Journal Description
Brain Sciences
Brain Sciences
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on neuroscience published monthly online by MDPI. The British Neuro-Oncology Society (BNOS) and Panhellenic Federation of Alzheimer's Disease and Related Disorders (PFADRD) are affiliated with Brain Sciences and their members receive a discount on article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, Embase, PSYNDEX, PsycInfo, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 16.2 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 1.9 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Journal Cluster of Neurosciences: Brain Sciences, Neurology International, NeuroSci, Clinical and Translational Neuroscience, Neuroglia, Psychiatry International, Clocks & Sleep and Journal of Dementia and Alzheimer's Disease.
Impact Factor:
2.8 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
3.1 (2024)
Latest Articles
The Interaction of Target and Masker Speech in Competing Speech Perception
Brain Sci. 2025, 15(8), 834; https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15080834 (registering DOI) - 4 Aug 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Speech perception typically takes place against a background of other speech or noise. The present study investigates the effectiveness of segregating speech streams within a competing speech signal, examining whether cues such as pitch, which typically denote a difference in talker,
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Speech perception typically takes place against a background of other speech or noise. The present study investigates the effectiveness of segregating speech streams within a competing speech signal, examining whether cues such as pitch, which typically denote a difference in talker, behave in the same way as cues such as speaking rate, which typically do not denote the presence of a new talker. Methods: Native English speakers listened to English target speech within English two-talker babble of a similar or different pitch and/or a similar or different speaking rate to identify whether mismatched properties between target speech and masker babble improve speech segregation. Additionally, Dutch and French masker babble was tested to identify whether an unknown language masker improves speech segregation capacity and whether the rhythm patterns of the unknown language modulate the improvement. Results: Results indicated that a difference in pitch or speaking rate between target and masker improved speech segregation, but when both pitch and speaking rate differed, only a difference in pitch improved speech segregation. Results also indicated improved speech segregation for an unknown language masker, with little to no role of rhythm pattern of the unknown language. Conclusions: This study increases the understanding of speech perception in a noisy ecologically valid context and suggests that there is a link between a cue’s potential to denote a new speaker and its ability to aid in speech segregation during competing speech perception.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Language Perception and Processing)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Unraveling Glioblastoma Heterogeneity: Advancing Immunological Insights and Therapeutic Innovations
by
Joshua H. Liu, Maksym Horiachok, Santosh Guru and Cecile L. Maire
Brain Sci. 2025, 15(8), 833; https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15080833 (registering DOI) - 2 Aug 2025
Abstract
Glioblastoma (GBM) remains one of the most aggressive and treatment-resistant brain tumors, largely due to its profound intratumoral heterogeneity and immunosuppressive microenvironment. Various classifications of GBM subtypes were created based on transcriptional and methylation profiles. This effort, followed by the development of new
[...] Read more.
Glioblastoma (GBM) remains one of the most aggressive and treatment-resistant brain tumors, largely due to its profound intratumoral heterogeneity and immunosuppressive microenvironment. Various classifications of GBM subtypes were created based on transcriptional and methylation profiles. This effort, followed by the development of new technology such as single-nuclei sequencing (snRNAseq) and spatial transcriptomics, led to a better understanding of the glioma cells’ plasticity and their ability to transition between diverse cellular states. GBM cells can mimic neurodevelopmental programs to resemble oligodendrocyte or neural progenitor behavior and hitchhike the local neuronal network to support their growth. The tumor microenvironment, especially under hypoxic conditions, drives the tumor cell clonal selection, which then reshapes the immune cells’ functions. These adaptations contribute to immune evasion by progressively disabling T cell and myeloid cell functions, ultimately establishing a highly immunosuppressive tumor milieu. This complex and metabolically constrained environment poses a major barrier to effective antitumor immunity and limits the success of conventional therapies. Understanding the dynamic interactions between glioma cells and their microenvironment is essential for the development of more effective immunotherapies and rational combination strategies aimed at overcoming resistance and improving patient outcomes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Recent Advances in Translational Neuro-Oncology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Acute Ischemic Stroke Treatment in Germany (2015–2023): Nationwide Trends in Thrombolysis and Thrombectomy by Age and Sex
by
Sara Hirsch, Karel Kostev, Christian Tanislav and Ali Hammed
Brain Sci. 2025, 15(8), 832; https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15080832 (registering DOI) - 2 Aug 2025
Abstract
Background: The implementation of intravenous thrombolysis (IVT) and mechanical thrombectomy (MT) in acute ischemic stroke (AIS) has proven effective, offering significant benefits for patient outcomes. We therefore investigated trends in the implementation of IVT and MT in Germany between 2015 and 2023. Methods:
[...] Read more.
