YOLO-WAS: A Lightweight Apple Target Detection Method Based on Improved YOLO11
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
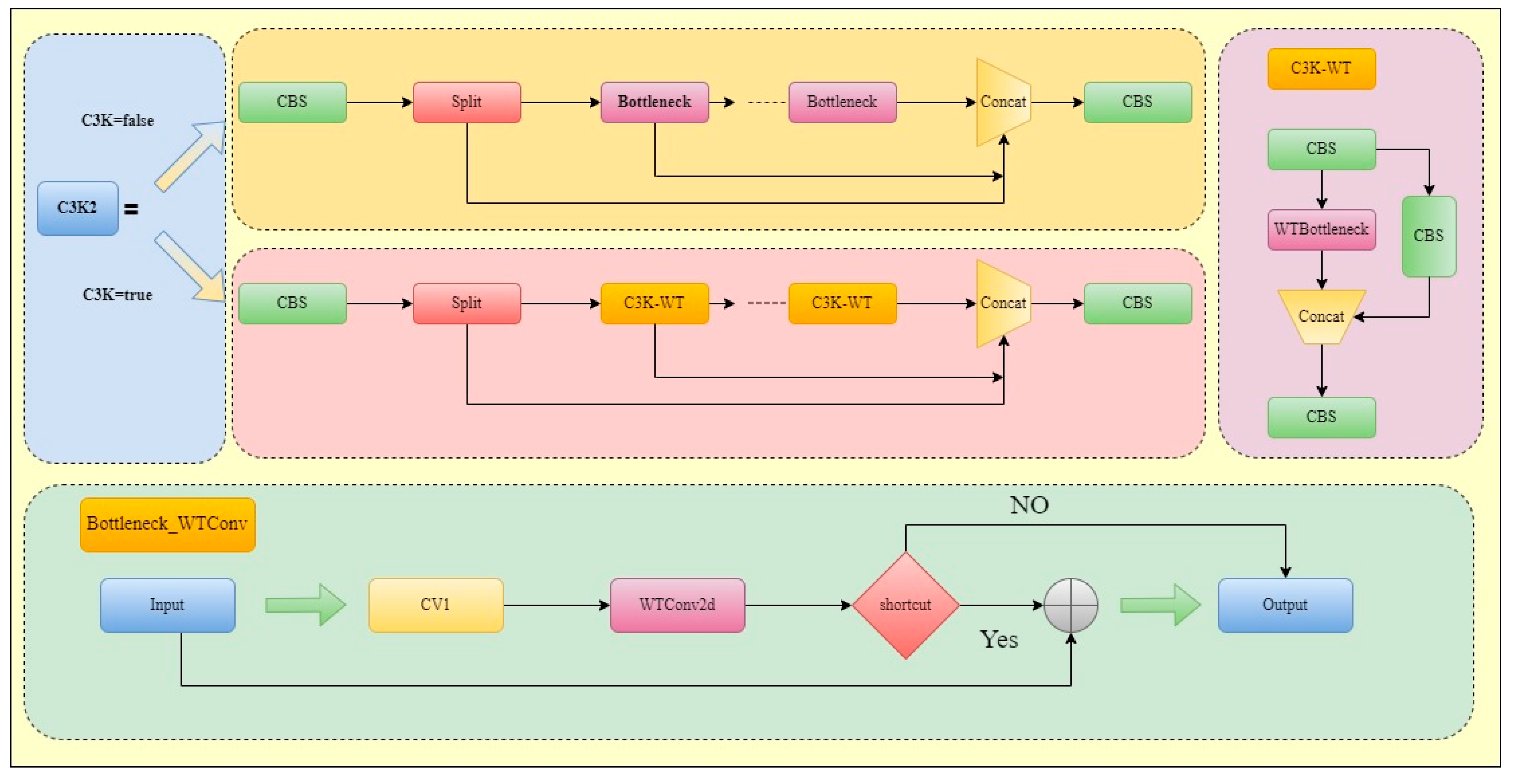
- In order to meet the requirements of real-time recognition of the three components, the model takes YOLO11 as the basic architecture. It combines the trunk C3K2 module with wavelet convolution WTConv and uses wavelet transform to solve the problem of over-parameterization encountered by convolutional neural networks (CNNS) when realizing large receptive fields. It provides a more efficient, robust, and easy-to-integrate convolutional layer solution.
