Journal Description
Cosmetics
Cosmetics
is an international, scientific, peer-reviewed, open access journal on the science and technology of cosmetics published bimonthly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, ESCI (Web of Science), CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q1 (Dermatology) / CiteScore - Q1 (Surgery)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 22.5 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 3.9 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Impact Factor:
3.2 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
3.9 (2024)
Latest Articles
Systems for Mitochondria-Protective Cosmetic Actives: Opportunities in Post-Oncologic Skin Regeneration
Cosmetics 2026, 13(1), 7; https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics13010007 (registering DOI) - 29 Dec 2025
Abstract
Post-oncologic skin is subject to multiple structural and functional impairments following chemotherapy and radiotherapy, including delayed epidermal turnover, compromised barrier integrity, and mitochondrial dysfunction. These changes can lead to persistent dryness, heightened reactivity, impaired regeneration, and reduced patient quality of life. In this
[...] Read more.
Post-oncologic skin is subject to multiple structural and functional impairments following chemotherapy and radiotherapy, including delayed epidermal turnover, compromised barrier integrity, and mitochondrial dysfunction. These changes can lead to persistent dryness, heightened reactivity, impaired regeneration, and reduced patient quality of life. In this context, topical dermocosmetic strategies are essential not only for improving comfort and hydration, but also for supporting key cellular pathways involved in mitochondrial protection and oxidative stress reduction. Despite the promise of natural antioxidant actives, their cutaneous efficacy is often limited by poor stability, low bioavailability, and insufficient penetration of the stratum corneum. The use of nanocarriers promotes deeper skin penetration, protects oxidation-prone antioxidant compounds, and enables a controlled and prolonged release profile. This review summarizes the current evidence (2020–2025) on skin delivery systems designed to enhance the efficacy, stability, and skin penetration of antioxidants. Knowledge gaps and future directions are outlined, highlighting how rationally engineered delivery systems for mitochondria-targeted actives could contribute to safer, more effective strategies for post-oncologic skin regeneration.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Fine Chemicals from Natural Sources with Potential Application in the Cosmetic/Pharmaceutical Industry—Volume 2)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Concentration-Dependent Rheological and Sensory Effects of Walnut Leaf Extract in Cosmetic Emulsion Creams
by
Miljan Adamovic, Ana Adamovic, Ana Barjaktarevic, Marina Kostic, Olivera Kostic, Danijela Pecarski, Marijana Andjic, Jovana Dimitrijevic, Jelena Zivkovic and Marina Tomovic
Cosmetics 2026, 13(1), 6; https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics13010006 - 26 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Understanding how plant-derived extracts influence the rheological and sensory behavior of emulsions is crucial for developing stable and consumer-appealing formulations. Although walnut leaf extract (Juglans regia L.) is recognized for its bioactive properties, its structural impact on cosmetic emulsions has not
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Understanding how plant-derived extracts influence the rheological and sensory behavior of emulsions is crucial for developing stable and consumer-appealing formulations. Although walnut leaf extract (Juglans regia L.) is recognized for its bioactive properties, its structural impact on cosmetic emulsions has not been systematically characterized. This study aimed to investigate the effect of increasing walnut leaf extract concentration on the rheological profile, mechanical integrity during application, and sensory performance of oil-in-water creams. Methods: Four emulsion formulations (F1–F4) containing 0%, 1%, 3%, and 5% walnut leaf extract were prepared using Olivem 1000 and Olivem 300 as emulsifiers. Rheological measurements included amplitude sweep, flow curve, frequency sweep, and thixotropy tests to assess viscoelasticity, flow behavior, and recovery. A sensory evaluation was conducted by trained panelists to correlate rheological parameters with perceived product attributes. Results: All formulations exhibited pseudoplastic, shear-thinning behavior in well-structured cosmetic emulsions during application. The addition of walnut extract significantly modified rheological responses: at 1% concentration, an increase in storage modulus (G′) and shear-thinning ratio (η0/η∞) indicated structural reinforcement and improved spreadability, whereas higher concentrations (3–5%) led to structural softening and faster thixotropic recovery. The frequency sweep revealed a concentration-dependent shift from elastic- to viscous-dominant behavior. Sensory analysis confirmed these trends, with higher extract levels reducing stickiness and greasiness while enhancing absorption. Conclusions: Walnut leaf extract shows a concentration-dependent influence on the rheological behavior of the emulsions, strengthening the network structure at low levels while promoting softening and faster structural recovery at higher concentrations. The strong correlation between rheological and sensory parameters underscores the potential of walnut extract as a multifunctional ingredient for designing well-structured, non-greasy, and consumer-preferred cosmetic creams.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Cosmetic Formulations)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Artificial Intelligence in Cosmetic Dermatology with Regard to Laser Treatments: A Comparative Analysis of AI and Dermatologists’ Decision-Making
by
Alexandra Junge, Ali Mokhtari, Simone Cazzaniga, Ashraf Badawi, Flurin Brand, Simone Böll, Laurence Feldmeyer, Cindy Franklin, Hans-Joachim Laubach, Mathias Lehmann, Zora Martignoni, Sammy Murday, Dominik Obrist, Antonia Reimer-Taschenbrecker, Basil Signer, Roberta Vasconcelos-Berg, Charlotte Vogel, Nikhil Yawalkar, Kristine Heidemeyer and Seyed Morteza Seyed Jafari
Cosmetics 2026, 13(1), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics13010005 - 26 Dec 2025
Abstract
Introduction: Artificial intelligence (AI) has developed into an increasingly important tool in dermatology. While new technologies integrated within laser devices are emerging, there is a lack of data on the applicability of publicly available AI models. Methods: The prospective study used an online
[...] Read more.