Background: The implementation of intravenous thrombolysis (IVT) and mechanical thrombectomy (MT) in acute ischemic stroke (AIS) has proven effective, offering significant benefits for patient outcomes. We therefore investigated trends in the implementation of IVT and MT in Germany between 2015 and 2023. Methods: We conducted a retrospective analysis using German Diagnosis-Related Group (DRG) statistics from 2015 to 2023. Treatment numbers were analyzed annually based on OPS codes. We examined the age and sex distribution of patients undergoing these treatments. Additionally, we analyzed all hospital cases coded with ICD-10 for acute ischemic stroke (AIS). Results: Between 2015 and 2023, the number of AIS cases in Germany slightly declined from 250,802 to 248,107 (−1.1%), with the largest annual decrease (−4.3%) occurring during the COVID-19 pandemic (2019–2020). Despite this, the use of IVT increased from 40,766 cases (16.25%) in 2015 to 48,378 (19.50%) in 2023. MT usage rose even more sharply, from 7840 cases (3.13%) to 22,445 (9.05%). Among MT recipients, the proportion of patients aged ≥80 years rose significantly, from 27.2% to 42.1%. In this age group, women consistently comprised the majority of MT patients—65.4% in 2015 and 65.5% in 2023. Conclusions: Despite a stable stroke incidence, the use of IVT—and particularly MT—continued to increase in Germany from 2015 to 2023, even during the COVID-19 pandemic. MT usage nearly tripled, especially among patients aged ≥80 years. These trends highlight a resilient stroke care system and underscore the need for future planning to meet the rising demand for endovascular treatment in an aging population.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Management of Acute Stroke)
►▼
Show Figures
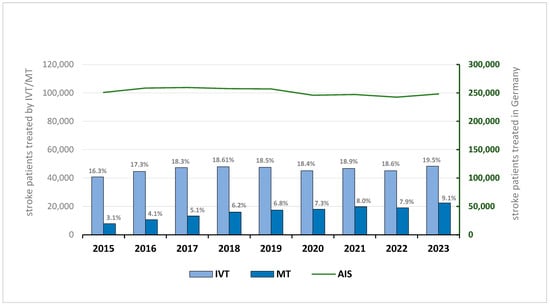
Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Advances in Research on Brain Structure and Activation Characteristics in Patients with Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: A Systematic Review
by
Jingyi Wang, Yaxiang Jia, Qiner Li, Longhui Li, Qiuyu Dong and Quan Fu
Brain Sci. 2025, 15(8), 831; https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15080831 (registering DOI) - 1 Aug 2025
Abstract
Objectives: To synthesize evidence on structural and functional neuroplasticity in patients after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction (ACLR) and its clinical implications. Methods: Adhering to the PRISMA guidelines for systematic reviews and meta-analyses, a literature search was conducted using PubMed, Embase, Web of
[...] Read more.
Objectives: To synthesize evidence on structural and functional neuroplasticity in patients after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction (ACLR) and its clinical implications. Methods: Adhering to the PRISMA guidelines for systematic reviews and meta-analyses, a literature search was conducted using PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, Scopus, and Cochrane CENTRAL (2018–2025) using specific keyword combinations, screening the results based on predetermined inclusion and exclusion criteria. Results: Among the 27 included studies were the following: (1) sensory cortex reorganization with compensatory visual dependence (5 EEG/fMRI studies); (2) reduced motor cortex efficiency evidenced by elevated AMT (TMS, 8 studies) and decreasedγ-CMC (EEG, 3 studies); (3) progressive corticospinal tract degeneration (increased radial diffusivity correlating with postoperative duration); (4) enhanced sensory-visual integration correlated with functional recovery. Conclusions: This review provides a novel synthesis of evidence from transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), electroencephalography (EEG), functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS), diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), and functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) studies. It delineates characteristic patterns of post-ACLR structural and functional neural reorganization. Targeting visual–cognitive integration and corticospinal facilitation may optimize rehabilitation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Diagnosis, Therapy and Rehabilitation in Neuromuscular Diseases)
Open AccessArticle
Transcranial Pulse Stimulation in Alzheimer’s: Long-Term Feasibility and a Multifocal Treatment Approach
by
Celine Cont-Richter, Nathalie Stute, Anastasia Galli, Christina Schulte and Lars Wojtecki
Brain Sci. 2025, 15(8), 830; https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15080830 (registering DOI) - 1 Aug 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Neuromodulation is under investigation as a possibly effective add-on therapy in Alzheimer’s disease (AD). While transcranial pulse stimulation (TPS) has shown positive short-term effects, long-term effects have not yet been fully explored. This study aims to evaluate the long-term feasibility, safety, and
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Neuromodulation is under investigation as a possibly effective add-on therapy in Alzheimer’s disease (AD). While transcranial pulse stimulation (TPS) has shown positive short-term effects, long-term effects have not yet been fully explored. This study aims to evaluate the long-term feasibility, safety, and potential cognitive benefits of TPS over one year in patients with Alzheimer’s disease, focusing on domains such as memory, speech, orientation, visuo-construction, and depressive symptoms. Methods: We analyzed preliminary data from the first ten out of thirty-five patients enrolled in a prospective TPS study who completed one year of follow-up and were included in a dedicated long-term database. The protocol consisted of six initial TPS sessions over two weeks, followed by monthly booster sessions delivering 6000 pulses each for twelve months. Patients underwent regular neuropsychological assessments using the Alzheimer Disease Assessment Scale (ADAS), Mini-Mental Status Examination (MMSE), Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA), and Beck Depression Inventory (BDI-II). All adverse events (AEs) were documented and monitored throughout the study. Results: Adverse events occurred in less than 1% of stimulation sessions and mainly included mild focal pain or transient unpleasant sensations, as well as some systemic behavioral or vigilance changes, particularly in patients with underlying medical conditions, with some potentially related to the device’s stimulation as adverse device reactions (ADRs). Cognitive test results showed significant improvement after the initial stimulation cycle (ADAS total improved significantly after the first stimulation cycle (M_pre = 28.44, M_post = 18.56; p = 0.001, d = 0.80, 95% CI (0.36, 1.25)), with stable scores across all domains over one year. Improvements were most notable in memory, speech, and mood. Conclusions: TPS appears to be a generally safe and feasible add-on treatment for AD, although careful patient selection and monitoring are advised. While a considerable number of participants were lost to follow-up for various reasons, adverse events and lack of treatment effect were unlikely primary causes. A multifocal stimulation approach (F-TOP2) is proposed to enhance effects across more cognitive domains.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Noninvasive Neuromodulation Applications in Research and Clinics)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Impact of Manganese on Neuronal Function: An Exploratory Multi-Omics Study on Ferroalloy Workers in Brescia, Italy
by
Somaiyeh Azmoun, Freeman C. Lewis, Daniel Shoieb, Yan Jin, Elena Colicino, Isha Mhatre-Winters, Haiwei Gu, Hari Krishnamurthy, Jason R. Richardson, Donatella Placidi, Luca Lambertini and Roberto G. Lucchini
Brain Sci. 2025, 15(8), 829; https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15080829 (registering DOI) - 31 Jul 2025
Abstract
Background: There is growing interest in the potential role of manganese (Mn) in the development of Alzheimer’s Disease and related dementias (ADRD). Methods: In this nested pilot study of a ferroalloy worker cohort, we investigated the impact of chronic occupational Mn exposure on
[...] Read more.
