-
 Sustainable Practices for Enhancing Soil Health and Crop Quality in Modern Agriculture: A Review
Sustainable Practices for Enhancing Soil Health and Crop Quality in Modern Agriculture: A Review -
 Only Detect Broilers Once (ODBO): A Method for Monitoring and Tracking Individual Behavior of Cage-Free Broilers
Only Detect Broilers Once (ODBO): A Method for Monitoring and Tracking Individual Behavior of Cage-Free Broilers -
 Soil Fertility and Plant Growth Enhancement Through Compost Treatments Under Varied Irrigation Conditions
Soil Fertility and Plant Growth Enhancement Through Compost Treatments Under Varied Irrigation Conditions -
 Biochar as a Feedstock for Sustainable Fertilizers: Recent Advances and Perspectives
Biochar as a Feedstock for Sustainable Fertilizers: Recent Advances and Perspectives -
 Potential Use of Microalgae Isolated from the Natural Environment as Biofertilizers for the Growth and Development of Pak Choi (Brassica rapa subsp. chinensis)
Potential Use of Microalgae Isolated from the Natural Environment as Biofertilizers for the Growth and Development of Pak Choi (Brassica rapa subsp. chinensis)
Journal Description
Agriculture
Agriculture
is an international, scientific peer-reviewed open access journal published semimonthly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubAg, AGRIS, RePEc, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q1 (Agronomy) / CiteScore - Q1 (Plant Science)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 18 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 1.9 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Companion journals for Agriculture include: Poultry, Grasses and Crops.
Impact Factor:
3.6 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
3.8 (2024)
Latest Articles
Design and Evaluation of a Novel Actuated End Effector for Selective Broccoli Harvesting in Dense Planting Conditions
Agriculture 2025, 15(14), 1537; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15141537 (registering DOI) - 16 Jul 2025
Abstract
The commercialization of selective broccoli harvesters, a critical response to agricultural labor shortages, is hampered by end effectors with large operational envelopes and poor adaptability to complex field conditions. To address these limitations, this study developed and evaluated a novel end-effector with an
[...] Read more.
The commercialization of selective broccoli harvesters, a critical response to agricultural labor shortages, is hampered by end effectors with large operational envelopes and poor adaptability to complex field conditions. To address these limitations, this study developed and evaluated a novel end-effector with an integrated transverse cutting mechanism and a foldable grasping cavity. Unlike conventional fixed cylindrical cavities, our design utilizes actuated grasping arms and a mechanical linkage system to significantly reduce the operational footprint and enhance maneuverability. Key design parameters were optimized based on broccoli morphological data and experimental measurements of the maximum stem cutting force. Furthermore, dynamic simulations were employed to validate the operational trajectory and ensure interference-free motion. Field tests demonstrated an operational success rate of 93.33% and a cutting success rate of 92.86%. The end effector successfully operated in dense planting environments, effectively avoiding interference with adjacent broccoli heads. This research provides a robust and promising solution that advances the automation of broccoli harvesting, paving the way for the commercial adoption of robotic harvesting technologies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic New Research on Automated and Efficient Agricultural Machineries)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Data-Efficient Sowing Position Estimation for Agricultural Robots Combining Image Analysis and Expert Knowledge
by
Shuntaro Aotake, Takuya Otani, Masatoshi Funabashi and Atsuo Takanishi
Agriculture 2025, 15(14), 1536; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15141536 - 16 Jul 2025
Abstract
We propose a data-efficient framework for automating sowing operations by agricultural robots in densely mixed polyculture environments. This study addresses the challenge of enabling robots to identify suitable sowing positions with minimal labeled data by integrating image-based field sensing with expert agricultural knowledge.
[...] Read more.
We propose a data-efficient framework for automating sowing operations by agricultural robots in densely mixed polyculture environments. This study addresses the challenge of enabling robots to identify suitable sowing positions with minimal labeled data by integrating image-based field sensing with expert agricultural knowledge. We collected 84 RGB-depth images from seven field sites, labeled by synecological farming practitioners of varying proficiency levels, and trained a regression model to estimate optimal sowing positions and seeding quantities. The model’s predictions were comparable to those of intermediate-to-advanced practitioners across diverse field conditions. To implement this estimation in practice, we mounted a Kinect v2 sensor on a robot arm and integrated its 3D spatial data with axis-specific movement control. We then applied a trajectory optimization algorithm based on the traveling salesman problem to generate efficient sowing paths. Simulated trials incorporating both computation and robotic control times showed that our method reduced sowing operation time by 51% compared to random planning. These findings highlight the potential of interpretable, low-data machine learning models for rapid adaptation to complex agroecological systems and demonstrate a practical approach to combining structured human expertise with sensor-based automation in biodiverse farming environments.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Research Progress on Agricultural Equipments for Precision Planting and Harvesting)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Transcriptomics and Metabolomics Reveal the Dwarfing Mechanism of Pepper Plants Under Ultraviolet Radiation
by
Zejin Zhang, Zhengnan Yan, Xiangyu Ding, Haoxu Shen, Qi Liu, Jinxiu Song, Ying Liang, Na Lu and Li Tang
Agriculture 2025, 15(14), 1535; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15141535 (registering DOI) - 16 Jul 2025
Abstract
As a globally significant economic crop, pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) plants display excessive plant height (etiolation) in greenhouse production under an undesirable environment, leading to lodging-prone plants with reduced stress resistance. In the present study, we provided supplementary ultraviolet-B (UV-B, 280–315 nm)
[...] Read more.
