-
 Uncovering Non-Invasive Biomarkers in Paediatric Severe Acute Asthma Using Targeted Exhaled Breath Analysis
Uncovering Non-Invasive Biomarkers in Paediatric Severe Acute Asthma Using Targeted Exhaled Breath Analysis -
 Urine Metabolomic Patterns to Discriminate the Burnout Levels and Night-Shift-Related Stress in Healthcare Professionals
Urine Metabolomic Patterns to Discriminate the Burnout Levels and Night-Shift-Related Stress in Healthcare Professionals -
 Targeted and Non-Targeted Metabolomic Evaluation of Cerebrospinal Fluid in Early Phase Schizophrenia
Targeted and Non-Targeted Metabolomic Evaluation of Cerebrospinal Fluid in Early Phase Schizophrenia
Journal Description
Metabolites
Metabolites
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal of metabolism and metabolomics, published monthly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, Embase, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Biochemistry and Molecular Biology) / CiteScore - Q2 (Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 14.4 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 3.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Impact Factor:
3.7 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
4.1 (2024)
Latest Articles
High-Coverage Profiling of Hydroxyl and Amino Compounds in Sauce-Flavor Baijiu Using Bromine Isotope Labeling and Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography–High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry
Metabolites 2025, 15(7), 464; https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070464 (registering DOI) - 9 Jul 2025
Abstract
Background: Hydroxyl and amino compounds play a significant role in defining the flavor and quality of sauce-flavor Baijiu, yet their comprehensive analysis remains challenging due to limitations in detection sensitivity. In this study, we developed a novel bromine isotope labeling approach combined
[...] Read more.
Background: Hydroxyl and amino compounds play a significant role in defining the flavor and quality of sauce-flavor Baijiu, yet their comprehensive analysis remains challenging due to limitations in detection sensitivity. In this study, we developed a novel bromine isotope labeling approach combined with ultra-high performance liquid chromatography–high-resolution mass spectrometry (UHPLC-HRMS) to achieve high-coverage profiling of these compounds in sauce-flavor Baijiu. Methods: The method employs 5-bromonicotinoyl chloride (BrNC) for rapid (30 s) and mild (room temperature) labeling of hydroxyl and amino functional groups, utilizing bromine’s natural isotopic pattern (Δm/z = 1.998 Da) for efficient screening. Annotation was performed hierarchically at five confidence levels by integrating retention time, accurate mass, and MS/MS spectra. Results: A total of 309 hydroxyl and amino compounds, including flavor substances (e.g., tyrosol and phenethyl alcohol) and bioactive compounds (e.g., 3-phenyllactic acid), were identified in sauce-flavor Baijiu. The method exhibited excellent analytical performance, with wide linearity (1–4 orders of magnitude), precision (RSD < 18.3%), and stability (RSD < 15% over 48 h). When applied to sauce-flavor Baijiu samples of different grades, distinct compositional patterns were observed: premium-grade products showed greater metabolite diversity and higher contents of bioactive compounds, whereas lower-grade samples exhibited elevated concentrations of acidic flavor compounds. Conclusions: These results demonstrate that the established method is efficient for the comprehensive analysis of hydroxyl and amino compounds in complex food matrices. The findings provide valuable insights for quality control and flavor modulation in sauce-flavor Baijiu production.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue New Analytical Techniques and Applications of Metabolomics and Lipidomics)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
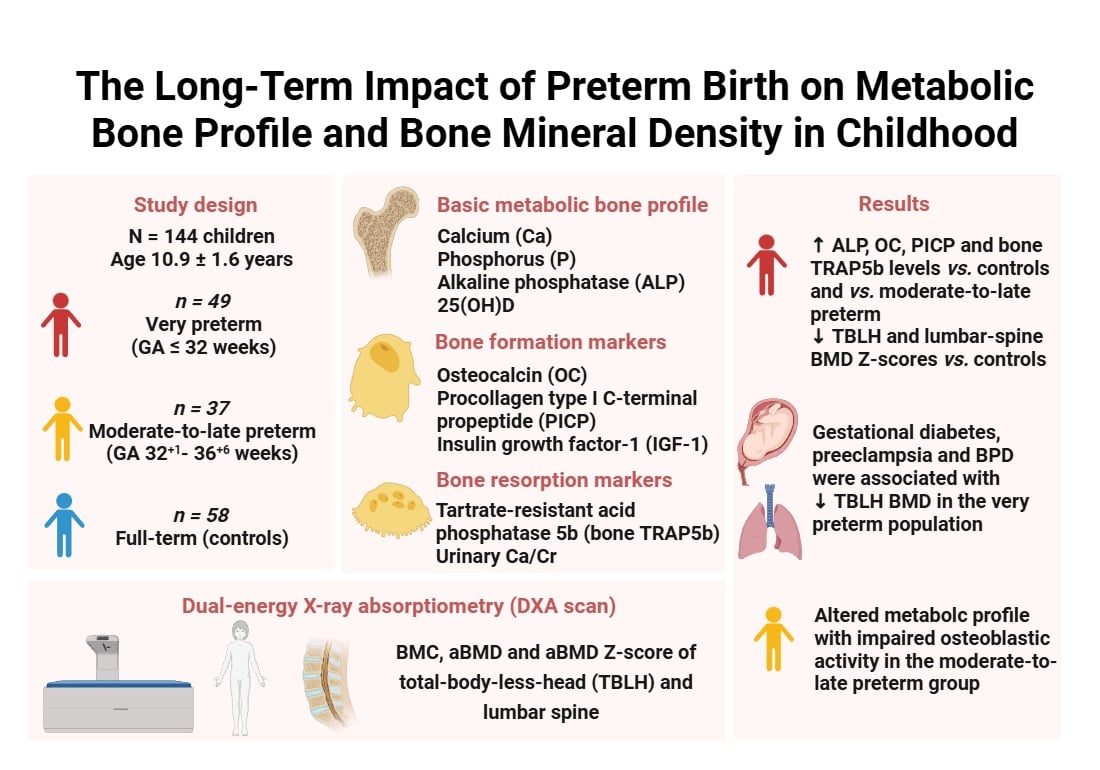
The Long-Term Impact of Preterm Birth on Metabolic Bone Profile and Bone Mineral Density in Childhood
by
Panagiota Markopoulou, Artemis Doulgeraki, Arsinoi Koutroumpa, Georgios Polyzois, Helen Athanasopoulou, Christina Kanaka-Gantenbein and Tania Siahanidou
Metabolites 2025, 15(7), 463; https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070463 - 8 Jul 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Recent data on long-term consequences of prematurity on bone health are conflicting. The aim of this study was to assess the metabolic bone profile and bone mineral density (BMD) in prepubertal children born prematurely and to examine possible associations between bone
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Recent data on long-term consequences of prematurity on bone health are conflicting. The aim of this study was to assess the metabolic bone profile and bone mineral density (BMD) in prepubertal children born prematurely and to examine possible associations between bone health parameters and perinatal morbidity factors. Methods: This cross-sectional observational study included 144 children of mean (SD) age 10.9 (1.6) years: 49 children born very preterm (≤32 gestational weeks), 37 moderate-to-late preterm (32+1 to 36+6 gestational weeks), and 58 born at term (controls). Serum levels of calcium/Ca, phosphorus/P, alkaline phosphatase/ALP, 25-hydroxyvitamin D/25(OH)D, bone formation markers (osteocalcin/OC, procollagen type I C-terminal propeptide/PICP, and insulin growth factor-1/IGF-1), and bone resorption markers (serum tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase 5b/bone TRAP5band urinary calcium-to-creatinine ratio) were measured. Total-body and lumbar-spine BMD and BMD Z-scores were calculated using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry/DXA. Results: Children born very preterm showed significantly higher ALP, OC, PICP, and bone TRAP5b levels compared to controls, as well as compared to children born moderate-to-late preterm. Total-body and lumbar-spine BMD Z-scores were significantly lower in the very preterm-born group compared to controls. Gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, and bronchopulmonary dysplasia were associated with lower total-body BMD in the very preterm-born population. Conclusions: Preterm birth is associated with impaired metabolic bone profile and lower total-body and lumbar-spine BMD in childhood. Moderate-to-late preterm-born children exhibit altered metabolic bone parameters compared to very preterm-born children. Further research in children might allow better insight into the long-term impact of preterm birth on bone health.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Endocrinology and Clinical Metabolic Research)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Understanding the Metabolic Effects of Surgically Induced Renal Ischemia in Humans: A Temporal Approach
