Human DLG1 and SCRIB Are Distinctly Regulated Independently of HPV-16 during the Progression of Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinomas: A Preliminary Analysis
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tissue Samples
2.2. DNA Detection and Genotyping
2.3. Antibodies
2.4. Immunohistochemistry
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
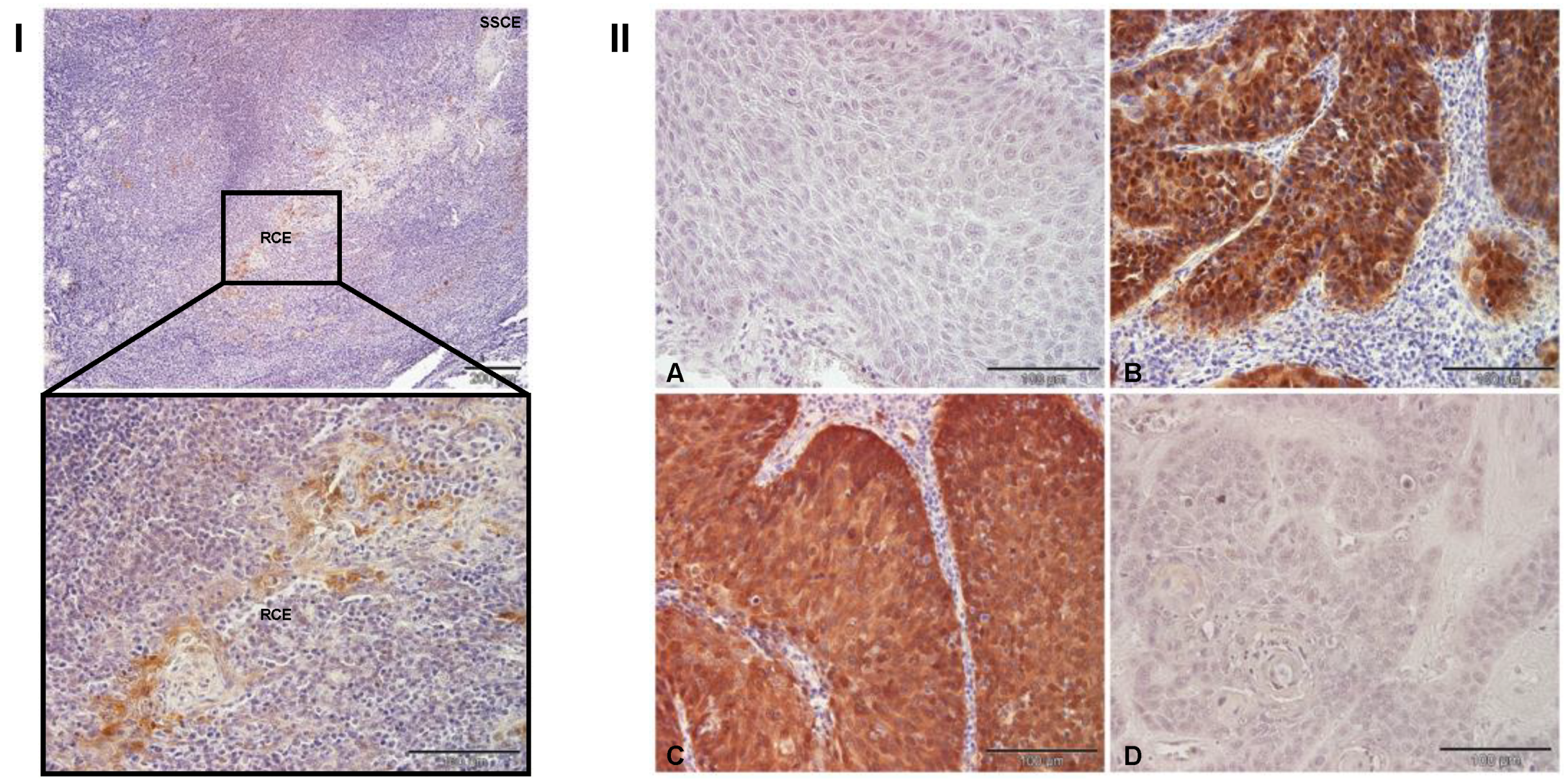
3.1. The Expression of p16
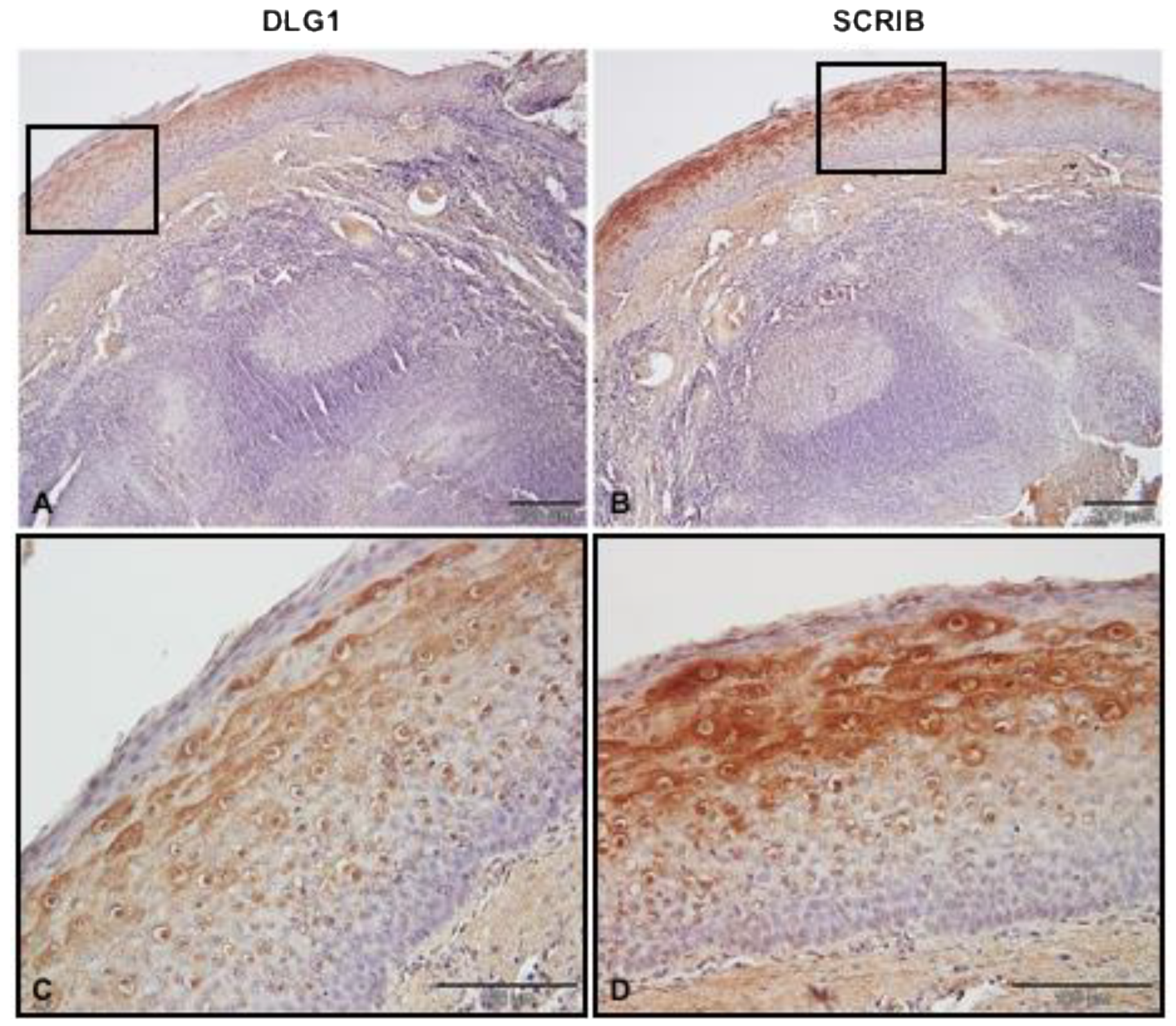