Background: There is growing interest in the potential role of manganese (Mn) in the development of Alzheimer’s Disease and related dementias (ADRD). Methods: In this nested pilot study of a ferroalloy worker cohort, we investigated the impact of chronic occupational Mn exposure on cognitive function through β-amyloid (Aβ) deposition and multi-omics profiling. We evaluated six male Mn-exposed workers (median age 63, exposure duration 31 years) and five historical controls (median age: 60 years), all of whom had undergone brain PET scans. Exposed individuals showed significantly higher Aβ deposition in exposed individuals (p < 0.05). The average annual cumulative respirable Mn was 329.23 ± 516.39 µg/m3 (geometric mean 118.59), and plasma Mn levels were significantly elevated in the exposed group (0.704 ± 0.2 ng/mL) compared to controls (0.397 ± 0.18 in controls). Results: LC-MS/MS-based pathway analyses revealed disruptions in olfactory signaling, mitochondrial fatty acid β-oxidation, biogenic amine synthesis, transmembrane transport, and choline metabolism. Simoa analysis showed notable alterations in ADRD-related plasma biomarkers. Protein microarray revealed significant differences (p < 0.05) in antibodies targeting neuronal and autoimmune proteins, including Aβ (25–35), GFAP, serotonin, NOVA1, and Siglec-1/CD169. Conclusion: These findings suggest Mn exposure is associated with neurodegenerative biomarker alterations and disrupted biological pathways relevant to cognitive decline.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue From Bench to Bedside: Motor–Cognitive Interactions—2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Effects of Handedness Consistency on the Identification of Own- and Cross-Race Faces
by
Raymond P. Voss, Jr., Ryan Corser, Stephen Prunier and John D. Jasper
Brain Sci. 2025, 15(8), 828; https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15080828 (registering DOI) - 31 Jul 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: People are better at recognizing the faces of racial in-group members than out-group members. This own-race bias relies on pattern recognition and memory processes, which rely on hemispheric specialization. We hypothesized that handedness, a proxy for hemispheric specialization, would moderate own-race
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: People are better at recognizing the faces of racial in-group members than out-group members. This own-race bias relies on pattern recognition and memory processes, which rely on hemispheric specialization. We hypothesized that handedness, a proxy for hemispheric specialization, would moderate own-race bias. Specifically, consistently handed individuals perform better on tasks that require the hemispheres to work independently, while inconsistently handed individuals perform better on tasks that require integration. This led to the hypothesis that inconsistently handed individuals would show less own-race bias, driven by an increase in accuracy. Methods: 281 participants completed the study in exchange for course credit. Of those, the sample was isolated to Caucasian (174) and African American individuals (41). Participants were shown two target faces (one Caucasian and one African American), given several distractor tasks, and then asked to identify the target faces during two sequential line-ups, each terminating when participants made an identification judgment. Results: Continuous handedness score and the match between participant race and target face race were entered into a binary logistic regression predicting correct/incorrect identifications. The overall model was statistically significant, Χ2 (3, N = 430) = 11.036, p = 0.012, Nagelkerke R2 = 0.038, culminating in 76% correct classifications. Analyses of the parameter estimates showed that the racial match, b = 0.53, SE = 0.23, Wald Χ2 (1) = 5.217, p = 0.022, OR = 1.703 and the interaction between handedness and the racial match, b = 0.51, SE = 0.23, Wald test = 4.813, p = 0.028, OR = 1.671 significantly contributed to the model. The model indicated that the probability of identification was similar for own- or cross-race targets amongst inconsistently handed individuals. Consistently handed individuals, by contrast, showed an increase in accuracy for the own-race target and a decrease in accuracy for cross-race targets. Conclusions: Results partially supported the hypotheses. Inconsistently handed individuals did show less own-race bias. This finding, however, seemed to be driven by differences in accuracy amongst consistently handed individuals rather than a hypothesized increase in accuracy amongst inconsistently handed individuals. Underlying hemispheric specialization, as measured by proxy with handedness, may impact the own-race bias in facial recognition. Future research is required to investigate the mechanisms, however, as the directional differences were different than hypothesized.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Face Perception and How Disorders Affect Face Perception)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Reinforcing Gaps? A Rapid Review of Innovation in Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) Treatment
by
Lionel Cailhol, Samuel St-Amour, Marie Désilets, Nadine Larivière, Jillian Mills and Rémy Klein
Brain Sci. 2025, 15(8), 827; https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15080827 (registering DOI) - 31 Jul 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) involves emotional dysregulation, interpersonal instability and impulsivity. Although treatments have advanced, evaluating the latest innovations remains essential. This rapid review aimed to (1) identify and classify recent therapeutic innovations for BPD, (2) assess their effects on clinical