by
Bhargav Arimilli, Tyler A. On, Vaishnavi S. Srirama, Ye Yang, Gitanjali Asampille, Jeffrey R. Brender, Murali C. Krishna, Jessica Y. Hseuh, Viraj P. Chegu, Zachary Kozel, Sandeep Gurram, Mark W. Ball, William Marston Linehan and Daniel R. Crooks
Metabolites 2025, 15(7), 462; https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070462 - 8 Jul 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Thousands of nephrectomies are performed annually in the United States, but the short-term metabolic effects of surgically induced renal ischemia remain unclear. The conventional metabolic markers used to characterize post-surgical renal function, such as creatinine and GFR, are measured in the
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Thousands of nephrectomies are performed annually in the United States, but the short-term metabolic effects of surgically induced renal ischemia remain unclear. The conventional metabolic markers used to characterize post-surgical renal function, such as creatinine and GFR, are measured in the serum but do not provide metabolic information about the renal parenchyma itself. We aimed to characterize the immediate metabolic effects of surgical ischemia on renal parenchyma within a temporal framework. Methods: Timed renal parenchyma biopsies were collected from eight patients undergoing nephrectomy for renal cell carcinoma both prior to and after ligation of the renal hilum. These samples were ground, extracted, and analyzed using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy to measure changes in lactate, succinate, glucose, alanine, and glycine levels. Results: Due to experimental limitations, we were only able to draw limited conclusions from three patients. Of the five remaining patients, all had significant increases in lactate and succinate levels as a function of time, though the degree to which these increases occurred varied between each patient. Glucose levels generally decreased in the renal parenchyma but did not necessarily correlate with lactate production, assuming all glucose underwent fermentation to lactate in a hypoxic environment. Alanine and glycine levels did not change in a predictable pattern across patients. Conclusions: There are significant changes in lactate, glucose and succinate levels within minutes of the onset of renal ischemia in human patients. The degree of change in the metabolites analyzed varied significantly between patients. The length of surgical ischemia must be considered during surgical procurement of tumor specimens for metabolomic analysis.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Nuclear Magnetic Resonance-Powered Metabolomics: Progress and Future Prospects)
►▼
Show Figures
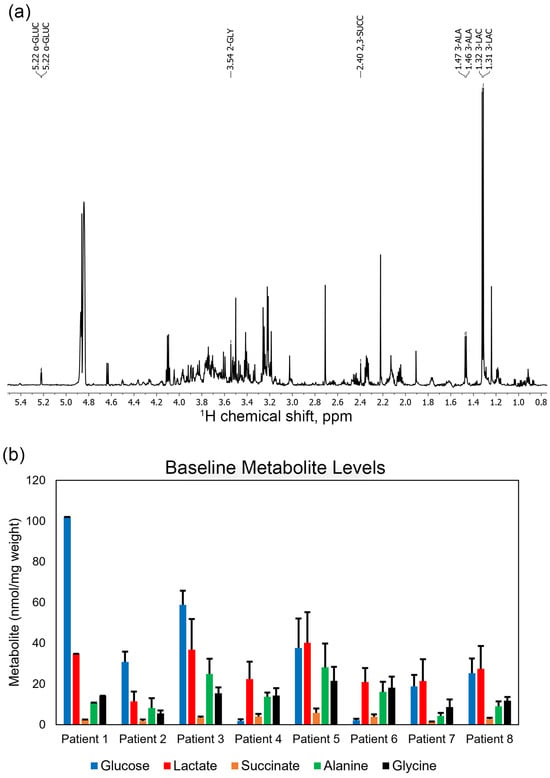
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
ATP Supply from Cytosol to Mitochondria Is an Additional Role of Aerobic Glycolysis to Prevent Programmed Cell Death by Maintenance of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential
by
Akane Sawai, Takeo Taniguchi, Kohsuke Noguchi, Taisuke Seike, Nobuyuki Okahashi, Masak Takaine and Fumio Matsuda
Metabolites 2025, 15(7), 461; https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070461 - 7 Jul 2025
Abstract
Eukaryotic cells generate ATP primarily via oxidative and substrate-level phosphorylation. Despite the superior efficiency of oxidative phosphorylation, eukaryotic cells often use both pathways as aerobic glycolysis, even in the presence of oxygen. However, its role in cell survival remains poorly understood. Objectives: In
[...] Read more.
Eukaryotic cells generate ATP primarily via oxidative and substrate-level phosphorylation. Despite the superior efficiency of oxidative phosphorylation, eukaryotic cells often use both pathways as aerobic glycolysis, even in the presence of oxygen. However, its role in cell survival remains poorly understood. Objectives: In this study, aerobic glycolysis was compared between the Warburg effect in breast cancer cells (MCF7) and the Crabtree effect in a laboratory strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae (S288C). Methods: The metabolic adaptations of MCF7 and S288C cells were compared following treatment with electron transport chain inhibitors, including FCCP, antimycin A, and oligomycin. Results: MCF7 and S288C cells exhibited strikingly similar metabolic rewiring toward substrate-level phosphorylation upon inhibitor treatment, suggesting that mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation and cytosolic substrate-level phosphorylation communicate through a common mechanism. Measurement of mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) and ATP concentrations further indicated that cytosolic ATP was transported into the mitochondria under conditions of reduced electron transport chain activity. This ATP was likely utilized in the reverse mode of H+/ATPase to maintain MMP, which contributed to the avoidance of programmed cell death. Conclusions: These results suggest that the ATP supply to mitochondria plays a conserved role in aerobic glycolysis in yeast and mammalian cancer cells. This mechanism likely contributes to cell survival under conditions of fluctuating oxygen availability.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Cell Metabolism)
►▼
Show Figures
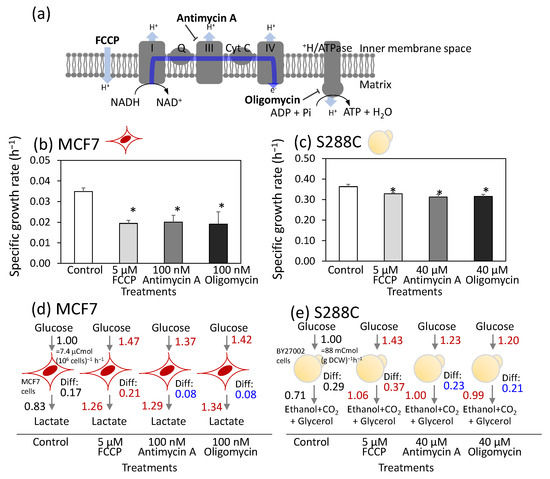
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Fracture Risk in Chronic Kidney Disease: Addressing an Overlooked Complication
by
Guido Gembillo, Concetto Sessa, Walter Morale, Luca Zanoli, Antonino Catalano, Salvatore Silipigni, Luca Soraci, Andrea Corsonello, Maria Princiotto, Carlo Lomonte and Domenico Santoro
Metabolites 2025, 15(7), 460; https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070460 - 7 Jul 2025
Abstract
Fracture risk is a serious yet underrecognized complication among patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD), especially in those with stages G3-G5D. The overlap between CKD-Mineral and Bone Disorder (CKD-MBD) and osteoporosis leads to complex bone changes that increase the likelihood of fragility fractures.
