Journal Description
Clocks & Sleep
Clocks & Sleep
is a peer-reviewed, open access journal that investigates a wide range of sleep related topics and is published quarterly online by MDPI. The Australasian Chronobiology Society, Society for Light, Rhythms, and Circadian Health, and Swiss Society of Sleep Research, Sleep Medicine and Chronobiology are affiliated with Clocks & Sleep and their society members receive a discount on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High visibility: indexed within Scopus, ESCI (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, FSTA, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: CiteScore - Q2 (Neuroscience (miscellaneous))
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 27.8 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 3.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Journal Cluster of Neurosciences: Brain Sciences, Neurology International, NeuroSci, Clinical and Translational Neuroscience, Neuroglia, Psychiatry International, Clocks & Sleep and Journal of Dementia and Alzheimer's Disease.
Impact Factor:
2.1 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.5 (2024)
Latest Articles
Prevalence of Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Adherence to CPAP for TAXI Drivers
Clocks & Sleep 2026, 8(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep8010004 - 7 Jan 2026
Abstract
We investigated the effects of Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) on blood pressure (BP) and vigilance in taxi drivers with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). This pilot study recruited taxi drivers aged ≥60 years to undergo polysomnography. Those diagnosed with OSA underwent 6 months
[...] Read more.
We investigated the effects of Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) on blood pressure (BP) and vigilance in taxi drivers with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). This pilot study recruited taxi drivers aged ≥60 years to undergo polysomnography. Those diagnosed with OSA underwent 6 months of CPAP therapy. Baseline and follow-up assessments included 24 h ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) and the psychomotor vigilance test (PVT). Among the 32 participants, 22 (68.8%) were diagnosed with OSA (median age 63.0 [62.0–65.0] years; 21 males). The average CPAP adherence was 3.1 ± 2.3 h per night, with 23.5% using CPAP for more than 4 h per night. There were no significant changes in 24 h mean systolic ABPM (125.9 [116.8–134.9] mmHg to 126.0 [118.3–133.7] mmHg; p = 0.93) or reaction times measured by PVT (2.0 [0.0–3.0] lapses to 2.0 [1.0–3.0] lapses; p = 0.82) after CPAP therapy. A high prevalence of OSA was observed among taxi drivers. CPAP adherence was suboptimal and did not result in significant improvements in BP or vigilance.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Disorders)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
People Living in Places with Limited Illuminance Declare Better Health and Higher Quality of Life in Environmental and Physical Domains
by
Jolanta Malinowska-Borowska, Anna Czupryna, Marta Buczkowska and Aleksandra Kulik
Clocks & Sleep 2026, 8(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep8010003 - 5 Jan 2026
Abstract
Background. Exposure to artificial light at night can lead to circadian disruption and health risks. It can cause mood swings, confusion, and depression. The aim of this cross-sectional study was to assess the relationship between the illuminance of urban lighting and the health
[...] Read more.
Background. Exposure to artificial light at night can lead to circadian disruption and health risks. It can cause mood swings, confusion, and depression. The aim of this cross-sectional study was to assess the relationship between the illuminance of urban lighting and the health of residents. Methods: This study was carried out among residents of two similar towns, one with typical street lighting and a Dark Sky Park characterized by reduced lighting. A total of 272 respondents participated in this study. A self-administered questionnaire and the WHOQOL-BREF were used among the respondents. Results. People living in the Dark Sky Park were more likely to be satisfied with their sleep (p < 0.001). In fact, 58.7% of Dark Sky Park residents reported no sleep problems. In the control town, only 49.25% did (p = 0.04). The sleep duration was similar in the two towns, but Dark Sky Park residents were statistically less likely to use sleeping pills and window blinds. People exposed to typical street lighting at night reported suffering from eye diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and mood changes more often than those living in the Dark Sky Park. The environmental and physical quality of life, as measured by the WHOQOL-BREF, were significantly higher in the Dark Sky Park residents than in the control town (p < 0.05). Conclusions. People living in places with limited illuminance declare better health and a higher quality of life in the physical and environmental domains.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Impact of Light & other Zeitgebers)
Open AccessConference Report
Thirty-Sixth Annual Meeting of the Society for Light, Rhythms, and Circadian Health (SLRCH), 14–16 June, Boston, MA, USA
by
Corrado Garbazza
Clocks & Sleep 2026, 8(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep8010002 - 31 Dec 2025
Abstract
It is my pleasure to present this collection of abstracts from the 36th Annual Meeting of the Society for Light, Rhythms, and Circadian Health (SLRCH), held in Boston, Massachusetts, at Simmons University and Brigham and Women’s Hospital [...]
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Human Basic Research & Neuroimaging)
Open AccessReview
Late-Night Feeding, Sleep Disturbance, and Nocturnal Congestion Mediated by Hyperglycemia, Renal Sodium Retention, and Cortisol: A Narrative Review
by
Ronald B. Brown
Clocks & Sleep 2026, 8(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep8010001 - 24 Dec 2025
Abstract
Late-night feeding, defined in the present review as feeding after 8:00 pm when evening insulin secretion and sensitivity are low, is increasingly prevalent in Western society and is recognized as a disruptor of metabolic homeostasis. Yet health problems related to late-night feeding are
[...] Read more.
