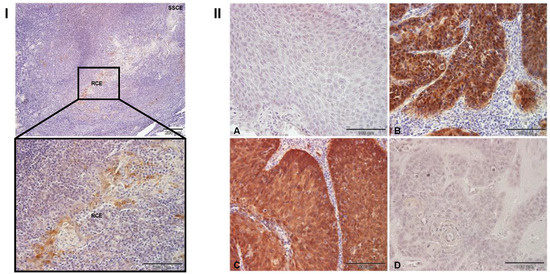
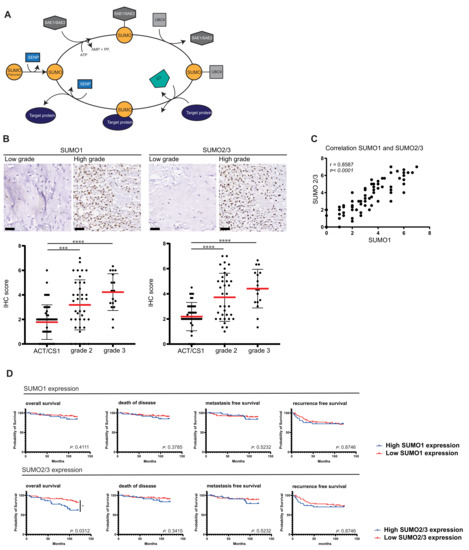
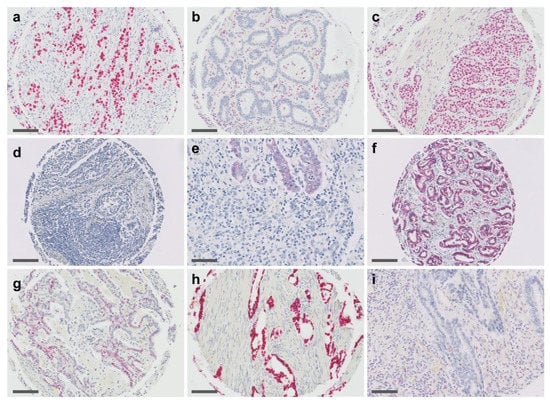
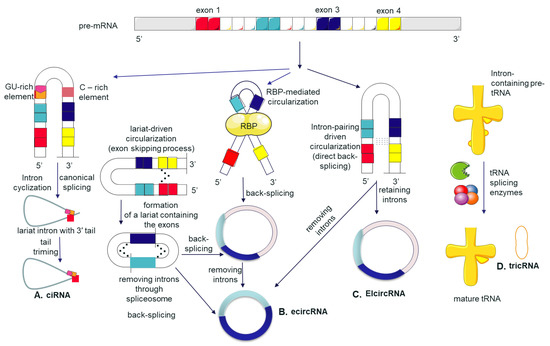
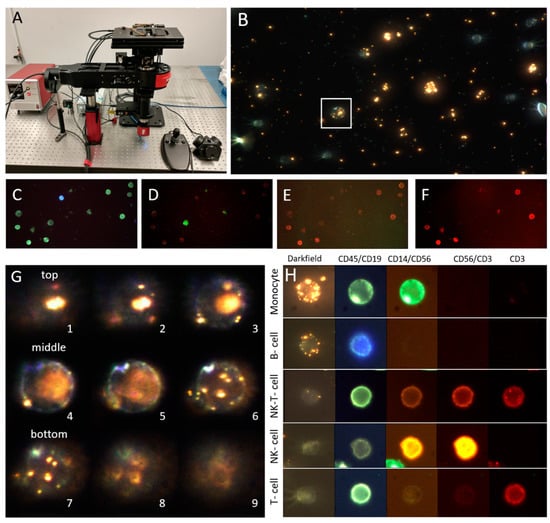
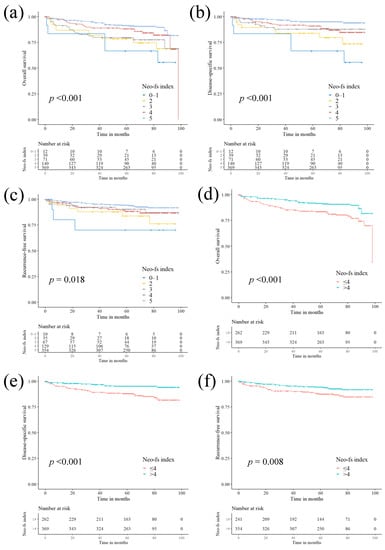