3.2. DLG1 and SCRIB Protein Expression Patterns in Non-Cancerous Tonsillar Tissue Samples
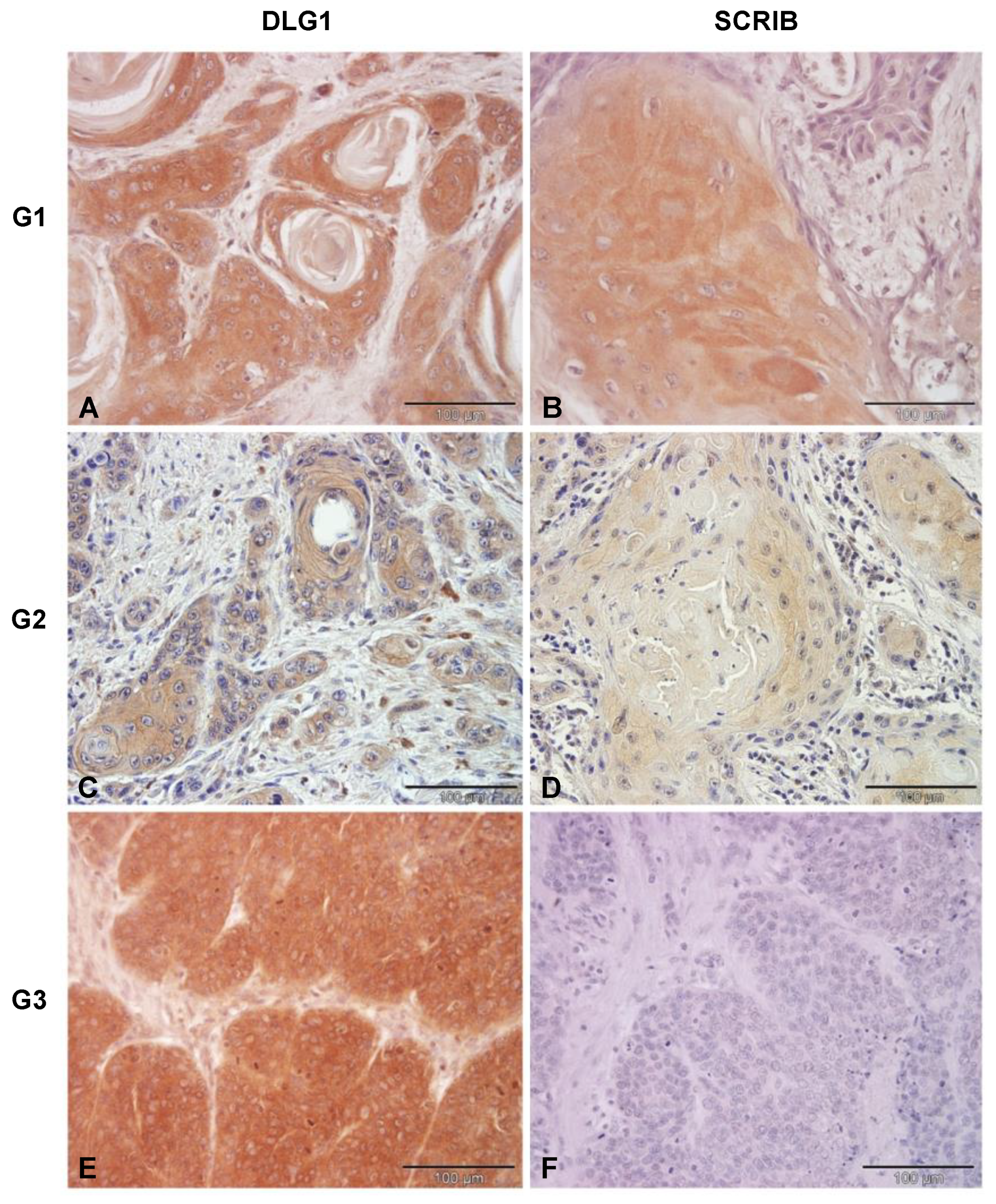
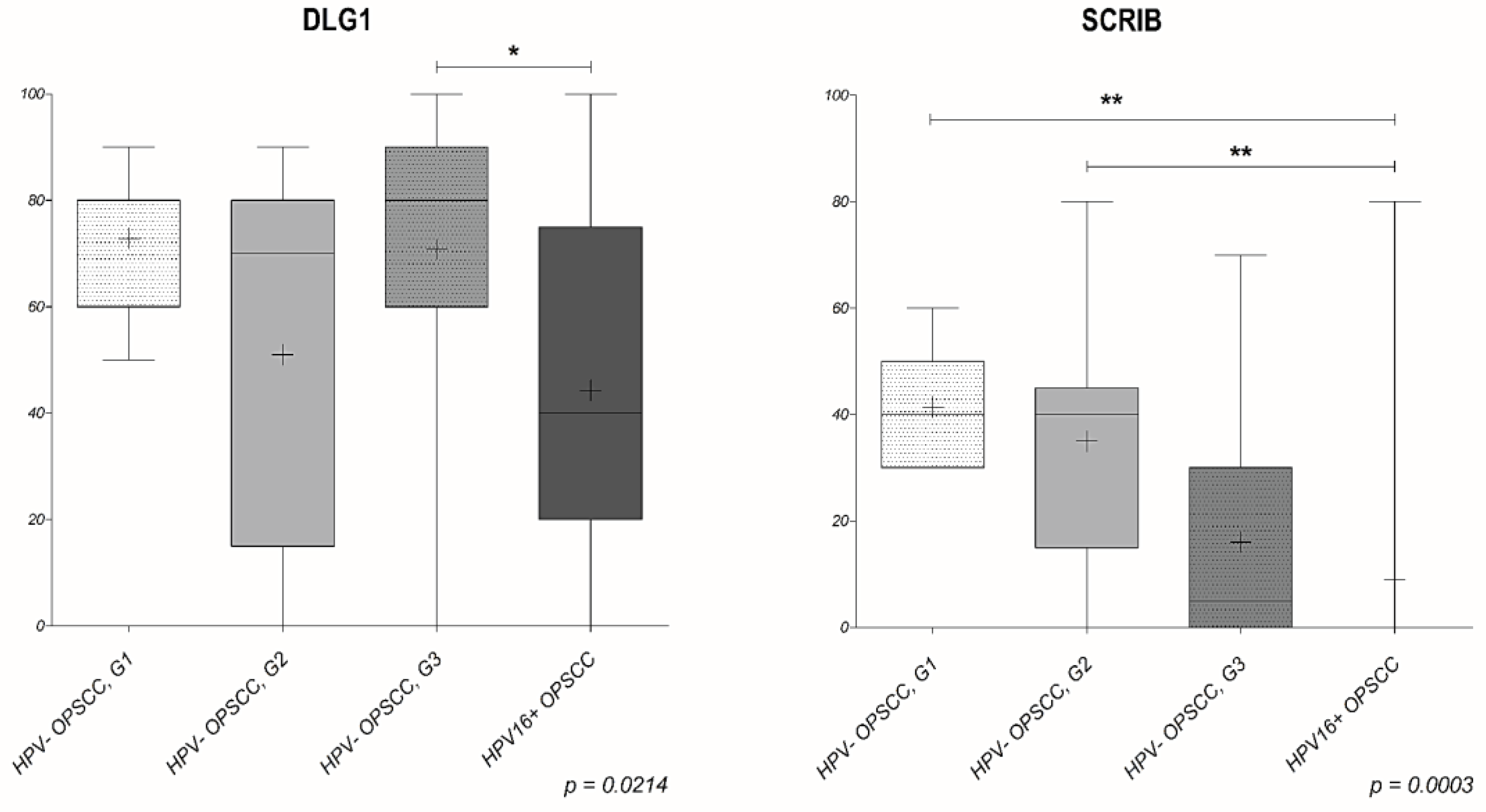
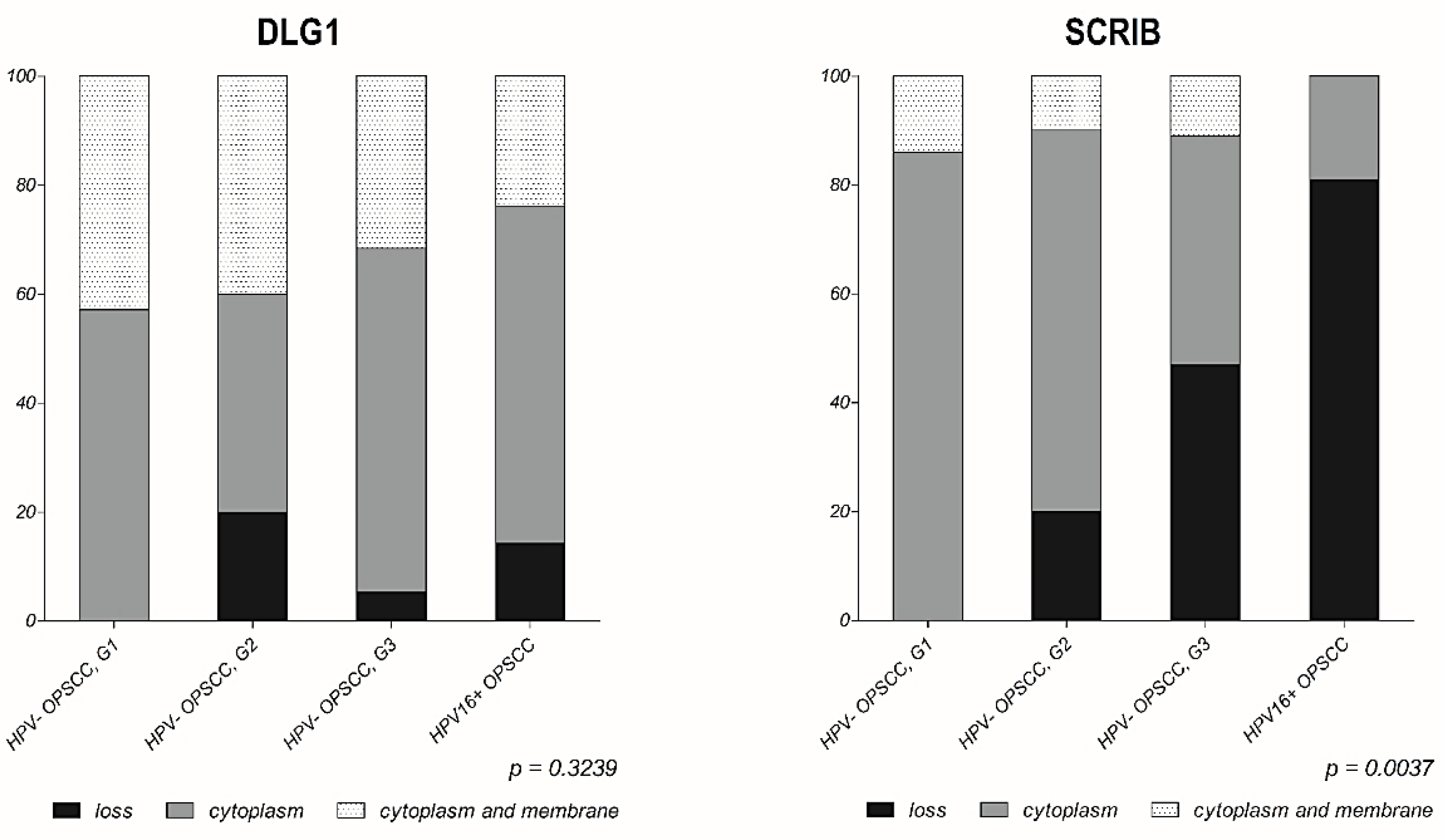