As a globally significant economic crop, pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) plants display excessive plant height (etiolation) in greenhouse production under an undesirable environment, leading to lodging-prone plants with reduced stress resistance. In the present study, we provided supplementary ultraviolet-B (UV-B, 280–315 nm) light to pepper plants grown in a greenhouse to assess the influences of UV-B on pepper growth, with an emphasis on the molecular mechanisms mediated through the gibberellin (GA) signaling pathway. The results indicated that UV-B significantly decreased the plant height and the fresh weight of pepper plants. However, no significant differences were observed in the chlorophyll content of pepper plants grown under natural light and supplementary UV-B radiation. The results of the transcriptomic and metabolomic analyses indicated that differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were significantly enriched in plant hormone signal transduction and that UV radiation altered the gibberellin synthesis pathway of pepper plants. Specifically, the GA3 content of the pepper plants grown with UV-B radiation decreased by 39.1% compared with those grown without supplementary UV-B radiation; however, the opposite trend was observed in GA34, GA7, and GA51 contents. In conclusion, UV-B exposure significantly reduced plant height, a phenotypic response mechanistically linked to an alteration in GA homeostasis, which may be caused by a decrease in GA3 content. Our study elucidated the interplay between UV-B and gibberellin biosynthesis in pepper morphogenesis, offering a theoretical rationale for developing UV-B photoregulation technologies as alternatives to chemical growth inhibitors.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Effects of LED Lighting on Crop Growth, Quality, and Yield)
►▼
Show Figures
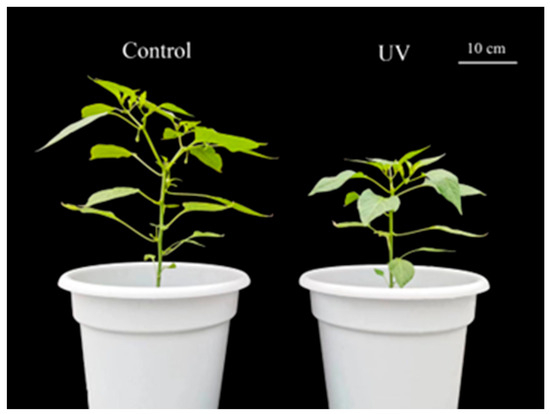

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Machine Learning (AutoML)-Driven Wheat Yield Prediction for European Varieties: Enhanced Accuracy Using Multispectral UAV Data
by
Krstan Kešelj, Zoran Stamenković, Marko Kostić, Vladimir Aćin, Dragana Tekić, Tihomir Novaković, Mladen Ivanišević, Aleksandar Ivezić and Nenad Magazin
Agriculture 2025, 15(14), 1534; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15141534 - 16 Jul 2025
Abstract
Accurate and timely wheat yield prediction is valuable globally for enhancing agricultural planning, optimizing resource use, and supporting trade strategies. Study addresses the need for precision in yield estimation by applying machine-learning (ML) regression models to high-resolution Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) multispectral (MS)
[...] Read more.
Accurate and timely wheat yield prediction is valuable globally for enhancing agricultural planning, optimizing resource use, and supporting trade strategies. Study addresses the need for precision in yield estimation by applying machine-learning (ML) regression models to high-resolution Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) multispectral (MS) and Red-Green-Blue (RGB) imagery. Research analyzes five European wheat cultivars across 400 experimental plots created by combining 20 nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium (NPK) fertilizer treatments. Yield variations from 1.41 to 6.42 t/ha strengthen model robustness with diverse data. The ML approach is automated using PyCaret, which optimized and evaluated 25 regression models based on 65 vegetation indices and yield data, resulting in 66 feature variables across 400 observations. The dataset, split into training (70%) and testing sets (30%), was used to predict yields at three growth stages: 9 May, 20 May, and 6 June 2022. Key models achieved high accuracy, with the Support Vector Regression (SVR) model reaching R2 = 0.95 on 9 May and R2 = 0.91 on 6 June, and the Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) Regressor attaining R2 = 0.94 on 20 May. The findings underscore the effectiveness of precisely measured MS indices and a rigorous experimental approach in achieving high-accuracy yield predictions. This study demonstrates how a precise experimental setup, large-scale field data, and AutoML can harness UAV and machine learning’s potential to enhance wheat yield predictions. The main limitations of this study lie in its focus on experimental fields under specific conditions; future research could explore adaptability to diverse environments and wheat varieties for broader applicability.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Applications of Remote Sensing in Agricultural Soil and Crop Mapping)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Is the Cultivation of Dictyophora indusiata with Grass-Based Substrates an Efficacious and Sustainable Approach for Enhancing the Understory Soil Environment?
by
Jing Li, Fengju Jiang, Xiaoyue Di, Qi Lai, Dongwei Feng, Yi Zeng, Yufang Lei, Yijia Yin, Biaosheng Lin, Xiuling He, Penghu Liu, Zhanxi Lin, Xiongjie Lin and Dongmei Lin
Agriculture 2025, 15(14), 1533; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15141533 - 16 Jul 2025
Abstract
The integration of forestry and agriculture has promoted edible fungi cultivation in forest understory spaces. However, the impact of spent mushroom substrates on forest soils remains unclear. This study explored the use of seafood mushroom spent substrates (SMS) and grass substrates to cultivate
[...] Read more.
The integration of forestry and agriculture has promoted edible fungi cultivation in forest understory spaces. However, the impact of spent mushroom substrates on forest soils remains unclear. This study explored the use of seafood mushroom spent substrates (SMS) and grass substrates to cultivate Dictyophora indusiata. After cultivation, soil pH stabilized, organic carbon increased by 34.02–62.24%, total nitrogen rose 1.1–1.9-fold, while soil catalase activity increased by 43.78–100.41% and laccase activity surged 3.3–11.2-fold. The 49% Cenchrus fungigraminus and 49% SMS treatment yielded the highest 4-coumaric acid levels in the soil, while all treatments reduced maslinic and pantothenic acid content. SMS as padding material with C. fungigraminus enhanced soil bacterial diversity in the first and following years. Environmental factors and organic acids influenced the recruitment of genus of Latescibacterota, Acidothermus, Rokubacteriales, Candidatus solibacter, and Bacillus, altering organic acid composition. In conclusion, cultivating D. indusiata understory enhanced environmental characteristics, microbial dynamics, and organic acid profiles in forests’ soil in short time.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Effects of Different Managements on Soil Quality and Crop Production)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Metagenomic Profiling of the Grapevine Virome in Canadian Vineyards
by
Bhadra Murthy Vemulapati, Kankana Ghoshal, Sylvain Lerat, Wendy Mcfadden-Smith, Mamadou L. Fall, José Ramón Úrbez-Torres, Peter Moffet, Ian Boyes, James Phelan, Lucas Bennouna, Debra L. Moreau, Mike Rott and Sudarsana Poojari
Agriculture 2025, 15(14), 1532; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15141532 - 16 Jul 2025
Abstract
A high-throughput sequencing-based grapevine metagenomic survey was conducted across all grape-growing Canadian provinces (British Columbia, Ontario, Nova Scotia, and Québec) with the objective of better understanding the grapevine virome composition. In total, 310 composite grapevine samples representing nine Vitis vinifera red; five V.