Late-night feeding, defined in the present review as feeding after 8:00 pm when evening insulin secretion and sensitivity are low, is increasingly prevalent in Western society and is recognized as a disruptor of metabolic homeostasis. Yet health problems related to late-night feeding are largely ignored in time-restricted feeding studies that generally do not extend past an 8:00 pm feeding window. This paper proposes a novel cascade linking late-night hyperglycemia with sleep disturbances and nasal congestion mediated by renal sodium retention, increased plasma osmolarity, and stress hormone release by hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis activation. The narrative describes the circadian decline in insulin sensitivity, which amplifies postprandial glucose surges following late-night feeding. Elevated glucose levels drive renal glucose reabsorption via sodium–glucose cotransporters, promoting sodium retention independent of insulin. Increased sodium retention raises extracellular osmolarity, activating hypothalamic osmoreceptors and stimulating the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis. Cortisol release promotes alertness, while fluid retention and mucosal edema contribute to nasal congestion and early waking. Supine fluid redistribution during sleep further exacerbates airway narrowing, increasing the risk of sleep fragmentation and obstructive sleep apnea. The present paper fills a gap in current time-restricted feeding literature by integrating renal, osmotic, and neuroendocrine pathways that may be overlooked as underlying mechanisms of dysregulated glucose control and hormone dysfunction. Reviewed evidence suggests that symptoms such as nocturnal congestion and sleep disruption are not merely incidental to late-night feeding but frame late night feeding as a risk factor with underlying physiological stressors that could contribute to cardiometabolic risk.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Human Basic Research & Neuroimaging)
►▼
Show Figures
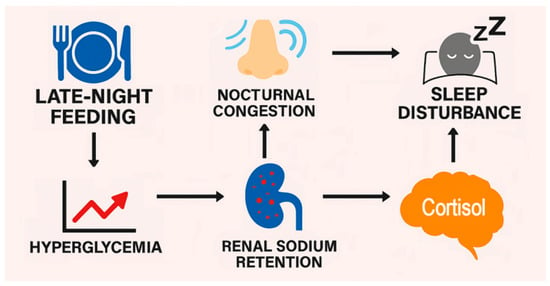
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Designing Infant Mattresses Tailored to Developmental Sleep Characteristics: A Comprehensive Review
by
Yasunori Oka, Akiko Tange and Yuki Maeda
Clocks & Sleep 2025, 7(4), 70; https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep7040070 - 8 Dec 2025
Abstract
This paper reviews existing research on infant mattress design to promote safe and comfortable sleep and proposes evidence-based design recommendations. Focusing on safety related to Sudden Unexpected Infant Death (SUID) and comfort associated with infant development and thermoregulation, we examine mattress firmness, pressure
[...] Read more.
This paper reviews existing research on infant mattress design to promote safe and comfortable sleep and proposes evidence-based design recommendations. Focusing on safety related to Sudden Unexpected Infant Death (SUID) and comfort associated with infant development and thermoregulation, we examine mattress firmness, pressure distribution, breathability, and thermal properties. Since infants have difficulty turning over and possess immature thermoregulatory functions, mattress characteristics directly influence sleep quality and safety. Based on international studies, we clarify the requirements for infant mattresses and provide insights into future product development and evaluation standards.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Circadian Rhythm Research in Infants and Young Children)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Effects of Digital Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia on Self-Reported Sleep Parameters: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
by
Ingrid Porto Araújo Leite, Viviane Akemi Kakazu, Lucca Andrade Teixeira de Carvalho, Sergio Tufik and Gabriel Natan Pires
Clocks & Sleep 2025, 7(4), 69; https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep7040069 - 8 Dec 2025
Abstract
Digital Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (dCBT-I) is an effective alternative to therapist-delivered CBT-I. However, there is a lack of meta-analyses assessing its effects on other sleep-related outcomes. We aimed to conduct a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) evaluating dCBT-I in adults
[...] Read more.
Digital Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (dCBT-I) is an effective alternative to therapist-delivered CBT-I. However, there is a lack of meta-analyses assessing its effects on other sleep-related outcomes. We aimed to conduct a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) evaluating dCBT-I in adults with insomnia through polysomnography (PSG) and sleep diary. Systematic searches were performed in PubMed and Web of Science. The outcomes considered were total sleep time (TST), sleep onset latency (SOL), sleep efficiency (SE), wake after sleep onset (WASO), and number of awakenings (NWAK). Meta-analyses were performed using random-effects models to compare dCBT-I with active (in-person or telehealth CBT-I) or inactive (waiting list, no treatment, or minimal intervention) control groups. Of the fourteen RCTs included, only three employed an active control. As no trials used PSG, the analyses relied solely on sleep diary data. DCBT-I showed no statistically significant differences from active controls, indicating comparable effects with therapist-delivered CBT-I. In contrast, it demonstrated statistically significant effects against inactive controls; TST increased by 0.20 h, SOL decreased by 15.53 min, SE improved by 7.91%, WASO reduced by 15.61 min, and NWAK decreased by 0.53. Future research should prioritize comparisons with therapist-delivered CBT-I and incorporate PSG for measuring these parameters.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Disorders)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Anticipation of Stress and Relaxation Dynamically Impacts Sleep
by
Sandrine Baselgia, Jonas Beck and Björn Rasch
Clocks & Sleep 2025, 7(4), 68; https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep7040068 - 3 Dec 2025
Abstract
Anticipation of stressful events can impair sleep quality. In a recent study, we reported that anticipating a stressful task before a nap led to negative changes in sleep parameters, particularly at the end of the nap. In our previous study, we compared stress
[...] Read more.