Introduction: Artificial intelligence (AI) has developed into an increasingly important tool in dermatology. While new technologies integrated within laser devices are emerging, there is a lack of data on the applicability of publicly available AI models. Methods: The prospective study used an online questionnaire where participants evaluated diagnosis and treatment for 25 dermatological cases shown as pictures. The same questions were given to AI models: ChatGPT-4o, Claude Sonnet 4, Gemini 2.5 Flash, and Grok-3. Results: Dermatologists outperformed AI in diagnostic accuracy (suspected primary diagnosis-SD 75.6%) in pooled dermatologists vs. pooled AI (SD 57.0%), with laser specialists achieving the highest accuracy (SD 82.0%) and residents the lowest (SD 66.0%). There was a high heterogeneity across AI models. Gemini approached dermatologist performance (SD 72.0%), while Claude showed a low accuracy (SD 40.0%). While AI models reached near 100% accuracy in some classic/common diagnoses (e.g., acne, rosacea, spider angioma, infantile hemangioma), their accuracy dropped to near 0% on rare or context-dependent cases (e.g., blue rubber bleb nevus syndrome, angiosarcoma, hirsutism, cutaneous siderosis). Inter-rater agreement was high among laser experts in terms of diagnostic accuracy and treatment choice. Agreement between residents and AI models was highest for diagnostic accuracy and treatment choice, while it was lowest between experts and AI models. Conclusions: Before AI-based tools can be integrated into daily practice, particularly regarding diagnosis and appropriate laser treatment recommendations, specific supervised medical training of the AI model is necessary, as open-source platforms currently lack the ability to contextualize presented data.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Cosmetics in 2025)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Systemic Lipid Dysregulation in Low-Hydration Skin: A Multi-Dimensional Analysis
by
Yumei Fan, Zheng Wang and Peixue Ling
Cosmetics 2026, 13(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics13010004 - 25 Dec 2025
Abstract
Skin hydration is a key indicator of skin health and stratum corneum (SC) integrity, yet its relationship with multi-dimensional physiological parameters remains incompletely understood. This study aimed to investigate the association between facial skin hydration and key physiological parameters and explored the lipidomic
[...] Read more.
Skin hydration is a key indicator of skin health and stratum corneum (SC) integrity, yet its relationship with multi-dimensional physiological parameters remains incompletely understood. This study aimed to investigate the association between facial skin hydration and key physiological parameters and explored the lipidomic differences between individuals with high and low hydration levels. We enrolled 60 healthy Chinese women (aged 30–55), divided into a low-hydration (LH, n = 11) group and a high-hydration (HH, n = 19) group based on Corneometer measurements. An integrated methodology was employed, including confocal Raman spectroscopy, multiphoton laser tomography, biophysical instruments, and untargeted lipidomics. Our results demonstrated a positive correlation between skin hydration and SC thickness, ceramides, and lactate levels. However, no significant correlation was identified in relation to wrinkles, color, or elasticity. The lipidomic analysis revealed eighty-three significantly upregulated lipids (VIP > 1.0, p < 0.05) in LH skin, among which ten lipids, including nine ceramides, exhibited strong negative correlations with hydration (|r| > 0.8, p < 0.05). These lipids were predominantly associated with sphingolipid and triacylglycerol metabolic pathways. Together, our findings suggest that low-hydration skin is characterized by systemic lipidomic dysregulation, rather than a deficiency of individual lipids. These findings represent novel insights into the mechanisms underlying skin hydration and identify potential therapeutic targets for addressing skin dryness and aging.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Lipids in Cosmetics)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Protective and Restorative Effects of a Bio-Based Crosslinking Complex on Chemically Damaged Hair
by
Flavio B. Camargo Junior, Alessandra M. Goshiyama, Gessica F. D. Oliveira, Marcos R. Rossan, Cleverson R. Princival, Edson Katekawa, Wagner Magalhães, Rafaela de Almeida Zito, Letícia Kakuda and Patrícia Maria Berardo Gonçalves Maia Campos
Cosmetics 2026, 13(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics13010003 - 24 Dec 2025
Abstract
This study addresses the growing consumer demand for effective and sustainable hair care solutions by evaluating a novel bioactive crosslink repair complex designed to restore chemically damaged hair. The complex comprises itaconic acid, arginine, D-panthenol, and polysaccharides from linseed and chia, which work
[...] Read more.
This study addresses the growing consumer demand for effective and sustainable hair care solutions by evaluating a novel bioactive crosslink repair complex designed to restore chemically damaged hair. The complex comprises itaconic acid, arginine, D-panthenol, and polysaccharides from linseed and chia, which work synergistically to promote fiber crosslinking, protein restructuring, and cuticle barrier restoration. The complex was incorporated into two formulations: a bleaching mixture as a protective agent and a leave-in conditioner as a repair treatment for chemically damaged hair. The protective efficacy was assessed through tensile strength measurements, differential scanning calorimetry, combability tests, shine evaluation, and scanning electron microscopy. The repair potential was evaluated using differential scanning calorimetry and tensile strength analysis. Results demonstrated that incorporating the complex into the bleaching mixture significantly enhanced break stress, denaturation enthalpy, shine, and combability, while maintaining improved cuticle alignment. The hair repair evaluation showed that post-treatment application of the complex successfully restored hair tensile strength and denaturation. These findings confirm the dual functionality of Bioactive Crosslink Repair Complex as both a protective and reparative agent, highlighting synergistic mechanisms in preventing and reversing chemical damage to hair fibers. This bioactive approach offers a promising alternative for hair care formulations targeting chemically treated hair.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Cosmetic Formulations)
►▼
Show Figures
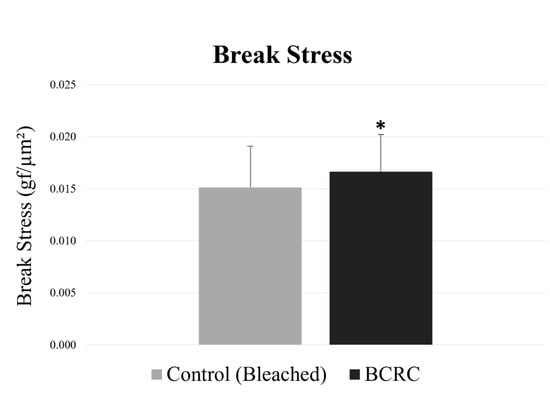
Figure 1
Open AccessEditorial
Skin Anti-Aging Strategies
by
Remo Campiche
Cosmetics 2026, 13(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics13010002 - 22 Dec 2025
Abstract
The pursuit of youthful, healthy skin remains one of the most compelling drivers in the cosmetics industry [...]