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) involves emotional dysregulation, interpersonal instability and impulsivity. Although treatments have advanced, evaluating the latest innovations remains essential. This rapid review aimed to (1) identify and classify recent therapeutic innovations for BPD, (2) assess their effects on clinical and functional outcomes, and (3) highlight research gaps to inform future priorities. Methods: Employing a rapid review design, we searched PubMed/MEDLINE, PsycINFO, and Embase for publications from 1 January 2019 to 28 March 2025. Eligible studies addressed adult or adolescent BPD populations and novel interventions—psychotherapies, pharmacological agents, digital tools, and neuromodulation. Two independent reviewers conducted screening, full-text review, and data extraction using a standardised form. Results: Sixty-nine studies—predominantly from Europe and North America—were included. Psychotherapeutic programmes dominated, ranging from entirely novel models to adaptations of established treatments (for example, extended or modified Dialectical Behavior Therapy). Pharmacological research offered fresh insights, particularly into ketamine, while holistic approaches such as adventure therapy and digital interventions also emerged. Most investigations centred on symptom reduction; far fewer examined psychosocial functioning, mortality, or social inclusion. Conclusions: Recent innovations show promise in BPD treatment but underserve the needs of mortality and societal-level outcomes. Future research should adopt inclusive, equity-focused agendas that align with patient-centred and recovery-oriented goals, supported by a coordinated, integrated research strategy.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Neuropsychiatry)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessTechnical Note
Usefulness of Direct Auricular Artery Injection as Refinement of the Well-Established Rabbit Blood Shunt Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Model
by
Stefan Wanderer, Michael von Gunten, Daniela Casoni, Stefano Di Santo, Jürgen Konczalla and Ali-Reza Fathi
Brain Sci. 2025, 15(8), 826; https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15080826 (registering DOI) - 31 Jul 2025
Abstract
Introduction: Given the impact of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (aSAH) on patients’ health, preclinical research is substantial to understand its pathophysiology and improve treatment strategies, which necessitates reliable and comprehensive animal models. Traditionally, aSAH models utilize iliac or subclavian access for angiography, requiring invasive
[...] Read more.
Introduction: Given the impact of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (aSAH) on patients’ health, preclinical research is substantial to understand its pathophysiology and improve treatment strategies, which necessitates reliable and comprehensive animal models. Traditionally, aSAH models utilize iliac or subclavian access for angiography, requiring invasive procedures that are associated with significant risks and animal burden. This pilot study explores a less invasive method of digital subtraction angiography (DSA) by using the auricular artery (AA) as an alternative access point. Our aim was to demonstrate the feasibility of this refined technique, with the intention of reducing procedural risks, providing shorter operation times with enhanced neurological recovery, and simplifying the process for both researchers and animals. Materials and Methods: In this study, six female New Zealand white rabbits (3.2–4.1 kg body weight) underwent experimental induction of aSAH via a subclavian-cisternal shunt. The initial steps of this procedure followed traditional techniques, consisting of subclavian access through microsurgical preparation, followed by DSA to analyze retrograde filling of the basilar artery (BA). To evaluate the alternative method, on day 3 after induction of aSAH, DSA was performed via the AA instead of the traditional subclavian or femoral access. A catheter was placed in the AA to allow retrograde filling of the BA. This approach aimed to simplify the procedure while maintaining comparable imaging quality. Results: All rabbits survived until the study endpoint. Postoperatively, two rabbits showed signs of hemisyndrome, which significantly improved by the time of follow-up. No additional morbidities were observed. Upon euthanasia and necropsy, all animals showed clear subarachnoid bleeding patterns. DSA via the AA produced strong contrasting of the BA comparable to the traditional method. Conclusions: This technical note presents an initial evaluation of AA access as a feasible and potentially advantageous method for DSA in a rabbit model of blood shunt subarachnoid hemorrhage. The method shows promise in reducing invasiveness and procedural complexity, but further studies are required to fully establish its efficacy and safety. Future research should focus on expanding the sample size, refining the anatomical understanding of the AA, and continuing to align with ethical considerations regarding animal welfare.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Current Research in Neurosurgery)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
CSF1R-Dependent Microglial Repopulation and Contact-Dependent Inhibition of Proliferation In Vitro
by
Rie Nakai, Kuniko Kohyama, Yasumasa Nishito and Hiroshi Sakuma
Brain Sci. 2025, 15(8), 825; https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15080825 (registering DOI) - 31 Jul 2025
Abstract
Murine microglia exhibit rapid self-renewal upon removal from the postnatal brain. However, the signaling pathways that regulate microglial repopulation remain largely unclear. To address this knowledge gap, we depleted microglia from mixed glial cultures using anti-CD11b magnetic particles and cultured them for 4
[...] Read more.