- (2)
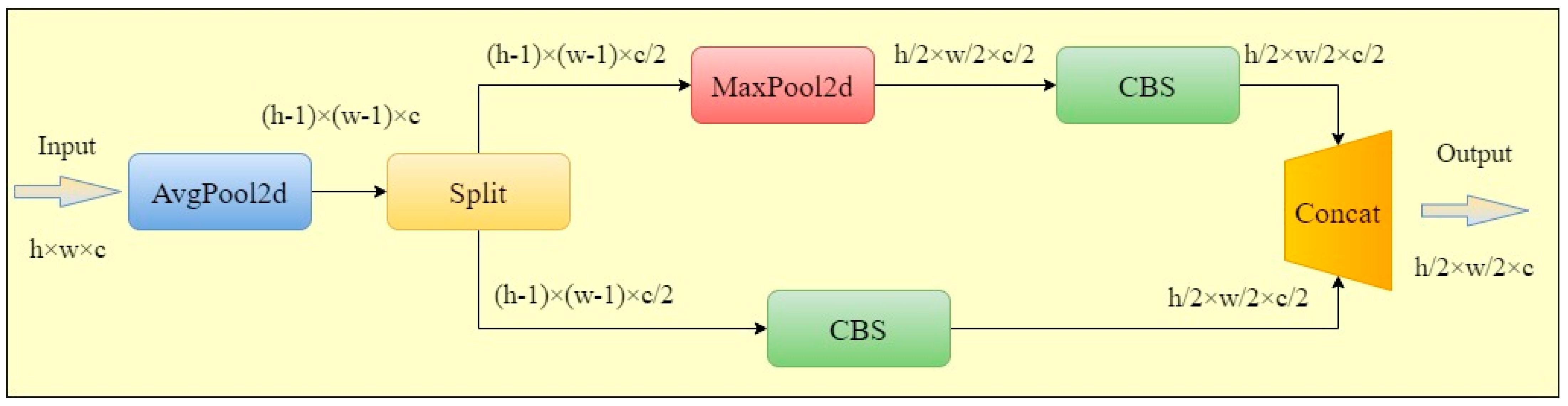
- The ADown module, originally proposed in YOLOv9, is adopted and adapted in this work to enhance the downsampling efficiency within the convolutional components of YOLOv11.
- (3)
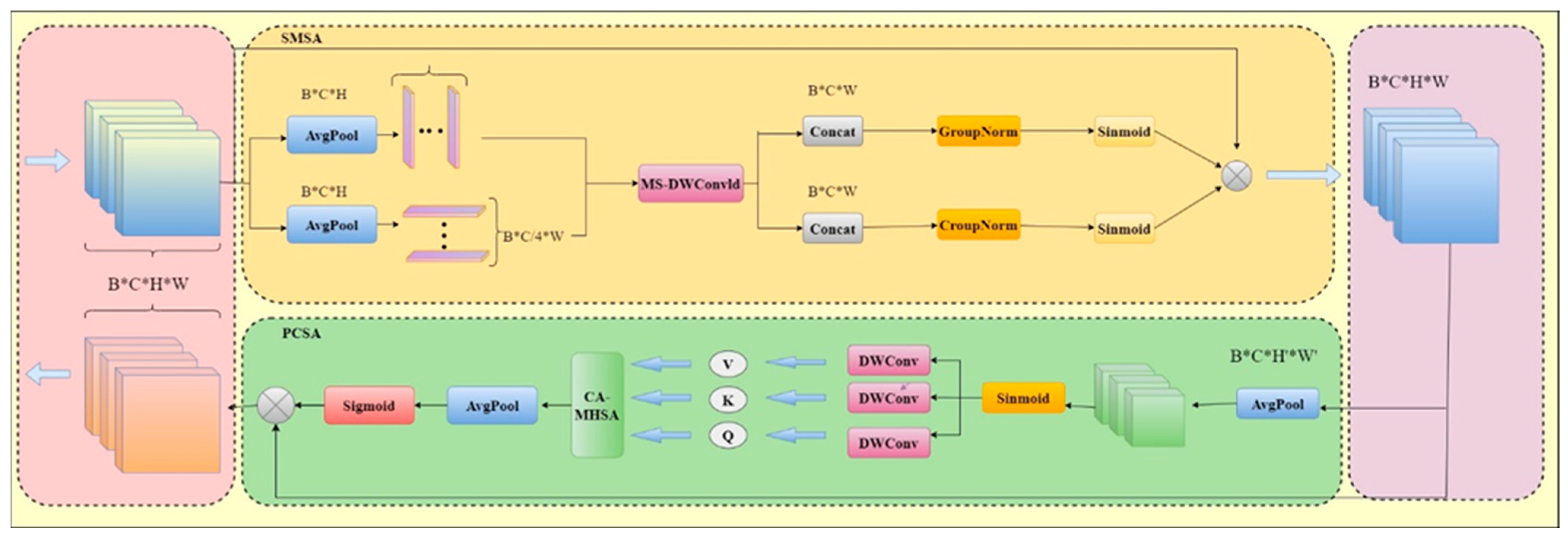
- The spatial and channel collaborative attention (SCSA) module is incorporated to further develop the existing C2PSA attention mechanism in YOLOv11, resulting in the C2PSA_SCSA module. This integration is intended to more effectively combine spatial and channel attention mechanisms and better exploit multi-scale semantic features.