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Skin Anti-Aging Strategies)
Open AccessArticle
Prospective Multicentre Real-World Study of a Bioregenerative Combination Therapy with Polynucleotide High-Purification Technology (PN HPT™) and Hyaluronic Acid for Moderate-to-Severe Atrophic Facial Acne Scars
by
Ting Song Lim, Chong Ian, Nurul Ain Abdullah, Tristan Tan, Kuok Tjun Ong, Leda Moro, Maria Tomat, Carmen De Luca, Simona Piscopo, Carolina Prussia and Carlotta Bortoletti
Cosmetics 2026, 13(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics13010001 - 22 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background: Facial atrophic acne scars have a significant impact on patients’ psychosocial well-being and remain a therapeutic challenge. Existing treatments options are frequently limited by modest efficacy and adverse effects. The combination of Polynucleotide High-Purification Technology (PN HPT™) and hyaluronic acid (HA) represents
[...] Read more.
Background: Facial atrophic acne scars have a significant impact on patients’ psychosocial well-being and remain a therapeutic challenge. Existing treatments options are frequently limited by modest efficacy and adverse effects. The combination of Polynucleotide High-Purification Technology (PN HPT™) and hyaluronic acid (HA) represents a novel bioregenerative strategy aimed at improving dermal remodelling and overall skin quality. Methods: This six-month, prospective, real-world study evaluated the efficacy and safety of Newest® (Mastelli S.r.l., Sanremo, Italy), a sterile intradermal gel containing highly purified polynucleotides (10 mg/mL) and HA (10 mg/mL). Eligible participants, aged 20–60 years with moderate-to-severe atrophic facial post-acne scars, underwent four treatment sessions in two-week intervals. Efficacy was assessed using the Acne Scar Assessment Scale (ASAS) and Global Aesthetic Improvement Scale (GAIS) at three and six months, while safety was monitored throughout the study. Results: A total of 62 patients (32 Caucasian, 30 Asian; 19 males, 43 females; mean age: 36.6 years) completed the study. At three and six months, 46.8% showed at least a one-grade reduction in ASAS score with respect to the baseline. Patient-reported GAIS indicated that 54.8% perceived an improvement in scar appearance, aligning with investigator assessments. Only one mild, transient adverse event (wheal formation) occurred, which resolved spontaneously without intervention. Conclusions: In this real-world study, treatment with Polynucleotide High-Purification Technology (10 mg/mL) combined with HA (10 mg/mL) was associated with observable improvementin atrophic facial acne scars, with an excellent safety and tolerability profile. These findings support the potential of polynucleotide-based therapies for use as well-tolerated options for managing moderate-to-severe atrophic acne scarring, while the need for further controlled studies to confirm efficacy is also acknowledged.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Cosmetic Dermatology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
High-Limonene Orange Peel Essential Oil as a Natural Antibacterial Agent in Hand Sanitizer Gels
by
Marcos A. Coronado, José R. Ayala, Beatriz E. Jaramillo-Colorado, Daniela G. Montes, Ernesto Beltrán-Partida, Benjamín A. Rojano, Andrés Felipe Alzate-Arbeláez and Ana M. Vázquez
Cosmetics 2025, 12(6), 288; https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12060288 - 18 Dec 2025
Abstract
Orange peel waste has potential to be valorized from agro-industrial and food sectors to formulate products for personal hygiene and public health. This study presents the formulation of alcohol-based antibacterial gels incorporating essential oils extracted from Citrus sinensis orange peel waste and its
[...] Read more.
Orange peel waste has potential to be valorized from agro-industrial and food sectors to formulate products for personal hygiene and public health. This study presents the formulation of alcohol-based antibacterial gels incorporating essential oils extracted from Citrus sinensis orange peel waste and its sensory evaluation among 770 participants in a holistic approach. The orange essential oil, obtained via hydrodistillation, demonstrated a high limonene content of 96.5% by GC-MS. Antibacterial activity assessed by agar diffusion assays showed orange essential oil efficacy against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus, with inhibition zones of 25.9 mm and 23.62 mm, respectively. Two gel prototypes, GSA and GSB, were developed and sensorily evaluated. GSA was preferred for its superior appearance, spreadability, absorption, and smell, with 99% acceptability. Appearance and spread sensory parameters were the differentiators between both formulations according to user preferences. Thus, 93% of respondents are willing to use either GSA or GSB as a daily hygiene product over commercial ones. Although the gels exhibited reduced antibacterial activity relative to essential oil, with inhibition zones measuring 8.3 mm for E. coli and 9.0 mm for S. aureus, they retained satisfactory user acceptability. These findings support the use of citrus biowaste-derived essential oils in sustainable personal hygiene products.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Fine Chemicals from Natural Sources with Potential Application in the Cosmetic/Pharmaceutical Industry—Volume 2)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Advancements in Bioactive Compounds and Therapeutic Agents for Alopecia: Trends and Future Perspectives
by
Eunmiri Roh
Cosmetics 2025, 12(6), 287; https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12060287 - 16 Dec 2025
Abstract
Alopecia is a multifactorial disorder in which immune, endocrine, metabolic, and microbial systems converge within the follicular microenvironment. In alopecia areata (AA), loss of immune privilege, together with interferon-γ- and interleukin-15-driven activation of the JAK/STAT cascade, promotes cytotoxic infiltration, whereas selective inhibitors, including
[...] Read more.