[...] Read more.
Fracture risk is a serious yet underrecognized complication among patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD), especially in those with stages G3-G5D. The overlap between CKD-Mineral and Bone Disorder (CKD-MBD) and osteoporosis leads to complex bone changes that increase the likelihood of fragility fractures. Studies show that 18% to 32% of CKD patients also have osteoporosis, and these individuals are more than 2.5 times as likely to suffer from fractures compared to those without CKD. In the advanced stages of the disease, fracture risk is up to four times higher than in the general population, with the femur, forearm, and humerus being the most commonly affected sites. Hip fractures are of particular concern as they are linked to longer hospital stays and higher rates of morbidity and mortality. Furthermore, dialysis patients who experience hip fractures have a mortality rate 2.4 times higher than those in the general population with similar fractures. This increased risk underscores the need for proactive bone health maintenance in CKD patients to prevent fractures and related complications. This review explores the underlying pathophysiological mechanisms, diagnostic challenges, and treatment options related to bone fragility in CKD. Diagnostic tools, such as bone mineral density (BMD) assessments, the trabecular bone score (TBS), and biochemical markers, remain underused, especially in advanced CKD stages. Recent treatment strategies emphasize a multidisciplinary, stage-specific approach, incorporating calcium and vitamin D supplements, anti-resorptive agents like denosumab, and anabolic therapies such as teriparatide and romosozumab. Effective management needs to be tailored to the patient’s bone turnover status and stage of CKD. Despite progress in understanding bone fragility in CKD, significant gaps remain in both diagnosis and treatment. Personalized care, guided by updated KDIGO recommendations and based on an interdisciplinary approach, is essential to reduce fracture risk and improve outcomes in this vulnerable population. Further research is needed to validate risk assessment tools and refine therapeutic protocols.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Multifaceted Roles of Biomarkers in Metabolic Disorders: From Diagnosis and Monitoring to Prediction, Management, and Treatment)
►▼
Show Figures
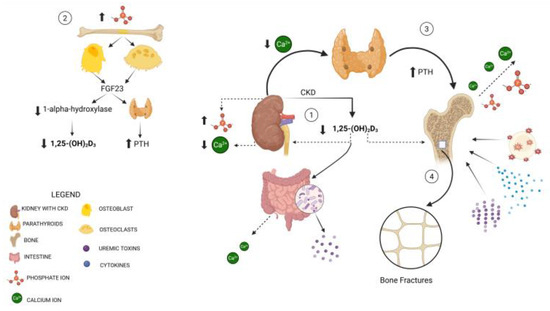
Figure 1
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Serum Osteopontin and Procollagen Type 1 N-Terminal Propeptide Concentrations: Links to Liver Function, Muscle Mass, and Bone Mineral Density in MASLD and Hypertension
by
Anna F. Sheptulina, Anastasia Yu. Elkina, Elvira M. Mamutova, Yuriy S. Timofeev, Victoria A. Metelskaya and Oxana M. Drapkina
Metabolites 2025, 15(7), 459; https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070459 - 6 Jul 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Increasing evidence suggests that metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) and hypertension (HTN), a well-established cardiometabolic risk factor, both negatively impact bone metabolism. This study aimed to investigate the associations between bone turnover markers (BTMs)—namely, osteopontin (OPN) and procollagen type 1 N-terminal
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Increasing evidence suggests that metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) and hypertension (HTN), a well-established cardiometabolic risk factor, both negatively impact bone metabolism. This study aimed to investigate the associations between bone turnover markers (BTMs)—namely, osteopontin (OPN) and procollagen type 1 N-terminal propeptide (P1NP)—and metabolic health indicators, non-invasive measures of liver disease severity, as well as skeletal muscle mass (SMM), muscle strength, and bone mineral density (BMD) in patients with MASLD and HTN. Methods: We enrolled 117 patients diagnosed with MASLD and HTN and conducted anthropometric measurements, laboratory analyses, abdominal ultrasound, and point shear-wave elastography. Muscle strength was evaluated using grip strength measurements and the Five Times Sit-to-Stand Test (FTSST). SMM and BMD were quantified using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA). Serum OPN and P1NP concentrations were quantified using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs). Results: Serum OPN concentrations below 2.89 ng/mL were associated with significantly elevated levels of AST (p = 0.001), ALT (p = 0.006), and GGT (p = 0.025), while serum P1NP concentrations above 47.5 pg/mL were associated only with significantly elevated GGT levels (p = 0.024). In addition, patients with MASLD and HTN with lower serum OPN levels had higher liver stiffness values (p = 0.003). Serum OPN concentrations were inversely associated with the following metabolic health indicators: waist circumference (WC, p < 0.001) and epicardial fat thickness (EFT, p = 0.001). In addition, they were significantly elevated in patients with MASLD and HTN who had decreased spinal BMD (p = 0.017). In turn, serum P1NP levels were reduced in patients with decreased SMM (p = 0.023). Conclusions: These findings in patients with MASLD and HTN suggest an association between serum P1NP levels and SMM, and between OPN levels and spinal BMD, indicating a potential interplay among liver function, muscle mass, and bone health. Furthermore, OPN appeared to be strongly associated with overall metabolic health indicators, such as WC and EFT, whereas P1NP exhibited a stronger association with muscle mass.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Endocrinology and Clinical Metabolic Research)
►▼
Show Figures
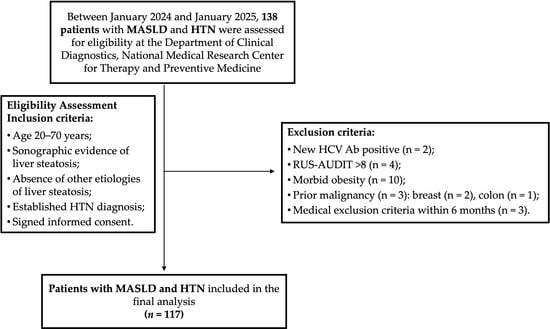
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Tissue-Based Metabolomic Profiling of Endometrial Cancer and Hyperplasia
by
Khalid Akkour, Afshan Masood, Maha Al Mogren, Reem H. AlMalki, Assim A. Alfadda, Salini Scaria Joy, Ali Bassi, Hani Alhalal, Maria Arafah, Othman Mahmoud Othman, Hadeel Mohammad Awwad, Anas M. Abdel Rahman and Hicham Benabdelkamel
Metabolites 2025, 15(7), 458; https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070458 - 5 Jul 2025
Abstract
Background: Endometrial cancer (EC) is the sixth most common cancer among women globally, with an estimated 420,000 new cases diagnosed annually. Methods: This study comprised patients with endometrial cancer (EC) (n = 17), hyperplasia (HY) (n = 17), and controls (CO)
[...] Read more.
