- Article
Personalized Combination Therapy in Bladder Cancer: cAMP Modulators Synergize with 5-FU and Modulate Redox Programs
- Eduarda Ribeiro and
- Nuno Vale
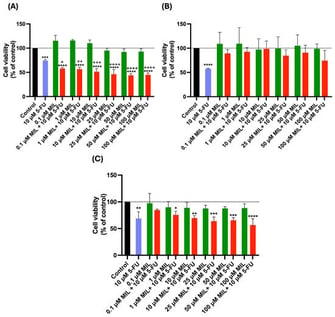
Background/Objectives: Repurposed cAMP-elevating agents may personalize fluoropyrimidine therapy by exploiting pathway-specific vulnerabilities. Methods: We tested the PDE3 inhibitor milrinone and the β2-agonist terbutaline alone or combined with 10 μM 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) in UM-UC-5 (bladder), A549 (lung), and PC-3 (prostate) cells. Viability, migration, clonogenicity, and intracellular ROS (DCFDA) were measured; drug interactions used Chou–Talalay/CompuSyn. Results: In UM-UC-5, both agents reduced viability, migration, and clonogenicity and synergized with 5-FU (CI < 1 across Fa ≈ 0.42–0.57). 5-FU increased ROS, whereas terbutaline consistently lowered ROS below baseline and blunted 5-FU-induced oxidative signals; milrinone showed a dose-dependent redox profile without consistent ROS suppression. A549 combinations did not outperform 5-FU; PC-3 was largely unresponsive. Conclusions: cAMP modulators selectively potentiate 5-FU in bladder cancer cells and modulate redox programs (notably with terbutaline), supporting a biomarker-guided combination strategy (e.g., β2-AR/PDE3/PI3K–Akt features) for personalized therapy in bladder cancer; mechanistic and in vivo validation are warranted.
9 February 2026