- Systematic Review
Perifollicular Elastolysis: A Systematic Review of Clinical Characteristics, Histopathology, and Therapeutic Outcomes
- Chime Eden and
- Weeratian Tawanwongsri
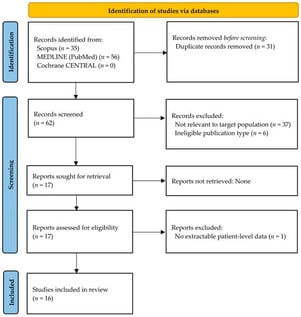
Perifollicular elastolysis (PE), frequently referred to as papular acne scars, is an underrecognized folliculocentric disorder; its clinicopathologic spectrum and management have not been comprehensively synthesized. We performed a systematic review by searching Scopus, MEDLINE (via PubMed), and Cochrane CENTRAL from inception to 16 December 2025, for primary PE reports, synthesized findings narratively, and appraised bias risk using Joanna Briggs Institute checklists. After applying relevant inclusion and exclusion criteria, 16 studies, largely case reports/series, were included. PE typically presents as asymptomatic, noninflammatory, discrete follicular papules, most often skin-colored to whitish/yellowish, occurring mainly on the face and other acne-prone sites. Histopathological investigations reproducibly have shown selective perifollicular loss and/or fragmentation of elastic fibers on staining, with variable perifollicular fibrotic or scar-like changes. Therapeutic evidence was sparse and heterogeneous; the largest interventional study evaluated fractional CO2 laser delivered in an artificial grid pattern (three sessions; 2-month intervals) and reported short-term improvement with transient post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation in 15.6% of patients. Overall, PE shows a consistent clinicopathologic signature, but high-certainty therapeutic evidence remains limited; future studies should standardize terminology, diagnostic criteria, and core outcomes and use prospective comparative designs to establish effective and safe treatments.
9 February 2026