Alopecia is a multifactorial disorder in which immune, endocrine, metabolic, and microbial systems converge within the follicular microenvironment. In alopecia areata (AA), loss of immune privilege, together with interferon-γ- and interleukin-15-driven activation of the JAK/STAT cascade, promotes cytotoxic infiltration, whereas selective inhibitors, including baricitinib, ritlecitinib, and durvalumab, restore immune balance and permit anagen reentry. In androgenetic alopecia (AGA), excess dihydrotestosterone and androgen receptor signaling increase DKK1 and prostaglandin D2, suppress Wnt and β-catenin activity, and drive follicular miniaturization. Combination approaches utilizing low-dose oral minoxidil, platelet-rich plasma, exosome formulations, and low-level light therapy enhance vascularization, improve mitochondrial function, and reactivate metabolism, collectively supporting sustained regrowth. Elucidation of intracellular axes such as JAK/STAT, Wnt/BMP, AMPK/mTOR, and mitochondrial redox regulation provides a mechanistic basis for rational, multimodal intervention. Advances in stem cell organoids, biomaterial scaffolds, and exosome-based therapeutics extend treatment from suppression toward structural follicle reconstruction. Recognition of microbiome and mitochondria crosstalk underscores the need to maintain microbial homeostasis and redox stability for durable regeneration. This review synthesizes molecular and preclinical advances in AA and AGA, outlining intersecting signaling networks and regenerative interfaces that define a framework for precision and sustained follicular regeneration.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Cosmetics in 2025)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Hemp Seed Extract-Enriched Oxygenating Facial Mask: Effects on Skin Hydration, Sebum Control, and Erythema Reduction
by
Oraphan Anurukvorakun and Suekanya Jarupinthusophon
Cosmetics 2025, 12(6), 286; https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12060286 - 15 Dec 2025
Abstract
This study introduces a novel oxygenating facial mask enriched with hemp seed extract, which uniquely combines advanced bubble-generating technology with botanically derived antioxidants for enhanced skin care. The innovative mask forms microbubbles that simulate targeted oxygen delivery, accelerating cell renewal and improving active
[...] Read more.
This study introduces a novel oxygenating facial mask enriched with hemp seed extract, which uniquely combines advanced bubble-generating technology with botanically derived antioxidants for enhanced skin care. The innovative mask forms microbubbles that simulate targeted oxygen delivery, accelerating cell renewal and improving active ingredient absorption. In a randomized, controlled trial, forty participants used either the hemp seed extract mask (F1) or a placebo (F2) over eight weeks. Both formulations demonstrated excellent physical stability for 60 days, maintaining consistent pH, color, fragrance, viscosity, and foaming properties. Notably, F1 demonstrated superior foam persistence and product stability. Clinically, the hemp mask significantly increased skin hydration (up to 65.7%, p < 0.05), reduced sebum levels (32.9%), and lowered erythema (up to 46.9 AU or 12.9%, p < 0.01), without altering skin color or causing adverse effects. Consumer satisfaction with F1 exceeded F2 by 10.7%. The novelty of this work lies in the integration of oxygenating bubble technology and hemp seed extract—demonstrating synergistic effects on skin barrier function, hydration, sebum control, and erythema reduction. These findings highlight the mask’s potential as a next-generation cosmeceutical with meaningful clinical and commercial value.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Cosmetic Technology)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Photoprotective Effects of Oral Coriander (Coriandrum sativum L.) Seed Oil Supplementation Against UV-Induced Skin Damage: Evidence from Two Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trials
by
Vincenzo Nobile, Stéphanie Dudonné, Catherine Kern, Gloria Roveda, Silvana Giardina and Christine Garcia
Cosmetics 2025, 12(6), 285; https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12060285 - 12 Dec 2025
Abstract
Skin is constantly exposed to UV radiation. While topical sunscreens are the main preventative measure, oral photoprotective agents are emerging as promising systemic adjuncts, offering uniform, continuous protection. This study presents the results of two clinical trials designed to evaluate the efficacy of
[...] Read more.
Skin is constantly exposed to UV radiation. While topical sunscreens are the main preventative measure, oral photoprotective agents are emerging as promising systemic adjuncts, offering uniform, continuous protection. This study presents the results of two clinical trials designed to evaluate the efficacy of supplementation with a standardized coriander (Coriandrum sativum L.) seed oil (CSO) in mitigating UV-induced skin damage, in comparison with a placebo. The first trial investigated the effects of CSO supplementation on women with reactive skin, assessing UVA+B-induced skin erythema and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) release. The second trial included women of all skin types and, in addition to the outcomes mentioned above, examined UVA-induced lipoperoxidation. Measurements were taken before and after 56 days of supplementation. CSO supplementation led to a significant reduction in UV-induced skin erythema and associated TNF-α levels in both cohorts, with decreases of 11.8% and 24.1% in the reactive skin group and 18.1% and 18.7% in the cohort with all skin types, respectively. In women of all skin types, UV-induced skin lipoperoxidation was reduced by 31.9% at 4 h and by 69.9% at 24 h post-exposure. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study reporting the photoprotective efficacy of CSO. This finding is attributed to CSO’s high petroselinic acid content and its known anti-inflammatory properties.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sunscreen Advances and Photoprotection Strategies in Cosmetics)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
A Multifaceted View on Ageing of the Hair and Scalp
by
Yi Shan Lim, Carine Nizard, Karl Pays, Cecilia Brun and Robin Kurfurst
Cosmetics 2025, 12(6), 284; https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12060284 - 12 Dec 2025
Abstract
Like with skin, both men and women—regardless of ethnicity—gradually lose satisfaction with changes in hair brought about by ageing. Especially when such transition is apparent by others, and that the hair condition has a significant role in an individual’s overall physical appearance and
[...] Read more.
Like with skin, both men and women—regardless of ethnicity—gradually lose satisfaction with changes in hair brought about by ageing. Especially when such transition is apparent by others, and that the hair condition has a significant role in an individual’s overall physical appearance and self-perception. Beyond the familiar age-related signs such as hair greying, hair loss, and hair fragility, this review includes current knowledge of biological processes underlying hair pigmentation and hair growth, highlights variations in gender and ethnicity, as well as delineates hair fibre diameter, ellipticity, and elasticity properties that collectively contribute to the characteristics of aged hair. Additionally, in view of the rising importance of enhancing scalp skin health to promote healthy hair growth, the latter part of the review focuses on age-associated alterations to the scalp skin and its microbiome. Consideration of the morphological changes in the hair fibre, biological processes occurring within the hair follicle and its enveloping scalp environment provide a unique, holistic overview of hair and scalp changes during ageing. Finally, after acknowledging the impact caused by chronological ageing and environmental stresses, it is important to recognise that healthy tresses are largely influenced by scalp skin care, and this stimulates the advancement of appropriate cosmetic solutions that help delay or improve the appearance of aged hair.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Cosmetic Dermatology)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Benefits of a Pequi Oil Formulation for Skin: A Clinical Study Using Instrumental Measurements and Sensorial Perception
by
Letícia Kakuda, Wanderley Pereira Oliveira and Patricia Maria Berardo Gonçalves Maia Campos
Cosmetics 2025, 12(6), 283; https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12060283 - 11 Dec 2025
Abstract
Pequi (Caryocar brasiliense) oil is a lipid-rich natural ingredient with potential cosmetic applications, but its time-dependent clinical effects on skin remain underexplored. This study aimed to characterize pequi oil using GC-MS, develop a minimalist serum formulation containing the oil, and evaluate
[...] Read more.