Background: Endometrial cancer (EC) is the sixth most common cancer among women globally, with an estimated 420,000 new cases diagnosed annually. Methods: This study comprised patients with endometrial cancer (EC) (n = 17), hyperplasia (HY) (n = 17), and controls (CO) (n = 20). Tissue was collected from the endometrium of all 54 patients, including patients with HY, EC, and CO, who underwent total hysterectomy. EC and HY diagnoses were confirmed based on histological examination. Untargeted metabolomics profiling was conducted using LC-HRMS. The partial least squares discriminant analysis (PLS-DA) and orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA) models were used for univariate and multivariate statistical analysis. The fitness of the model (R2Y) and predictive ability (Q2) were used to create OPLS-DA models. ROC analysis was carried out, followed by network analysis using Ingenuity Pathway Analysis. Results: The top metabolites that can discriminate EC and HY from CO were identified. This revealed a decrease in the levels of the lipid species, specifically phosphatidic acid (PA) (PA (14:1/14:0), PA(10:0/17:0), PA(18:1-O(12,13)/12:0)), PG(a-13:0/a-13:0), ganglioside GA1 (d18:1/18:1), PS(14:1/14:0), TG(20:0/18:4/14:1), and CDP-DG(PGF2alpha/18:2), while the levels of 3-Dehydro-L-gulonate, Uridine diphosphate-N-acetylglucosamine, ganglioside GT2 (d18:1/14:0), gamma-glutamyl glutamic acid and oxidized glutathione were increased in cases of EC and HY as compared to CO. Bioinformatics analysis, specifically using Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA), revealed distinct pathway enrichments for EC and HY. For EC, the most highly scored pathways were associated with cell-to-cell signaling and interaction, skeletal and muscular system development and function, and small-molecule biochemistry. In contrast, HY cases showed the highest scoring pathways related to inflammatory disease, inflammatory response, and organismal injury and abnormalities. Conclusions: Developing sensitive biomarkers could improve diagnosis and guide treatment decisions, particularly in identifying which patients with HY may safely avoid hysterectomy and be managed with hormonal therapy.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics for Advancing Personalized Medicine)
►▼
Show Figures
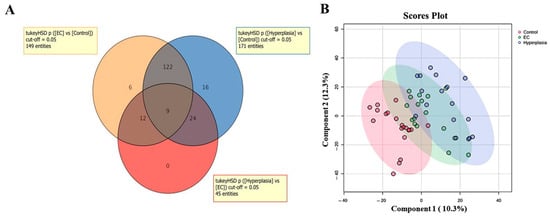
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Nutraceutical Potential of Havardia pallens and Vachellia rigidula in the Diet Formulation for Male Goat
by
Jesús Humberto Reyna-Fuentes, Cecilia Carmela Zapata-Campos, Jorge Ariel Torres-Castillo, Daniel López-Aguirre, Juan Antonio Núñez-Colima, Luis Eliezer Cruz-Bacab, Fabián Eliseo Olazarán-Santibáñez, Fernando Sánchez-Dávila, Aida Isabel Leal-Robles and Juan Antonio Granados-Montelongo
Metabolites 2025, 15(7), 457; https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070457 - 5 Jul 2025
Abstract
Background: Xerophilous scrubland is a semi-desert ecosystem characterized by a wide diversity of shrubs, which have secondary compounds with nutraceutical potential that could be used as feed for livestock, specifically by goats, since this species has developed behavioral and physiological adaptations that
[...] Read more.
Background: Xerophilous scrubland is a semi-desert ecosystem characterized by a wide diversity of shrubs, which have secondary compounds with nutraceutical potential that could be used as feed for livestock, specifically by goats, since this species has developed behavioral and physiological adaptations that allow it to take advantage of the plant resources of said scrubland. Objective: To evaluate the nutraceutical potential of Havardia pallens and Vachellia rigidula, native species of the xerophilous scrubland, when incorporated as ingredients in goat diets. Methods: Integral diets for male goats were prepared, formulated with 35% inclusion of Havardia pallens, Vachellia rigidula, and Medicago sativa, the latter used as a plant control species. The content of flavonoids and total phenols was compared using colorimetric methods, and the antioxidant capacity was measured using the FRAP method. RP-HPLC-ESI-MS characterized the bioactive compounds in the different extracts. Statistical analysis was performed by ANOVA. Results: The aqueous extraction of Vachellia rigidula showed the highest concentration of total phenols (
(This article belongs to the Section Food Metabolomics)
Open AccessArticle
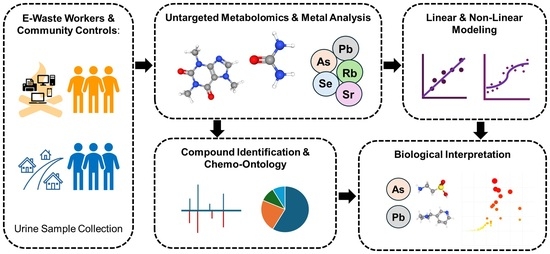
Integrative Modeling of Urinary Metabolomics and Metal Exposure Reveals Systemic Impacts of Electronic Waste in Exposed Populations
by
Fiona Hui, Zhiqiang Pang, Charles Viau, Gerd U. Balcke, Julius N. Fobil, Niladri Basu and Jianguo Xia
Metabolites 2025, 15(7), 456; https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070456 - 5 Jul 2025
Abstract
Background: Informal electronic waste (e-waste) recycling practices release a complex mixture of pollutants, particularly heavy metals, into the environment. Chronic exposure to these contaminants has been linked to a range of health risks, but the molecular underpinnings remain poorly understood. In this
[...] Read more.
Background: Informal electronic waste (e-waste) recycling practices release a complex mixture of pollutants, particularly heavy metals, into the environment. Chronic exposure to these contaminants has been linked to a range of health risks, but the molecular underpinnings remain poorly understood. In this study, we investigated the alterations in metabolic profiles due to e-waste exposure and linked these metabolites to systemic biological effects. Methods: We applied untargeted high-resolution metabolomics using dual-column LC-MS/MS and a multi-step analysis workflow combining MS1 feature detection, MS2 annotation, and chemical ontology classification, to characterize urinary metabolic alterations in 91 e-waste workers and 51 community controls associated with the Agbogbloshie site (Accra, Ghana). The impacts of heavy metal exposure in e-waste workers were assessed by establishing linear regression and four-parameter logistic (4PL) models between heavy metal levels and metabolite concentrations. Results: Significant metal-associated metabolomic changes were identified. Both linear and nonlinear models revealed distinct sets of exposure-responsive compounds, highlighting diverse biological responses. Ontology-informed annotation revealed systemic effects on lipid metabolism, oxidative stress pathways, and xenobiotic biotransformation. This study demonstrates how integrating chemical ontology and nonlinear modeling facilitates exposome interpretation in complex environments and provides a scalable template for environmental biomarker discovery. Conclusions: Integrating dose–response modeling and chemical ontology analysis enables robust interpretation of exposomics datasets when direct compound identification is limited. Our findings indicate that e-waste exposure induces systemic metabolic alterations that can underlie health risks and diseases.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Method Development in Metabolomics and Exposomics)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Effects of Eight Weeks of Aerobic Training Combined with Carbohydrate Mouth Rinse on Body Composition and Exercise Performance in Adult Men with Obesity: Evidence from Korea
by
Jae-Myun Ko, Wi-Young So and Sung-Eun Park
Metabolites 2025, 15(7), 455; https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070455 - 5 Jul 2025
Abstract
Background: Considering that the prevalence of obesity has risen rapidly in recent decades, the aim of this study was to investigate the effects of a carbohydrate mouth rinse (CMR) on the outcomes of aerobic training among adult men with obesity, focusing particularly on
[...] Read more.