Anticipation of stressful events can impair sleep quality. In a recent study, we reported that anticipating a stressful task before a nap led to negative changes in sleep parameters, particularly at the end of the nap. In our previous study, we compared stress anticipation with the anticipation of relaxation; thus, the observed effects may have been amplified by sleep quality improvements in the relaxation condition. In the current study, we aimed to replicate these findings using an alternative neutral control condition. The data from a newly collected sample (n = 31) were compared with the data from our previous study (n = 33) using identical analyses. The results reveal an opposite pattern from our previous study: participants in the neutral control condition showed poorer sleep (longer sleep onset latency, reduced slow-wave sleep, and lower SWA/beta ratio) compared to those anticipating stress. In a direct comparison of both studies, sleep parameters in the stress conditions were highly similar across the two studies, suggesting that the divergent outcomes are driven by differences in the control conditions. The temporal dynamic changes observed in our previous study could not be replicated. These findings highlight the importance of carefully considering control conditions in experimental sleep research and suggest that even “neutral” instructions can evoke anticipatory effects. Moreover, the observed benefits of anticipating post-sleep relaxation highlight opportunities for relaxation-based interventions to improve sleep quality.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Human Basic Research & Neuroimaging)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Estimation of the Circadian Phase Difference in Weekend Sleep and Further Evidence for Our Failure to Sleep More on Weekends to Catch Up on Lost Sleep
by
Arcady A. Putilov, Evgeniy G. Verevkin, Dmitry S. Sveshnikov, Zarina V. Bakaeva, Elena B. Yakunina, Olga V. Mankaeva, Vladimir I. Torshin, Elena A. Trutneva, Michael M. Lapkin, Zhanna N. Lopatskaya, Roman O. Budkevich, Elena V. Budkevich, Marina P. Dyakovich, Olga G. Donskaya, Dmitry E. Shumov, Natalya V. Ligun, Alexandra N. Puchkova and Vladimir B. Dorokhov
Clocks & Sleep 2025, 7(4), 67; https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep7040067 - 27 Nov 2025
Abstract
The circadian phase difference between morning and evening types is a fundamental aspect of chronotype. However, results of categorizations into chronotypes based on reported sleep times show low concordance with those based on measurements of the hormonal or physiological or molecular rhythm–markers of
[...] Read more.
The circadian phase difference between morning and evening types is a fundamental aspect of chronotype. However, results of categorizations into chronotypes based on reported sleep times show low concordance with those based on measurements of the hormonal or physiological or molecular rhythm–markers of the circadian phase. This might be partially explained by the profound individual differences in the phase angle between the sleep–wake cycle and these rhythms that depends on chronotype, age, sex, and other factors. Here, we examined the possibility of using self-reported sleep times in the condition of 5-days-on/2-days-off school/work schedule to estimate circadian phase differences between various chronotypes. In an in silico study, we determined that, for such an estimation, similarities of the compared chronotypes in weekend sleep duration and weekend–weekday gap and in risetime are required. In the following empirical and simulation studies of sleep times reported by 4940 survey participants, we provided examples of the estimation of circadian differences between chronotypes, and the model-based simulations of sleep times in morning and evening types exemplified a way to confirm such estimations. The results of in silico, empirical, and simulation studies underscore the possibility of using bedtimes and risetimes for direct estimation of the circadian phase differences between individuals in real-life situations, such as a 5-days-on/2-days-off school/work schedule. Additionally, the results of these studies on different chronotypes provided further mathematical modeling and empirical evidence for our failure to sleep more on weekends to recover/compensate/pay back/ catch up on lost sleep.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Human Basic Research & Neuroimaging)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Sleep as a Developmental Process: A Systematic Review of Cognitive, Emotional, and Behavioral Outcomes in Children Aged 6–12 Years
by
Adriana Félix and Adelinda Candeias
Clocks & Sleep 2025, 7(4), 66; https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep7040066 - 14 Nov 2025
Abstract
Sleep is essential for child development, influencing cognition, emotional regulation, behavior, and physical health. Recent studies increasingly frame sleep as both a key developmental process and a modifiable factor shaped by, and shaping environmental risks—including digital screen exposure and psychosocial stress. This systematic
[...] Read more.