3.3. Analysis of DLG1 and SCRIB Protein Expression and Localization in HPV-Negative OPSCC Samples
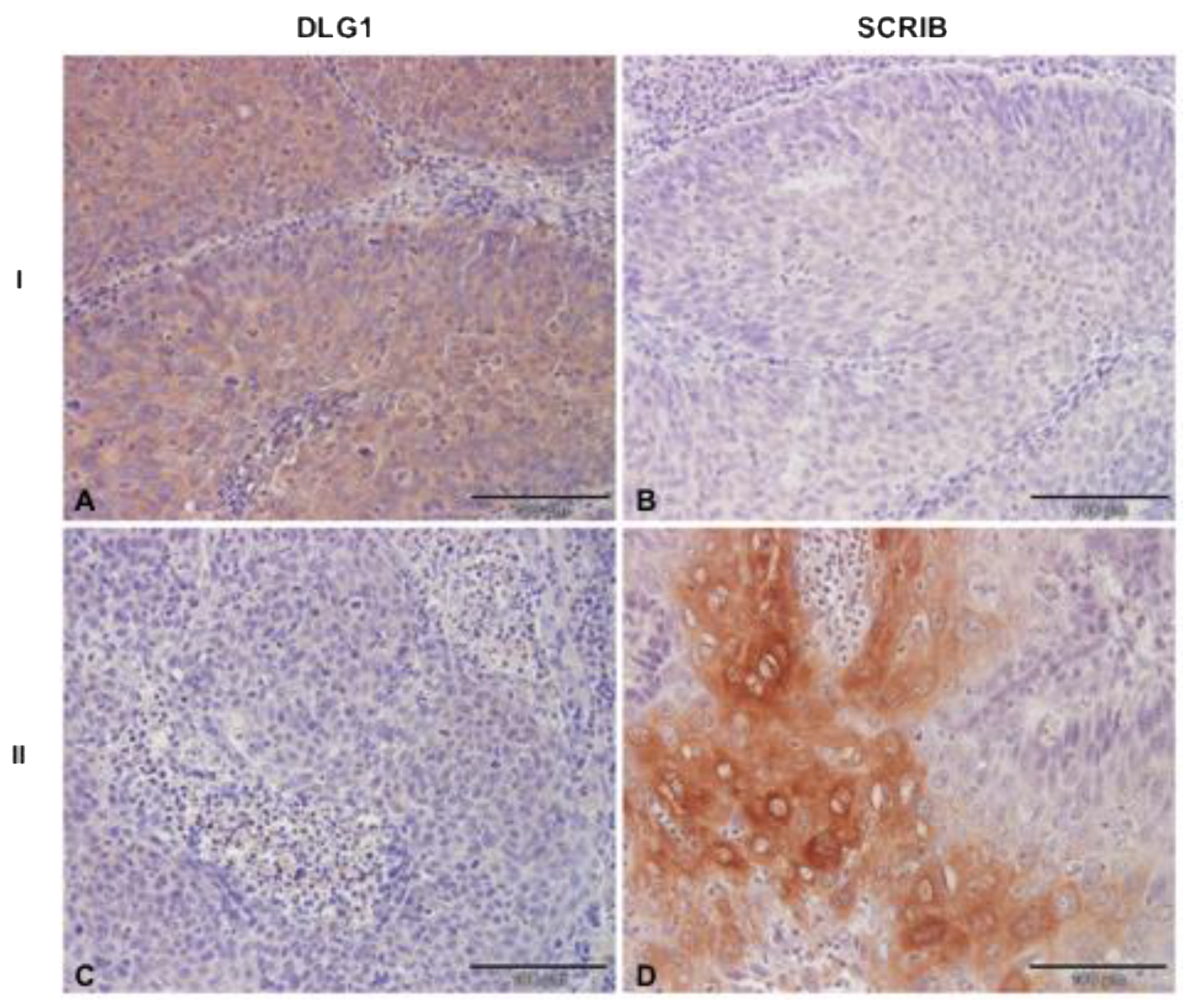
3.4. Analysis of DLG1 and SCRIB Protein Expression and Localization in HPV16+ OPSCC Samples
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Agency for Cancer Research IARC monographs 100B—Human papillomaviruses. 2012. 2005. Available online: https://monographs.iarc.who.int/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/mono100B-11.pdf (accessed on 20 July 2021).