[...] Read more.
A high-throughput sequencing-based grapevine metagenomic survey was conducted across all grape-growing Canadian provinces (British Columbia, Ontario, Nova Scotia, and Québec) with the objective of better understanding the grapevine virome composition. In total, 310 composite grapevine samples representing nine Vitis vinifera red; five V. vinifera white; seven American–French red; and five white hybrid cultivars were analyzed. dsRNA, enriched using two different methods, was used as the starting material and source of viral nucleic acids in HTS. The virome status on the distribution and incidence in different regions and grapevine cultivars is addressed. Results from this study revealed the presence of 20 viruses and 3 viroids in the samples tested. Twelve viruses, which are in the regulated viruses list under grapevine certification, were identified in this survey. The major viruses detected in this survey and their incidence rates are GRSPaV (26% to 100%), GLRaV-2 (1% to 18%), GLRaV-3 (15% to 63%), GRVFV (0% to 52%), GRGV (0% to 52%), GPGV (3.3% to 77%), GFkV (1.5% to 31.6%), and GRBV (0% to 19.4%). This survey is the first comprehensive virome study using viral dsRNA and a metagenomics approach on grapevine samples from the British Columbia, Ontario, Nova Scotia, and Quebec provinces in Canada. Results from this survey highlight the grapevine virome distribution across four major grapevine-growing regions and their cultivars. The outcome of this survey underlines the need for strengthening current management options to mitigate the impact of virus spread, and the implementation of a domestic grapevine clean plant program to improve the sanitary status of the grapevine ecosystem.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Crop Protection, Diseases, Pests and Weeds)
►▼
Show Figures
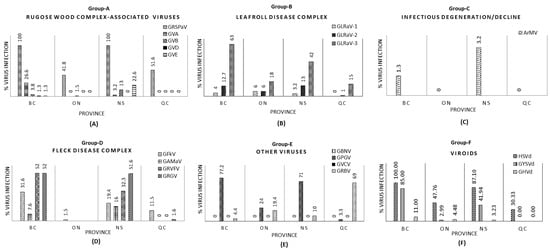
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Mapping Soil Available Nitrogen Using Crop-Specific Growth Information and Remote Sensing
by
Xinle Zhang, Yihan Ma, Shinai Ma, Chuan Qin, Yiang Wang, Huanjun Liu, Lu Chen and Xiaomeng Zhu
Agriculture 2025, 15(14), 1531; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15141531 - 15 Jul 2025
Abstract
Soil available nitrogen (AN) is a critical nutrient for plant absorption and utilization. Accurately mapping its spatial distribution is essential for improving crop yields and advancing precision agriculture. In this study, 188 AN soil samples (0–20 cm) were collected at Heshan Farm, Nenjiang
[...] Read more.
Soil available nitrogen (AN) is a critical nutrient for plant absorption and utilization. Accurately mapping its spatial distribution is essential for improving crop yields and advancing precision agriculture. In this study, 188 AN soil samples (0–20 cm) were collected at Heshan Farm, Nenjiang County, Heihe City, Heilongjiang Province, in 2023. The soil available nitrogen content ranged from 65.81 to 387.10 mg kg−1, with a mean value of 213.85 ± 61.16 mg kg−1. Sentinel-2 images and normalized vegetation index (NDVI) and enhanced vegetation index (EVI) time series data were acquired on the Google Earth Engine (GEE) platform in the study area during the bare soil period (April, May, and October) and the growth period (June–September). These remote sensing variables were combined with soil sample data, crop type information, and crop growth period data as predictive factors and input into a Random Forest (RF) model optimized using the Optuna hyperparameter tuning algorithm. The accuracy of different strategies was evaluated using 5-fold cross-validation. The research results indicate that (1) the introduction of growth information at different growth periods of soybean and maize has different effects on the accuracy of soil AN mapping. In soybean plantations, the introduction of EVI data during the pod setting period increased the mapping accuracy R2 by 0.024–0.088 compared to other growth periods. In maize plantations, the introduction of EVI data during the grouting period increased R2 by 0.004–0.033 compared to other growth periods, which is closely related to the nitrogen absorption intensity and spectral response characteristics during the reproductive growth period of crops. (2) Combining the crop types and their optimal period growth information could improve the mapping accuracy, compared with only using the bare soil period image (R2 = 0.597)—the R2 increased by 0.035, the root mean square error (RMSE) decreased by 0.504%, and the mapping accuracy of R2 could be up to 0.632. (3) The mapping accuracy of the bare soil period image differed significantly among different months, with a higher mapping accuracy for the spring data than the fall, the R2 value improved by 0.106 and 0.100 compared with that of the fall, and the month of April was the optimal window period of the bare soil period in the present study area. The study shows that when mapping the soil AN content in arable land, different crop types, data collection time, and crop growth differences should be considered comprehensively, and the combination of specific crop types and their optimal period growth information has a greater potential to improve the accuracy of mapping soil AN content. This method not only opens up a new technological path to improve the accuracy of remote sensing mapping of soil attributes but also lays a solid foundation for the research and development of precision agriculture and sustainability.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Advances in Smart Agriculture with Remote Sensing as the Core and Its Applications in Crops Field)
►▼
Show Figures
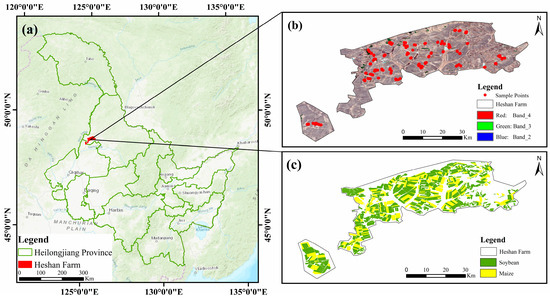
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Growth Stages Discrimination of Multi-Cultivar Navel Oranges Using the Fusion of Near-Infrared Hyperspectral Imaging and Machine Vision with Deep Learning
by
Chunyan Zhao, Zhong Ren, Yue Li, Jia Zhang and Weinan Shi
Agriculture 2025, 15(14), 1530; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15141530 - 15 Jul 2025
Abstract
To noninvasively and precisely discriminate among the growth stages of multiple cultivars of navel oranges simultaneously, the fusion of the technologies of near-infrared (NIR) hyperspectral imaging (HSI) combined with machine vision (MV) and deep learning is employed. NIR reflectance spectra and hyperspectral and
[...] Read more.