Sleep is essential for child development, influencing cognition, emotional regulation, behavior, and physical health. Recent studies increasingly frame sleep as both a key developmental process and a modifiable factor shaped by, and shaping environmental risks—including digital screen exposure and psychosocial stress. This systematic review synthesized empirical findings from cross-sectional and cohort studies published between 2019 and 2024 on the associations between sleep duration, quality, and patterns and developmental outcomes in typically developing children aged 6–12 years. Searches were conducted in EBSCO, Scopus, and Web of Science databases, yielding 99 records, of which 20 met inclusion criteria. Methodological quality was evaluated using Joanna Briggs Institute tools. Findings show consistent associations between better sleep and enhanced cognitive performance, emotional well-being, and reduced behavioral problems. Some studies identified sleep as a mediator between screen use and behavioral difficulties, whit additional moderating effects related to gender and socioeconomic status. However, most studies used cross-sectional designs and self-reported measures, limiting causal interpretation. Overall, sleep emerge as a potentially modifiable factor influencing developmental outcomes, based on correlational evidence. Future research should prioritize longitudinal and ecologically valid designs, objective measures, and computational approaches to identify sleep-related risk profiles and guide early interventions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Circadian Rhythm Research in Infants and Young Children)
►▼
Show Figures
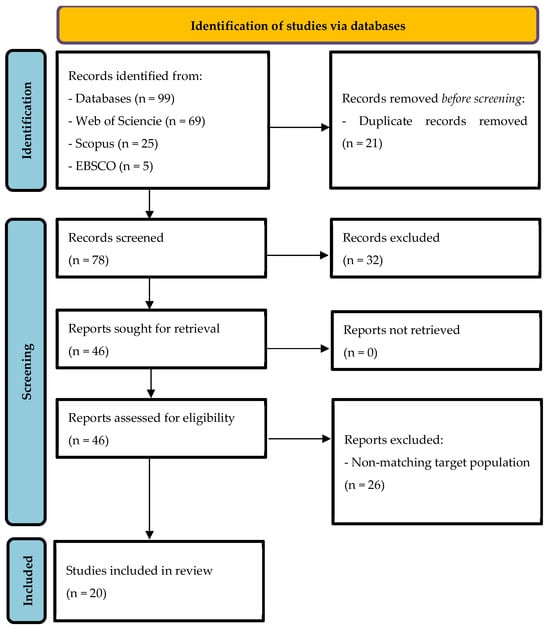
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Sex-Related Differences in the Association Between Sleep Apnea and Subsequent Urinary Incontinence Diagnosis
by
Lara Ilona Becker, Céline Vetter, Karel Kostev and Matthias Kalder
Clocks & Sleep 2025, 7(4), 65; https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep7040065 - 7 Nov 2025
Abstract
Objective: An association between sleep apnea and various urological symptoms has been reported in the literature. Therefore, the aim of this study is to analyze sex-related differences in the association between sleep apnea und subsequent urinary incontinence diagnosis. Methods: This study examined the
[...] Read more.
Objective: An association between sleep apnea and various urological symptoms has been reported in the literature. Therefore, the aim of this study is to analyze sex-related differences in the association between sleep apnea und subsequent urinary incontinence diagnosis. Methods: This study examined the incidence of urinary incontinence in a matched pair cohort with and without sleep apnea treated in 1293 general practices in Germany between January 2005 and December 2022 (74,453 vs. 372,256 individuals). The five-year cumulative incidence of urinary incontinence in the cohorts with and without sleep apnea was studied using Kaplan–Meier curves and log-rank tests. Finally, a univariable Cox regression analysis was conducted to assess the association between sleep apnea and urinary incontinence. Stratified analyses were conducted by sex (male/female) and age group (18–50 years, 51–60 years, 61–70 years, >70 years). Results: Sleep apnea was significantly associated with urinary incontinence as compared to individuals without sleep disorder diagnosis (5.1% vs. 4.3%; p < 0.001), and this association remained robust in females (HR: 1.38; 95% CI: 1.29–1.46), but not in males (HR: 1.02; 95% CI: 0.96–1.08) In females, the association was strongest in the age group 51–60 years (HR: 1.98; 95% CI: 1.71–2.30). Conclusions: In conclusion, this study reports a significant association between sleep apnea and subsequent urinary incontinence diagnosis. Sex- and age-related differences should be taken into account, as associations were stronger for middle-aged females followed by younger females and no significant association was found regarding males.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Disorders)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Sleep and Psychosocial Risk Factors Associated with Social Jet Lag and Sleep Duration Among Colombian University Students
by
Andrés Camargo, Leandro P. Casiraghi, Diego A. Golombek, Edith Villalobos, Viviana González, Carlos Orozco, Elena Jiménez, Danny Sanjuanelo, Oscar Pianeta and Rafael Vargas
Clocks & Sleep 2025, 7(4), 64; https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep7040064 - 7 Nov 2025
Abstract
Undergraduate students and healthcare professionals often experience irregular sleep patterns, social jet lag (SJL), and rotating shifts that affect their performance. This study examined the association between SJL, sleep duration, and psychosocial factors among 1409 Colombian undergraduate students (mean age 24.4 ± 6.7
[...] Read more.
Undergraduate students and healthcare professionals often experience irregular sleep patterns, social jet lag (SJL), and rotating shifts that affect their performance. This study examined the association between SJL, sleep duration, and psychosocial factors among 1409 Colombian undergraduate students (mean age 24.4 ± 6.7 years) using data from the Ultra-Short Version of the Munich ChronoType Questionnaire collected between June and September 2023. Multivariable linear regression analysis identified factors associated with SJL. The prevalence of SJL exceeding two hours was high (84.6%), with an average magnitude of 4.4 h. Chronotype (MSFsc) was negatively correlated with SJL, indicating that students with later chronotypes tended to experience greater misalignment between biological and social time. Younger age and a higher number of working days were significantly associated with increased SJL, whereas substance use and mental health history showed no significant effects. These findings highlight that work-related demands, particularly frequent working days, play a key role in exacerbating social jet lag. The results underscore the need for institutional strategies to promote sleep health among Colombian university students and health professionals.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Circadian Rhythm Research in Infants and Young Children)
Open AccessReview
The Biological Clock Influenced by Burnout, Hormonal Dysregulation and Circadian Misalignment: A Systematic Review
by
Alexandru Ungurianu and Virginia Marina
Clocks & Sleep 2025, 7(4), 63; https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep7040063 - 3 Nov 2025
Abstract
Burnout is increasingly recognized as both a psychosocial and a chronobiological disorder characterized by endocrine dysregulation and circadian disruption. It arises from chronic occupational stress and manifests through psychological, physical, and physiological symptoms. Although psychosocial determinants are well established, the biological and chronobiological
[...] Read more.