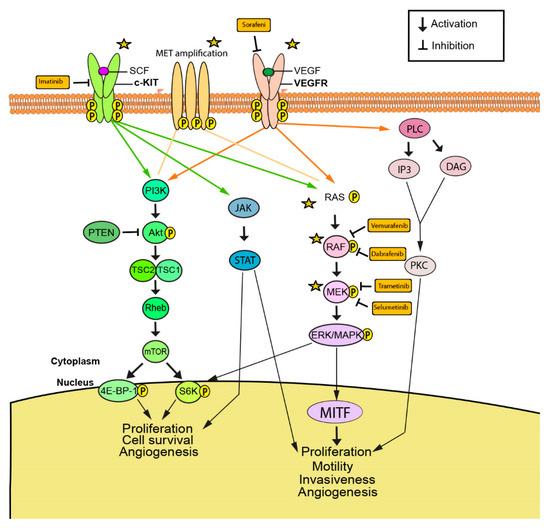
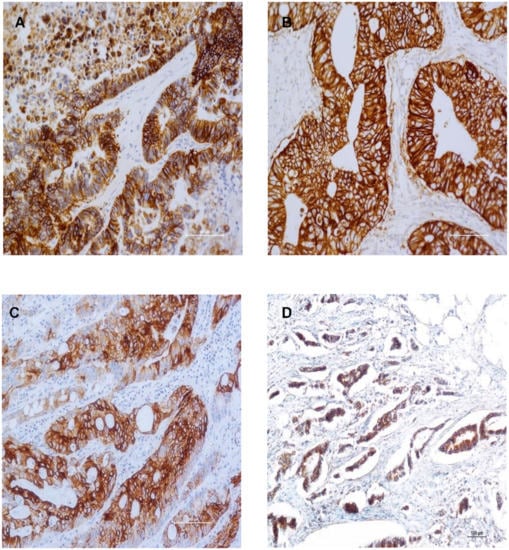
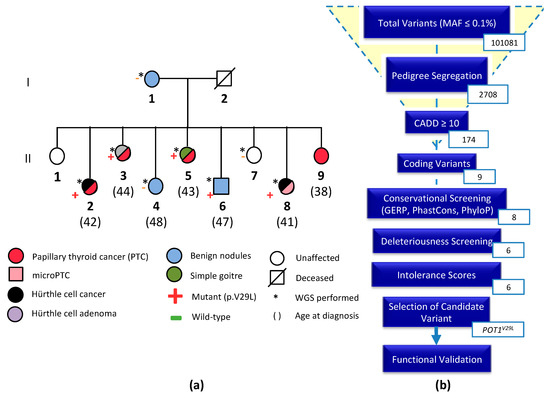
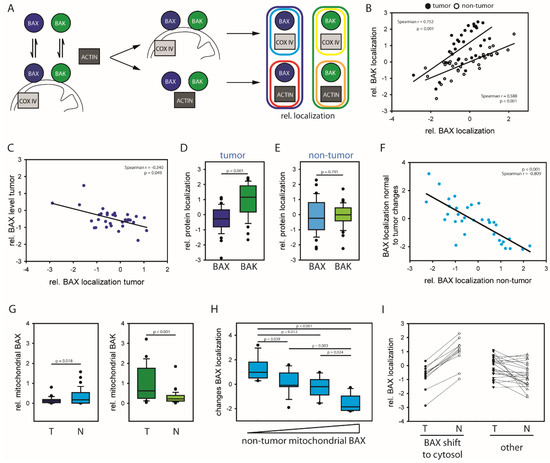
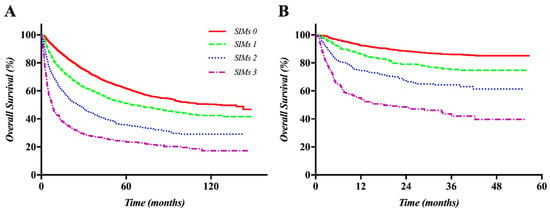
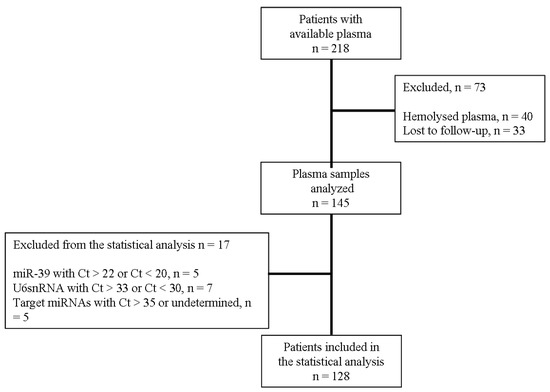
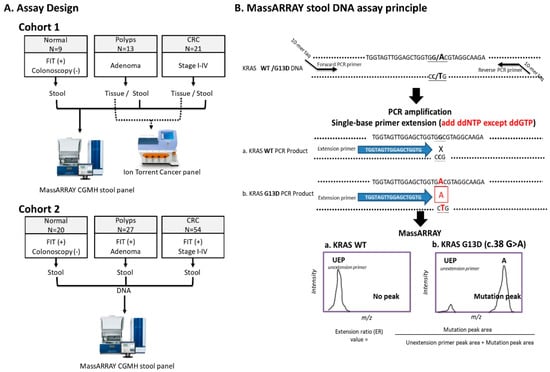