2. Materials and Methods
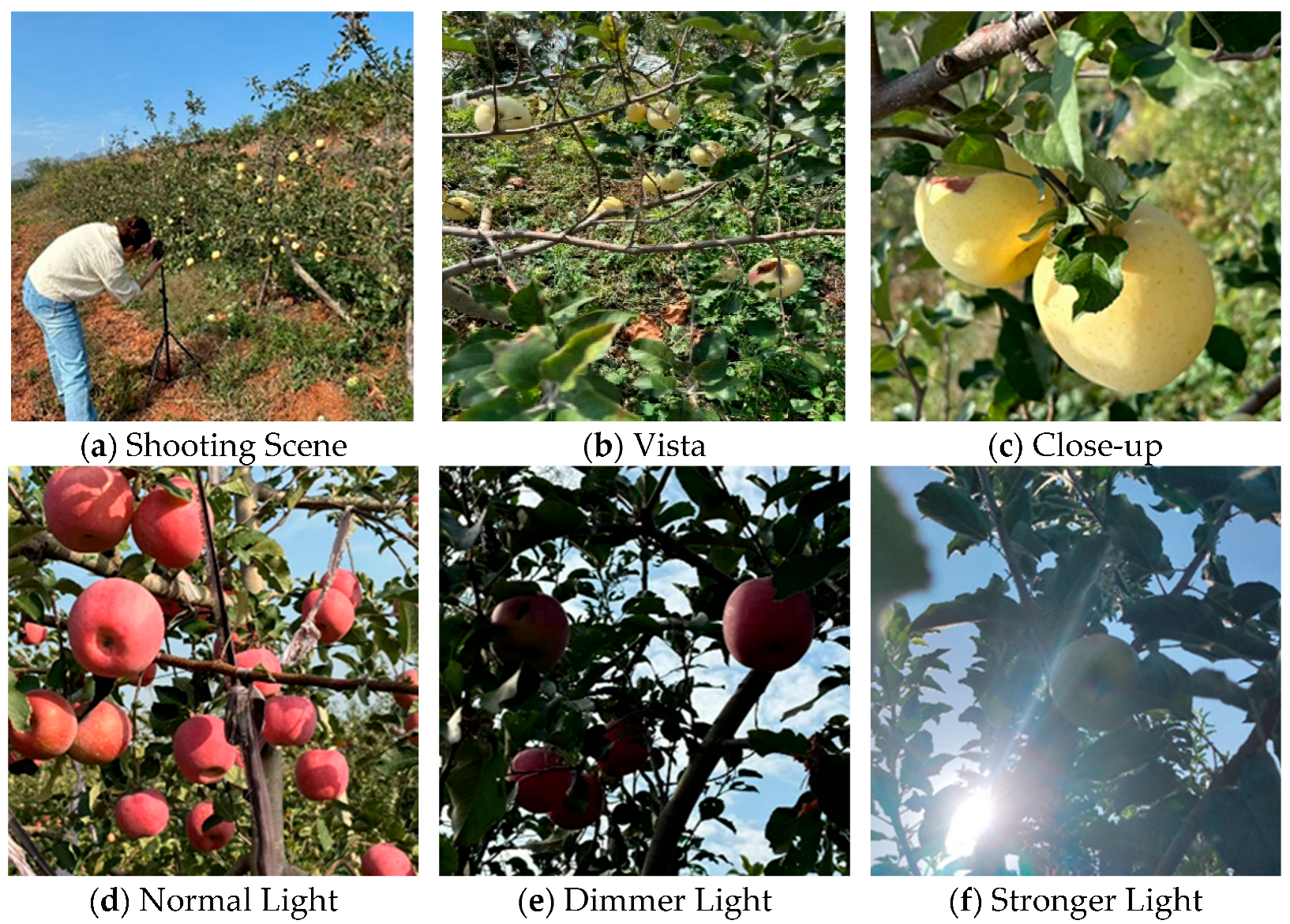
2.1. Dataset Construction
2.1.1. Dataset Acquisition
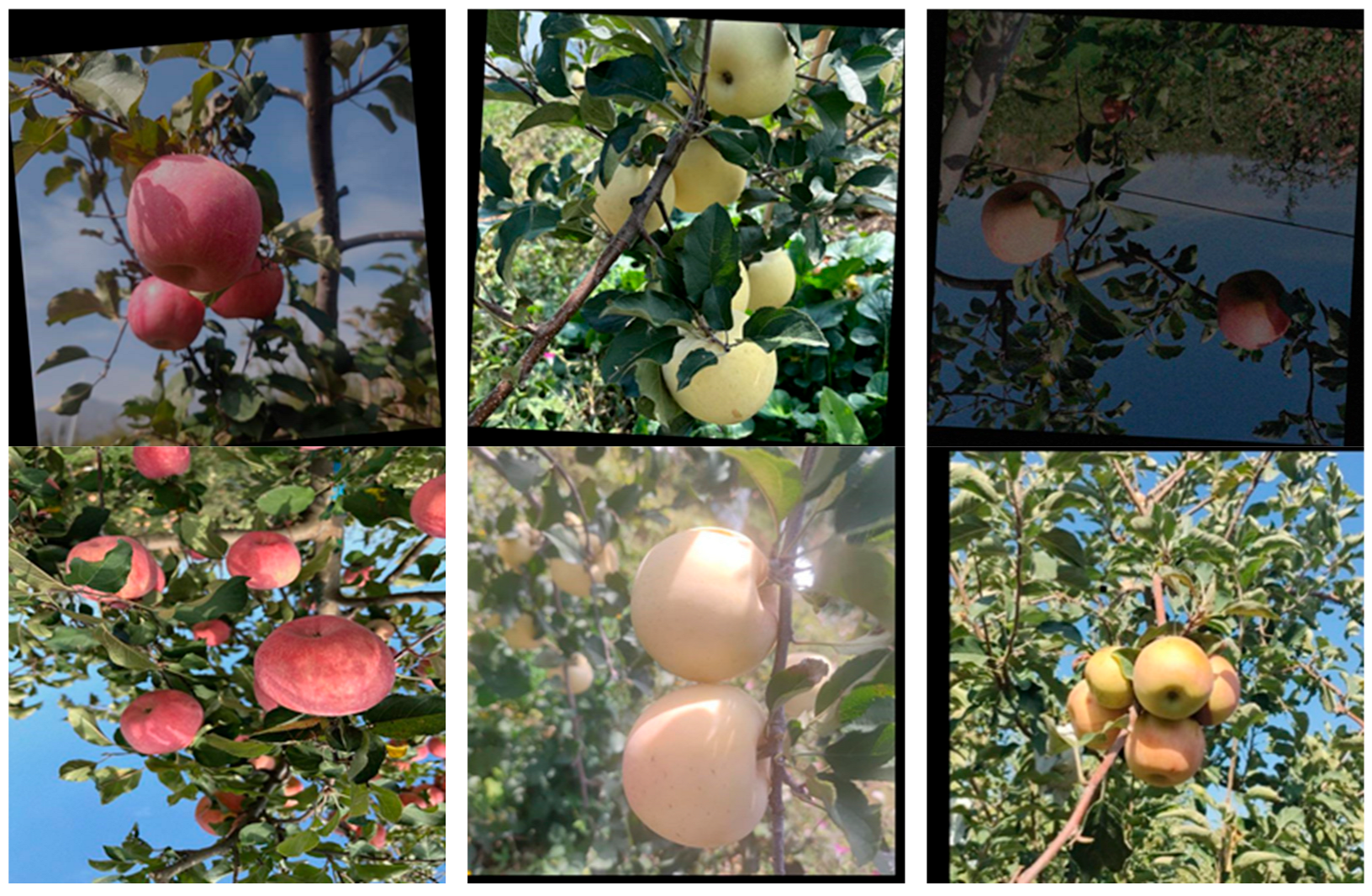
2.1.2. Dataset Creation
2.2. Model Improvement
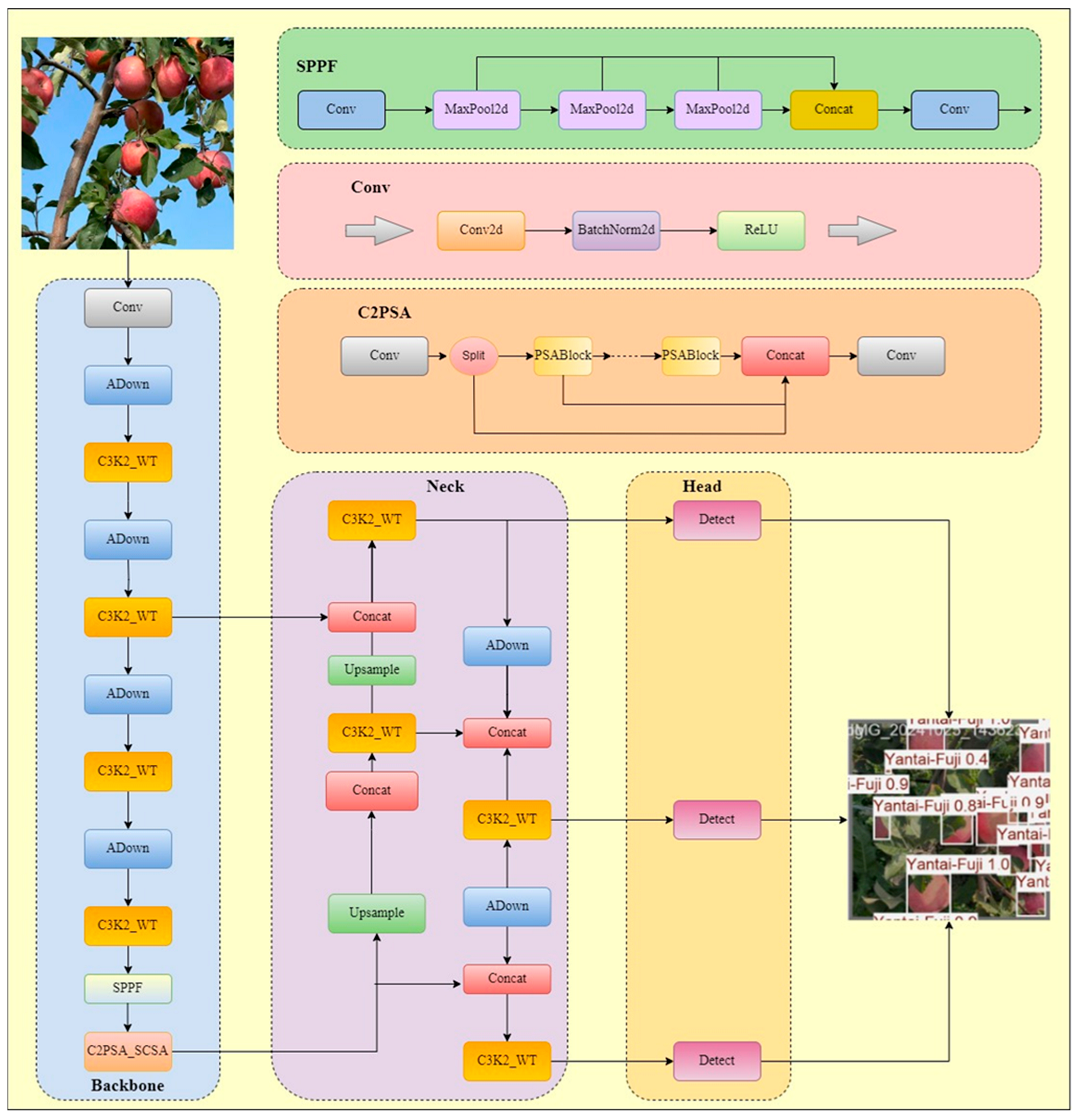
2.2.1. WAS-YOLO11 Model
2.2.2. C3K2_WT Module
2.2.3. ADown Module
2.2.4. C2PSA_SCSA Module
2.2.5. Model Evaluation Index
3. Model Training Results
3.1. Experimental Environment
3.2. Ablation Test
3.3. Comparative Experiments on Attention Mechanisms
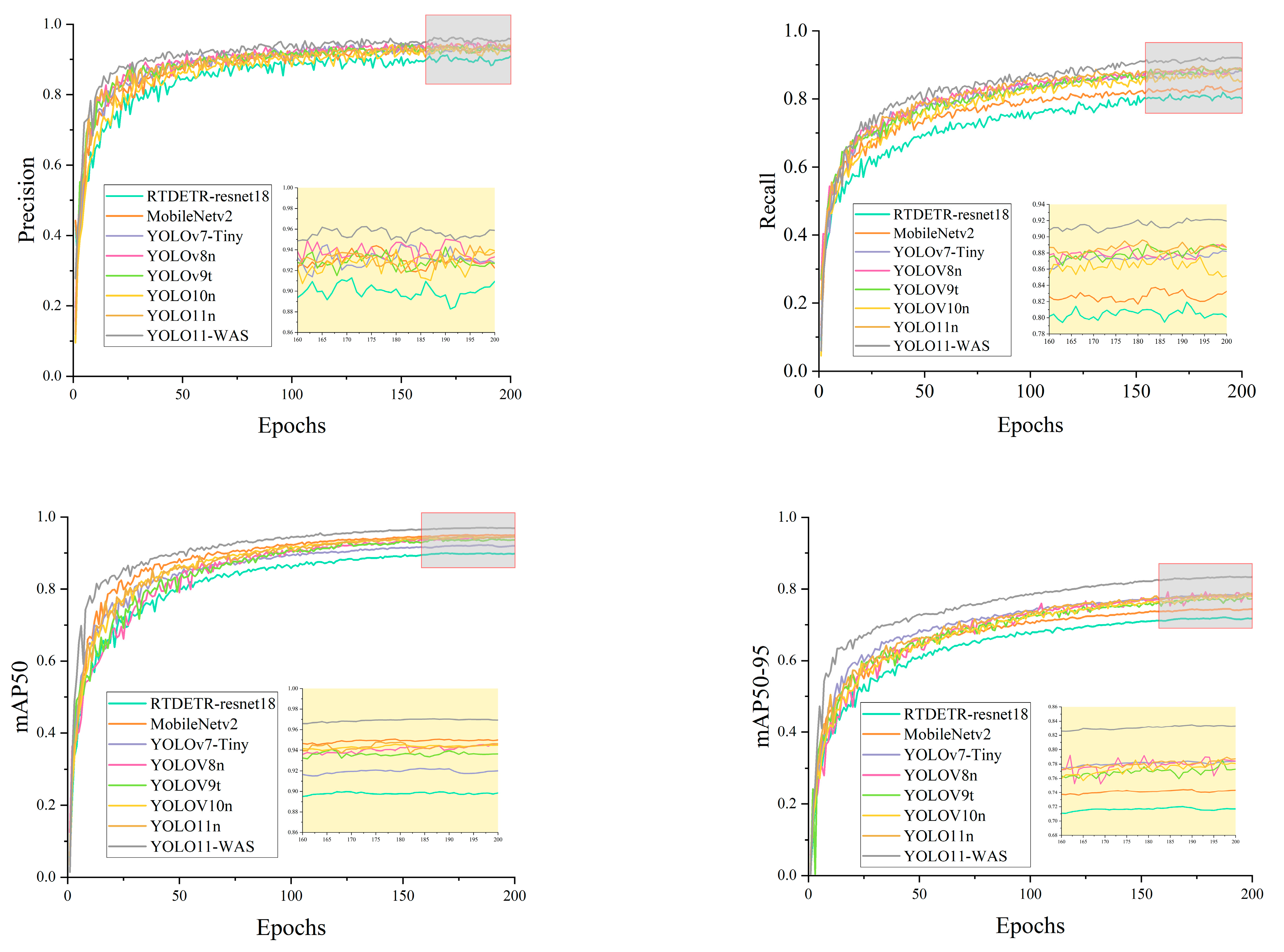
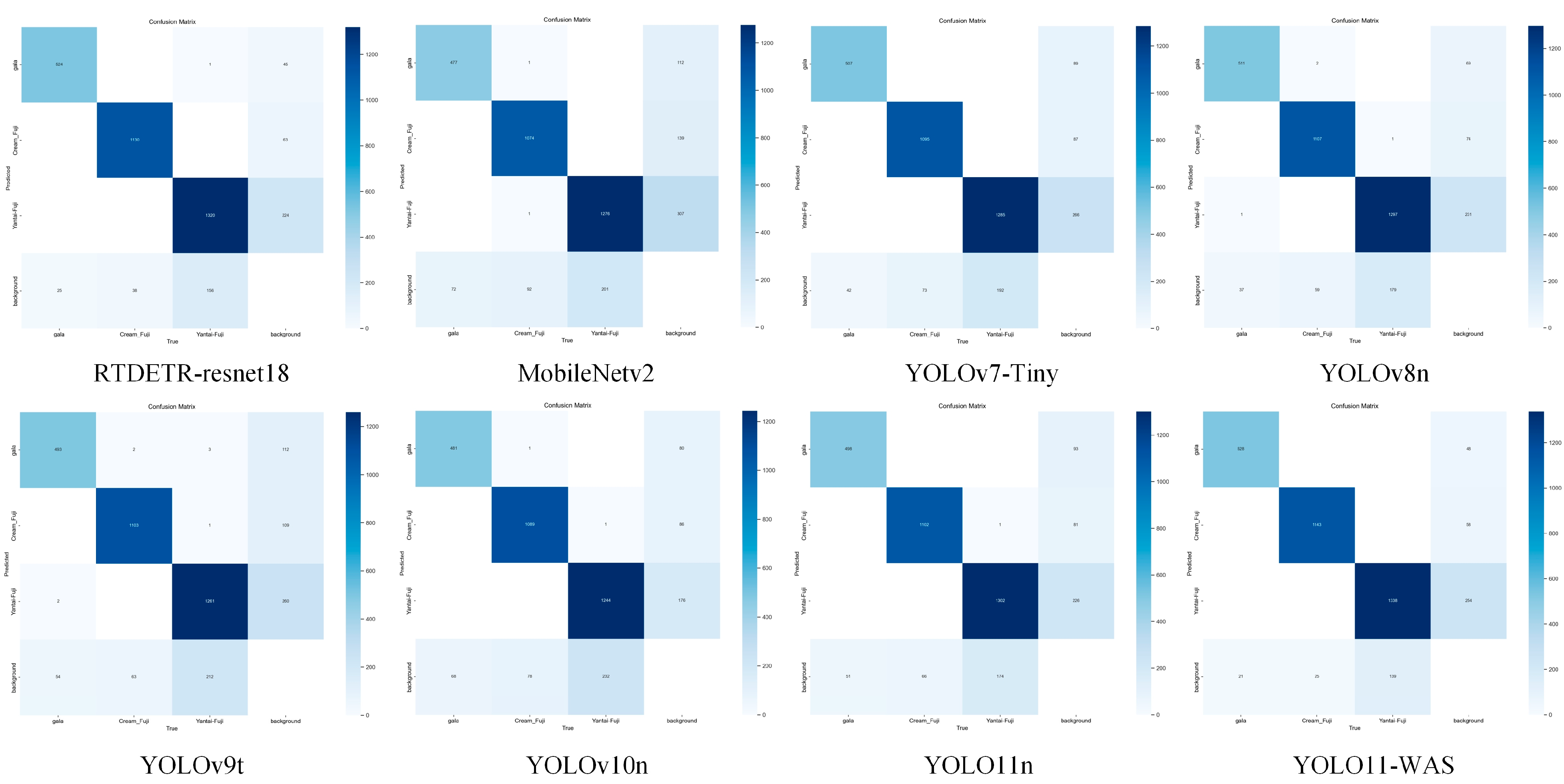
3.4. Performance Comparison of Different Models
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, C.L.; Pan, W.Y.; Zou, T.L.; Li, C.J.; Han, Q.Y.; Wang, H.M.; Yang, J.; Zou, X.J. A Review of Perception Technologies for Berry Fruit-Picking Robots: Advantages, Disadvantages, Challenges, and Prospects. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, W.J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W.Q.; Liu, X.H.; Hu, C.; He, Y.C.; Mhamed, M.; Li, X.L.; Dong, H.X.; Saha, C.K.; et al. Key technologies in apple harvesting robot for standardized orchards: A comprehensive review of innovations, challenges, and future directions. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2025, 235, 110343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Yi, D.; Bo, X.; Guangyu, C.Y.; Dean, Z. Adaptive Variable Parameter Impedance Control for Apple Harvesting Robot Compliant Picking. Complexity 2020, 2020, 4812657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Karkee, M.; Zhang, Q.; Xiao, K.H.; Feng, T. Characterizing apple picking patterns for robotic harvesting. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2016, 127, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.R.; Zhou, J.G.; Chen, Q.Y.; Luo, T.Y.; Li, P.H.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Chen, J. Effects of different picking patterns and sequences on the vibration of apples on the same branch. Biosyst. Eng. 2024, 237, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Q.; Luo, Q.; Zhu, H. Key Issues and Countermeasures of Machine Vision for Fruit and Vegetable Picking Robot. Adv. Transdiscipl. Eng. 2024, 46, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, W.H.; Wu, L.J.; Chen, S.; Hu, X.L.; Li, J.; Tang, J.H.; Yang, J. Generalized