) within 1–3 months post-treatment, involving a total of 210 seeds. Migration sites included lungs, vasculature, and seminal vesicles. Hematogenous migration was significantly associated with higher seed counts. Seminal vesicle migration was linked to increased needle usage and absence of neoadjuvant hormone therapy. No significant differences were observed in V100, D90, or bRFS between patients with or without seed migration. However, migration of ≥3 seeds correlated with significantly lower V100 and with a trend toward decreased bRFS. Limited seed migration appears to have minimal clinical impact. However, ≥3 migrated seeds may reduce dosimetric quality and affect treatment efficacy. Risk factors include larger prostate volume as well as higher seed and needle counts. Improved planning and using linked seeds may reduce migration and improve outcomes in LDR-BT for prostate cancer.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Genitourinary Oncology)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
SUVmax-IPI as a New Prognostic Index in Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Receiving Nivolumab
by
Nagihan Kolkıran, Atike Pınar Erdoğan, Mustafa Şahbazlar, Semra Taş, Gamze Gököz Doğu, Kübra Canaslan, İlkay Tuğba Ünek, Özge Demirkıran, Bilgin Demir, Güler Nur Teküstün, Özgür Tanrıverdi and Ferhat Ekinci
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(10), 566; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32100566 - 9 Oct 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Nivolumab has significantly improved outcomes in patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC); however, reliable prognostic biomarkers remain an unmet need. To address this gap, we developed the SUVmax-IPI, a novel prognostic index combining maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax) from 18
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Nivolumab has significantly improved outcomes in patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC); however, reliable prognostic biomarkers remain an unmet need. To address this gap, we developed the SUVmax-IPI, a novel prognostic index combining maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax) from 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) with systemic inflammatory markers. This study aimed to evaluate the prognostic value of SUVmax-IPI in patients with NSCLC receiving nivolumab therapy. Methods: This multicenter retrospective analysis included 187 patients with metastatic NSCLC receiving nivolumab across 5 tertiary institutions. The SUVmax-IPI incorporated pretreatment SUVmax and laboratory-based inflammatory prognostic index (IPI) parameters. Survival outcomes were evaluated using Kaplan–Meier analysis with log-rank testing and multivariate cox regression. Results: Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis established an optimal SUVmax-IPI cut-off of 241.9. Patients with SUVmax-IPI ≤ 241.9 had significantly better survival outcomes: median overall survival (OS) was 35 versus 15 months (p = 0.002). For progression-free survival (PFS), although a numerical difference favored patients with SUVmax-IPI ≤ 241.9 (median: 15 vs. 8 months), this did not reach statistical significance (log-rank p = 0.175). Multivariate analysis confirmed SUVmax-IPI as an independent predictor of survival (p = 0.002). Conclusions: The SUVmax-IPI represents a promising prognostic tool for patients with metastatic NSCLC who received at least 3 months of nivolumab, integrating metabolic and inflammatory parameters to predict survival outcomes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Thoracic Oncology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessEditorial
Cervical Cancer Elimination Requires Systems, Trust, and Action
by
Samara Perez
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(10), 565; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32100565 - 8 Oct 2025
Abstract
Cervical cancer has a clear and achievable path to elimination [...]
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Action and Impact: Prevention and Screening Strategies Contributing to the Elimination of Cervical Cancer)
Open AccessArticle
Supporting Employment After Cancer: A Mixed-Methods Evaluation of a Vocational Integration Programme for Childhood, Adolescent, and Young Adult Cancer Survivors
by
Margherita Dionisi-Vici, Anna Schneider-Kamp, Ilenia Giacoppo, Alessandro Godono, Eleonora Biasin, Antonella Varetto, Emanuela Arvat, Francesco Felicetti, Giulia Zucchetti and Franca Fagioli
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(10), 564; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32100564 - 8 Oct 2025
Abstract
Childhood, adolescent, and young adult cancer (CAYAC) survivors often face challenges entering the workforce due to long-term physical, cognitive, and psychological late effects, defined as chronic health conditions resulting from cancer and its treatments. This study evaluated a vocational integration programme that addresses
[...] Read more.
