- Article
Two-Week Interval Hypofractionated Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Benign Intracranial Tumors: Volumetric Kinetics and Radiobiological Rationale
- Seung Woo Hong,
- Junhyung Kim and
- Won Seok Chang
- + 5 authors
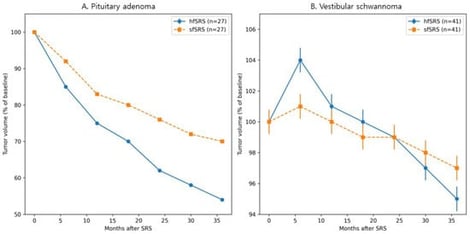
Background/Objectives: Hypofractionated stereotactic radiosurgery (hfSRS) is increasingly used for benign intracranial tumors that are large or located near critical neural structures to reduce treatment-related toxicity. However, the optimal interval between fractions remains poorly defined, particularly for slowly proliferating benign tumors. This study evaluated clinical outcomes and longitudinal volumetric response patterns following Gamma Knife hfSRS delivered at fixed two-week intervals, with particular attention to the biological relevance of fraction timing. Methods: We retrospectively analyzed 126 patients with benign intracranial tumors, including meningioma, non-functioning pituitary neuroendocrine tumor (PitNET), vestibular schwannoma, and craniopharyngioma, treated between 2016 and 2022. Treatment was delivered in 2–5 fractions at fixed two-week intervals using Gamma Knife radiosurgery. Radiological outcomes included tumor control rate and longitudinal volumetric changes, while clinical outcomes included visual, auditory, and endocrine function. Propensity score matching was performed in PitNET and vestibular schwannoma cohorts to compare hfSRS with single-fraction stereotactic radiosurgery while minimizing baseline imbalances. Results: The overall tumor control rate was 98.4%. Across the entire cohort, tumors demonstrated a median volume reduction of −0.64% per month. In the propensity score–matched PitNET cohort, tumor control was comparable between treatment groups, whereas hfSRS was associated with earlier and greater volumetric reduction over time compared with single-fraction treatment. In the matched vestibular schwannoma cohort, long-term tumor control was similar between groups; however, transient tumor enlargement occurred more frequently after hfSRS without adversely affecting long-term tumor control or functional hearing outcomes. Conclusions: Hypofractionated stereotactic radiosurgery delivered at fixed two-week intervals achieved excellent tumor control with acceptable toxicity in selected benign intracranial tumors. These findings support the clinical feasibility of a fixed two-week inter-fraction interval and suggest that fraction timing may represent a biologically relevant treatment parameter influencing early volumetric response patterns without compromising long-term outcomes.
13 February 2026