- Case Report
Transcutaneous Spinal Cord Stimulation Improves Upper and Lower Limbs’ Motor and Sensory Function in a Subject with Central Cord Syndrome: A Case Report
- Fernando Reyes,
- Camila Parker and
- Carlos A. Cuellar
- + 6 authors
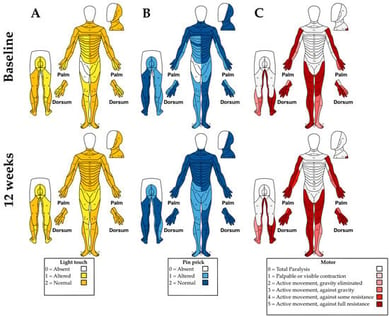
Background: Central cord syndrome (CCS) is the most common incomplete spinal cord injury, producing more severe motor deficits in the upper than lower extremities and impairing sensory and autonomic function. Although transcutaneous spinal cord stimulation (tSCS) has shown benefits in motor and sensory recovery after spinal cord injury, studies have not explicitly documented whether CCS subjects were included. The aim of this study was to assess the effects of tSCS over 12 weeks on motor and sensory outcomes in a subject with CCS. Methods: A 20-year-old male with a C7 injury was evaluated at baseline and after 12 weeks with the American Spinal Cord Injury Impairment scale, Modified Ashworth Scale, Penn and Spasm Frequency Scale, 3-Meter Walk Test and 6-Minute Walk Test, 9-Hole Peg Test, Box and Block Test, hand dynamometry, and lower-limb EMG. tSCS was applied between T9 and L1 at 30 Hz. Results: At 12 weeks, upper-limb motor and sensory scores improved, while spasm frequency and hand spasticity were reduced. Manual dexterity improved bilaterally in the 9-Hole Peg and Box and Block Tests, with a 2 kg gain in right-hand grip strength. In the 6-Minute Walk Test, the distance covered increased from 224.4 m to 295.2 m, and a 1.36 s reduction in 3-Meter walking time was achieved. Conclusions: tSCS improved motor and sensory function and reduced spasticity and spasms. These findings suggest that tSCS may serve as an effective complementary intervention for motor and sensory rehabilitation in individuals with mild cervical injuries, including CCS.
10 February 2026