Childhood, adolescent, and young adult cancer (CAYAC) survivors often face challenges entering the workforce due to long-term physical, cognitive, and psychological late effects, defined as chronic health conditions resulting from cancer and its treatments. This study evaluated a vocational integration programme that addresses these barriers and promotes psychosocial well-being. The multidisciplinary intervention combined career guidance, soft-skills training, and a paid internship. Using a mixed-method design with questionnaires and semi-structured interviews, we assessed feasibility, satisfaction, and psychosocial outcomes. Thirteen participants (mean-age-at-diagnosis: 12.9 years, SD 5.2; mean-age-at-interview: 27.2 years, SD 5.3) reported over 40 late effects, mostly of moderate severity. Health-Related Quality of Life (HRQoL), measured by the SF-12, showed a Physical Component Score mean of 45.2 (SD 9.1) and a Mental Component Score mean of 43.5 (SD 11.2), indicating greater psychological impact. The programme received high satisfaction ratings (mean 8.3/10) and was described as motivating and valuable, enhancing self-confidence and career prospects. Social support emerged as a key facilitator, while participants noted the need for flexibility and individualised pacing. Despite a limited sample size and potential recruitment bias, this study provides preliminary insights into the feasibility and perceived value of tailored vocational programmes, emphasising the importance of adaptable, socially supportive interventions for CAYAC survivors.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Interventions to Prevent and Reduce Late Effects in Childhood, Adolescent, and Young Adult Cancer Survivors)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Health Effects of Ergonomics and Personal Protective Equipment on Chemotherapy Professionals
by
Ana Reis, Vítor Silva, João José Joaquim, Luís Valadares, Cristiano Matos, Carolina Valeiro, Ramona Mateos-Campos and Fernando Moreira
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(10), 563; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32100563 - 8 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
(1) Background: With the increasing incidence of cancer, the need for handling cytotoxic drugs has also grown. However, manipulating these drugs exposes healthcare professionals to significant risks, including occupational exposure to hazardous chemicals. Therefore, it is important to adopt protective measures, including personal
[...] Read more.
(1) Background: With the increasing incidence of cancer, the need for handling cytotoxic drugs has also grown. However, manipulating these drugs exposes healthcare professionals to significant risks, including occupational exposure to hazardous chemicals. Therefore, it is important to adopt protective measures, including personal protective equipment (PPE) and correct ergonomic practices, to ensure safe drug preparation and minimize health risks for the operators. However, while chemical exposure and PPE have been extensively addressed in the literature, the combined impact of ergonomic practices and protective measures remains insufficiently emphasized, representing a critical gap this review aims to address. Accordingly, the objective of this literature review was to analyze the ergonomic and individual protection practices during the handling of cytostatic drugs and all the implications that bad ergonomic practices and/or poor individual protection have on the operator’s health; (2) Methods: In order to perform this integrative review, a structured literature search was conducted using online databases (Web of Science®, Google Scholar®, and PubMed®) from January 2005 to June 2025. (3) Results: A total of 19 articles were analyzed, with 17 focusing on PPE and 17 on ergonomics. The findings emphasize that PPE, such as gloves, masks, gowns, sleeves and safety glasses, plays a critical role in the safe handling of cytotoxic drugs, particularly when combined with other safety measures. Additionally, maintaining correct ergonomic posture is important in preventing musculoskeletal disorders; (4) Conclusions: This review emphasizes the significance of integrating appropriate PPE use with sound ergonomic procedures. Although PPE is still the secondary line of defense against occupational exposure, ergonomic issues must also be addressed to avoid chronic musculoskeletal problems. Continuous training, rigorous attention to safety procedures, and ergonomic enhancements should be prioritized by healthcare facilities as a key element of occupational safety programs to reduce the short-term and long-term health hazards for personnel handling dangerous drugs.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Feasibility of a Physiatry Assessment Clinic to Address Physical Impairment in Head and Neck Cancer Patients Following Neck Resection and Free Flap Reconstruction
by
Lauren C. Capozzi, Chad Wagoner, Julia T. Daun, Lisa Murphy, Steven C. Nakoneshny, George J. Francis, Joseph C. Dort, Khara Sauro and S. Nicole Culos-Reed
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(10), 562; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32100562 - 7 Oct 2025
Abstract
Individuals with head and neck cancers are living longer than ever before, yet many live with the long-term effects of their cancer and treatment. The purpose of this study was to assess the feasibility of a physiatry assessment clinic (PAC) following neck resection
[...] Read more.