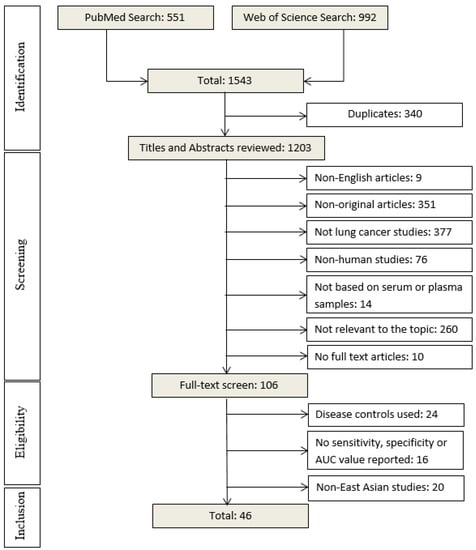
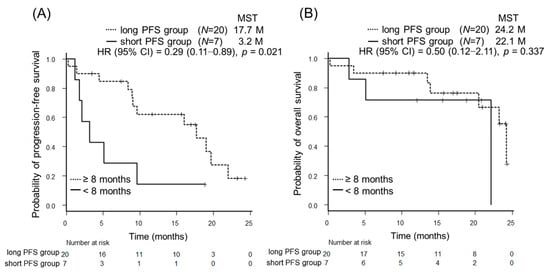
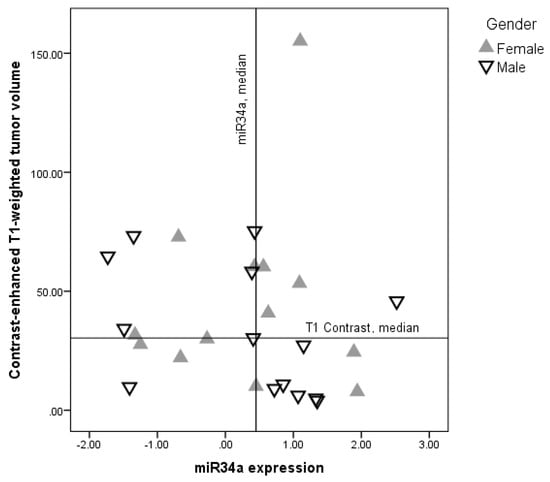
Cancer Biomarkers
A topical collection in Cancers (ISSN 2072-6694). This collection belongs to the section "Cancer Biomarkers".