Murine microglia exhibit rapid self-renewal upon removal from the postnatal brain. However, the signaling pathways that regulate microglial repopulation remain largely unclear. To address this knowledge gap, we depleted microglia from mixed glial cultures using anti-CD11b magnetic particles and cultured them for 4 weeks to monitor their repopulation ability in vitro. Flow cytometry and immunocytochemistry revealed that anti-CD11b bead treatment effectively eliminated >95% of microglia in mixed glial cultures. Following removal, the number of CX3CR1-positive microglia gradually increased; when a specific threshold was reached, repopulation ceased without any discernable rise in cell death. Cell cycle and 5-ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine incorporation assays suggested the active proliferation of repopulating microglia at d7. Time-lapse imaging demonstrated post-removal division of microglia. Colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor-phosphoinositide 3-kinase-protein kinase B signaling was identified as crucial for microglial repopulation, as pharmacological inhibition or neutralization of the pathway significantly abrogated repopulation. Transwell cocultures revealed that resident microglia competitively inhibited microglial proliferation probably through contact inhibition. This in vitro microglial removal system provides valuable insights into the mechanisms underlying microglial proliferation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Neuroglia)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessSystematic Review
Exploring the Autistic Brain: A Systematic Review of Diffusion Tensor Imaging Studies on Neural Connectivity in Autism Spectrum Disorder
by
Giuseppe Marano, Georgios D. Kotzalidis, Maria Benedetta Anesini, Sara Barbonetti, Sara Rossi, Miriam Milintenda, Antonio Restaino, Mariateresa Acanfora, Gianandrea Traversi, Giorgio Veneziani, Maria Picilli, Tommaso Callovini, Carlo Lai, Eugenio Maria Mercuri, Gabriele Sani and Marianna Mazza
Brain Sci. 2025, 15(8), 824; https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15080824 (registering DOI) - 31 Jul 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) has been extensively studied through neuroimaging, primarily focusing on grey matter and more in children than in adults. Studies in children and adolescents fail to capture changes that may dampen with age, thus leaving only changes specific
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) has been extensively studied through neuroimaging, primarily focusing on grey matter and more in children than in adults. Studies in children and adolescents fail to capture changes that may dampen with age, thus leaving only changes specific to ASD. While grey matter has been the primary focus, white matter (WM) may be more specific in identifying the particular biological signature of the neurodiversity of ASD. Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) is the more appropriate tool to investigate WM in ASD. Despite being introduced in 1994, its application to ASD research began in 2001. Studies employing DTI identify altered fractional anisotropy (FA), mean diffusivity, and radial diffusivity (RD) in individuals with ASD compared to typically developing (TD) individuals. Methods: We systematically reviewed literature on 21 May 2025 on PubMed using the following strategy: (“autism spectrum”[ti] OR autistic[ti] OR ASD[ti] OR “high-functioning autism” OR Asperger*[ti] OR Rett*[ti]) AND (DTI[ti] OR “diffusion tensor”[ti] OR multimodal[ti] OR “white matter”[ti] OR tractograph*[ti]). Our search yielded 239 results, of which 26 were adult human studies and eligible. Results: Analysing the evidence, we obtained regionally diverse WM alterations in adult ASD, specifically in FA, MD, RD, axial diffusivity and kurtosis, neurite density, and orientation dispersion index, compared to TD individuals, mostly in frontal and interhemispheric tracts, association fibres, and subcortical projection pathways. These alterations were less prominent than those of children and adolescents, indicating that individuals with ASD may improve during brain maturation. Conclusions: Our findings suggest that white matter alterations in adults with ASD are regionally diverse but generally less pronounced than in younger populations. This may indicate a potential improvement or adaptation of brain structure during maturation. Further research is needed to clarify the neurobiological mechanisms underlying these changes and their implications for clinical outcomes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Chronic Non-Infectious Diseases with a High Impact on the Central Nervous System)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Combining Coronal and Axial DWI for Accurate Diagnosis of Brainstem Ischemic Strokes: Volume-Based Correlation with Stroke Severity
by
Omar Alhaj Omar, Mesut Yenigün, Farzat Alchayah, Priyanka Boettger, Francesca Culaj, Toska Maxhuni, Norma J. Diel, Stefan T. Gerner, Maxime Viard, Hagen B. Huttner, Martin Juenemann, Julia Heinrichs and Tobias Braun
Brain Sci. 2025, 15(8), 823; https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15080823 (registering DOI) - 31 Jul 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Brainstem ischemic strokes comprise 10% of ischemic strokes and are challenging to diagnose due to small lesion size and complex presentations. Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) is crucial for detecting ischemia, yet it can miss small lesions, especially when only axial slices are employed.
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Brainstem ischemic strokes comprise 10% of ischemic strokes and are challenging to diagnose due to small lesion size and complex presentations. Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) is crucial for detecting ischemia, yet it can miss small lesions, especially when only axial slices are employed. This study investigated whether ischemic lesions visible in a single imaging plane correspond to smaller volumes and whether coronal DWI enhances detection compared to axial DWI alone. Methods: This retrospective single-center study examined 134 patients with brainstem ischemic strokes between December 2018 and November 2023. All patients underwent axial and coronal DWI. Clinical data, NIH Stroke Scale (NIHSS) scores, and modified Rankin Scale (mRS) scores were recorded. Diffusion-restricted lesion volumes were calculated using multiple models (planimetric, ellipsoid, and spherical), and lesion visibility per imaging plane was analyzed. Results: Brainstem ischemic strokes were detected in 85.8% of patients. Coronal DWI alone identified 6% of lesions that were undetectable on axial DWI; meanwhile, axial DWI alone identified 6.7%. Combining both improved overall sensitivity to 86.6%. Ischemic lesions visible in only one plane were significantly smaller across all volume models. Higher NIHSS scores were strongly correlated with larger diffusion-restricted lesion volumes. Coronal DWI correlated better with clinical severity than axial DWI, especially in the midbrain and medulla. Conclusions: Coronal DWI significantly improves the detection of small brainstem infarcts and should be incorporated into routine stroke imaging protocols. Infarcts visible in only one plane are typically smaller, yet still clinically relevant. Combined imaging enhances diagnostic accuracy and supports early and precise intervention in posterior circulation strokes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Management of Acute Stroke)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Synergistic Effect of Heat Therapy and Electroacupuncture Treatment in Inflammatory Pain Mouse Models
by
Boon Khai Teoh, Sharmely Sharon Ballon Romero, Tran Van Bao Quach, Hsin-Yi Chung and Yi-Hung Chen
Brain Sci. 2025, 15(8), 822; https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15080822 (registering DOI) - 31 Jul 2025
Abstract
Background: Heat therapy (HT) and electroacupuncture (EA) are widely utilized pain relief methods, but the analgesic mechanisms of their combined application remain unclear. Methods: In acetic acid (AA)-induced writhing test and complete Freund’s adjuvant (CFA)-induced inflammatory pain tests, mice received one of three
[...] Read more.