Burnout is increasingly recognized as both a psychosocial and a chronobiological disorder characterized by endocrine dysregulation and circadian disruption. It arises from chronic occupational stress and manifests through psychological, physical, and physiological symptoms. Although psychosocial determinants are well established, the biological and chronobiological mechanisms, particularly those involving cortisol and melatonin, remain less explored. This systematic review synthesizes current evidence on hormonal and circadian dysregulation in burnout and complements it with exploratory observational data from healthcare professionals. Peer-reviewed studies evaluating endocrine or circadian biomarkers in individuals with burnout were systematically reviewed. In addition, an exploratory observational analysis was carried out among 195 Romanian clinicians using an adapted Maslach Burnout Inventory. Morning salivary cortisol was measured once at 9 a.m. in a small subsample (n = 26) to provide preliminary physiological data. Because only a single time point was obtained, these values were interpreted as indicative of stress-related activation rather than circadian rhythm. Thirty-seven studies met the inclusion criteria. Across the literature, burnout was associated with altered HPA-axis activity, blunted diurnal cortisol variation, and irregular melatonin secretion related to shift work and disrupted sleep–wake cycles. Complementary exploratory data from our Romanian cohort indicated strong correlations between burnout severity, physical symptoms, and higher morning cortisol values among shift-working clinicians. These findings are preliminary and not representative of full circadian profiles. Burnout should be considered both a psychosocial and a systemic disorder influenced by endocrine and circadian dysregulation. Recognizing alterations in cortisol and melatonin as objective indicators may facilitate earlier detection and inform chronobiological interventions such as optimized scheduling, light exposure management, or melatonin therapy. The observational data presented here is preliminary and intended to generate hypotheses; future research should employ repeated cortisol sampling under controlled Zeitgeber conditions to confirm circadian associations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Human Basic Research & Neuroimaging)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Modafinil for Promoting Wakefulness in Critically Ill Patients: Current Evidence and Perspectives
by
Sotirios Kakavas and Dimitrios Karayiannis
Clocks & Sleep 2025, 7(4), 62; https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep7040062 - 27 Oct 2025
Abstract
Critically ill patients are predisposed to developing cognitive dysfunction, excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS), and fatigue during their stay in the intensive care unit (ICU). Modafinil, a wakefulness-promoting agent, has demonstrated potential benefits in enhancing alertness, cognitive performance, and activity levels in various clinical
[...] Read more.
Critically ill patients are predisposed to developing cognitive dysfunction, excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS), and fatigue during their stay in the intensive care unit (ICU). Modafinil, a wakefulness-promoting agent, has demonstrated potential benefits in enhancing alertness, cognitive performance, and activity levels in various clinical populations. The present narrative review aims to systematically evaluate the existing literature regarding the administration of modafinil for the treatment of EDS and fatigue in the ICU context. A comprehensive literature search was performed using the Embase, MEDLINE, Web of Science, and Google Scholar databases, covering publications up to 20 June 2025. Studies investigating the use of modafinil to improve wakefulness in ICU patients were identified. A total of nine relevant studies were included, comprising two randomized controlled trials (RCTs), two case series, and five retrospective cohort studies (n = 950 patients). Four of these studies focused on patients with traumatic brain injury or post-stroke conditions, whereas the remaining studies addressed heterogeneous ICU populations. Preliminary evidence indicates that modafinil may enhance wakefulness in selected critically ill patients and potentially facilitate their participation in rehabilitative interventions, such as physical therapy. Nonetheless, robust conclusions regarding efficacy and safety remain limited by the small sample sizes and methodological constraints of the available studies. Consequently, further large-scale RCTs are warranted to elucidate the therapeutic role of modafinil in the management of EDS and hypoactivity among ICU patients.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Disorders)
►▼
Show Figures
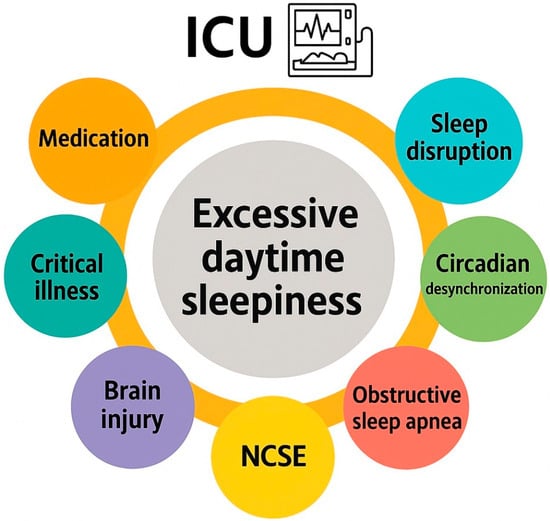
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Psychometric Validation and Arabic Translation of the 11-Item Circadian Type Inventory (CTI-11A) Among Shift Workers
by
Sara Ahmed Mansoor AlBuhmaid, Muneera Jasim Al-Rumaihi, Mohammed Adel M Albalawi, Ahmed Abdullatif Ahmed Almufarrij, Waqar Husain and Haitham Jahrami
Clocks & Sleep 2025, 7(4), 61; https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep7040061 - 25 Oct 2025
Abstract
Circadian rhythm disruptions from shiftwork impact sleep quality and work performance, yet validated tools to assess circadian preferences in Arabic-speaking populations are scarce. This study aimed to translate and validate the 11-item Circadian Type Inventory (CTI-11) into Arabic (CTI-11A), evaluate its psychometric properties,
[...] Read more.