To noninvasively and precisely discriminate among the growth stages of multiple cultivars of navel oranges simultaneously, the fusion of the technologies of near-infrared (NIR) hyperspectral imaging (HSI) combined with machine vision (MV) and deep learning is employed. NIR reflectance spectra and hyperspectral and RGB images for 740 Gannan navel oranges of five cultivars are collected. Based on preprocessed spectra, optimally selected hyperspectral images, and registered RGB images, a dual-branch multi-modal feature fusion convolutional neural network (CNN) model is established. In this model, a spectral branch is designed to extract spectral features reflecting internal compositional variations, while the image branch is utilized to extract external color and texture features from the integration of hyperspectral and RGB images. Finally, growth stages are determined via the fusion of features. To validate the availability of the proposed method, various machine-learning and deep-learning models are compared for single-modal and multi-modal data. The results demonstrate that multi-modal feature fusion of HSI and MV combined with the constructed dual-branch CNN deep-learning model yields excellent growth stage discrimination in navel oranges, achieving an accuracy, recall rate, precision, F1 score, and kappa coefficient on the testing set are 95.95%, 96.66%, 96.76%, 96.69%, and 0.9481, respectively, providing a prominent way to precisely monitor the growth stages of fruits.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Multi- and Hyper-Spectral Imaging Technologies for Crop Monitoring—2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures
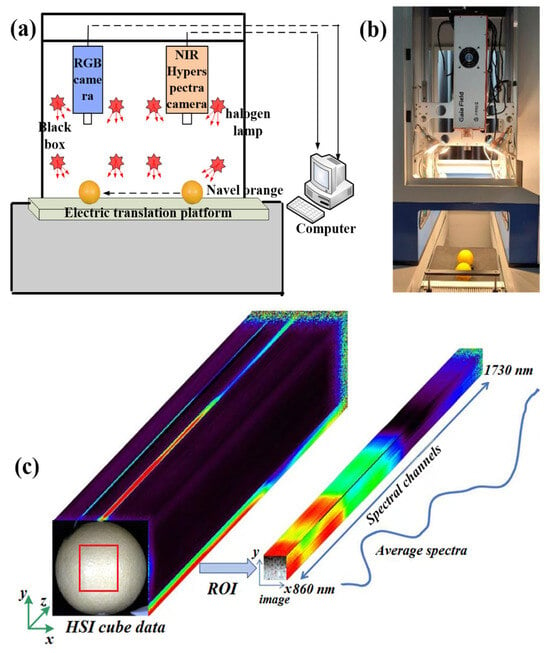
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
An Object Detection Algorithm for Orchard Vehicles Based on AGO-PointPillars
by
Pengyu Ren, Xuyun Qiu, Qi Gao and Yumin Song
Agriculture 2025, 15(14), 1529; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15141529 - 15 Jul 2025
Abstract
With the continuous expansion of the orchard planting area, there is an urgent need for autonomous orchard vehicles that can reduce the labor intensity of fruit farmers and improve the efficiency of operations to assist operators in the process of orchard operations. An
[...] Read more.
With the continuous expansion of the orchard planting area, there is an urgent need for autonomous orchard vehicles that can reduce the labor intensity of fruit farmers and improve the efficiency of operations to assist operators in the process of orchard operations. An object detection system that can accurately identify potholes, trees, and other orchard objects is essential to achieve unmanned operation of the orchard vehicle. Aiming to improve upon existing object detection algorithms, which have the problem of low object recognition accuracy in orchard operation scenes, we propose an orchard vehicle object detection algorithm based on Attention-Guided Orchard PointPillars (AGO-PointPillars). Firstly, we use an RGB-D camera as the sensing hardware to collect the orchard road information and convert the depth image data obtained by the RGB-D camera into 3D point cloud data. Then, Efficient Channel Attention (ECA) and Efficient Up-Convolution Block (EUCB) are introduced based on the PointPillars, which can enhance the ability of feature extraction for orchard objects. Finally, we establish an orchard object detection dataset and validate the proposed algorithm. The results show that, compared to the PointPillars, the AGO-PointPillars proposed in this study has an average detection accuracy improvement of 4.64% for typical orchard objects such as potholes and trees, which can prove the reliability of our algorithm.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Agricultural Technology)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
A Review of Pressure Regulation Technologies for Irrigation Pipeline Systems
by
Fan Yang, Hong Li and Yue Jiang
Agriculture 2025, 15(14), 1528; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15141528 - 15 Jul 2025
Abstract
This review examines water pressure regulation technologies in irrigation systems tailored for hilly and mountainous terrains. In such areas, effective water management is crucial due to the terrain’s complexity and variability, which can greatly affect water distribution and resource efficiency. This text analyzes
[...] Read more.
This review examines water pressure regulation technologies in irrigation systems tailored for hilly and mountainous terrains. In such areas, effective water management is crucial due to the terrain’s complexity and variability, which can greatly affect water distribution and resource efficiency. This text analyzes various types of pressure-regulating devices, including direct-acting and pilot-operated regulators, delving into their working principles, performance characteristics, and practical advantages and disadvantages. This summary also addresses the current research trends in these technologies, focusing on design optimization and performance enhancements. By summarizing existing studies and highlighting areas for future research, this review aims to provide a solid foundation for technological advancements in agricultural irrigation systems suited to challenging landscapes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Agricultural Water Management)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Peer Effects and Rural Households’ Online Shopping Behavior: Evidence from China
by
Jiaxi Zhou, Guoxiong Zhao and Liuyang Yao
Agriculture 2025, 15(14), 1527; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15141527 - 15 Jul 2025
Abstract
Amid the rapid expansion of the digital economy, online shopping has become increasingly common among rural households in China, yet the social interaction mechanisms driving such behavior remain insufficiently explored. This study examines the impact of peer effects on farmers’ online shopping behavior
[...] Read more.
