- Article
Clinical Efficacy, Cost-Effectiveness, and Caregiver Satisfaction in Clinical Practice Compared to Standard Care: 12-Month Longitudinal Analysis of the Application of Parkinson’s KinetiGraph
- Vinod Metta,
- Huzaifa Ibrahim and
- Kallol Ray Chaudhuri
- + 13 authors
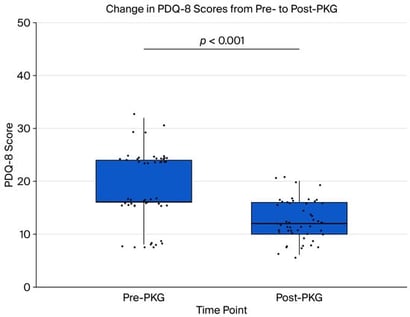
Background: Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder marked by both motor and non-motor symptoms. The home-based wearable sensor monitoring Parkinson’s KinetiGraph (PKG) evaluates clinical efficacy, caregiver satisfaction, and cost-effectiveness in the clinical management of Parkinson’s disease (PD) compared to prior usual standard care. Methods: We analyzed 50 patients with Parkinson’s disease, comparing baseline clinical outcomes, healthcare utilization, and caregiver burden without PKG to follow-up data after 12 months with PKG. We used IBM SPSS Statistics for the analysis. Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05 for hypothesis testing. We employed the Wilcoxon signed-rank test to evaluate differences between the two time points, while exploratory bivariate associations between caregiver burden (Zarit score) and various outcomes were examined using Spearman’s rank correlation. Results: Over a 12-month period following the implementation of PKG-guided care, significant improvements were observed in various clinical, functional, and economic areas for the patients. Key findings include the following: motor function improved, with UPDRS Part III scores showing a 20% median reduction (from 25 to 20); medication adjustments decreased by 40% (from 5 to 3); outpatient visits were reduced by 60% (from 5 to 2); hospital admissions decreased by 100% (from 1 to 0); caregiver burden, as measured using the Zarit caregiver burden score, declined by 37.5% (from 48 to 30); and total direct medical costs decreased by 17.9% (from AED 261,800 to AED 215,000). Conclusions: These findings indicate substantial reductions in healthcare utilization, costs, and caregiver burden following the integration of PKG monitoring into clinical practice.
3 February 2026