Pequi (Caryocar brasiliense) oil is a lipid-rich natural ingredient with potential cosmetic applications, but its time-dependent clinical effects on skin remain underexplored. This study aimed to characterize pequi oil using GC-MS, develop a minimalist serum formulation containing the oil, and evaluate its immediate, short-term, and long-term clinical efficacy, as well as perceived efficacy. A serum with 3% pequi oil (SPO) and a vehicle control (SV) were developed and tested in twenty healthy female participants (22–30 years). Stratum corneum water content, transepidermal water loss (TEWL), and sebum content were measured on the malar region at baseline (t0) and after 2 h (t2h), 7 days (t7d), and 28 days (t28d) of application. Porphyrin count and sebaceous gland activity were assessed at t7d and t28d and skin microrelief at t28d. GC-MS revealed oleic acid (55.89%) and palmitic acid (34.90%) as the oil’s main constituents. SPO reduced TEWL and increased skin hydration at t2h and t28d compared to baseline values (p < 0.05). At t28d, SPO significantly reduced oily spots and porphyrin scores and improved skin microrelief. Long-term perceived efficacy indicated better hydration, oil control, and skin feel compared with SV. These findings suggest that pequi oil reduced sebum content and sebaceous gland activity, thereby enhancing skin barrier function, hydration, microrelief, and hydrolipidic balance, supporting its potential as an effective cosmetic ingredient.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Cosmetic Technology)
►▼
Show Figures
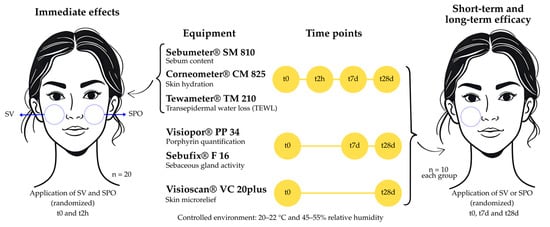
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
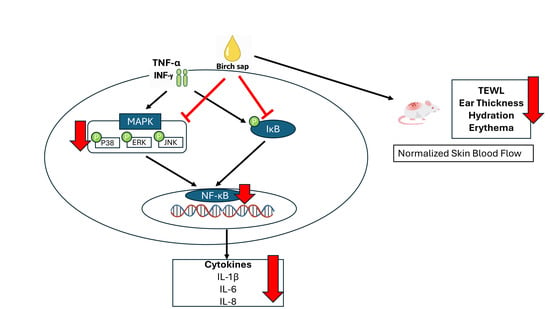
Birch Sap Attenuates Inflammatory Cytokines and Improves Skin Parameters in Cellular and Animal Models of Skin Irritation
by
Chao-Hsien Sung, Chien-Fen Huang, Yu-Jou Hsu, Chi-Ming Pu, Chia-Chi Kung, Thomas W. Chu and Chi-Feng Hung
Cosmetics 2025, 12(6), 282; https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12060282 - 11 Dec 2025
Abstract
Natural ingredients with soothing and skin-protecting effects are becoming increasingly popular in cosmetic science. Great interest has been directed to birch sap, a nutrient-rich fluid from Betula species. This study aimed to investigate whether birch sap can modulate inflammatory responses and maintain skin
[...] Read more.
Natural ingredients with soothing and skin-protecting effects are becoming increasingly popular in cosmetic science. Great interest has been directed to birch sap, a nutrient-rich fluid from Betula species. This study aimed to investigate whether birch sap can modulate inflammatory responses and maintain skin barrier functions in both cell and animal models. The polysaccharide composition of birch sap was characterized. TNF-α/IFN-γ-stimulated HaCaT keratinocytes were used to assess the effects of birch sap on inflammatory cytokine expression and activation of MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways. An in vivo model of chemically induced skin irritation was further used to examine the effects of oral birch sap administration on skin hydration, transepidermal water loss, histological features, and cutaneous blood flow. Birch sap significantly reduced IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-8 expression and attenuated MAPK and NF-κB phosphorylation. In vivo, birch sap improved hydration, reduced transepidermal water loss, epidermal thickening and erythema, and decreased elevated skin blood flow associated with inflammation. These results demonstrate that birch sap provides modulatory effects on inflammation and barrier-supportive effects in both cellular and animal models, suggesting its potential as a naturally derived cosmetic ingredient for promoting skin comfort and maintaining epidermal barrier integrity.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Cosmetic Dermatology)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Micronized Prinsepia utilis Royle Seed Powder as a Natural, Antioxidant-Enriched Pickering Stabilizer for Green Cosmetic Emulsions
by
Chuanjun Ye, Kangfu Zhou, Zhicheng Ye, Yazhuo Shang and Feifei Wang
Cosmetics 2025, 12(6), 281; https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12060281 - 11 Dec 2025
Abstract
The valorization of agricultural byproducts into functional cosmetic ingredients is a promising strategy for sustainable formulation development. In this work, raw Prinsepia utilis Royle seed residue powder (RPURSRP) which was discarded after oil pressing was upcycled and micronized Prinsepia utilis Royle seed powder
[...] Read more.