Individuals with head and neck cancers are living longer than ever before, yet many live with the long-term effects of their cancer and treatment. The purpose of this study was to assess the feasibility of a physiatry assessment clinic (PAC) following neck resection and free flap reconstruction, during which physical function was assessed. Methods: Adult patients participating in a larger prehabilitation study were included. Attendance and the ability to complete the physical function assessment were examined. Exploratory analyses were completed to describe physical function, fitness, shoulder, and neck function among PAC attenders. To further understand PAC feasibility, patient-reported outcomes among PAC attenders and non-attenders were examined over 12 months (QuickDASH, NDII, EAT-10). Results: A total of 36 eligible participants (78.2%) from the larger prehabilitation study were approached to participate in the PAC, and 19 of the 36 attended (52.8%). Participants attended on average 8.6 ± 3.6 weeks post surgery, and 100% were able to complete the functional measures. Exploratory data suggest that those who did not attend (17 of 36 approached) had more advanced disease compared to those who attended (p < 0.05). Patient-reported outcomes suggested better shoulder function and swallow function at 6 months among those who attended the clinic versus those who did not. Conclusions: While recruitment to the PAC and assessment completion demonstrated feasibility, attendance posed challenges for patients. These findings highlight the need for innovative approaches to screening patients and tailoring rehabilitation services based on physical impairment.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Cancer Rehabilitation: Innovations in Practice & Enhancing Survivorship Care)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
The Emerging Role of CKAP4 in GI Cancer: From Molecular Pathways to Clinical Applications
by
Markos Despotidis, Orestis Lyros, Tatiana S. Driva, Panagiotis Sakarellos, René Thieme, Andreas Mamilos, Stratigoula Sakellariou and Dimitrios Schizas
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(10), 561; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32100561 - 7 Oct 2025
Abstract
Cytoskeleton-associated protein 4 (CKAP4) has emerged as a critical player in gastrointestinal (GI) cancer progression, diagnosis, and therapy. This comprehensive review synthesizes current knowledge on CKAP4′s multifaceted roles across GI malignancies, providing novel insights into its mechanisms of action and clinical potential. Its
[...] Read more.
Cytoskeleton-associated protein 4 (CKAP4) has emerged as a critical player in gastrointestinal (GI) cancer progression, diagnosis, and therapy. This comprehensive review synthesizes current knowledge on CKAP4′s multifaceted roles across GI malignancies, providing novel insights into its mechanisms of action and clinical potential. Its interaction with DKK1 and subsequent activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway underscores its role in promoting tumor growth. This review also highlights novel insights into CKAP4′s mechanisms of action beyond the well-established DKK1-CKAP4 axis, including its interaction with integrin β1 and involvement in angiogenesis through the FMNL2/EGFL6/CKAP4/ERK pathway. CKAP4′s impact on tumor microenvironment and immune evasion is elucidated, offering a new perspective on its contribution to cancer progression. In addition, CKAP4 arises as a promising serum biomarker for early detection and prognosis across multiple GI cancers, emphasizing its potential superiority over traditional markers. The therapeutic potential of targeting CKAP4 is extensively explored, including novel approaches like anti-CKAP4 antibodies and aptamers, and their synergistic effects with existing treatments. By integrating findings from esophageal, gastric, pancreatic, and colorectal cancers, this review provides a unique, comprehensive overview of CKAP4 in GI oncology, underscoring CKAP4′s potential to revolutionize GI cancer diagnosis and treatment and paving the way for future translational research.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Advances in Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease: From Physiological Mechanisms to Clinical Practice, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Baseline Characteristics of Individuals with Metastatic Cancer Enrolled in the Alberta Cancer Exercise Study and 12-Week Findings for Symptom-Related and Physical Fitness Measures
by
Shirin M. Shallwani, S. Nicole Culos-Reed, Kerry S. Courneya, Tanya Williamson, Christopher Sellar, Harold Lau, Anil Abraham Joy, Jacob C. Easaw, Michelle Audoin, Edith Pituskin and Margaret L. McNeely
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(10), 560; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32100560 - 7 Oct 2025
Abstract
Exercise has been found to be safe and beneficial for people with advanced cancers, but more research is needed to understand how best to design and implement exercise programming. The Alberta Cancer Exercise (ACE) study examines the effectiveness and implementation of a 12-week
[...] Read more.