Background: Heat therapy (HT) and electroacupuncture (EA) are widely utilized pain relief methods, but the analgesic mechanisms of their combined application remain unclear. Methods: In acetic acid (AA)-induced writhing test and complete Freund’s adjuvant (CFA)-induced inflammatory pain tests, mice received one of three treatments: EA at bilateral ST36, HT via a 45 °C heating pad, or the combination (EA + HT). To probe underlying pathways, separate groups were pretreated with caffeine, DPCPX (a selective adenosine A1 receptor antagonist), or naloxone (an opioid receptor antagonist). Spinal expression of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and phosphorylated p38 (p-p38) was examined by Western blot and immunofluorescence. Results: Both EA and HT individually reduced AA-induced writhing, with the combination (EA + HT) exhibiting the greatest analgesic effect. EA’s analgesic effect was reversed by caffeine and DPCPX and partially by naloxone, while HT’s effect was reversed by caffeine and DPCPX but was unaffected by naloxone. AA injection elevated spinal p-p38 and GFAP expression, which were attenuated by either EA or HT, with the most substantial suppression observed in the EA + HT group. In the CFA model, both treatments alleviated mechanical allodynia, while the combined treatment resulted in significantly greater analgesia compared to either treatment alone. Conclusions: EA combined with HT synergistically enhances analgesia in both AA and CFA pain models, accompanied by reduced spinal inflammation and astrocyte activation. EA’s analgesic effects appear to involve adenosine A1 receptor pathways and, to a lesser extent, opioid receptor mechanisms, whereas HT’s effects involve adenosine A1 receptor pathways.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Application of Nerve Stimulation: Current Status and Future Directions—2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
AI-Assisted Edema Map Optimization Improves Infarction Detection in Twin-Spiral Dual-Energy CT
by
Ludwig Singer, Daniel Heinze, Tim Alexius Möhle, Alexander Sekita, Angelika Mennecke, Stefan Lang, Stefan T. Gerner, Stefan Schwab, Arnd Dörfler and Manuel Alexander Schmidt
Brain Sci. 2025, 15(8), 821; https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15080821 (registering DOI) - 31 Jul 2025
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to evaluate whether modifying the post-processing algorithm of Twin-Spiral Dual-Energy computed tomography (DECT) improves infarct detection compared to conventional Dual-Energy CT (DECT) and Single-Energy CT (SECT) following endovascular therapy (EVT) for large vessel occlusion (LVO). Methods: We retrospectively analyzed
[...] Read more.
Objective: This study aimed to evaluate whether modifying the post-processing algorithm of Twin-Spiral Dual-Energy computed tomography (DECT) improves infarct detection compared to conventional Dual-Energy CT (DECT) and Single-Energy CT (SECT) following endovascular therapy (EVT) for large vessel occlusion (LVO). Methods: We retrospectively analyzed 52 patients who underwent Twin-Spiral DECT after endovascular stroke therapy. Ten patients were used to generate a device-specific parameter (“y”) using an AI-based neural network (SynthSR). This parameter was integrated into the post-processing algorithm for edema map generation. Quantitative Hounsfield unit (HU) measurements were used to assess density differences in ischemic brain tissue across conventional virtual non-contrast (VNC) images and edema maps. Results: The median HU of infarcted tissue in conventional mixed DECT was 33.73 ± 4.58, compared to 22.96 ± 3.81 in default VNC images. Edema maps with different smoothing filter settings showed values of 14.39 ± 4.96, 14.50 ± 3.75, and 15.05 ± 2.65, respectively. All edema maps demonstrated statistically significant HU differences of infarcted tissue compared to conventional VNC images (
(This article belongs to the Section Neurotechnology and Neuroimaging)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Musical Distractions: Music-Based Rhythmic Auditory Stimulation Fails to Improve Gait in Huntington’s Disease
by
Sidney T. Baudendistel, Lauren E. Tueth, Allison M. Haussler and Gammon M. Earhart
Brain Sci. 2025, 15(8), 820; https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15080820 (registering DOI) - 31 Jul 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Huntington’s disease (HD) is a neurodegenerative disorder involving the basal ganglia and is characterized by psychiatric, cognitive, and movement dysfunction, including gait and balance impairment. Given the limited efficacy of pharmacological treatments for HD motor symptoms, nonpharmacological approaches like rhythmic auditory stimulation
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Huntington’s disease (HD) is a neurodegenerative disorder involving the basal ganglia and is characterized by psychiatric, cognitive, and movement dysfunction, including gait and balance impairment. Given the limited efficacy of pharmacological treatments for HD motor symptoms, nonpharmacological approaches like rhythmic auditory stimulation are being explored. This study aims to describe walking performance in people with HD during rhythmic auditory stimulation using external musical cues and internal singing cues. Methods: Individuals in the manifest stage of HD performed walking in four conditions: (1) comfortable pace, (2) cognitive dual task, (3) musical cue (music was played aloud), and (4) singing cue (participants sang aloud). Sensors measured cadence, velocity, stride length, and variability. Relationships between change in cadence and motor and cognitive measures were explored. Results: While no direct measurements of synchronization were performed, limiting our interpretation, neither the external musical cue nor the singing cue significantly improved walking performance. Both cues increased variability, similar to what was observed during the dual task. Greater subjective balance confidence and better cognitive performance were associated with positive cadence change during cueing. Conclusions: Musical cues may be too cognitively demanding for individuals with Huntington’s disease as they worsen gait variability without increasing gait speed, cadence, or stride length. Although global cognition and perceived balance confidence were related to the ability to increase cadence, very few people were able to increase their cadence during either cue. Therefore, the results do not support the use of musical cues to improve gait for individuals with Huntington’s disease.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Focusing on the Rhythmic Interventions in Movement Disorders)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Timing of Intervals Between Utterances in Typically Developing Infants and Infants Later Diagnosed with Autism Spectrum Disorder
by
Zahra Poursoroush, Gordon Ramsay, Ching-Chi Yang, Eugene H. Buder, Edina R. Bene, Pumpki Lei Su, Hyunjoo Yoo, Helen L. Long, Cheryl Klaiman, Moira L. Pileggi, Natalie Brane and D. Kimbrough Oller
Brain Sci. 2025, 15(8), 819; https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15080819 (registering DOI) - 30 Jul 2025
Abstract
Background: Understanding the origin and natural organization of early infant vocalizations is important for predicting communication and language abilities in later years. The very frequent production of speech-like vocalizations (hereafter “protophones”), occurring largely independently of interaction, is part of this developmental process. Objectives:
[...] Read more.
