- Article
Selection of Morphoagronomic Traits for Screening Tropical Forage Genotypes for Waterlogging Tolerance Under Controlled Conditions
- Clemeson Silva de Souza,
- Marcio de Oliveira Martins and
- Giselle Mariano Lessa de Assis
- + 4 authors
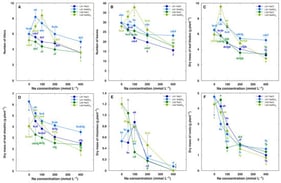
Poorly drained pastures in tropical America are recurrently degraded by Marandu Death Syndrome (MDS), affecting beef and dairy production. This study screened genotypes of Megathyrsus maximus and Urochloa spp. for waterlogging tolerance under controlled conditions to identify discriminant, easily measurable morphoagronomic traits suitable for breeding programs. Four experiments were conducted in factorial arrangement (five genotypes × two water regimes, with four replications), where morphoagronomic and physiological variables were analyzed using multivariate techniques. The first two principal components explained 75.17–88.60% of the total variation and stayed above 70% after variable reduction, without significantly altering genotype dispersion. Physiological responses showed a strong correlation with morphoagronomic traits. The most informative traits were the number of yellow and senescent leaves, number of tillers, SPAD index, leaf dry mass, and root dry mass. Genotypes were grouped by tolerance level. Among M. maximus, ‘Mombaça’ was the most tolerant, while PM13 and PM21 were the least. In Urochloa spp., U. humidicola cv. Tully was the most tolerant and ‘Marandu’ the least tolerant. Screening under controlled conditions is an alternative to distinguish genotypes with contrasting tolerance; however, because controlled environments do not fully reproduce the multifactorial nature of MDS, this approach is recommended only for early stages of breeding programs. Nevertheless, field evaluations on poorly drained soils under grazing remain essential to confirm tolerance to MDS.
15 January 2026