Exercise has been found to be safe and beneficial for people with advanced cancers, but more research is needed to understand how best to design and implement exercise programming. The Alberta Cancer Exercise (ACE) study examines the effectiveness and implementation of a 12-week community-based exercise program in Alberta, Canada, for people diagnosed with cancer. Here, we describe the characteristics of individuals with metastatic cancer enrolled in the ACE program and report 12-week changes in self-reported and objective outcomes. Of 306 participants, 274 (89.5%) completed the 12-week study. Many participants were female (65.4%), with ≥1 comorbidity (71.9%), and on active cancer treatment (74.8%). Common cancer types included breast (33.7%), genitourinary (16.7%), and digestive (15.0%). Frequent sites of metastasis were bone (44.8%), liver (28.8%), and lung (25.8%). The mean exercise attendance rate was 73.6%. One exercise-related adverse event (0.3%) and one non-exercise-related adverse event (0.3%) occurred, both in individuals with brain metastases. Participants demonstrated strong interest and engagement in exercise, with significant improvements in weekly physical activity, symptoms, quality of life, and physical fitness. Greater benefits were found among subgroups of male participants, those not undergoing chemotherapy, and those receiving group personal training or virtual circuit training. A low rate of adverse events is anticipated.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Building Hope for the Next Decade of Psychosocial Oncology: Optimizing the Integration of Supportive Care into Oncology Care)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Oncotype DX Recurrence Score Predicts Survival in Invasive Micropapillary Breast Carcinoma: A National Cancer Database Analysis
by
Ali J. Haider, Mohummad Kazmi, Kyle Chang, Waqar M. Haque, Efstathia Polychronopoulou, Jonathon S. Cummock, Sandra S. Hatch, Andrew M. Farach, Upendra Parvathaneni, E. Brian Butler and Bin S. Teh
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(10), 559; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32100559 - 5 Oct 2025
Abstract
(1) Background: Invasive micropapillary carcinoma (IMPC) is a rare, aggressive breast cancer subtype marked by high lymph node metastasis rates. While Oncotype DX recurrence score (RS) offers prognostic information for patients with hormone-receptor-positive (HR+) breast cancer, its utility in IMPC—a histology with distinct
[...] Read more.