Background: Considering that the prevalence of obesity has risen rapidly in recent decades, the aim of this study was to investigate the effects of a carbohydrate mouth rinse (CMR) on the outcomes of aerobic training among adult men with obesity, focusing particularly on the effects of repeated use on body composition and exercise performance. Methods: The intervention targeted 20 men with obesity in their 20s and 30s randomly assigned to either a CMR group (n = 10) or a placebo mouth rinse (PMR) group (n = 10). Both groups completed treadmill-based aerobic training three times per week for eight weeks. Prior to each session, participants used a mouth rinse at 60, 40, and 20 s before the start of each exercise, holding either a 6% maltodextrin solution (CMR) or purified water (PMR) in their mouths for 5 to 10 s before expectorating. Pre- and post-intervention assessments included body composition (body weight and body fat percentage), resting metabolic rate (RMR), maximal oxygen uptake (VO2max), and exercise performance (rate of perceived exertion [RPE], exercise distance, speed, and time). Data were analyzed using 2 × 2 repeated measures analysis of variance. Results: Following the intervention, the CMR group showed significantly greater improvements than the PMR group did in body fat percentage, RMR, VO2max, exercise distance, speed, and time (p < 0.01). However, the interaction effect for RPE was not statistically significant between the groups (p = 0.175). Overall, the repeated use of the CMR during aerobic training contributed to enhanced exercise performance and favorable physiological changes without additional caloric intake. Conclusions: A CMR may be a practical and non-caloric ergogenic aid to support exercise performance and metabolic function in individuals with obesity. Its repeated use during aerobic training appears to be effective and safe, especially when fasting while exercising, when improving endurance without compromising fat loss is essential.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Effects of Various Exercise Methods on Metabolic Health)
Open AccessReview
Extracellular Vesicle Metabolomics Holds Promise for Adult Axon Regeneration
by
Maria D. Cabrera Gonzalez, Jackson Watson, Laura Leal, Isabella Moceri, Camille Plummer, Biraj Mahato, Abdelrahman Y. Fouda and Sanjoy K. Bhattacharya
Metabolites 2025, 15(7), 454; https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070454 - 4 Jul 2025
Abstract
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are bilayer lipid membrane particles that are released by every cell type. These secretions are further classified as exosomes, ectosomes, and microvesicles. They contain biomolecules (RNAs, proteins, metabolites, and lipids) with the ability to modulate various biological processes and have
[...] Read more.
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are bilayer lipid membrane particles that are released by every cell type. These secretions are further classified as exosomes, ectosomes, and microvesicles. They contain biomolecules (RNAs, proteins, metabolites, and lipids) with the ability to modulate various biological processes and have been shown to play a role in intercellular communication and cellular rejuvenation. Various studies suggest exosomes and/or microvesicles as a potential platform for drug delivery. EVs may deliver lipids and nucleotides directly to an injury site in an axon, promoting growth cone stabilization and membrane expansion as well as repair, thus positively modulating adult axon regeneration. In this review, we will provide a perspective on the metabolite composition of EVs in adult axonal regeneration relevant to the central nervous system (CNS), specifically that pertaining to the optic nerve. We will present an overview of the methods for isolation, enrichment, omics data analysis and quantification of extracellular vesicles with the goal of providing direction for future studies relevant to axon regeneration. We will also include current resources for multi-omics data integration relevant to extracellular vesicles from diverse cell types.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Molecular Cargo of Extracellular Vesicles: A Key to Understanding Their Biological Role)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Human Digestive Physiology and Evolutionary Diet: A Metabolomic Perspective on Carnivorous and Scavenger Adaptations
by
Vicente Javier Clemente-Suárez, Laura Redondo-Flórez, Ana Isabel Beltrán-Velasco, Rodrigo Yáñez-Sepúlveda, Alejandro Rubio-Zarapuz, Alexandra Martín-Rodríguez, Eduardo Navarro-Jimenez and José Francisco Tornero-Aguilera
Metabolites 2025, 15(7), 453; https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070453 - 4 Jul 2025
Abstract
This review examines human digestive physiology and metabolic adaptations in the context of evolutionary dietary patterns, particularly those emphasizing carnivorous and scavenging behaviors. By integrating metabolomic data with archaeological, anatomical, and microbiological evidence, the study explores how early hominins adapted to intermittent but
[...] Read more.
This review examines human digestive physiology and metabolic adaptations in the context of evolutionary dietary patterns, particularly those emphasizing carnivorous and scavenging behaviors. By integrating metabolomic data with archaeological, anatomical, and microbiological evidence, the study explores how early hominins adapted to intermittent but energy-dense animal-based diets. The analysis highlights the development of hepatic insulin resistance, enhanced fat and protein metabolism, and shifts in gut microbiota diversity as physiological signatures of meat consumption. Comparative evaluations of digestive enzyme profiles, intestinal morphology, and salivary composition underscore humans’ omnivorous flexibility and partial carnivorous specialization. Additionally, biomarkers such as ketone bodies, branched-chain amino acids, and trimethylamine-N-oxide are identified as metabolic indicators of habitual meat intake. These adaptations, though once evolutionarily advantageous, are discussed in relation to current metabolic disorders in modern nutritional contexts. Overall, this review presents a metabolomic framework for understanding the evolutionary trajectory of human digestion and its implications for health and dietary recommendations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Advances in Metabolomics)
Open AccessArticle
In Vitro Metabolism of Doping Agents (Stanozolol, LGD-4033, Anastrozole, GW1516, Trimetazidine) by Human Seminal Vesicle and Liver Fractions
by
Johanna Sternberg, Insa Peters, Nana Naumann, Andreas Thomas and Mario Thevis
Metabolites 2025, 15(7), 452; https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070452 - 4 Jul 2025
Abstract
Background: In order to address complex scenarios in anti-doping science, especially in cases where an unintentional exposure of athletes to prohibited substances and a corresponding contamination of doping control samples at the collection event are argued, an understanding of tissue-specific drug metabolism is
[...] Read more.