Amid the rapid expansion of the digital economy, online shopping has become increasingly common among rural households in China, yet the social interaction mechanisms driving such behavior remain insufficiently explored. This study examines the impact of peer effects on farmers’ online shopping behavior using data from the China Family Panel Studies (CFPS) covering the years 2014 to 2022. A Logit model is applied to estimate peer influence, and interaction terms are introduced to assess the moderating roles of land assets and social expenditures. The results reveal that peer behavior significantly increases the likelihood of rural households participating in online shopping, with the effect being particularly strong among low-income, less-educated households and those in western regions. Additionally, both land-rich households and those with higher social expenditures demonstrate greater responsiveness to peer influence. These findings highlight the importance of local social interaction in shaping rural online shopping behavior and provide theoretical and practical implications for digital inclusion and rural e-commerce strategies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Agricultural Economics, Policies and Rural Management)
Open AccessArticle
GDFC-YOLO: An Efficient Perception Detection Model for Precise Wheat Disease Recognition
by
Jiawei Qian, Chenxu Dai, Zhanlin Ji and Jinyun Liu
Agriculture 2025, 15(14), 1526; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15141526 - 15 Jul 2025
Abstract
Wheat disease detection is a crucial component of intelligent agricultural systems in modern agriculture. However, at present, its detection accuracy still has certain limitations. The existing models hardly capture the irregular and fine-grained texture features of the lesions, and the results of spatial
[...] Read more.
Wheat disease detection is a crucial component of intelligent agricultural systems in modern agriculture. However, at present, its detection accuracy still has certain limitations. The existing models hardly capture the irregular and fine-grained texture features of the lesions, and the results of spatial information reconstruction caused by standard upsampling operations are inaccuracy. In this work, the GDFC-YOLO method is proposed to address these limitations and enhance the accuracy of detection. This method is based on YOLOv11 and encompasses three key aspects of improvement: (1) a newly designed Ghost Dynamic Feature Core (GDFC) in the backbone, which improves the efficiency of disease feature extraction and enhances the model’s ability to capture informative representations; (2) a redesigned neck structure, Disease-Focused Neck (DF-Neck), which further strengthens feature expressiveness, to improve multi-scale fusion and refine feature processing pipelines; and (3) the integration of the Powerful Intersection over Union v2 (PIoUv2) loss function to optimize the regression accuracy and convergence speed. The results showed that GDFC-YOLO improved the average accuracy from 0.86 to 0.90 when the cross-overmerge threshold was 0.5 (mAP@0.5), its accuracy reached 0.899, its recall rate reached 0.821, and it still maintained a structure with only 9.27 M parameters. From these results, it can be known that GDFC-YOLO has a good detection performance and stronger practicability relatively. It is a solution that can accurately and efficiently detect crop diseases in real agricultural scenarios.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue AI-Powered UAVs and Imaging Systems for Precision Wheat and Rice Management)
►▼
Show Figures
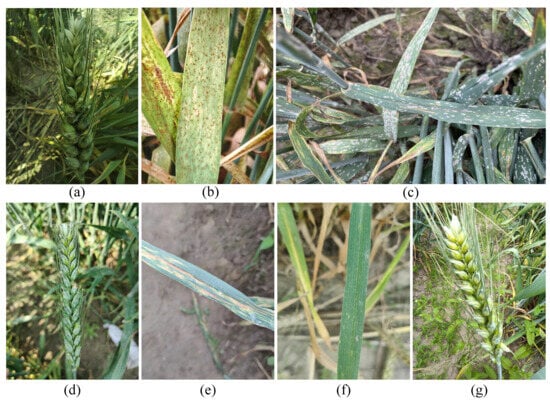

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Field Validation of the DNDC-Rice Model for Crop Yield, Nitrous Oxide Emissions and Carbon Sequestration in a Soybean System with Rye Cover Crop Management
by
Qiliang Huang, Nobuko Katayanagi, Masakazu Komatsuzaki and Tamon Fumoto
Agriculture 2025, 15(14), 1525; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15141525 - 15 Jul 2025
Abstract
The DNDC-Rice model effectively simulates yield and greenhouse gas emissions within a paddy system, while its performance under upland conditions remains unclear. Using data from a long-term cover crop experiment (fallow [FA] vs. rye [RY]) in a soybean field, this study validated the
[...] Read more.
The DNDC-Rice model effectively simulates yield and greenhouse gas emissions within a paddy system, while its performance under upland conditions remains unclear. Using data from a long-term cover crop experiment (fallow [FA] vs. rye [RY]) in a soybean field, this study validated the DNDC-Rice model’s performance in simulating soil dynamics, crop growth, and C-N cycling processes in upland systems through various indicators, including soil temperature, water-filled pore space (WFPS), soybean biomass and yield, CO2 and N2O fluxes, and soil organic carbon (SOC). Based on simulated results, the underestimation of cumulative N2O flux (25.6% in FA and 5.1% in RY) was attributed to both underestimated WFPS and the algorithm’s limitations in simulating N2O emission pulses. Overestimated soybean growth increased respiration, leading to the overestimation of CO2 flux. Although the model captured trends in SOC stock, the simulated annual values differed from observations (−9.9% to +10.1%), potentially due to sampling errors. These findings indicate that the DNDC-Rice model requires improvements in its N cycling algorithm and crop growth sub-models to improve predictions for upland systems. This study provides validation evidence for applying DNDC-Rice to upland systems and offers direction for improving model simulation in paddy-upland rotation systems, thereby enhancing its applicability in such contexts.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Detection and Management of Agricultural Non-Point Source Pollution)
►▼
Show Figures
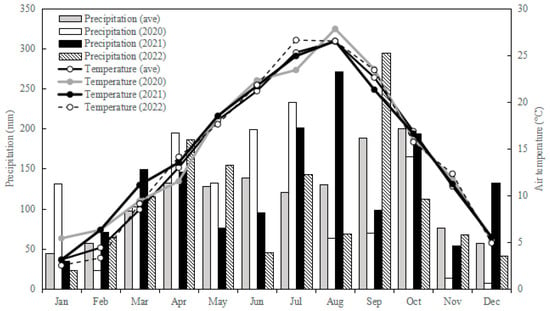
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Detection Line Counting Method Based on Multi-Target Detection and Tracking for Precision Rearing and High-Quality Breeding of Young Silkworm (Bombyx mori)
by
Zhenghao Li, Hao Chang, Mingrui Shang, Zhanhua Song, Fuyang Tian, Fade Li, Guizheng Zhang, Tingju Sun, Yinfa Yan and Mochen Liu
Agriculture 2025, 15(14), 1524; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15141524 - 15 Jul 2025
Abstract
The co-rearing model for young silkworms (Bombyx mori) utilizing artificial feed is currently undergoing significant promotion within the sericulture industry in China. Within this model, accurately counting the number of young silkworms serves as a crucial foundation for achieving precision rearing
[...] Read more.