(1) Background: Invasive micropapillary carcinoma (IMPC) is a rare, aggressive breast cancer subtype marked by high lymph node metastasis rates. While Oncotype DX recurrence score (RS) offers prognostic information for patients with hormone-receptor-positive (HR+) breast cancer, its utility in IMPC—a histology with distinct biologic behavior—remains unvalidated. This study evaluates whether Oncotype DX offers prognostic information with respect to overall survival (OS) in non-metastatic, early-stage patients with IMPC of the breast. (2) Methods: The National Cancer Database (2004–2020) was queried to select for women with ER+/HER2−, T1-T2N0-N1 IMPC who underwent Oncotype DX testing and received no neoadjuvant therapy. Patients were stratified by RS: low (≤11), intermediate (12–25), and high (>25). Kaplan–Meier survival curves and log-rank tests compared 5-year OS between groups. Multivariable Cox proportional hazards models assessed RS as an independent predictor, adjusting for age, race, comorbidities, grade, radiation, and insurance status. (3) Results: A total of 1325 women met the selection criteria. The cohort demonstrated significant survival disparities by RS (log-rank p = 0.017). Five-year OS rates were 97.5%, 97.5%, and 93.7% for low, intermediate, and high-risk patients, respectively. Adjusted multivariate analysis confirmed RS as an independent prognosticator: low (HR = 0.31, 95% CI: 0.15–0.75) and intermediate (HR = 0.32, 95% CI: 0.15–0.75) scores correlated with reduced mortality versus high RS. Omission of radiation therapy (HR = 2.68, 95% CI: 1.05–6.86) and higher comorbidity burden (0 comorbidities vs. ≥2: HR = 0.25, 95% CI: 0.10–0.61) were significantly associated with worse survival. (4) Conclusions: Oncotype DX is predictive for OS in IMPC, with high RS (>25) portending poorer outcomes. The survival detriment associated with RT omission aligns with prior studies demonstrating RT benefit in higher-risk cohorts. These findings validate RS as a prognostic tool in IMPC and underscore its potential to refine adjuvant therapy, particularly RT utilization. Future studies should explore RS-driven treatment personalization in IMPC, including comorbidity management and adjuvant radiation to improve outcomes in this distinct patient population.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Breast Cancer)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Incidence of Hypothyroidism and Thyroid Function Monitoring After Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy Completion for Lung Cancer: A Nationwide Analysis of a Japanese Claims Database
by
Hiroaki Ohta, Hinako Tsugane and Takeo Yasu
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(10), 558; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32100558 - 4 Oct 2025
Abstract
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) improve lung cancer prognosis but are associated with immune-related adverse events, most commonly thyroid dysfunction. While prior studies and guidelines have focused on thyroid dysfunction during ICI therapy, data on hypothyroidism and its monitoring after ICI therapy remain limited.
[...] Read more.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) improve lung cancer prognosis but are associated with immune-related adverse events, most commonly thyroid dysfunction. While prior studies and guidelines have focused on thyroid dysfunction during ICI therapy, data on hypothyroidism and its monitoring after ICI therapy remain limited. We aimed to investigate hypothyroidism incidence and implementation of thyroid function monitoring after ICI therapy completion in patients with lung cancer. We conducted a retrospective observational study using the DeSC claims database of approximately 12 million individuals in Japan. Patients with lung cancer who received ICI therapy between April 2014 and August 2023 were included; those with a history of thyroid hormone replacement or insufficient follow-up were excluded. Among 6883 eligible patients, 277 (4.0%) developed hypothyroidism requiring hormone replacement post-ICI therapy completion (median onset, 67.0 d). Risk factors included ICI plus bevacizumab therapy and a history of myasthenia gravis, while steroid use for ≥28 d during ICI therapy lowered the risk. Post-ICI therapy completion thyroid monitoring was performed in 73.7% of patients, with test date distribution showing a median of 126.0 d and mode of 21.0 d. Hypothyroidism was frequently found to develop within 2 months post-ICI therapy completion, highlighting the need for continued thyroid monitoring and prospective studies to establish optimal surveillance strategies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Thoracic Oncology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Perceived Quality-of-Life Importance Among Saudi Gynecologic Cancer Survivors: Latent Class Analysis
by
Wedad M. Almutairi, Fatmah Alsharif, Ahlam Al-Zahrani, Noura Bin Afeef, Alkhnsa Alkeai, Haneen Alfakeeh, Arwa Alzahrani, Nouran Essam Katooa, Fathia Khamis Kassem and Wafa A. Faheem
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(10), 557; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32100557 - 4 Oct 2025
Abstract
Quality-of-life (QoL) needs among gynecologic cancer survivors are multifaceted and culturally mediated, yet limited research has examined how survivors in the Middle East prioritize key domains such as sexual function, emotional well-being, and relational quality. This study aimed to identify subgroups of survivors
[...] Read more.
