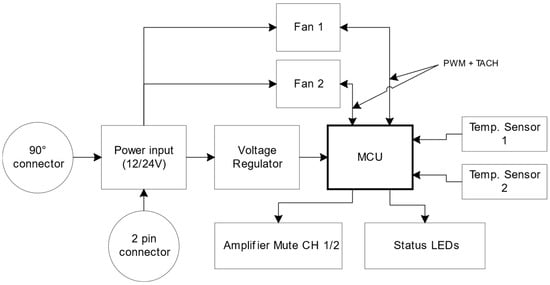
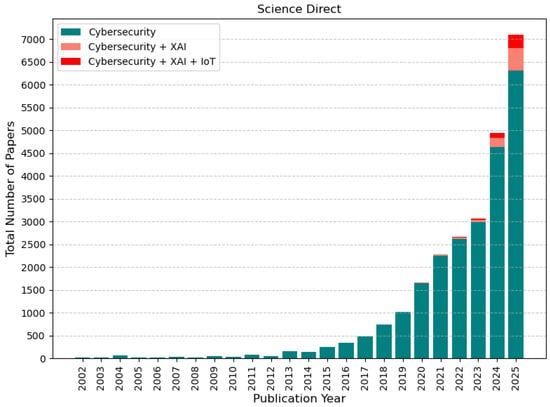
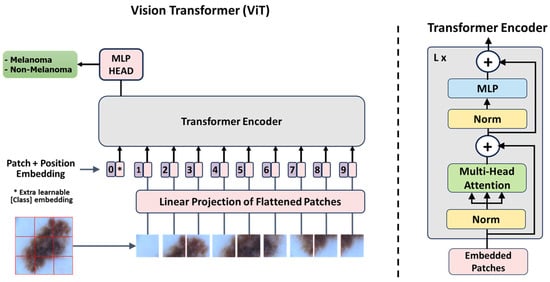
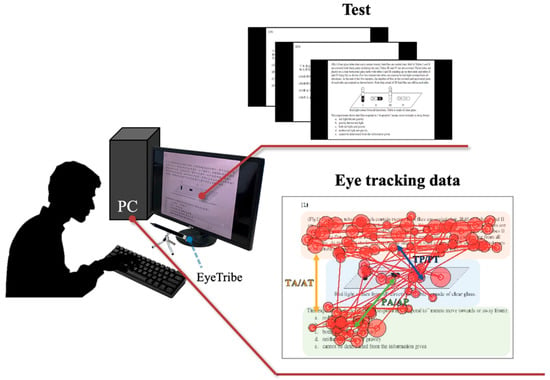
Journal Description
Applied System Innovation
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, ESCI (Web of Science), Inspec, Ei Compendex and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Engineering, Electrical and Electronic) / CiteScore - Q1 (Applied Mathematics)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 22 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 4.8 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Journal Cluster of Information Systems and Technology: Analytics, Applied System Innovation, Cryptography, Data, Digital, Informatics, Information, Journal of Cybersecurity and Privacy and Multimedia.
Latest Articles
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Meet Us Virtually at the 1st International Online Conference on Sensor and Actuator Networks (CSAN 2026), 9–10 July 2026

MDPI Launches the Michele Parrinello Award for Pioneering Contributions in Computational Physical Science

Topics
Deadline: 31 March 2026
Deadline: 30 April 2026
Deadline: 31 May 2026
Deadline: 31 July 2026
Conferences
Special Issues
Deadline: 20 March 2026
Deadline: 20 March 2026
Deadline: 20 March 2026
Deadline: 20 April 2026