Background: Understanding the origin and natural organization of early infant vocalizations is important for predicting communication and language abilities in later years. The very frequent production of speech-like vocalizations (hereafter “protophones”), occurring largely independently of interaction, is part of this developmental process. Objectives: This study aims to investigate the gap durations (time intervals) between protophones, comparing typically developing (TD) infants and infants later diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in a naturalistic setting where endogenous protophones occur frequently. Additionally, we explore potential age-related variations and sex differences in gap durations. Methods: We analyzed ~1500 five min recording segments from longitudinal all-day home recordings of 147 infants (103 TD infants and 44 autistic infants) during their first year of life. The data included over 90,000 infant protophones. Human coding was employed to ensure maximally accurate timing data. This method included the human judgment of gap durations specified based on time-domain and spectrographic displays. Results and Conclusions: Short gap durations occurred between protophones produced by infants, with a mode between 301 and 400 ms, roughly the length of an infant syllable, across all diagnoses, sex, and age groups. However, we found significant differences in the gap duration distributions between ASD and TD groups when infant-directed speech (IDS) was relatively frequent, as well as across age groups and sexes. The Generalized Linear Modeling (GLM) results confirmed these findings and revealed longer gap durations associated with higher IDS, female sex, older age, and TD diagnosis. Age-related differences and sex differences were highly significant for both diagnosis groups.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Biomarker Development in the Early Identification of Autism Spectrum Disorders)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Gender Moderates the Neural Impact of Problematic Media Use on Working Memory in Preschoolers: An fNIRS Study
by
Keya Ding, Xinyi Dong, Yu Xue and Hui Li
Brain Sci. 2025, 15(8), 818; https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15080818 - 30 Jul 2025
Abstract
Background: This study investigated the relationship between problematic media use (PMU) and working memory in preschoolers. Methods: Parents of children aged 3 to 7 (260 boys, 257 girls; Mage = 5.57, SD = 0.73) in Jinan, China, completed questionnaires assessing children’s PMU
[...] Read more.
Background: This study investigated the relationship between problematic media use (PMU) and working memory in preschoolers. Methods: Parents of children aged 3 to 7 (260 boys, 257 girls; Mage = 5.57, SD = 0.73) in Jinan, China, completed questionnaires assessing children’s PMU and working memory. Subsequently, High (nhigh = 32, Mage = 4.53, SD = 0.67) and Low (nlow = 30, Mage = 4.67, SD = 0.66) PMU groups, based on the survey data, complete a dual 1-back task during functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) recording. Results: Behavioral accuracy and reaction time showed no significant group differences. However, a significant interaction between the PMU group and gender on prefrontal activation was observed, F(1, 60) = 5.88–7.59, ps < 0.05, ηp2 = 0.09–0.12. High-PMU boys exhibited greater left prefrontal activation than low-PMU boys, while low-PMU girls showed greater activation in these same areas compared to low-PMU boys. A three-way interaction of group, task condition, and gender on prefrontal activation was also found, F(2, 60) = 5.81–6.42, p < 0.01, ηp2 = 0.10–0.19, suggesting that neural responses varied by task and participant characteristics. Conclusions: These findings indicate that PMU may be associated with altered prefrontal activation during working memory tasks in preschoolers, with gender playing a moderating role.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Developmental Neuroscience)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessCorrection
Correction: Wayland et al. Lenition in L2 Spanish: The Impact of Study Abroad on Phonological Acquisition. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 946
by
Ratree Wayland, Rachel Meyer, Sophia Vellozzi and Kevin Tang
Brain Sci. 2025, 15(8), 817; https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15080817 - 30 Jul 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In the original publication [...]