Quality-of-life (QoL) needs among gynecologic cancer survivors are multifaceted and culturally mediated, yet limited research has examined how survivors in the Middle East prioritize key domains such as sexual function, emotional well-being, and relational quality. This study aimed to identify subgroups of survivors based on the perceived importance of these domains and to explore demographic and clinical predictors of subgroups within the Saudi Arabian context. We conducted a cross-sectional, survey-based study among 129 women with a history of breast or cervical cancer attending a tertiary oncology center in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Participants rated the importance of sexual, emotional, and relational QoL domains using a 4-point Likert scale. Latent class analysis (LCA) was used to segment survivors based on their perceived domain importance. Differences in demographic and clinical characteristics across classes were assessed using chi-square tests. A decision tree classifier was employed. Three latent classes emerged: Class 0 (48.8%) prioritized all domains highly; Class 1 (17.8%) reported low importance across domains; and Class 2 (33.3%) emphasized emotional and relational domains while downplaying sexual function. Class group was significantly associated with age (p = 0.001), education (p = 0.04), nationality (p = 0.03), and number of children (p < 0.001). Decision tree analysis identified number of children, age, and marital status as the strongest predictors of high-importance class group. Gynecologic cancer survivors in Saudi Arabia hold diverse priorities regarding QoL domains, primarily shaped by sociocultural context than clinical variables. Tailored survivorship interventions that reflect survivors’ lived values, particularly in relation to age, family structure, and cultural norms, are critical for person-centered oncology care in the region.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Gynecologic Oncology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Locoregional Treatment in De Novo Bone-Only Metastatic Breast Cancer: Prospective, Multi-Institutional Real-World Data, BOMETIN, Protocol MF14-1a
by
Atilla Soran, Berk Göktepe, Berkay Demirors, Ozgur Aytac, Serdar Ozbas, Lutfi Dogan, Didem Can Trablus, Jamila Al-Azhri, Kazım Senol, Shruti Zaveri, Salyna Meas, Umut Demirci, Hasan Karanlik, Aykut Soyder, Ahmet Dag, Ahmet Bilici, Mutlu Dogan, Mehmet Ali Nahit Sendur, Hande Koksal, Mehmet Ali Gulcelik, Neslihan Cabioglu, Levent Yeniay, Zafer Utkan, Nuri Karadurmus, Gul Daglar, Turgay Simsek, Birol Yildiz, Cihan Uras, Mustafa Tukenmez, Cihangir Ozaslan, Niyazi Karaman, Arda Isik, Efe Sezgin, Vahit Ozmen and Anthony Lucciadd
Show full author list
remove
Hide full author list
Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32(10), 556; https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32100556 - 3 Oct 2025
Abstract
Introduction: The impact of locoregional treatment (LRT) on survival in de novo bone-only metastatic breast cancer (dnBOMBC) is controversial. This study aims to assess the effect of LRT on survival, utilizing international, prospectively acquired data in this cohort of patients. Materials and
[...] Read more.