Circadian rhythm disruptions from shiftwork impact sleep quality and work performance, yet validated tools to assess circadian preferences in Arabic-speaking populations are scarce. This study aimed to translate and validate the 11-item Circadian Type Inventory (CTI-11) into Arabic (CTI-11A), evaluate its psychometric properties, and explore latent circadian profiles in relation to sleep quality. A cross-sectional survey in Bahrain involved 468 Arabic-speaking adults recruited via social media. The CTI-11A, assessing Languid/Vigorous (LV) and Flexible/Rigid (FR) subscales, and the Jenkins Sleep Scale (JSS) were administered. Confirmatory factor analysis (CFA), reliability tests, and latent class analysis (LCA) were conducted. Participants (mean age: 36.18 ± 10.35) showed CTI-11A total scores of 35.40 ± 6.61 and JSS scores of 5.76 ± 3.48. CFA confirmed the two-factor structure (RMSEA = 0.06, SRMR = 0.05, CFI = 0.93, TLI = 0.91), with Cronbach’s α of 0.72 (total CTI-11A). Test–retest reliability was high (ICC = 0.91). CTI-11A correlated moderately with JSS (r = 0.40, p < 0.001), with stronger FR-JSS (r = 0.36) than LV-JSS (r = 0.25) associations. LCA identified two classes (Class 1: 52%, vigorous/flexible; Class 2: 48%, languid/rigid), with Class 2 showing poorer sleep quality. The CTI-11A is a reliable and valid tool for assessing circadian preferences in Arabic-speaking populations, with distinct circadian profiles linked to sleep quality. While flexible/vigorous profiles associated with better sleep, languid/rigid profiles indicate higher sleep disturbance risk, informing targeted shiftwork interventions. Further refinement of the factor structure and broader regional validation are needed.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue New Advances in Shift Work)
Open AccessArticle
Influence of Maternal Working Hours on Children’s Sleep: A Preliminary Study on Disparities Between Day and Night Shifts
by
Patrícia Andrade Nehme, Jefferson Santos, Ana Amélia Benedito-Silva, José Cipolla-Neto and Claudia R. C. Moreno
Clocks & Sleep 2025, 7(4), 60; https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep7040060 - 23 Oct 2025
Abstract
Background: Shift work necessitates alterations in daily routines, which can be detrimental to workers’ health and may also influence the activity and rest patterns of their children. Aim: The aim of this study was to evaluate the concordance between activity and rest parameters
[...] Read more.
Background: Shift work necessitates alterations in daily routines, which can be detrimental to workers’ health and may also influence the activity and rest patterns of their children. Aim: The aim of this study was to evaluate the concordance between activity and rest parameters of mothers and their children, according to the mothers’ work shift (day vs. night). Methods: Twelve mother–child dyads participated in this study, including six mothers working night shifts and six working day shifts. All mothers followed a 12/36 h rotating schedule (07:00–19:00 for day shifts; 19:00–07:00 for night shifts). Participants wore actigraphy devices for 10 consecutive days. Sleep and motor activity parameters were analyzed using the Bland–Altman method. Results: Analysis of the five least active hours (L5) revealed increased nocturnal activity among the night shift group. The period of the 10 most active hours (M10) suggested greater activity in the day shift group, with a smaller difference between mother and child in the day shift group. The relative amplitude (RA) in the night shift group was lower among mothers compared to the day group. Interdaily stability (IS) was lower, and intradaily variability (IV) was higher in the night shift group, suggesting more irregular activity patterns. Bedtime data showed greater variability in the night shift group, with night shift mothers typically going to bed later than their children—a pattern that was also observed for wake times. In the day shift group, total sleep time did not differ between mothers and children; however, in the night shift group, discrepancies increased proportionally with total sleep duration. Sleep efficiency was lower among mothers in both groups, but the difference between mother and child was more pronounced in the night shift group. Conclusions: Night shift work among mothers appears to negatively affect both their own and their children’s activity and sleep parameters when compared to those in the day shift group.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Society)
►▼
Show Figures
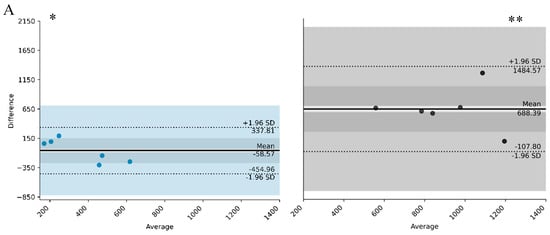
Figure 1
Open AccessCommunication
Sleep Health Inequities: Sociodemographic, Psychosocial, and Structural Determinants of Short Sleep in U.S. Adults
by
Lourdes M. DelRosso and Mamatha Vodapally
Clocks & Sleep 2025, 7(4), 59; https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep7040059 - 16 Oct 2025
Abstract
Short sleep duration (≤6 h) is a public health concern linked to cardiometabolic disease and premature mortality. However, persistent disparities across sociodemographic, psychosocial, and structural domains remain underexplored in recent nationally representative samples. We analyzed 2022 Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) data,
[...] Read more.