Focal Loss: Learning Qualified and Distributed Bounding Boxes for Dense Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 34th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), Electr. Network, Virtual, 6–12 December 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, B.B.; Li, H.T. Object Identification and Location Used by the Fruit and Vegetable Picking Robot Based on Human-decision Making. In Proceedings of the 10th International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, BioMedical Engineering and Informatics (CISP-BMEI), E China Normal University, Shanghai, China, 14–16 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Wan, X.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y. Research on fruit picking recognition based on deep learning. In Proceedings of the Optoelectronic Imaging and Multimedia Technology X 2023, Beijing, China, 15–16 October 2023; Chinese Optical Society (COS): Beijing, China; The Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE): Bellingham, WA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, P.Y.; Li, Z.J.; Lammers, K.; Lu, R.F.; Liu, X.M. Deep learning-based apple detection using a suppression mask R-CNN. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2021, 147, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, Y.L.; Zhang, H.C.; Zeng, Y.; Zheng, J.Q.; Ge, Y.F. Intelligent detection of Multi-Class pitaya fruits in target picking row based on WGB-YOLO network. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 208, 107780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Kang, N.B.; Qu, Q.J.; Zhou, L.H.; Zhang, H.B. Automatic fruit picking technology: A comprehensive review of research advances. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2024, 57, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Lan, H. Multi-type fruit picking image recognition method based on deep learning. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Internet of Things and Machine Learning, IoTML 2021, Dalian, China, 17–19 December 2021; Academic Exchange Information Center (AEIC): Guangzhou, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Yuan, X.; Wang, C. A review on structural development and recognition–localization methods for end-effector of fruit–vegetable picking robots. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2022, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, S.; Gerbino, S.; Sekehravani, E.A.; Russo, M.B.; Carillo, P. Crop Growth Analysis Using Automatic Annotations and Transfer Learning in Multi-Date Aerial Images and Ortho-Mosaics. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.Q.; Jia, K.; Lan, J.H.; Li, Y.W.; Zeng, Y.L.; Wang, C.M. Automatic method of fruit object extraction under complex agricultural background for vision system of fruit picking robot. Optik 2014, 125, 5684–5689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moallem, P.; Serajoddin, A.; Pourghassem, H. Computer vision-based apple grading for golden delicious apples based on surface features. Inf. Process. Agric. 2017, 4, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Cao, C.Y.; Zhang, X.D.; Li, K.; Xu, W.L. Design of Strawberry Picking Hybrid Robot Based on Kinect Sensor. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Sensing, Diagnostics, Prognostics and Control (SDPC), Xi’an, China, 15–17 August 2018; pp. 248–251. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.C.; Qiu, J.J.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Wu, D.X.; Cao, Y.H.; Zhao, K.X.; Zhu, L.X. Optimization strategies of fruit detection to overcome the challenge of unstructured background in field orchard environment: A review. Precis. Agric. 2023, 24, 1183–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.H.; Xun, Y.; Wang, Y.K.; Yang, Q.H. Review of smart robots for fruit and vegetable picking in agriculture. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2022, 15, 33–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.H.; Xue, J.L.; Zhang, T.Y.; Lv, P.F.; Qin, H.H.; Zhao, T.X. Research progress and prospect of key technologies of fruit target recognition for robotic fruit picking. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1423338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedi, P.; Gole, P.; Marwaha, S. PDSE-Lite: Lightweight framework for plant disease severity estimation based on Convolutional Autoencoder and Few-Shot Learning. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 14, 1319894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasiri, A.; Taheri-Garavand, A.; Zhang, Y.D. Image-based deep learning automated sorting of date fruit. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2019, 153, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.T.; Mo, X.T.; Wen, S.J.; Wu, K.L.; Ye, Y.; Wang, Y.M.; Zhang, Y.H. DNE-YOLO: A method for apple fruit detection in Diverse Natural Environments. J. King Saud Univ.-Comput. Inf. Sci. 2024, 36, 102220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.F.; Abeyrathna, R.; Sampurno, R.M.; Nakaguchi, V.M.; Ahamed, T. Faster-YOLO-AP: A lightweight apple detection algorithm based on improved YOLOv8 with a new efficient PDWConv in orchard. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 223, 109118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.X.; Hou, C.K.; Xia, X.L.; Hu, Y.H.; Yang, H. Improved young fruiting apples target recognition method based on YOLOv7 model. Neurocomputing 2025, 623, 129186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.X.; Su, Y.H.; Yao, J.H.; Liu, M.; Du, Y.R.; Wu, X.; Huang, L.; Zhao, M.H. Apple rapid recognition and processing method based on an improved version of YOLOv5. Ecol. Inform. 2023, 77, 102196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedi, P.; Gole, P. PlantGhostNet: An Efficient Novel Convolutional Neural Network Model to Identify Plant Diseases Automatically. In Proceedings of the 9th IEEE International Conference on Reliability, Infocom Technologies and Optimization (Trends and Future Directions), ICRITO 2021, Noida, India, 3–4 September 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.T.; Xia, Y.J.; Xia, P.C.; Liu, Z.Y.; Wang, H.D.; Qin, C.J.; Gong, L.; Liu, C.L. YOLO11-ARAF: An Accurate and Lightweight Method for Apple Detection in Real-World Complex Orchard Environments. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.J.; Li, Y.J.; Urtasun, R.; Zemel, R. Understanding the Effective Receptive Field in Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 30th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), Barcelona, Spain, 5–10 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Finder, S.E.; Amoyal, R.; Treister, E.; Freifeld, O. Wavelet Convolutions for Large Receptive Fields. In Proceedings of the 18th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Milan, Italy, 29 September–4 October 2024; pp. 363–380. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.Y.; Cheng, H.Y.; Pan, J.C.; Zhong, L.L.; Zhang, Q.C. Wavelet-Enhanced YOLO for Intelligent Detection of Welding Defects in X-Ray Films. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.X. Theory of deep convolutional neural networks: Downsampling. Neural Netw. 2020, 124, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.J.; Gao, W.Q.; Zou, Y.; Ma, S.Y. ATW-YOLO: Reconstructing the downsampling process and attention mechanism of yolo network for rail foreign body detection. Signal Image Video Process. 2025, 19, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.S.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, S.H.; Guo, J.T. AAB-YOLO: An Improved YOLOv11 Network for Apple Detection in Natural Environments. Agriculture 2025, 15, 836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.X.; Zhou, R.G.; Li, Y.C.; Ren, P.J. Enhanced underwater object detection with YOLO-LDFE: A model for improved accuracy with balanced efficiency. J. Real-Time Image Process. 2025, 22, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, W.; Dong, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, H. SCSA: Exploring the Synergistic Effects Between Spatial and Channel Attention. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.05128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Huang, L.D.; Gan, X.S.; Lu, Y.F.; Shi, S.X. A heterogeneous attention YOLO model for traffic sign detection. J. Supercomput. 2025, 81, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yang, D.G.; Tang, L.; Zhou, X.; Deng, Y. A Lightweight Object Detector Based on Spatial-Coordinate Self-Attention for UAV Aerial Images. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| C3K2_WT | ADown | C2PSA_SCSA | P | R | mAP50 | mAP50-95 | Parameters | GFLOPs | Speed (FPS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | - | - | 0.934 | 0.870 | 0.945 | 0.784 | 2,582,737 | 6.3 | 192.307 |
| √ | - | 0.942 | 0.894 | 0.955 | 0.803 | 2,523,385 | 6.3 | 185.185 | |
| - | √ | - | 0.951 | 0.896 | 0.96 | 0.805 | 2,100,177 | 5.1 | 243.902 |
| - | - | √ | 0.936 | 0.884 | 0.953 | 0.801 | 2,534,865 | 6.3 | 192.307 |
| √ | √ | - | 0.949 | 0.902 | 0.964 | 0.810 | 2,040,825 | 5.1 | 232.558 |
| √ | √ | 0.936 | 0.89 | 0.957 | 0.802 | 2,475,513 | 6.2 | 153.846 | |