Introduction: The impact of locoregional treatment (LRT) on survival in de novo bone-only metastatic breast cancer (dnBOMBC) is controversial. This study aims to assess the effect of LRT on survival, utilizing international, prospectively acquired data in this cohort of patients. Materials and Methods: Patients with dnBOMBC were divided into two groups: those receiving systemic therapy only (ST) and those undergoing LRT. Further, patients who received LRT were divided into two subgroups: those who received ST after LRT (LRT+ST group) and those who received ST prior to LRT (ST+LRT group). Factors associated with disease progression, including solitary or multiple bone metastases, were analyzed. Results: There was a total of 744 patients with dnBOMBC treated at each of the participating institutions between 2014 and 2022, with 372 (50%) participants in each arm. Median follow-up was 48 months (32–66, 25–75%). Patients in the LRT group were significantly younger than the ST group [50 (42, 60) vs. 55 (44, 66), p = 0.0001]. There were no significant differences in grade, HER2 status, triple-negative status, receipt of hormonal therapy, or intervention to metastatic sites. During follow-up, 58% (n = 217) of patients in the ST group and 32% (n = 120) of patients in the LRT group died (p < 0.001). Local progression was observed in 20% of the patients in the ST group, whereas 9% progressed in the LRT group (p = 0.0001). Systemic progression occurred more in the ST group; 66% (n = 244) compared to 41% (n = 152) of patients in the LRT group (p < 0.001). The hazard of death was 64% lower in the LRT group than in the ST group (HR: 0.36, 95% CI: 0.29–0.45, p < 0.0001). The burden of metastatic disease differed significantly between the two groups, with a higher rate of solitary bone metastases in the LRT group compared to the ST group (50% vs. 24%, p < 0.001). However, the LRT group had better overall survival (OS) for both solitary (HR: 0.38, 95% Cl: 0.26–0.55) and multiple (HR: 0.38, 95% Cl: 0.29–0.51) bone metastasis patients. Within the LRT group, survival rates were similar whether the breast surgery was performed before or after ST. Multivariate Cox analysis showed that LRT and ER/PR positivity significantly decrease the hazard of death (p < 0.05). Conclusions: Analysis of this large multi-institutional patient cohort provides further evidence that LRT is associated with longer OS and lower locoregional recurrence rates in patients with dnBOMBC. In breast cancer patients with bone-only metastases at presentation, the decision for LRT should be made through a multidisciplinary approach with consideration of surgical therapy at the primary tumor.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Breast Cancer)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Current Oncology Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal Browser-
arrow_forward_ios
Forthcoming issue
arrow_forward_ios Current issue - Volumes not published by MDPI
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Biomedicines, Cancers, Current Oncology, Diagnostics, JCM
Advances in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Its Role in Radiation Therapy
Topic Editors: Indra J. Das, Minsong CaoDeadline: 31 October 2025
Topic in
Cancers, IJMS, Pharmaceuticals, Pharmaceutics, Sci. Pharm., Current Oncology, Molecules
Recent Advances in Anticancer Strategies, 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Hassan Bousbaa, Zhiwei HuDeadline: 31 March 2026
Topic in
Brain Sciences, Cancers, JCM, Neurology International, Diagnostics, Therapeutics, Current Oncology
Innovations in Brain Tumor Surgery: Techniques and Outcomes
Topic Editors: Maria Caffo, Teresa SommaDeadline: 30 June 2026
Topic in
Cancers, Current Oncology, JCM, Medicina, Onco
Cancer Biology and Radiation Therapy: 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Chang Ming Charlie Ma, Ka Yu Tse, Ming-Yii Huang, Mukund SeshadriDeadline: 25 July 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Current Oncology
Evolution of Treatments of Prostate Cancer: From Biology to Current Advanced Technologies
Guest Editor: Fernando MunozDeadline: 31 October 2025
Special Issue in
Current Oncology
Sarcoma Surgeries: Oncological Outcomes and Prognostic Factors
Guest Editor: Mai-Kim GervaisDeadline: 31 October 2025
Special Issue in
Current Oncology
The Evolving Role of Surgery in Multidisciplinary Care for Sarcoma Patients
Guest Editors: Russell G. Witt, Elizabeth Lilley, Heather LyuDeadline: 31 October 2025
Special Issue in
Current Oncology
Exploring Rare Gynecologic Tumors: A Cutting-Edge Perspective on Modern Diagnostic and Therapeutic Strategies
Guest Editors: Brigida Anna Maiorano, Vera LoizziDeadline: 31 October 2025
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Current Oncology
New Insights into Prostate Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment
Collection Editor: Sazan Rasul
Topical Collection in
Current Oncology
New Insights into Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment
Collection Editors: Filippo Pesapane, Matteo Suter
Topical Collection in
Current Oncology
Editorial Board Members’ Collection Series in "Exercise and Cancer Management"
Collection Editors: Linda Denehy, Ravi Mehrotra, Nicole Culos-Reed
Topical Collection in
Current Oncology
Editorial Board Members’ Collection Series: Contemporary Perioperative Concepts in Cancer Surgery
Collection Editors: Vijaya Gottumukkala, Jörg Kleeff