Submission Status: Closed | Viewed by 447237Editor
2. Department of Biomedical Informatics, Emory University, Atlanta, GA 30322, USA
Interests: prostate cancer; breast cancer; bioinformatics; genomics; transcription; biomarkers
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
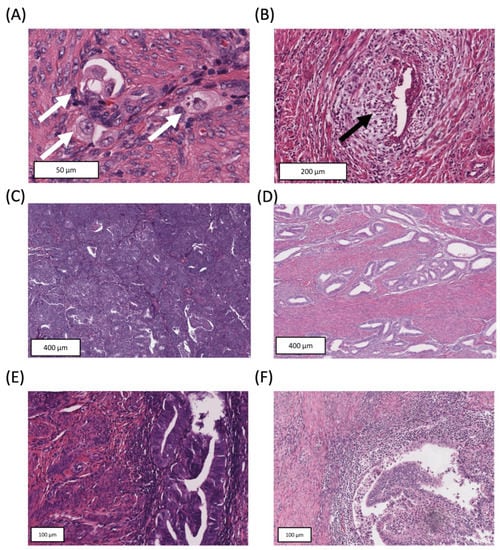
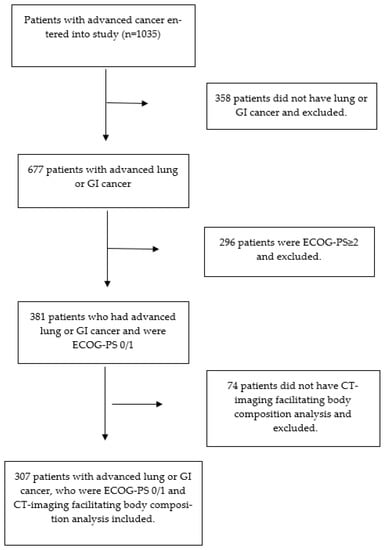
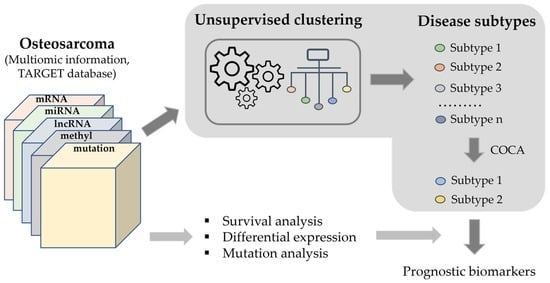
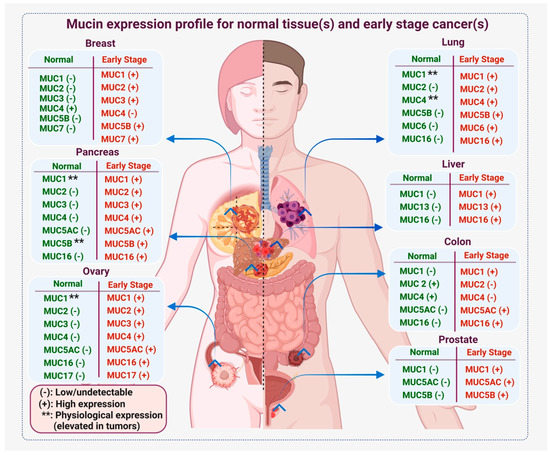
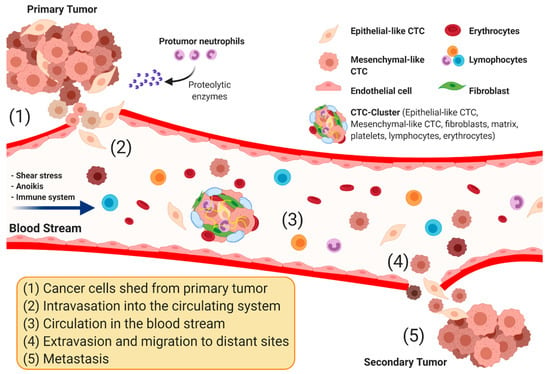
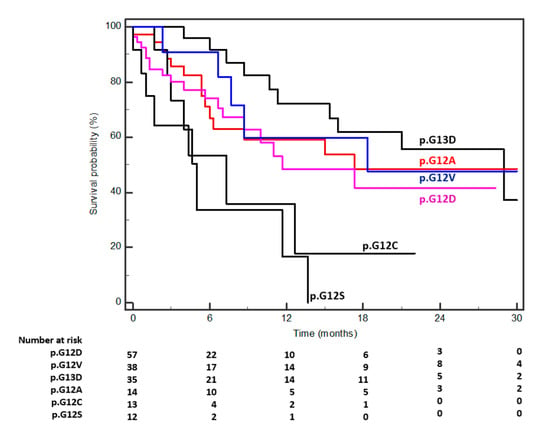
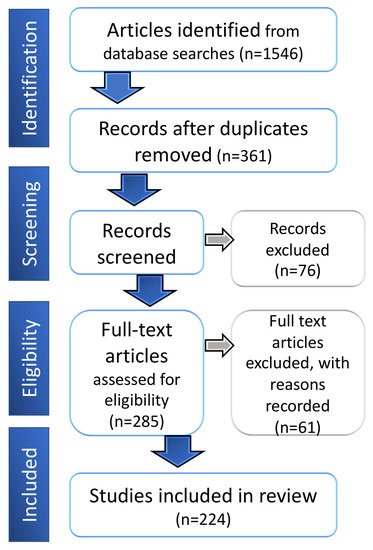
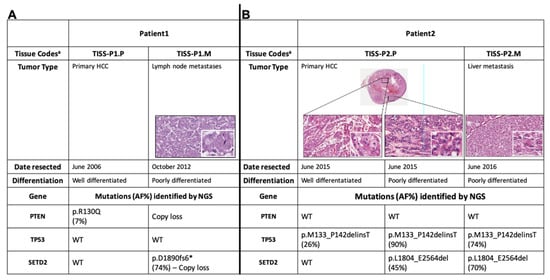
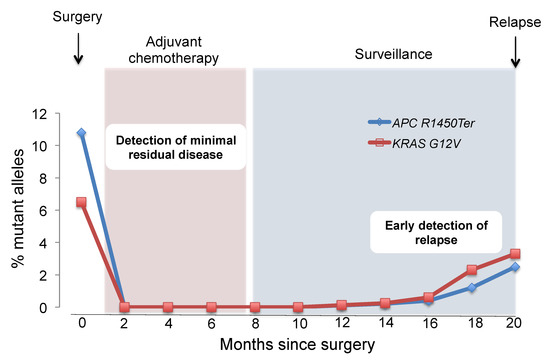
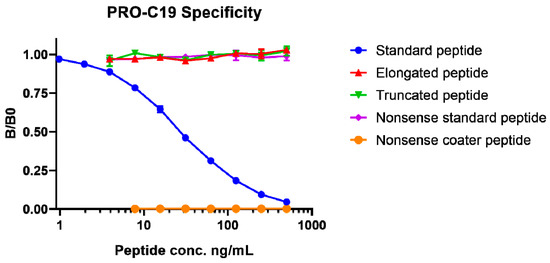
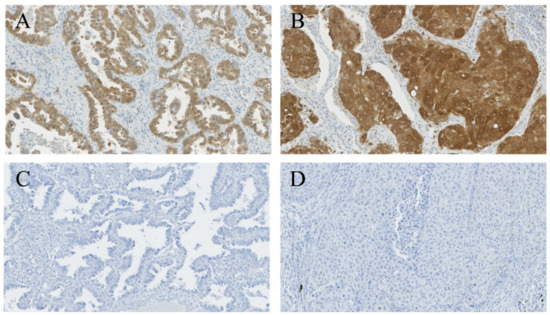
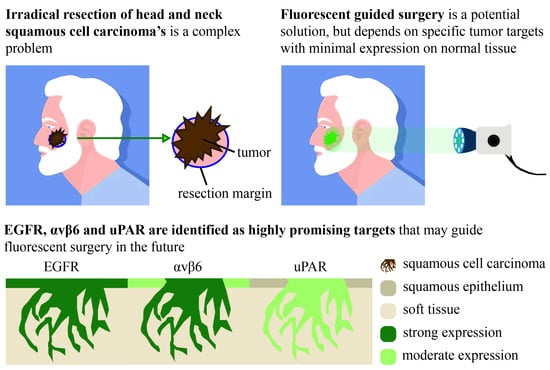
Biomarkers are playing an ever-increasingly important role in the diagnosis, treatment, and management of cancer patients. Advances in detection technologies, including next generation sequencing, circulating tumor cells, and multicolor flow cytometry, among others, have enabled scientists and clinicians to gain greater insights into the molecular mechanisms that underlie the pathologies of a variety of malignancies. Furthermore, targeted precision therapies often require the identification of subsets of patients who will benefit from these therapies, and cancer biomarkers are essential to obtaining FDA approval for many drugs under development and investigation. Additionally, biomarkers are currently in clinical practice to identify patients with favorable prognoses who can safely avoid overtreatment. Nevertheless, challenges remain in development of new non-invasive biomarkers with greater sensitivity, specificity, and clinical utility. This Topical Collection will review the current state of cancer biomarker development and the prospects for improving cancer care with new technologies and biomarkers to improve cancer patient diagnoses, management, and outcomes.
Dr. Carlos S. Moreno
Guest Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 250 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for assessment.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Cancers is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2900 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Biomarkers
- Precision Medicine
- Diagnosis
- Prognosis
- Liquid Biopsy
- Companion Diagnostics