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
The Effect of Mental Health First Aid Training on Pharmacist and Pharmacy Student Confidence and Knowledge: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
by
David Frond, Shannon Habba, Brittany Stewart and Kyle J. Burghardt
Brain Sci. 2025, 15(8), 816; https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15080816 - 29 Jul 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Pharmacists are highly accessible healthcare providers who have frequent, repeated contact with diverse patient populations. They are poised to offer expanded and comprehensive healthcare, including mental health services. One potential barrier to this is a lack of knowledge, confidence, or training in
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Pharmacists are highly accessible healthcare providers who have frequent, repeated contact with diverse patient populations. They are poised to offer expanded and comprehensive healthcare, including mental health services. One potential barrier to this is a lack of knowledge, confidence, or training in mental health, which may be overcome with a program like Mental Health First Aid (MHFA) training. The aim of this systematic review and meta-analysis is to fill this gap in knowledge by critically evaluating all studies of MHFA training for pharmacists or pharmacy students that report on knowledge, attitudes, or self-efficacy outcomes. Methods: A systematic review was performed to identify all relevant studies. Data was extracted and a random-effects meta-analysis was performed for knowledge and attitudes/self-efficacy outcomes, respectively. Subgroup analyses were performed based on survey question type, geographic location, and population studied. Results: Overall, MHFA training significantly increased pharmacists’ and pharmacy students’ knowledge (Hedges’ g = 0.228) and combined attitudinal/self-efficacy measures (Hedges’ g = 0.376). Subgroup analyses based on question type, study quality, design, population studied, and location showed similar, significant effects. Conclusions: MHFA training appears to have significant effects on pharmacist and pharmacy student knowledge, attitudes, and self-efficacy. Future work should establish the durability of these effects.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Pharmacy and Mental Health)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Fear Detection Using Electroencephalogram and Artificial Intelligence: A Systematic Review
by
Bladimir Serna, Ricardo Salazar, Gustavo A. Alonso-Silverio, Rosario Baltazar, Elías Ventura-Molina and Antonio Alarcón-Paredes
Brain Sci. 2025, 15(8), 815; https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15080815 - 29 Jul 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Fear detection through EEG signals has gained increasing attention due to its applications in affective computing, mental health monitoring, and intelligent safety systems. This systematic review aimed to identify the most effective methods, algorithms, and configurations reported in the literature for detecting
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Fear detection through EEG signals has gained increasing attention due to its applications in affective computing, mental health monitoring, and intelligent safety systems. This systematic review aimed to identify the most effective methods, algorithms, and configurations reported in the literature for detecting fear from EEG signals using artificial intelligence (AI). Methods: Following the PRISMA 2020 methodology, a structured search was conducted using the string (“fear detection” AND “artificial intelligence” OR “machine learning” AND NOT “fnirs OR mri OR ct OR pet OR image”). After applying inclusion and exclusion criteria, 11 relevant studies were selected. Results: The review examined key methodological aspects such as algorithms (e.g., SVM, CNN, Decision Trees), EEG devices (Emotiv, Biosemi), experimental paradigms (videos, interactive games), dominant brainwave bands (beta, gamma, alpha), and electrode placement. Non-linear models, particularly when combined with immersive stimulation, achieved the highest classification accuracy (up to 92%). Beta and gamma frequencies were consistently associated with fear states, while frontotemporal electrode positioning and proprietary datasets further enhanced model performance. Conclusions: EEG-based fear detection using AI demonstrates high potential and rapid growth, offering significant interdisciplinary applications in healthcare, safety systems, and affective computing.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Neuropeptides, Behavior and Psychiatric Disorders)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Brain Sciences Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Behavioral Sciences, Brain Sciences, Children, Education Sciences
Risk and Protective Factors in Social Interactions: Behavioral and Neural Evidence
Topic Editors: Xuechen Ding, Wan Ding, Liyang SaiDeadline: 1 September 2025
Topic in
JCM, Diagnostics, JPM, Brain Sciences, JVD
Diagnosis and Management of Acute Ischemic Stroke
Topic Editors: Hyo Suk Nam, Byung Moon Kim, Tae-jin Song, Minho HanDeadline: 20 September 2025
Topic in
Brain Sciences, Neurology International, NeuroSci
Management of Multiple Sclerosis: Past, Present and Promise
Topic Editors: Salvatore Iacono, Paolo RagoneseDeadline: 5 November 2025
Topic in
Brain Sciences, CIMB, Epigenomes, Genes, IJMS, DNA
Genetics and Epigenetics of Substance Use Disorders
Topic Editors: Aleksandra Suchanecka, Anna Maria Grzywacz, Kszysztof ChmielowiecDeadline: 15 November 2025

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Brain Sciences
The Latest Exploration of Gaming Disorders and Related Mental Health Issues
Guest Editors: Masaru Tateno, Takanobu MatsuzakiDeadline: 8 August 2025
Special Issue in
Brain Sciences
Latest Research on the Treatments of Speech and Language Disorders
Guest Editors: Jubin Abutalebi, Mehdi BakhtiarDeadline: 10 August 2025
Special Issue in
Brain Sciences
The Role and Research Progress of Neuroinflammation in Neurodegenerative Diseases
Guest Editors: Flavio Veras, Bruno Marcel Silva de MeloDeadline: 15 August 2025
Special Issue in
Brain Sciences
Current Basic and Clinical Approaches in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Diagnostics and Therapeutics
Guest Editors: Genaro G. Ortiz, Gloria A. Benítez-KingDeadline: 15 August 2025
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Brain Sciences
Nonmotor Symptoms in Parkinson's Disease (PD)
Collection Editor: Andrea Loftus
Topical Collection in
Brain Sciences
Collection on Systems Neuroscience
Collection Editor: Konstantin V. Slavin
Topical Collection in
Brain Sciences
Human Ultrasound Neuromodulation: State of the Art
Collection Editor: Roland Beisteiner
Topical Collection in
Brain Sciences
Visuospatial Function in Early Alzheimer’s Disease, Healthy Elderly and MCI People
Collection Editor: Tina Iachini