Background: In order to address complex scenarios in anti-doping science, especially in cases where an unintentional exposure of athletes to prohibited substances and a corresponding contamination of doping control samples at the collection event are argued, an understanding of tissue-specific drug metabolism is essential. Hence, in this study, the metabolic capacity of the seminal vesicle using in vitro assays was investigated. Methods: The aim was to assess whether selected doping-relevant substances—stanozolol, LGD-4033, GW1516, trimetazidine, and anastrozole—are metabolised in seminal vesicle cellular fractions (SV-S9) and how that metabolism compares to biotransformations induced by human liver S9 fractions (HL-S9). Liquid chromatography coupled to high-resolution/accurate mass spectrometry (LC HRAM MS) enabled the sensitive detection and identification of metabolites, revealing a limited metabolic activity of SV-S9. Results: For LGD-4033, GW1516, and trimetazidine, minor metabolic transformations were observed, whereas no metabolites of stanozolol or anastrozole were detected. Gene expression analysis using digital polymerase chain reaction (dPCR) confirmed transcripts of CYP2D6, CYP2E1, and CYP2C9 in SV-S9, though no enzymatic activity was detected. Gene expression and enzymatic activity in CYP3A4 and CYP1A2—major hepatic enzymes—were absent in SV-S9. Conclusions: Overall, these pilot study results suggest that the seminal vesicle has only a low capacity for xenobiotic metabolism, which translates into a limited role in the biotransformation of drugs and, hence, the metabolic pattern.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Pharmacology and Drug Metabolism)
►▼
Show Figures
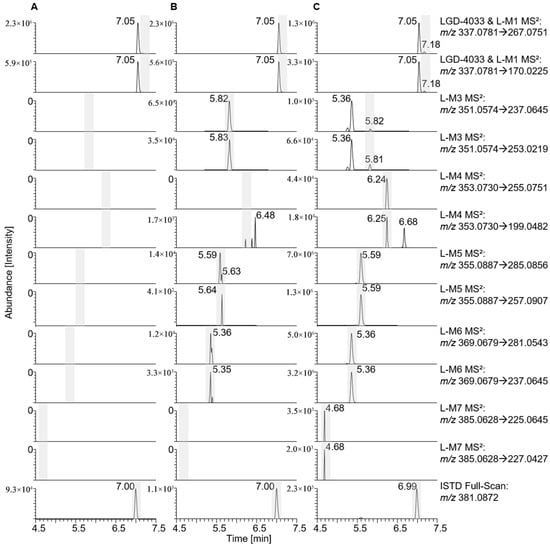
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Assessment of Metabolic Alterations Induced by Halogenated Additives and Antifungal Activity of Extracts from the Endophytic Fungus Fusarium sp. Associated with Dizygostemon riparius (Plantaginaceae)
by
Hilzimar de Jesus Freitas Sá, Anne Karoline Maiorana Santos, Adriano Souza Fonseca, Lourivaldo da Silva Santos, Josivan Regis Farias, Rosane Nassar Meireles Guerra, Edson Rodrigues-Filho, Gilmar Silverio da Silva, Cleydlenne Costa Vasconcelos, Alberto Jorge Oliveira Lopes and Antônio José Cantanhede Filho
Metabolites 2025, 15(7), 451; https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070451 - 4 Jul 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Endophytic fungi are valuable sources of bioactive compounds with potential therapeutic applications. This study aimed to evaluate the antifungal activity of secondary metabolites produced by Fusarium sp. isolated from Dizygostemon riparius, with particular focus on the impact of culture medium
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Endophytic fungi are valuable sources of bioactive compounds with potential therapeutic applications. This study aimed to evaluate the antifungal activity of secondary metabolites produced by Fusarium sp. isolated from Dizygostemon riparius, with particular focus on the impact of culture medium supplementation with halogenated and metallic additives on metabolite production. Methods: The fungus was cultivated in standard Czapek medium and media supplemented with NH4Br or MnCl2. Methanolic extracts were obtained, fractionated, and chemically characterised via LC-ESI-HRMS. In vitro antifungal assays, including MIC and MFC determinations and biofilm inhibition tests, were performed against Candida albicans strains. In vivo toxicity and efficacy were assessed using Tenebrio molitor larvae. Results: Fifteen metabolites were annotated, including known antifungals such as fusaric acid and cyclosporin A. Fractions EMBr4 and EMC5 demonstrated fungicidal activity with MIC values close to fluconazole and significantly inhibited biofilm formation and maturation. In vivo, these fractions displayed low acute toxicity and improved survival in infected larvae, comparable to fluconazole treatment. Conclusions: The results indicate that culture medium modulation enhances the production of bioactive metabolites by Fusarium sp., leading to extracts with notable antifungal efficacy and safety. EMBr4 and EMC5 are promising candidates for further development as antifungal agents, particularly for targeting biofilm-associated Candida infections. These findings support the potential of endophytic fungi as sources of novel therapeutics and warrant further mechanistic and pharmacological investigations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Secondary Metabolites and Their Activities: From the Identification to the Biological Investigation)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Interaction Between CYP1A2-Related Caffeine Metabolism and Vitamin B12/Folate Status in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome: A Novel Biomarker Axis
by
Laura Claudia Popa, Ahmed Abu-Awwad, Simona Sorina Farcas, Simona-Alina Abu-Awwad and Nicoleta Ioana Andreescu
Metabolites 2025, 15(7), 450; https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070450 - 4 Jul 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: The prevalence of metabolic syndrome (MetS) is steadily increasing worldwide, driven by complex genetic, nutritional, and environmental factors. Caffeine metabolism, primarily mediated by CYP1A2 (though other enzymes such as CYP1A1 may also be involved), and the status of micronutrients such as
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: The prevalence of metabolic syndrome (MetS) is steadily increasing worldwide, driven by complex genetic, nutritional, and environmental factors. Caffeine metabolism, primarily mediated by CYP1A2 (though other enzymes such as CYP1A1 may also be involved), and the status of micronutrients such as vitamin B12 and folate have each been linked to MetS components. This study investigates the interaction between CYP1A2 genetic variants and vitamin B12/folate levels in patients with MetS, aiming to identify a novel biomarker axis with potential implications for personalized interventions. Methods: This cross-sectional observational study included 356 adults diagnosed with MetS, recruited from Western Romania. Genotyping for CYP1A2 rs762551 was performed using TaqMan PCR assays. Daily caffeine intake was assessed via validated dietary questionnaires. Serum levels of folate and vitamin B12 were measured using chemiluminescence immunoassays. Results: AA genotype patients with a moderate coffee intake (1–2 cups/day) had significantly higher folate and B12 levels than AC or CC carriers. These nutritional advantages were associated with more favorable BMI and triglyceride profiles. The interaction between CYP1A2 genotype and coffee intake was significant for both micronutrient levels and metabolic parameters, particularly in the AA group. No significant associations were found in high-coffee-intake subgroups (≥3 cups/day). Conclusions: The interplay between CYP1A2 polymorphisms and B-vitamin status may represent a clinically relevant biomarker axis in MetS. Moderate caffeine intake in slow metabolizers (AA genotype) may boost micronutrient status and metabolic health, supporting personalized nutrition.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Endocrinology and Clinical Metabolic Research)
►▼
Show Figures
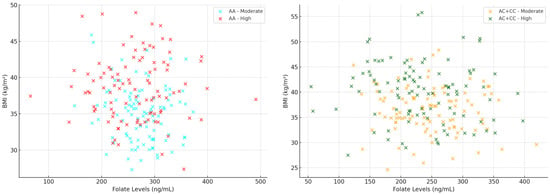
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Metabolic Changes in Zebrafish Larvae Infected with Mycobacterium marinum: A Widely Targeted Metabolomic Analysis
by
Chongyuan Sima, Qifan Zhang, Xiaoli Yu, Bo Yan and Shulin Zhang
Metabolites 2025, 15(7), 449; https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070449 - 4 Jul 2025
Abstract
Objectives: To explore the metabolic changes in zebrafish larvae after infection with Mycobacterium marinum, this study adopted a widely targeted metabolomic approach to analyze the changes in the overall metabolic profiles of zebrafish larvae infected for 5 days. Methods: Data were collected
[...] Read more.