The valorization of agricultural byproducts into functional cosmetic ingredients is a promising strategy for sustainable formulation development. In this work, raw Prinsepia utilis Royle seed residue powder (RPURSRP) which was discarded after oil pressing was upcycled and micronized Prinsepia utilis Royle seed powder (MPURSRP) was obtained by micronization as an eco-friendly Pickering stabilizer. The physicochemical properties of MPURSRP have been studied comprehensively. The results have shown that the MPURSRP (20.28 ± 0.00 μm) exhibited a spherical shape, which is significantly smaller than the RPURSRP (61.49 ± 2.28 μm). The MPURSRP particles tend to reside at the interface between oil and water, allowing them to function as emulsifiers that promote the formation of Pickering emulsions. The emulsifying properties of MPURSRP were investigated systematically. The results revealed that the MPURSRP displayed a better emulsifying performance for non-polar oils. Meanwhile, the existence of polyphenols—an endogenous substance of the Prinsepia utilis Royle seed, endows the prepared Pickering emulsion with good antioxidant activity. As the MPURSRP concentration increased from 0% to 3.0 wt%, more MPURSRP adsorbed at the oil–water interface, and the DPPH radical scavenging rate of the emulsion increased from 9.99 ± 0.63% to 91.71 ± 4.22% (p < 0.001). By upcycling agricultural waste into amphiphilic particles with interfacial properties, we establish a green strategy for stabilizing Pickering emulsions with endogenous antioxidant functionality, offering meaningful guidance toward sustainable colloid systems. This work aligns with the growing demand for natural, bioactive ingredients in green cosmetic formulations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Cosmetic Formulations)
►▼
Show Figures
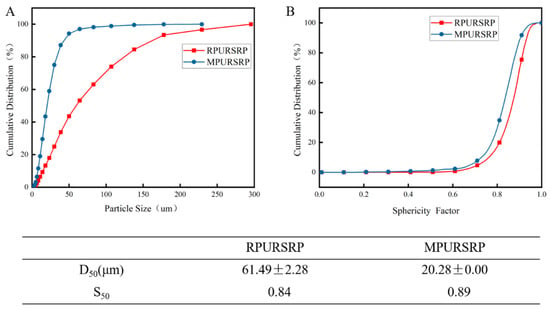
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Non-Invasive Imaging to Detect the Effects of Topical N-Butanoyl Glutathione (GSH-C4) and Hyaluronic Acid in Inflammatory Eczematous Dermatitis
by
Maria Elisabetta Greco, Antonio Di Guardo, Annunziata Dattola, Silvana Ciardo, Elena Campione, Domenico Marrapodi, Camilla Chello, Carmen Cantisani, Simone Michelini, Terenzio Cosio, Simone Amato, Enrico Garaci, Raimondo Crimi, Steven Paul Nisticò and Giovanni Pellacani
Cosmetics 2025, 12(6), 280; https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12060280 - 11 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background: Eczematous dermatitis refers to a group of inflammatory skin disorders—including seborrheic, atopic, and contact dermatitis—characterized by epidermal barrier dysfunction and chronic inflammation. Disrupting the itch–scratch cycle and reversing microscopic skin changes are key to improving patient outcomes and quality of life. Aims:
[...] Read more.
Background: Eczematous dermatitis refers to a group of inflammatory skin disorders—including seborrheic, atopic, and contact dermatitis—characterized by epidermal barrier dysfunction and chronic inflammation. Disrupting the itch–scratch cycle and reversing microscopic skin changes are key to improving patient outcomes and quality of life. Aims: This study aimed to assess the clinical and microscopic effects of a topical medical device containing N-butanoyl glutathione (GSH-C4) and hyaluronic acid in patients with inflammatory eczematous dermatitis, combining clinical scores with in vivo confocal and OCT imaging. Methods: A prospective clinical trial enrolled 30 patients with active eczematous lesions. Participants applied a GSH-C4/hyaluronic acid-based product (GSEBA®) for 28 days. Clinical improvement was evaluated at baseline, day 14, and day 28 using the Investigator’s Global Assessment (IGA), a Visual Analog Scale (VAS) for itching, and a self-reported index of disease impact on quality of life (IDL). Microscopic changes were assessed using optical coherence tomography (OCT) and reflectance confocal microscopy (RCM). Results: After 28 days, the mean IGA score improved from 2.48 to 0.18 (p < 0.001), VAS itching score decreased from 4.52 to 0.32 (p < 0.001), and IDL dropped from 4.86 to 0.79 (p < 0.001). RCM analysis showed significant reductions in key inflammatory features such as spongiosis, vesiculation, and inflammatory infiltrate. OCT revealed a significant decrease in vascularization at 150 μm depth, with no change in collagen density. Conclusions: The GSH-C4/hyaluronic acid-based mousse (GSEBA®) demonstrated strong clinical efficacy and excellent tolerability in managing eczematous dermatitis. It effectively reduced both symptoms and microscopic markers of inflammation without compromising dermal structure.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Cosmetics in 2025)
►▼
Show Figures
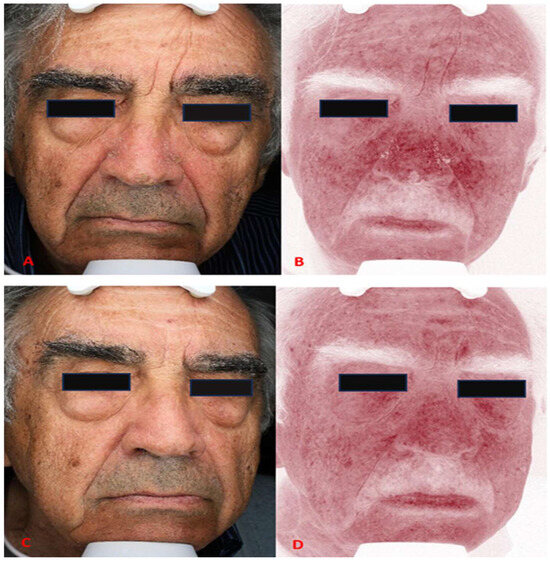
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Ex Vivo Human Skin as a Platform to Study Cosmetic Modulation of Specialized Pro-Resolving Mediators
by
Michele Massironi, Lorenzo Zanella, Francesca Benato, Camila Paz Quezada Meza, Chiara Rompietti, Sandro Rosa, Dominik Stuhlmann, Martina Herrmann and Marco Massironi
Cosmetics 2025, 12(6), 279; https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12060279 - 10 Dec 2025
Abstract
Chronic low-grade inflammation and oxidative stress induced by the exposome represent key drivers of skin aging and related imperfections. The development of experimental models suitable for studying these metabolic processes is therefore of primary importance for the cosmetic industry. In recent years, the
[...] Read more.