Short sleep duration (≤6 h) is a public health concern linked to cardiometabolic disease and premature mortality. However, persistent disparities across sociodemographic, psychosocial, and structural domains remain underexplored in recent nationally representative samples. We analyzed 2022 Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) data, including 228,463 adults (weighted N ≈ 122 million). Sleep duration was dichotomized as short (≤6 h) versus adequate (≥7 h). Complex samples logistic regression estimated associations between sociodemographic, psychosocial, behavioral, and structural determinants and short sleep, accounting for survey design. The weighted prevalence of short sleep was 33.2%. Non-Hispanic Black (AOR = 1.56, 95% CI: 1.46–1.65) and American Indian/Alaska Native adults (AOR = 1.46, 95% CI: 1.29–1.65) were disproportionately affected compared with non-Hispanic White adults. Psychosocial factors contributed strongly: life dissatisfaction, limited emotional support, and low social connectedness increased odds, whereas high connectedness was protective. Food insecurity and smoking were significant structural and behavioral risks, while binge drinking and urbanicity were not. One-third of U.S. adults report short sleep, with marked disparities across demographic, socioeconomic status, psychosocial stressors, and structural barriers. Findings highlight the multifactorial nature of sleep health inequities and the need for multilevel interventions addressing both individual behaviors and upstream determinants.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Society)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Cross-Sectional Analysis of Sleep Quality and Vascular Health in Shift- and Day-Working Nurses
by
Gleb Saharov, Barbara Salti, Maram Bareya, Anat Keren-Politansky, Yona Nadir and Tamar Shochat
Clocks & Sleep 2025, 7(4), 58; https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep7040058 - 11 Oct 2025
Abstract
Sleep disturbances and shift work are associated with increased cardiovascular risk, possibly through disruptions in endothelial and hemostatic function. While prior studies link acute sleep deprivation to vascular dysfunction, the impact of chronic sleep quality and circadian misalignment on endothelial health in healthy
[...] Read more.
Sleep disturbances and shift work are associated with increased cardiovascular risk, possibly through disruptions in endothelial and hemostatic function. While prior studies link acute sleep deprivation to vascular dysfunction, the impact of chronic sleep quality and circadian misalignment on endothelial health in healthy individuals, particularly shift workers, remains underexplored. The aim of this study was to examine the association between objectively measured sleep quality and endothelial/hemostatic function in healthy female hospital nurses, comparing shift and day workers, and considering time-of-day variation. In this repeated-measures study, 100 female nurses (51 shift, 49 day workers) aged 25–50 wore actigraphy devices for 7–14 days to assess total sleep time (TST), sleep efficiency (SEF), and wake after sleep onset (WASO). Endothelial function was measured using EndoPAT (Reactive Hyperemia Index—RHI). Hemostatic markers included plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1), von Willebrand factor (VWF), heparanase and heparanase procoagulant activity assessed by ELISA, and chromogenic assays in morning and evening. TST was not associated with any vascular outcomes. Poor sleep quality (low SEF, high WASO) was significantly associated with reduced RHI and elevated PAI-1 level, heparanase level, and heparanase procoagulant activity levels. Regression models revealed significant main effects of SEF and WASO on endothelial and coagulation markers, with some interactions depending on shift type and time of measurement. No significant associations were found for VWF. Impaired sleep quality, but not sleep duration, is associated with endothelial dysfunction and procoagulant activation, particularly among shift-working nurses. These findings suggest that sleep quality may play a critical role in vascular health and support the use of sleep-based interventions to reduce cardiovascular risk in shift-working populations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Human Basic Research & Neuroimaging)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Does Daytime Sleepiness Moderate the Relationship Between Working Memory and Academic Performance in Schoolchildren? A Pilot Study
by
Sergey Malykh and Valeriia Demareva
Clocks & Sleep 2025, 7(4), 57; https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep7040057 - 8 Oct 2025
Abstract
Academic performance in adolescence is influenced by both cognitive capacity and physiological factors such as sleepiness. However, the interaction between these dimensions remains understudied. This pilot study examined whether daytime sleepiness moderates the relationship between working memory and academic achievement in a sample
[...] Read more.
Academic performance in adolescence is influenced by both cognitive capacity and physiological factors such as sleepiness. However, the interaction between these dimensions remains understudied. This pilot study examined whether daytime sleepiness moderates the relationship between working memory and academic achievement in a sample of 601 schoolchildren aged 11 to 17 years. Participants completed a digital visuospatial working memory task and self-reported their daytime sleepiness using the Pediatric Daytime Sleepiness Scale (PDSS). Academic performance was assessed through official grades in Mathematics, Language, and Literature. Regression analyses showed that working memory (total score and average reaction time) and daytime sleepiness were independent predictors of academic performance. These findings support our hypotheses that cognitive and physiological factors each contribute to school success. However, no significant moderation effects were found in the full sample. Subgroup analyses revealed that working memory predicted academic outcomes only among students with normal sleepiness levels, whereas in high-sleepiness students, cognitive predictors lost significance and PDSS scores emerged as the dominant predictor. These results suggest that elevated daytime sleepiness can undermine the positive impact of working memory on academic performance. The findings highlight the importance of assessing both cognitive skills and physiological readiness when evaluating students. They also suggest that sleep-focused interventions may improve learning outcomes, especially during adolescence.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Human Basic Research & Neuroimaging)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Self-Reported Insomnia and Poor Sleep Quality Are Associated with Self-Reported Cognitive Changes in Older Adults
by
Julia Glueck, Celina Pluim McDowell, Yakeel T. Quiroz, Alice Cronin-Golomb and Jeanne F. Duffy
Clocks & Sleep 2025, 7(4), 56; https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep7040056 - 2 Oct 2025
Abstract
Older adults are vulnerable to changes in sleep with age. Poor sleep quality is associated with self-reported cognitive changes, which can occur before the onset of objective cognitive decline associated with Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. The objective of this study was
[...] Read more.