| √ | √ | 0.941 | 0.908 | 0.96 | 0.813 | 2,052,305 | 5.1 | 227.273 | |
| √ | √ | √ | 0.958 | 0.921 | 0.970 | 0.835 | 1,992,953 | 5.0 | 243.902 |
| Model | P | R | mAP50 | mAP50-95 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLO11 | 0.934 | 0.870 | 0.945 | 0.784 |
| YOLO11-SHSA | 0.921 | 0.881 | 0.948 | 0.788 |
| YOLO11-SEAM | 0.926 | 0.876 | 0.945 | 0.793 |
| YOLO11-MLCA | 0.935 | 0.876 | 0.95 | 0.787 |
| YOLO11-CBAM | 0.936 | 0.880 | 0.952 | 0.799 |
| YOLO11-SCSA | 0.936 | 0.884 | 0.953 | 0.801 |
| Model | P | R | mAP50 | mAP50-95 | Parameters | GFLOPs | Speed (FPS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RTDETR-resnet18 | 0.897 | 0.808 | 0.9 | 0.72 | 21,799,409 | 52.3 | 100.692 |
| MobileNetv2 | 0.927 | 0.834 | 0.922 | 0.744 | 4,757,846 | 10.2 | 120.320 |
| YOLOv7-Tiny | 0.927 | 0.870 | 0.944 | 0.790 | 6,007,596 | 13.1 | 50.505 |
| YOLOv8n | 0.936 | 0.860 | 0.945 | 0.785 | 3,066,233 | 8.1 | 200.000 |
| YOLOv9t | 0.919 | 0.847 | 0.937 | 0.773 | 1,971,369 | 7.6 | 200.000 |
| YOLOv10n | 0.919 | 0.853 | 0.935 | 0.781 | 2,695,586 | 8.2 | 250.000 |
| YOLO11n | 0.934 | 0.870 | 0.945 | 0.784 | 2,582,737 | 6.3 | 192.307 |
| YOLO11-WAS | 0.958 | 0.921 | 0.970 | 0.835 | 1,992,953 | 5.0 | 243.902 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, T.; Chen, X.; Yu, X.; Wang, H. YOLO-WAS: A Lightweight Apple Target Detection Method Based on Improved YOLO11. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1521. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15141521
Du X, Zhang X, Li T, Chen X, Yu X, Wang H. YOLO-WAS: A Lightweight Apple Target Detection Method Based on Improved YOLO11. Agriculture. 2025; 15(14):1521. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15141521
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Xinwu, Xiaoxuan Zhang, Tingting Li, Xiangyu Chen, Xiufang Yu, and Heng Wang. 2025. "YOLO-WAS: A Lightweight Apple Target Detection Method Based on Improved YOLO11" Agriculture 15, no. 14: 1521. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15141521
APA StyleDu, X., Zhang, X., Li, T., Chen, X., Yu, X., & Wang, H. (2025). YOLO-WAS: A Lightweight Apple Target Detection Method Based on Improved YOLO11. Agriculture, 15(14), 1521. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15141521