Chronic low-grade inflammation and oxidative stress induced by the exposome represent key drivers of skin aging and related imperfections. The development of experimental models suitable for studying these metabolic processes is therefore of primary importance for the cosmetic industry. In recent years, the role of specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPMs) in the resolution of inflammation has been highlighted; however, in vitro skin models to investigate them are still lacking. In this work, we developed an ex vivo human skin culture model that allows the quantification of maresin 1 (MaR1) production by measuring its concentration in the conditioned culture medium using an ELISA-based assay. The presence and survival of MaR1-synthesizing immune cells, namely Langerhans cells and leukocytes, were quantified during the first days of culture. The model’s ability to modulate MaR1 production was assessed in response to treatment with its precursor, docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), and with a DHA-rich cosmetic ingredient named Isochrysis Galbana Extract. Results demonstrated that the model produces MaR1 even in the absence of stimulation and responds to treatments with a further increase in MaR1 production. Furthermore, the tissue-to-medium ratio required to obtain MaR1 concentrations suitable for effective ELISA quantification was optimized. This model establishes a reproducible and scalable experimental platform for quantifying SPMs and evaluating DHA-based formulations, supporting both cosmetic research and mechanistic investigations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Cosmetic Dermatology)
►▼
Show Figures
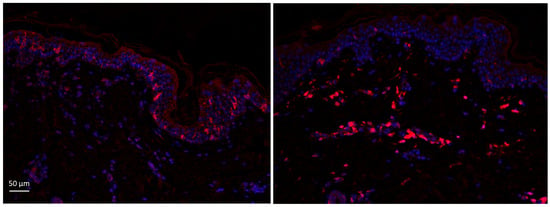
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Efficacy of a Mesotherapy-Inspired Cosmetic Serum vs. Meso-Injections: Proteomic Insights and Clinical Results
by
Nadège Durand, Sayantani Goswami, Roxane Henry, Aaron Cohen, Jin Namkoong, Joanna Wu, Karima Bourougaa and Lysianne Sanchez-Manoilov
Cosmetics 2025, 12(6), 278; https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12060278 - 10 Dec 2025
Abstract
Aesthetic mesotherapy—the subcutaneous injection of key ingredients for cellular function—has gained popularity as a skin rejuvenation treatment. We developed a cosmetic serum, incorporating 11 ingredients frequently used in meso-injections that are partially encapsulated in multilamellar vesicles. We evaluated the ingredients, and their formulation
[...] Read more.
Aesthetic mesotherapy—the subcutaneous injection of key ingredients for cellular function—has gained popularity as a skin rejuvenation treatment. We developed a cosmetic serum, incorporating 11 ingredients frequently used in meso-injections that are partially encapsulated in multilamellar vesicles. We evaluated the ingredients, and their formulation into a topical serum and in mesotherapy injections, for their efficacy at modulating skin rejuvenation in vitro, ex vivo and in vivo. Proteomic profiling of skin explants subjected to a meso-injection identified 47 differentially regulated proteins, whereas topical ingredient applications modulated 149 proteins, predominantly by upregulating them. These proteins mapped to gene ontology pathways relating to ER-Golgi transport, protein trafficking, energy metabolism, integrin signalling, extracellular matrix organisation, and regulation of cell proliferation. The impact of some ingredient classes appeared pathway-specific, while broader responses possibly reflected synergistic interactions. Consistently, topical ingredient application increased ATP levels in reconstructed skin, suggesting enhanced metabolic activity. Clinically, twice-daily serum applications over 63 days yielded improvements in skin smoothness, complexion radiance and complexion homogeneity comparable to those observed after three meso-injections. However, results appeared to vary with age, and the combination of serum application with meso-injection may offer benefits, particularly for skin firmness, acting in combination with mesotherapy to improve skin quality.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Cosmetic Dermatology)
►▼
Show Figures
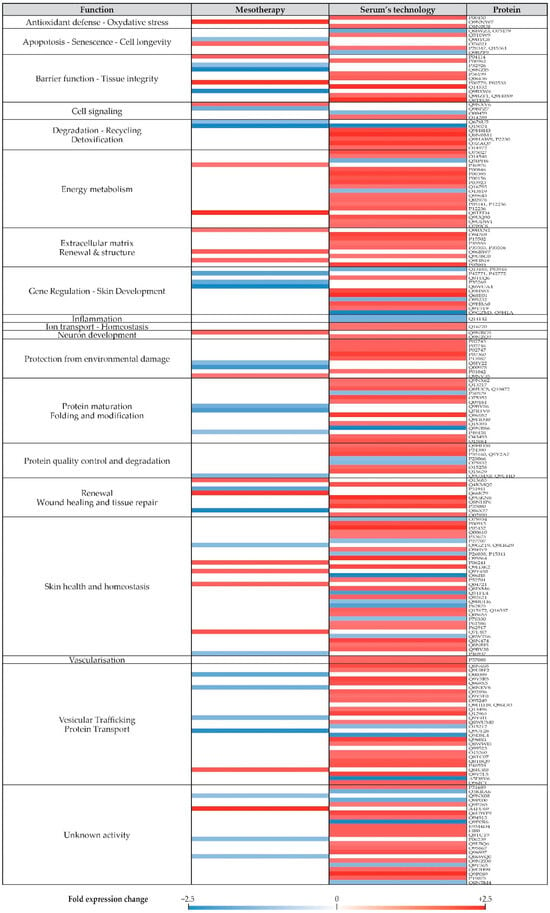
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Anti-Aging Evaluation of Cosmetics on a Tri-Layered Chitosan Membrane: An Alternative to Animal Testing
by
Rocío Guerle-Cavero and Albert Balfagón-Costa
Cosmetics 2025, 12(6), 277; https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12060277 - 10 Dec 2025
Abstract
The search for alternatives to animal testing in cosmetics has encouraged the development of in vitro systems capable of evaluating formulation-driven biophysical parameters assessed on human skin. This study presents a cell-free tri-layered chitosan membrane as a material-based model for characterizing the physicochemical
[...] Read more.