The co-rearing model for young silkworms (Bombyx mori) utilizing artificial feed is currently undergoing significant promotion within the sericulture industry in China. Within this model, accurately counting the number of young silkworms serves as a crucial foundation for achieving precision rearing and high-quality breeding. Currently, manual counting remains the prevalent method for enumerating young silkworms, yet it is highly subjective. A dataset of young silkworm bodies has been constructed, and the Young Silkworm Counting (YSC) method has been proposed. This method combines an improved detector, incorporating an optimized multi-scale feature fusion module and the Efficient Multi-Scale Attention Fusion Cross Stage Partial (EMA-CSP) mechanism, with an optimized tracker (based on ByteTrack with improved detection box matching), alongside the implementation of a ‘detection line’ approach. The experimental results demonstrate that the recall, precision, and average precision (AP50:95) of the improved detection algorithm are 87.9%, 91.3% and 72.7%, respectively. Additionally, the enhanced ByteTrack method attains a multiple-object tracking accuracy (MOTA) of 88.3%, an IDF1 of 90.2%, and a higher-order tracking accuracy (HOTA) of 78.1%. Experimental validation demonstrates a counting accuracy exceeding 90%. The present study achieves precise counting of young silkworms in complex environments through an improved detection-tracking method combined with a detection line approach.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Farm Animal Production)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
AgriFusionNet: A Lightweight Deep Learning Model for Multisource Plant Disease Diagnosis
by
Saleh Albahli
Agriculture 2025, 15(14), 1523; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15141523 - 15 Jul 2025
Abstract
Timely and accurate identification of plant diseases is critical to mitigating crop losses and enhancing yield in precision agriculture. This paper proposes AgriFusionNet, a lightweight and efficient deep learning model designed to diagnose plant diseases using multimodal data sources. The framework integrates RGB
[...] Read more.
Timely and accurate identification of plant diseases is critical to mitigating crop losses and enhancing yield in precision agriculture. This paper proposes AgriFusionNet, a lightweight and efficient deep learning model designed to diagnose plant diseases using multimodal data sources. The framework integrates RGB and multispectral drone imagery with IoT-based environmental sensor data (e.g., temperature, humidity, soil moisture), recorded over six months across multiple agricultural zones. Built on the EfficientNetV2-B4 backbone, AgriFusionNet incorporates Fused-MBConv blocks and Swish activation to improve gradient flow, capture fine-grained disease patterns, and reduce inference latency. The model was evaluated using a comprehensive dataset composed of real-world and benchmarked samples, showing superior performance with 94.3% classification accuracy, 28.5 ms inference time, and a 30% reduction in model parameters compared to state-of-the-art models such as Vision Transformers and InceptionV4. Extensive comparisons with both traditional machine learning and advanced deep learning methods underscore its robustness, generalization, and suitability for deployment on edge devices. Ablation studies and confusion matrix analyses further confirm its diagnostic precision, even in visually ambiguous cases. The proposed framework offers a scalable, practical solution for real-time crop health monitoring, contributing toward smart and sustainable agricultural ecosystems.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Computational, AI and IT Solutions Helping Agriculture)
►▼
Show Figures
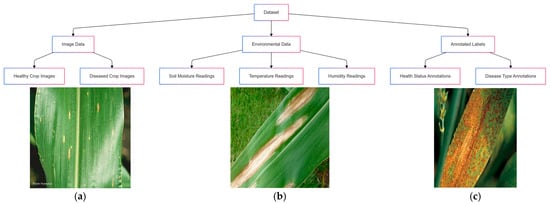
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Transcriptome Analysis Elucidates the Mechanism of an Endophytic Fungus Cladosporium sp. ‘BF-F’ in Enhancing the Growth of Sesuvium portulacastrum
by
Dan Wang, Wenbin Zhang, Dinging Cao and Xiangying Wei
Agriculture 2025, 15(14), 1522; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15141522 - 15 Jul 2025
Abstract
Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) are beneficial rhizosphere microorganisms for plants. They can promote plant absorption of nutrients, inhibit pathogenic microorganisms, enhance plant tolerance to abiotic and biotic stresses, and improve plant growth. Isolating new beneficial microbes and elucidating their promoting mechanisms can facilitate
[...] Read more.
Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) are beneficial rhizosphere microorganisms for plants. They can promote plant absorption of nutrients, inhibit pathogenic microorganisms, enhance plant tolerance to abiotic and biotic stresses, and improve plant growth. Isolating new beneficial microbes and elucidating their promoting mechanisms can facilitate the development of microbial fertilizers. This study combined transcriptome sequencing and related experiments to analyze the mechanism by which the endophytic fungus ‘BF-F’ promotes the growth of Sesuvium portulacastrum. We inoculated the ‘BF-F’ fungus beside S. portulacastrum seedlings as the experimental group. Meanwhile, S. portulacastrum seedlings not inoculated with ‘BF-F’ were set as the control group. After inoculation for 0 d, 7 d, 14 d, 21 d, and 28 d, the plant height and the number of roots were measured. Furthermore, transcriptome sequencing on the roots and leaves of the S. portulacastrum was conducted. Differentially expressed genes were screened, and KEGG enrichment analysis was performed. Nitrogen metabolism-related genes were selected, and qRT-PCR was conducted on these genes. Furthermore, we analyzed the metabolomics of ‘BF-F’ and its hormone products. The results showed that inoculation of ‘BF-F’ significantly promoted the growth of S. portulacastrum. After ‘BF-F’ inoculation, a large number of genes in S. portulacastrum were differentially expressed. The KEGG pathway enrichment results indicated that the ‘BF-F’ treatment affected multiple metabolic pathways in S. portulacastrum, including hormone signal transduction and nitrogen metabolism. The auxin signaling pathway was enhanced because of a decrease in AUX expression and an increase in ARF expression. Contrary to the auxin signal transduction pathway, the zeatin (ZT) signaling pathway was suppressed after the ‘BF-F’ treatment. ‘BF-F’ increased the expression of genes related to nitrogen metabolism (NRT, AMT, NR, and GAGOT), thereby promoting the nitrogen content in S. portulacastrum. The metabolites of ‘BF-F’ were analyzed, and we found that ‘BF-F’ can synthesize IAA and ZT, which are important for plant growth. Overall, ‘BF-F’ can produce IAA and enhance the nitrogen use efficiency of plants, which could have the potential to be used for developing a microbial fertilizer.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Crop Genetics, Genomics and Breeding)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
YOLO-WAS: A Lightweight Apple Target Detection Method Based on Improved YOLO11
by
Xinwu Du, Xiaoxuan Zhang, Tingting Li, Xiangyu Chen, Xiufang Yu and Heng Wang
Agriculture 2025, 15(14), 1521; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15141521 - 14 Jul 2025
Abstract
Target detection is the key technology of the apple-picking robot. To overcome the limitations of existing apple target detection methods, including low recognition accuracy of multi-species apples in complex orchard environments and a complex network architecture that occupies large memory, a lightweight apple
[...] Read more.
Target detection is the key technology of the apple-picking robot. To overcome the limitations of existing apple target detection methods, including low recognition accuracy of multi-species apples in complex orchard environments and a complex network architecture that occupies large memory, a lightweight apple recognition model based on the improved YOLO11 model was proposed, named YOLO-WAS model. The model aims to achieve efficient and accurate automatic multi-species apple identification while reducing computational resource consumption and facilitating real-time applications on low-power devices. First, the study constructed a high-quality multi-species apple dataset and improved the complexity and diversity of the dataset through various data enhancement techniques. The YOLO-WAS model replaced the ordinary convolution module of YOLO11 with the Adown module proposed in YOLOv9, the backbone C3K2 module combined with Wavelet Transform Convolution (WTConv), and the spatial and channel synergistic attention module Self-Calibrated Spatial Attention (SCSA) combined with the C2PSA attention mechanism to form the C2PSA_SCSA module was also introduced. Through these improvements, the model not only ensured lightweight but also significantly improved performance. Experimental results show that the proposed YOLO-WAS model achieves a precision (P) of 0.958, a recall (R) of 0.921, and mean average precision at IoU threshold of 0.5 (mAP@50) of 0.970 and mean average precision from IoU threshold of 0.5 to 0.95 with step 0.05 (mAP@50:95) of 0.835. Compared to the baseline model, the YOLO-WAS exhibits reduced computational complexity, with the number of parameters and floating-point operations decreased by 22.8% and 20.6%, respectively. These results demonstrate that the model performs competitively in apple detection tasks and holds potential to meet real-time detection requirements in resource-constrained environments, thereby contributing to the advancement of automated orchard management.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Digital Agriculture)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Comprehensive Analysis of Soil Physicochemical Properties and Optimization Strategies for “Yantai Fuji 3” Apple Orchards
by
Zhantian Zhang, Zhihan Zhang, Zhaobo Fan, Weifeng Leng, Tianjing Yang, Jie Yao, Haining Chen and Baoyou Liu
Agriculture 2025, 15(14), 1520; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15141520 - 14 Jul 2025
Abstract
Based on an integrated analysis, this study summarized the current status of soil quality in Yantai apple orchards, developed a multivariate regulation model for key soil physicochemical properties, and proposed optimized fertilization strategies to improve soil quality in the region. The study analyzed
[...] Read more.
Based on an integrated analysis, this study summarized the current status of soil quality in Yantai apple orchards, developed a multivariate regulation model for key soil physicochemical properties, and proposed optimized fertilization strategies to improve soil quality in the region. The study analyzed the physicochemical properties of the topsoil (0–30 cm) in 19 representative apple orchards across Yantai, including indicators like pH, organic matter (OM), major nutrient ions, and salinity indicators, using standardized measurements and multivariate statistical methods, including descriptive statistics analysis, frequency distribution analysis, canonical correlation analysis, stepwise regression equation analysis, and regression fit model analysis. The results demonstrated that in apple orchards across the Yantai region, reductions in pH were significantly mitigated under the combined increased OM and exchangeable calcium (Ca). Exchangeable potassium (EK) rose in response to the joint elevation of OM and available nitrogen (AN), and AN was also positively influenced by EK, while OM also exhibited a promotive effect on Olsen phosphorus (OP). Furthermore, Ca increased with higher pH. AN and EK jointly contributed to the increases in electrical conductivity (EC) and chloride ions (Cl), while elevated exchangeable sodium (Na) and soluble salts (SS) were primarily driven by EK. Accordingly, enhancing organic and calcium source fertilizers is recommended to boost OM and Ca levels, reduce acidification, and maintain EC within optimal limits. By primarily reducing potassium’s application, followed by nitrogen and phosphorus source fertilizers, the supply of macronutrients can be optimized, and the accumulation of Na, Cl, and SS can be controlled. Collectively, the combined analysis of soil quality status and the multivariate regulation model clarified the optimized fertilization strategies, thereby establishing a solid theoretical and practical foundation for recognizing the necessity of soil testing and formula fertilization, the urgency of improving soil quality, and the scientific rationale for nutrient input management in Yantai apple orchards.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Agricultural Soils)
►▼
Show Figures
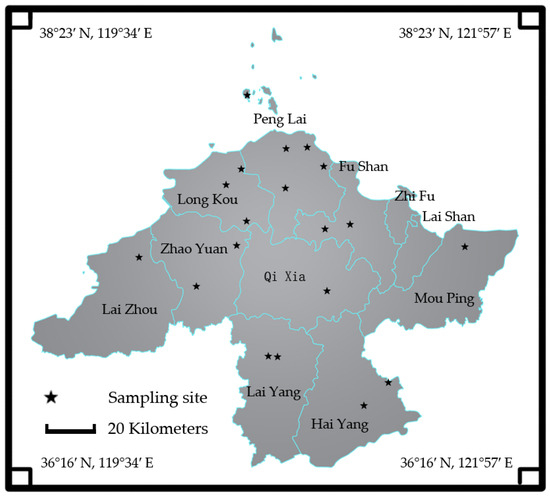
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
The Influence of Microorganism on Insect-Related Pesticide Resistance
by
Qiqi Fan, Hong Sun and Pei Liang
Agriculture 2025, 15(14), 1519; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15141519 - 14 Jul 2025
Abstract
Insect pests inflict significant agricultural and economic losses on crops globally. Chemical control refers to the use of agrochemicals, such as insecticides, herbicides, and fungicides, to manage pests and diseases. Chemical control is still the prioritized method, as insecticides are highly effective and
[...] Read more.