Older adults are vulnerable to changes in sleep with age. Poor sleep quality is associated with self-reported cognitive changes, which can occur before the onset of objective cognitive decline associated with Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. The objective of this study was to examine associations between self-reported sleep complaints, objective sleep quality, and self-reported cognitive changes and their relations to symptoms of depression and anxiety in a group of community-dwelling older adults. Adults aged ≥ 50 without dementia (n = 45) were recruited and completed 1–2 weeks of rest-activity monitoring using a wrist-worn device, underwent a test of global cognitive functioning (Mini-Mental State Examination; MMSE), and completed questionnaires assessing insomnia (Insomnia Severity Index; ISI), subjective sleep quality (Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index; PSQI), self-reported cognitive changes (Cognitive Function Instrument; CFI), and symptoms of depression and anxiety (Beck Depression Inventory-II; BDI-II and Generalized Anxiety Disorder 7-item assessment; GAD-7). Pearson partial correlations assessed relations among subjective and objective sleep quality, insomnia ratings, CFI ratings, and global cognition, while controlling for BDI-II and GAD-7 ratings. Exploratory analyses examined the correlation between PSQI component scores and CFI ratings and global cognition. Greater ISI (r = 0.50, p ≤ 0.001) ratings significantly correlated with higher CFI scores. PSQI total ratings and actigraphy-based measures (n = 41) did not significantly correlate with CFI scores. Exploratory PSQI subscale analyses revealed that worse subjective sleep quality (r = 0.31, p = 0.048), shorter sleep duration (r = 0.32, p = 0.04), and greater use of sleep medications (r = 0.31, p = 0.048) correlated with higher CFI scores. Poorer sleep quality due to less time spent asleep, fragmented or disturbed sleep, and requiring medications to sleep, may be associated with greater memory concerns. Alternatively, worries about cognition may deleteriously affect sleep. Subjective measures of sleep quality may be useful to identify older adults at increased risk of cognitive decline.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Human Basic Research & Neuroimaging)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Under the Covers: The Effect of a Temperature-Controlled Mattress Cover on Sleep and Perceptual Measures in Healthy Adults
by
Shauna Stevenson, Haresh Suppiah, Toby Mündel and Matthew Driller
Clocks & Sleep 2025, 7(4), 55; https://doi.org/10.3390/clockssleep7040055 - 1 Oct 2025
Abstract
Ambient temperature and thermoregulation influence sleep quality. This study investigated the effects of a temperature-controlled mattress cover on sleep and perceptual outcomes in healthy adults. In a randomised, counterbalanced, crossover design, 34 healthy adults (20 F, 14 M; age, 30 ± 5 y)
[...] Read more.
Ambient temperature and thermoregulation influence sleep quality. This study investigated the effects of a temperature-controlled mattress cover on sleep and perceptual outcomes in healthy adults. In a randomised, counterbalanced, crossover design, 34 healthy adults (20 F, 14 M; age, 30 ± 5 y) used a temperature-controlled mattress cover for 14 nights, following ≥3 nights of familiarisation. The temperature feature was on for 7 nights (POD) and off for 7 nights (CON). Sleep was assessed via wrist actigraphy, while heart rate (HR), heart rate variability (HRV), and respiratory rate (RR) were recorded by embedded sensors in the mattress cover. Participants completed daily and weekly questionnaires evaluating sleep quality, thermal comfort, and thermal sensation. Linear mixed models showed significant main effects of condition favouring POD over CON for all daily perceived outcomes (all p < 0.05). A large, significant improvement in perceived sleep quality was observed (p = 0.001, d = 0.92). No significant differences were found in objective sleep metrics or biometric measures (all p ≥ 0.05). A temperature-controlled mattress cover was associated with improved subjective sleep quality and thermal-related perceptions despite minimal changes in objective or biometric outcomes, which may in part reflect expectancy, or placebo effects. Further research is needed to explore whether these perceptual benefits lead to physiological improvements over time.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Human Basic Research & Neuroimaging)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Brain Sciences, Clocks & Sleep, Neurology International, NeuroSci
Translational Advances in Neurodegenerative Dementias, Second Edition
Topic Editors: Francesco Di Lorenzo, Annibale AntonioniDeadline: 30 September 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Clocks & Sleep
The Circadian Rhythm Research in Infants and Young Children
Guest Editor: Teruhisa MiikeDeadline: 31 January 2026
Special Issue in
Clocks & Sleep
New Advances in Shift Work
Guest Editor: Eva SchernhammerDeadline: 30 April 2026
Special Issue in
Clocks & Sleep
Emerging Trends in Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Guest Editor: Ali Albert el-SolhDeadline: 31 May 2026
Special Issue in
Clocks & Sleep
Circadian Rhythm Research in Aquatic Animals
Guest Editor: Yingdong LiDeadline: 30 June 2026
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Clocks & Sleep
Featured Papers from Australasian Chronobiology Society
Collection Editors: Sean Cain, Elise McGlashan