The search for alternatives to animal testing in cosmetics has encouraged the development of in vitro systems capable of evaluating formulation-driven biophysical parameters assessed on human skin. This study presents a cell-free tri-layered chitosan membrane as a material-based model for characterizing the physicochemical anti-aging performance of topical formulations. Three cosmetic products were incorporated either in the top layer (1L(t)) or across all layers (3L), and key parameters—including pore area, water permeation, firmness, elasticity, swelling and moisture retention—were quantified. VitCOil produced consistent effects across configurations, reducing pore area by 52–56% and decreasing water permeation by 54–61%, while increasing moisture retention by 36–38%. OilSerum showed a marked layer-dependent response, enhancing swelling by +70% in 3L and +35% in 1L(t), and increasing water permeation by 16% (3L) and 4% (1L(t)). EyeCr improved firmness and elasticity at low concentration, with stronger elastic response in the top layer (+27% in 3L; +34% in 1L(t)). Overall, this novel platform strengthens early-stage physicochemical screening by linking formulation-dependent mechanisms with directional biophysical trends observed clinically.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Cosmetics in 2025)
►▼
Show Figures
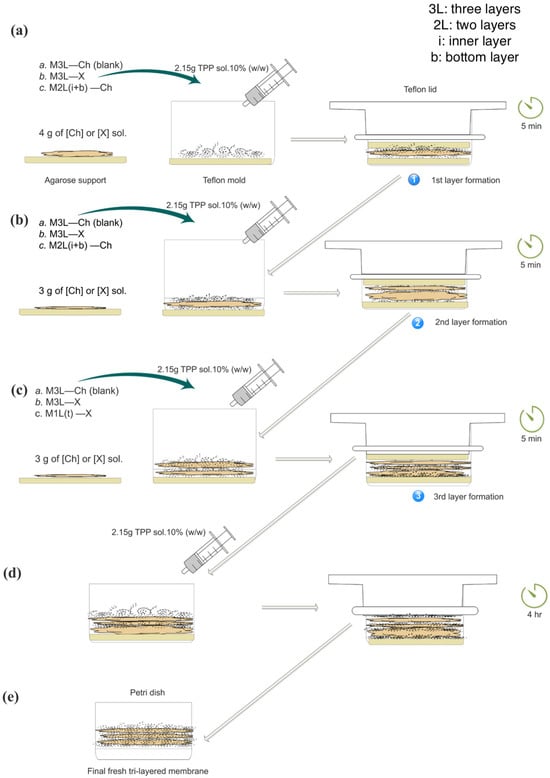
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Evaluation of the Degree of Melasma Reduction After Application of a Chemical Skin Stimulation Product in Combination with a Lightening Serum—Preliminary Observations
by
Anna Deda, Magdalena Hartman-Petrycka, Dominika Wcisło-Dziadecka, Agnieszka Lubczyńska and Sławomir Wilczyński
Cosmetics 2025, 12(6), 276; https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12060276 - 8 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background: Melasma is a chronic hyperpigmentation disorder, often therapy-resistant. Minimally invasive combinations of chemical stimulators and serums show promise. This study evaluated trichloroacetic acid stabilized with hydrogen peroxide and kojic acid, plus a serum with niacinamide, tranexamic acid, lactoferrin, ferulic acid, alpha-lipoic acid,
[...] Read more.
Background: Melasma is a chronic hyperpigmentation disorder, often therapy-resistant. Minimally invasive combinations of chemical stimulators and serums show promise. This study evaluated trichloroacetic acid stabilized with hydrogen peroxide and kojic acid, plus a serum with niacinamide, tranexamic acid, lactoferrin, ferulic acid, alpha-lipoic acid, and physic acid. Methods: Ten female volunteers with clinically diagnosed melasma underwent six treatment sessions. Each procedure involved application of the chemical stimulator followed by the serum, with strict photoprotection advised. Clinical improvement was assessed using the modified Melasma Area and Severity Index (mMASI) by three independent experts. Objective analysis of pigmentation and texture was performed with photographic documentation processed by the Grey Level Co-Occurrence Matrix (GLCM), measuring contrast and homogeneity in selected facial regions. Results: After six treatments, significant improvement was observed. Mean mMASI scores decreased by 62.3% after 2 weeks and 62.9% after 8 weeks. GLCM confirmed pigmentation reduction, showing decreased contrast and increased homogeneity across all regions, with the chin responding best. Correlation analysis indicated a positive trend between mMASI reduction and contrast changes. No serious adverse events or post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation were reported. Conclusions: The combined protocol significantly reduced melasma hyperpigmentation both clinically and objectively. GLCM analysis complements traditional scales and may provide a valuable quantitative tool for future research.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Cosmetic Dermatology)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Antioxidants, Biomedicines, IJMS, Life, Oxygen, Cosmetics, Nutraceuticals
Oxidative Stress and Inflammation, 3rd Edition
Topic Editors: Maria Letizia Manca, Amparo Nacher, Matteo Perra, Ines Castangia, Mohamad AllawDeadline: 31 July 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Cosmetics
Feature Papers in Cosmetics in 2025
Guest Editor: Enzo BerardescaDeadline: 31 December 2025
Special Issue in
Cosmetics
Functional Molecules as Novel Cosmetic Ingredients
Guest Editors: Jing Wang, Zhong LiuDeadline: 31 December 2025
Special Issue in
Cosmetics
Recent Advances in the Development of Sustainable Cosmetic Products With Nanotechnology
Guest Editor: Eduardo Ricci JuniorDeadline: 31 December 2025
Special Issue in
Cosmetics
Bioactive Natural Compounds for Skin Rejuvenation: Advances in Cosmetic Science
Guest Editor: Aura RusuDeadline: 31 January 2026
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Cosmetics
Editorial Board Members' Collection Series: "Sustainability in Materials and Processes in Cosmetic Science"
Collection Editors: Pierfrancesco Morganti, Alina Sionkowska
Topical Collection in
Cosmetics
Editorial Board Members' Collection Series: "Novel Delivery Systems for Dermocosmetic Applications"
Collection Editors: Elisabetta Esposito, Debora Santonocito