Insect pests inflict significant agricultural and economic losses on crops globally. Chemical control refers to the use of agrochemicals, such as insecticides, herbicides, and fungicides, to manage pests and diseases. Chemical control is still the prioritized method, as insecticides are highly effective and toxic to insect pests. However, it reduces the quality of the environment, threatens human health, and causes serious 3R (reduce, reuse, and recycle) problems. Current advances in the mining of functional symbiotic bacteria resources provide the potential to assuage the use of insecticides while maintaining an acceptably low level of crop damage. Recent research on insect–microbe symbiosis has uncovered a mechanism labeled “detoxifying symbiosis”, where symbiotic microorganisms increase host insect resistance through the metabolism of toxins. In addition, the physiological compensation effect caused by insect resistance affects the ability of the host to regulate the community composition of symbiotic bacteria. This paper reviews the relationship between symbiotic bacteria, insects, and insecticide resistance, focusing on the effects of insecticide resistance on the composition of symbiotic bacteria and the role of symbiotic bacteria in the formation of resistance. The functional symbiotic bacteria resources and their mechanisms of action need to be further explored in the future so as to provide theoretical support for the development of pest control strategies based on microbial regulation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Crop Protection, Diseases, Pests and Weeds)
Open AccessArticle
Combined High Irradiance and Water Deficit Alters the Anatomy and Physiology of Photomorphogenic Mutant Micro-Tom Plants
by
Ariana Bertola Carnevale, Alan Carlos da Costa, Emily Carolina Duarte Santos, Adinan Alves da Silva, Priscila Ferreira Batista, Fábia Barbosa da Silva, Luciana Minervina de Freitas Moura and Caroline Müller
Agriculture 2025, 15(14), 1518; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15141518 - 14 Jul 2025
Abstract
Plants are continuously exposed to multiple environmental stressors throughout their lifecycle. Understanding their integrated physiological, biochemical, and anatomical responses under combined stress conditions is crucial for developing effective approaches to improve stress tolerance and maintain crop productivity. This study aimed to investigate the
[...] Read more.
Plants are continuously exposed to multiple environmental stressors throughout their lifecycle. Understanding their integrated physiological, biochemical, and anatomical responses under combined stress conditions is crucial for developing effective approaches to improve stress tolerance and maintain crop productivity. This study aimed to investigate the physiological, biochemical, and anatomical changes in photomorphogenic Micro-Tom plants exposed to high irradiance and water deficit—an abiotic stress combination that commonly co-occurs in natural environments but remains poorly understood in light-sensitive genotypes. We hypothesized that the high pigment 1 (hp1) mutant, due to its enhanced light responsiveness, would display improved stress acclimation compared to the wild-type when exposed to combined stress factors. This study was conducted in a controlled plant growth chamber, using a randomized block design with five replicates. Two Micro-Tom genotypes (wt and hp1) were exposed to control (soil at field capacity (FC) + 450 μmol m−2 s−1 PPFD) and combined stress (40% FC + 1800 μmol m−2 s−1 PPFD) conditions. Despite the higher concentration of chloroplast pigments in hp1, its photosynthetic performance under combined stress was not significantly improved, and its defense mechanisms did not effectively mitigate the stress impacts. Anatomically, wt exhibited greater structural adjustment, observed by adaptations in the spongy parenchyma and mesophyll. Overall, the wt genotype showed stronger defense mechanisms, while hp1 was more susceptible to combined abiotic stress.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Influence of Light, Temperature and Irrigation on Crop Production and Quality)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Agriculture Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Agriculture, Agronomy, Forests, Plants, Stresses
The Effect of Climate Change on Crops and Natural Ecosystems, 2nd Volume
Topic Editors: Arnd Jürgen Kuhn, Giuseppe FenuDeadline: 31 July 2025
Topic in
Agriculture, Atmosphere, Sustainability, Land, Environments, Agronomy, Energies
Greenhouse Gas Emission Reductions and Carbon Sequestration in Agriculture
Topic Editors: Dimitrios Aidonis, Dionysis Bochtis, Charisios AchillasDeadline: 31 August 2025
Topic in
Agriculture, Analytica, Chemistry, Environments, JoX
Exploring the Interplay of Agriculture, Analytical Chemistry, Environments and Toxics
Topic Editors: Bruno Lemos Batista, Tatiana Pedron, Camila Neves LangeDeadline: 20 September 2025
Topic in
Agriculture, Agronomy, Forests, Remote Sensing, Sustainability
Challenges, Development and Frontiers of Smart Agriculture and Forestry—2nd Volume
Topic Editors: Xiaoli Zhang, Dengsheng Lu, Xiujuan Chai, Guijun Yang, Langning HuoDeadline: 30 September 2025

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Agriculture
Effects of Salt Stress on Crop Production—2nd Edition
Guest Editor: Guisheng ZhouDeadline: 20 July 2025
Special Issue in
Agriculture
Herbicide Resistance in Weeds: Detection, Mechanisms, and Management
Guest Editor: Roland BeffaDeadline: 20 July 2025
Special Issue in
Agriculture
Application of Smart Agricultural Technologies in Mountain Farming Systems
Guest Editors: Weibin Wu, Jun Li, Jiehao LiDeadline: 20 July 2025
Special Issue in
Agriculture
Challenges and Opportunities in Genetic Improvement of Livestock
Guest Editors: Jelena Ramljak, Ante Kasap, Valentino Držaić, Marija ŠpeharDeadline: 20 July 2025