Objectives: To explore the metabolic changes in zebrafish larvae after infection with Mycobacterium marinum, this study adopted a widely targeted metabolomic approach to analyze the changes in the overall metabolic profiles of zebrafish larvae infected for 5 days. Methods: Data were collected by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). Mass spectrometry data were processed using Analyst 1.6.3 and MultiQuant 3.0.3 software, and multivariate statistical analysis was carried out. The KEGG database, HMDB database, and CHEBI database were used to screen and identify differential metabolites, and metabolic pathway enrichment analysis was performed through KEGG pathways. Results: A total of 329 metabolites were detected, among which 61 differential metabolites were screened. Specifically, 41 metabolites, such as kynurenine, isoallolithocholic acid, 2′-deoxyguanosine, indole-3-carboxaldehyde, and L-lactic acid, were downregulated, while 20 metabolites, such as L-palmitoylcarnitine, myristoyl-L-carnitine, dodecanoylcarnitine, 2-isopropyl-malic acid, and 2-methylsuccinic acid, were upregulated. KEGG metabolic pathway enrichment analysis indicated that these differential metabolites were mainly involved in metabolic pathways such as pyrimidine metabolism, nucleotide metabolism, the pentose phosphate pathway, and purine metabolism. Conclusions: This study demonstrated that significant changes occurred in multiple metabolites and metabolic pathways in zebrafish larvae after infection with M. marinum. The research results have improved the understanding of zebrafish as a model organism in the field of Mycobacterium research and laid a solid foundation for subsequent metabolomic-related research using zebrafish.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Advances in Metabolomics)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Metabolomic Prediction of Naphthalene Pneumo-Toxicity in the Snail Helix aspersa maxima
by
Aude Devalckeneer, Marion Bouviez and Jean-Marie Colet
Metabolites 2025, 15(7), 448; https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070448 - 3 Jul 2025
Abstract
Background: Polluted soils represent a major problem in many industrialized countries that urgently requires appropriate health risk assessment. The One Health concept that considers a close relationship between human and animal health and ecosystems relies, among other techniques, on continuous monitoring through the
[...] Read more.
Background: Polluted soils represent a major problem in many industrialized countries that urgently requires appropriate health risk assessment. The One Health concept that considers a close relationship between human and animal health and ecosystems relies, among other techniques, on continuous monitoring through the use of animal species as bioindicators. In this context, terrestrial gastropods, already recognized as relevant indicators due to their anatomo-physiology, provide a reliable model to study the pneumotoxic effects of pollutants. On the other hand, risk assessment is based on multi-biomarker studies. Therefore, omic approaches seem particularly useful since they can simultaneously detect numerous early biological changes. Methods: In this study, Helix aspersa maxima was exposed to naphthalene, a highly volatile aromatic hydrocarbon responsible for numerous respiratory disorders. Pulmonary membrane extracts and hemolymph samples were analyzed by 1H-NMR spectroscopy after single or repeated exposures to naphthalene. Results: Numerous metabolic changes were observed, which could be related to membrane lesions, energy, anti-inflammatory, and tumorigenesis pathways. Conclusions: Our findings highlight the potential of combining animal indicator and omics techniques to predict respiratory health risks in cases of exposure to polluted soils.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Feature Papers in Assessing Environmental Health and Function)
►▼
Show Figures
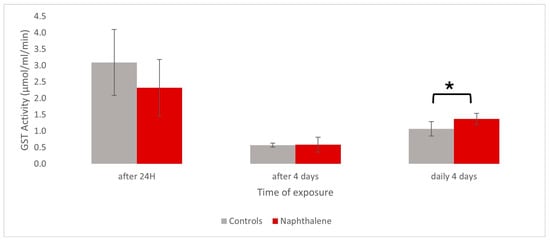
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Multi-Omics Analysis of Gut Microbiota and Sperm Quality in Tibetan Breeding Boars
by
Mingxuan Zhao, Mengjia Han, Hongliang Zhang, Xiangdong Wang, Yikai Yin, Jian Zhang and Peng Shang
Metabolites 2025, 15(7), 447; https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070447 - 2 Jul 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Reproductive efficiency in breeding boars critically impacts swine industry productivity, with sperm quality being multifactorially regulated by gut microbiota. This study aimed to elucidate the microbiota–metabolite interactions underlying sperm quality differences in Tibetan boars. Methods: Integrated 16S rRNA sequencing and untargeted metabolomics
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Reproductive efficiency in breeding boars critically impacts swine industry productivity, with sperm quality being multifactorially regulated by gut microbiota. This study aimed to elucidate the microbiota–metabolite interactions underlying sperm quality differences in Tibetan boars. Methods: Integrated 16S rRNA sequencing and untargeted metabolomics were performed on fecal and semen samples from eight healthy Tibetan boars (31–33 months old), stratified into low-semen (CJ) and high-semen utilization (HJ) groups. Analyses included sperm quality assessment, microbial profiling, and metabolic pathway enrichment. Results: The HJ group exhibited significantly enhanced sperm motility and semen utilization rates (p < 0.05). Gut microbiota composition differed markedly, with Firmicutes and Proteobacteria enriched in HJ boars. Metabolomics identified key metabolites positively correlated with sperm quality (e.g., butyrate, phenyllactic acid), while lithocholic acid showed negative associations. KEGG analysis revealed predominant involvement in butanoate metabolism and bile acid biosynthesis. Core microbiota (e.g., Ruminococcus) modulated sperm quality through short-chain fatty acid networks and bile acid homeostasis. Conclusions: Gut microbiota regulated the sperm microenvironment via a “metabolic-immune” dual pathway mediated by the gut–testis axis. These findings establish a theoretical basis for probiotic or metabolite-targeted strategies to improve boar reproductive performance.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Animal Metabolism)
►▼
Show Figures
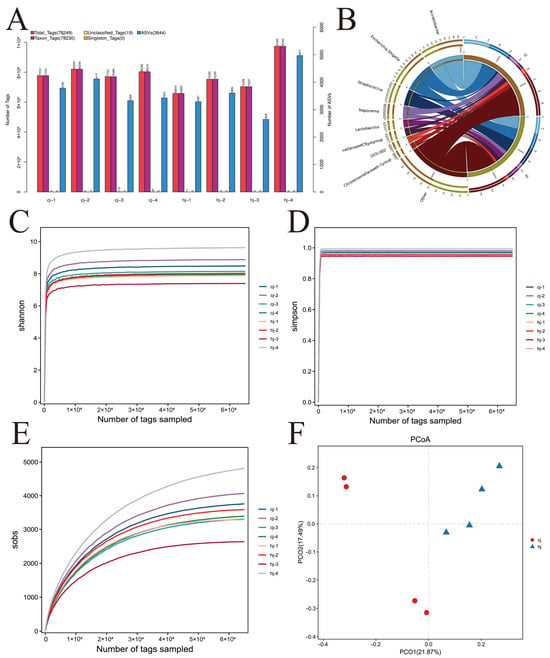
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Amino Acid Metabolism in Liver Mitochondria: From Homeostasis to Disease
by
Ranya Erdal, Kıvanç Birsoy and Gokhan Unlu
Metabolites 2025, 15(7), 446; https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070446 - 2 Jul 2025
Abstract
Hepatic mitochondria play critical roles in sustaining systemic nutrient balance, nitrogen detoxification, and cellular bioenergetics. These functions depend on tightly regulated mitochondrial processes, including amino acid catabolism, ammonia clearance via the urea cycle, and transport through specialized solute carriers. Genetic disruptions in these
[...] Read more.