- Gillison, M.L.; Koch, W.M.; Capone, R.B.; Spafford, M.; Westra, W.H.; Wu, L.; Zahurak, M.L.; Daniel, R.W.; Viglione, M.; Symer, D.E.; et al. Evidence for a Causal Association Between Human Papillomavirus and a Subset of Head and Neck Cancers. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2000, 92, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Božinović, K.; Sabol, I.; Rakušić, Z.; Jakovčević, A.; Šekerija, M.; Lukinović, J.; Prgomet, D.; Grce, M. HPV-driven oropharyngeal squamous cell cancer in Croatia—Demography and survival. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elrefaey, S.; Massaro, M.; Chiocca, S.; Chiesa, F.; Ansarin, M. HPV in oropharyngeal cancer: The basics to know in clinical practice. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2014, 34, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Đukić, A.; Lulić, L.; Thomas, M.; Skelin, J.; Saidu, N.E.B.; Grce, M.; Banks, L.; Tomaić, V. HPV Oncoproteins and the Ubiquitin Proteasome System: A Signature of Malignancy? Pathogens 2020, 9, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scheffner, M.; Huibregtse, J.M.; Vierstra, R.D.; Howley, P. The HPV-16 E6 and E6-AP complex functions as a ubiquitin-protein ligase in the ubiquitination of p53. Cell 1993, 75, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Münger, K.; Werness, B.; Dyson, N.; Phelps, W.; Harlow, E.; Howley, P. Complex formation of human papillomavirus E7 proteins with the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor gene product. EMBO J. 1989, 8, 4099–4105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, R.R.; Duensing, S.; Brake, T.; Münger, K.; Lambert, P.F.; Arbeit, J.M. Dissection of human papillomavirus E6 and E7 function in transgenic mouse models of cervical carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 4862–4871. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Strati, K.; Lambert, P.F. Role of Rb-Dependent and Rb-Independent Functions of Papillomavirus E7 Oncogene in Head and Neck Cancer. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 11585–11593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ganti, K.; Broniarczyk, J.; Manoubi, W.; Massimi, P.; Mittal, S.; Pim, D.; Szalmas, A.; Thatte, J.; Thomas, M.; Tomaić, V.; et al. The Human Papillomavirus E6 PDZ Binding Motif: From Life Cycle to Malignancy. Viruses 2015, 7, 3530–3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomas, M.; Narayan, N.; Pim, D.; Tomaić, V.; Massimi, P.; Nagasaka, K.; Kranjec, C.; Gammoh, N.; Banks, L.; Tomai, V. Human papillomaviruses, cervical cancer and cell polarity. Oncogene 2008, 27, 7018–7030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pim, D.; Bergant, M.; Boon, S.S.; Ganti, K.; Kranjec, C.; Massimi, P.; Subbaiah, V.K.; Thomas, M.; Tomaić, V.; Banks, L. Human papillomaviruses and the specificity of PDZ domain targeting. FEBS J. 2012, 279, 3530–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.; Dasgupta, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Banks, L. Analysis of specificity determinants in the interactions of different HPV E6 proteins with their PDZ domain-containing substrates. Virology 2008, 376, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakagawa, S.; Huibregtse, J.M. Human Scribble (Vartul) Is Targeted for Ubiquitin-Mediated Degradation by the High-Risk Papillomavirus E6 Proteins and the E6AP Ubiquitin-Protein Ligase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 8244–8253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snijders, P.J.F.; Steenbergen, R.; Heideman, D.A.M.; Meijer, C.J.L.M. HPV-mediated cervical carcinogenesis: Concepts and clinical implications. J. Pathol. 2005, 208, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grce, M.; Mravak-Stipetić, M. Human papillomavirus–associated diseases. Clin. Dermatol. 2014, 32, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, F.Z.; Ronchi, A.; Stilo, M.; Cozzolino, I.; La Mantia, E.; Colacurci, N.; Colella, G.; Franco, R. Multiplex HPV RNA in situ hybridization/p16 immunohistochemistry: A novel approach to detect papillomavirus in HPV-related cancers. A novel multiplex ISH/IHC assay to detect HPV. Infect. Agents Cancer 2020, 15, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dok, R.; Nuyts, S. HPV Positive Head and Neck Cancers: Molecular Pathogenesis and Evolving Treatment Strategies. Cancers 2016, 8, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Golusinski, P.; Pazdrowski, J.; Szewczyk, M.; Misiołek, M.; Pietruszewska, W.; Klatka, J.; Okła, S.; Kaźmierczak, H.; Marszałek, A.; Filas, V.; et al. Is immunohistochemical evaluation of p16 in oropharyngeal cancer enough to predict the HPV positivity? Rep. Pract. Oncol. Radiother. 2017, 22, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dizanzo, M.P.; Marziali, F.; Avalos, C.B.; Valdano, M.B.; Leiva, S.; Cavatorta, A.L.; Gardiol, D. HPV E6 and E7 oncoproteins cooperatively alter the expression of Disc Large 1 polarity protein in epithelial cells. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavatorta, A.L.; Di Gregorio, A.; Valdano, M.B.; Marziali, F.; Cabral, M.; Bottai, H.; Cittadini, J.; Nocito, A.L.; Gardiol, D. DLG1 polarity protein expression associates with the disease progress of low-grade cervical intraepithelial lesions. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2017, 102, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Santoni, M.-J.; Kashyap, R.; Camoin, L.; Borg, J.-P. The Scribble family in cancer: Twentieth anniversary. Oncogene 2020, 39, 7019–7033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, M.; Massimi, P.; Navarro, C.; Borg, J.-P.; Banks, L. The hScrib/Dlg apico-basal control complex is differentially targeted by HPV-16 and HPV-18 E6 proteins. Oncogene 2005, 24, 6222–6230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lesnikova, I.; Lidang, M.; Hamilton-Dutoit, S.; Koch, J. Rapid, sensitive, type specific PCR detection of the E7 region of human papillomavirus type 16 and 18 from paraffin embedded sections of cervical carcinoma. Infect. Agents Cancer 2010, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Snijders, P.J.F.; Brule, A.J.C.V.D.; Schrijnemakers, H.F.J.; Snow, G.; Meijer, C.J.L.M.; Walboomers, J.M.M. The Use of General Primers in the Polymerase Chain Reaction Permits the Detection of a Broad Spectrum of Human Papillomavirus Genotypes. J. Gen. Virol. 1990, 71, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- José, F.X.B.; Quint, W.G.; Alemany, L.; Geraets, D.T.; Klaustermeier, J.E.; Lloveras, B.; Tous, S.; Felix, A.; Bravo, L.E.; Shin, H.-R.; et al. Human papillomavirus genotype attribution in invasive cervical cancer: A retrospective cross-sectional worldwide study. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 1048–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milutin-Gasperov, N.; Sabol, I.; Halec, G.; Matovina, M.; Grce, M. Retrospective study of the prevalence of high-risk human papillomaviruses among Croatian women. Coll. Antropol. 2007, 31, 89–96. [Google Scholar]
- Baay, M.F.; Quint, W.G.; Koudstaal, J.; Hollema, H.; Duk, J.M.; Burger, M.P.; Stolz, E.; Herbrink, P. Comprehensive study of several general and type-specific primer pairs for detection of human papillomavirus DNA by PCR in paraffin-embedded cervical carcinomas. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1996, 34, 745–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Klingenberg, B.; Hafkamp, H.C.; Haesevoets, A.; Manni, J.J.; Slootweg, P.J.; Weissenborn, S.J.; Klussmann, J.P.; Speel, E.M. p16INK4A overexpression is frequently detected in tumour-free tonsil tissue without association with HPV. Histopathology 2010, 56, 957–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marziali, F.; Dizanzo, M.P.; Cavatorta, A.L.; Gardiol, D. Differential expression of DLG1 as a common trait in different human diseases: An encouraging issue in molecular pathology. Biol. Chem. 2019, 400, 699–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sotelo, N.S.; Valiente, M.; Gil, A.; Pulido, R. A functional network of the tumor suppressors APC, hDlg, and PTEN, that relies on recognition of specific PDZ-domains. J. Cell. Biochem. 2012, 113, 2661–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zheng, B.; DeRan, M.; Jarugumilli, G.K.; Fu, J.; Brooks, Y.S.; Wu, X.; DeRan, M. ZDHHC7-mediated S-palmitoylation of Scribble regulates cell polarity. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2016, 12, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elsum, I.A.; Humbert, P.O. Localization, Not Important in All Tumor-Suppressing Properties: A Lesson Learnt from Scribble. Cells Tissues Organs 2013, 198, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardiol, D.; Zacchi, A.; Petrera, F.; Stanta, G.; Banks, L. Human discs large and scrib are localized at the same regions in colon mucosa and changes in their expression patterns are correlated with loss of tissue architecture during malignant progression. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 119, 1285–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoury, M.J.; Bilder, D. Distinct activities of Scrib module proteins organize epithelial polarity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 11531–11540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavatorta, A.L.; Chouhy, D.; Aguirre, R.; Giri, A.A.; Banks, L.; Gardiol, D. Differential expression of the human homologue ofdrosophila discs large oncosuppressor in histologic samples from human papillomavirus-associated lesions as a marker for progression to malignancy. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 111, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-T.; Steller, M.; Aish, L.; Hanada, T.; Chishti, A.H. Differential expression of human Dlg in cervical intraepithelial neoplasias. Gynecol. Oncol. 2004, 93, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabatini, M.E.; Chiocca, S. Human papillomavirus as a driver of head and neck cancers. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 122, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiwert, T.Y. Ties That Bind: p16 As a Prognostic Biomarker and the Need for High-Accuracy Human Papillomavirus Testing. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 3914–3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilder, D. Epithelial polarity and proliferation control: Links from the Drosophila neoplastic tumor suppressors. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 1909–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Human Protein Atlas. Available online: https://www.proteinatlas.org/ (accessed on 20 July 2021).