Hepatic mitochondria play critical roles in sustaining systemic nutrient balance, nitrogen detoxification, and cellular bioenergetics. These functions depend on tightly regulated mitochondrial processes, including amino acid catabolism, ammonia clearance via the urea cycle, and transport through specialized solute carriers. Genetic disruptions in these pathways underlie a range of inborn errors of metabolism, often resulting in systemic toxicity and neurological dysfunction. Here, we review the physiological functions of hepatic mitochondrial amino acid metabolism, with a focus on subcellular compartmentalization, disease mechanisms, and therapeutic strategies. We discuss how emerging genetic and metabolic interventions—including dietary modulation, cofactor replacement, and gene therapy—are reshaping treatment of liver-based metabolic disorders. Understanding these pathways offers mechanistic insights into metabolic homeostasis and reveals actionable vulnerabilities in metabolic disease and cancer.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Multifaceted Roles of Biomarkers in Metabolic Disorders: From Diagnosis and Monitoring to Prediction, Management, and Treatment)
►▼
Show Figures
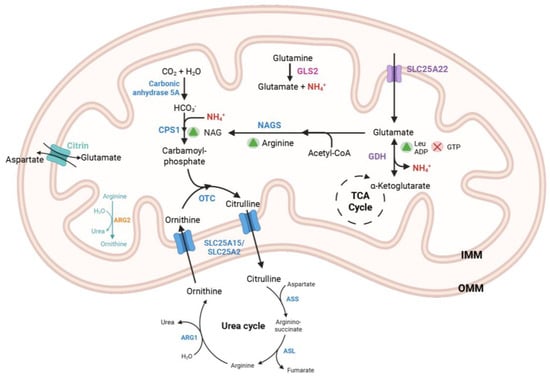
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Impacts of Protease Sources on Growth and Carcass Response, Gut Health, Nutrient Digestibility, and Cecal Microbiota Profiles in Broilers Fed Poultry-by-Product-Meal-Based Diets
by
Muhammad Shahbaz Zafar, Shafqat Nawaz Qaisrani, Saima, Zafar Hayat and Kashif Nauman
Metabolites 2025, 15(7), 445; https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15070445 - 2 Jul 2025
Abstract
Background: The current study aimed to evaluate the effects of the supplementation of protease sources on growth and carcass response, gut health, nutrient digestibility, and cecal microbiota profiles in broilers fed poultry-by-product-meal (PBM)-containing diets. Methods: In total, 800 one-day-old mixed-sex broilers (Arbor Acres)
[...] Read more.
Background: The current study aimed to evaluate the effects of the supplementation of protease sources on growth and carcass response, gut health, nutrient digestibility, and cecal microbiota profiles in broilers fed poultry-by-product-meal (PBM)-containing diets. Methods: In total, 800 one-day-old mixed-sex broilers (Arbor Acres) were weighed and allocated to one of the four dietary treatments in a completely randomized design, with eight replicates and 25 birds each per replicate. The treatments were as follows: (1) T0, control diet (without protease supplementation and 3% PBM); (2) T1, control diet supplemented with acidic protease at 100 g/ton (50,000 U/g); (3) T2, control diet supplemented with alkaline protease at 200 g/ton (25,000 U/g); (4) T3, control diet supplemented with neutral protease at 200 g/ton (25,000 U/g). Results: Protease supplementation enhanced (p < 0.05) body weight gain and the feed conversion ratio, predominantly in broilers fed PBM-based diets containing alkaline protease. Alkaline protease supplementation increased (p < 0.05) the apparent ileal digestibility of proteins (AIDP) by 4.3% and the apparent ileal digestibility of amino acids (AIDAA) by up to 5.8%, except for ornithine. Increments (p < 0.05) in carcass, breast, and leg quarter yields due to protease supplementation were evident, particularly in broilers fed diets containing alkaline protease. Alkaline protease improved (p < 0.05) the duodenal villus height (VH), reduced the crypt depth (CD), and increased the villus height to crypt depth ratio (VCR). Alkaline protease supplementation reduced (p < 0.05) cecal counts of Salmonella, Escherichia coli, and Clostridium in the broilers, whereas it increased (p < 0.05) the Lactobacillus counts. Conclusions: the supplemented alkaline protease resulted in improved growth performance and carcass traits, better gut health, as well as improved ileal digestibility of nutrients, including crude protein (CP) and acid insoluble ash (AIA), with a more balanced cecal microbial composition in broilers.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Animal Metabolism)

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Metabolites Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Biomolecules, Foods, Metabolites, Microorganisms, Pathogens, Bacteria
Bioinformatics, Machine Learning and Risk Assessment in Food Industry
Topic Editors: Bing Niu, Suren Rao Sooranna, Pufeng DuDeadline: 31 July 2025
Topic in
Animals, Dairy, Microorganisms, Veterinary Sciences, Metabolites, Life, Parasitologia
The Complexity of Parasites in Animals: Impacts, Innovation, and Interventions
Topic Editors: Kun Li, Rongjun Wang, Ningbo Xia, Md. F. KulyarDeadline: 31 August 2025
Topic in
Agronomy, Metabolites, Microorganisms, Plants, Soil Systems
Interactions between Plants and Soil Microbes in Natural Ecosystem
Topic Editors: Chao Zhang, Jie WangDeadline: 31 October 2025
Topic in
Cells, Chemistry, IJMS, Molecules, Metabolites
Bioactive Compounds and Therapeutics: Molecular Aspects, Metabolic Profiles, and Omics Studies 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Michele Costanzo, Giovanni N. Roviello, Armando CeveniniDeadline: 20 November 2025

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Metabolites
Lipid Metabolism Disorders in Obesity
Guest Editors: Klaudia Sztolsztener, Elzbieta SupruniukDeadline: 10 July 2025
Special Issue in
Metabolites
Climate Change-Related Stresses and Plant Metabolism
Guest Editor: Eva CollakovaDeadline: 14 July 2025
Special Issue in
Metabolites
Psoriasis and Metabolic Syndrome
Guest Editor: Anna BaranDeadline: 15 July 2025
Special Issue in
Metabolites
Drug Metabolism: Latest Advances and Prospects
Guest Editors: Michel Kranendonk, Bernardo Brito PalmaDeadline: 15 July 2025
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Metabolites
Feature Papers Related to Metabolomic Profiling Technology
Collection Editor: Thusitha Rupasinghe
Topical Collection in
Metabolites
Feature Papers in Assessing Environmental Health and Function
Collection Editor: David J. Beale
Topical Collection in
Metabolites
Metabolic Effects of Animal Growth Promoters
Collection Editor: Chi Chen