- Elsum, I.; Yates, L.; Humbert, P.O.; Richardson, H. The Scribble–Dlg–Lgl polarity module in development and cancer: From flies to man. Essays Biochem. 2012, 53, 141–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, R.; Lim, K.; Portela, M.; Kvansakul, M.; Humbert, P.; Richardson, H.E. The Scribble Cell Polarity Module in the Regulation of Cell Signaling in Tissue Development and Tumorigenesis. J. Mol. Biol. 2018, 430, 3585–3612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapil, S.; Sharma, B.K.; Patil, M.; Elattar, S.; Yuan, J.; Hou, S.X.; Kolhe, R.; Satyanarayana, A. The cell polarity protein Scrib functions as a tumor suppressor in liver cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 26515–26531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vaira, V.; Faversani, A.; Dohi, T.; Maggioni, M.; Nosotti, M.; Tosi, D.; Altieri, D.C.; Bosari, S. Aberrant Overexpression of the Cell Polarity Module Scribble in Human Cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 178, 2478–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Bian, Y.; An, J.; Duan, X.; Wan, J.; Yao, X.; Du, C.; Ni, C.; Zhu, L.; et al. Low SCRIB expression in fibroblasts promotes invasion of lung cancer cells. Life Sci. 2020, 256, 117955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feigin, M.; Akshinthala, S.D.; Araki, K.; Rosenberg, A.; Muthuswamy, L.B.; Martin, B.; Lehmann, B.; Berman, H.K.; Pietenpol, J.A.; Cardiff, R.D.; et al. Mislocalization of the Cell Polarity Protein Scribble Promotes Mammary Tumorigenesis and Is Associated with Basal Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 3180–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhan, L.; Rosenberg, A.; Bergami, K.C.; Yu, M.; Xuan, Z.; Jaffe, A.; Allred, C.; Muthuswamy, S.K. Deregulation of Scribble Promotes Mammary Tumorigenesis and Reveals a Role for Cell Polarity in Carcinoma. Cell 2008, 135, 865–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lulić, L.; Jakovčević, A.; Manojlović, L.; Dediol, E.; Banks, L.; Tomaić, V. Human DLG1 and SCRIB Are Distinctly Regulated Independently of HPV-16 during the Progression of Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinomas: A Preliminary Analysis. Cancers 2021, 13, 4461. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174461
Lulić L, Jakovčević A, Manojlović L, Dediol E, Banks L, Tomaić V. Human DLG1 and SCRIB Are Distinctly Regulated Independently of HPV-16 during the Progression of Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinomas: A Preliminary Analysis. Cancers. 2021; 13(17):4461. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174461
Chicago/Turabian StyleLulić, Lucija, Antonia Jakovčević, Luka Manojlović, Emil Dediol, Lawrence Banks, and Vjekoslav Tomaić. 2021. "Human DLG1 and SCRIB Are Distinctly Regulated Independently of HPV-16 during the Progression of Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinomas: A Preliminary Analysis" Cancers 13, no. 17: 4461. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174461
APA StyleLulić, L., Jakovčević, A., Manojlović, L., Dediol, E., Banks, L., & Tomaić, V. (2021). Human DLG1 and SCRIB Are Distinctly Regulated Independently of HPV-16 during the Progression of Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinomas: A Preliminary Analysis. Cancers, 13(17), 4461. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174461







