-
 Digital Cultural Heritage in Southeast Asia: Knowledge Structures and Resources in GLAM Institutions
Digital Cultural Heritage in Southeast Asia: Knowledge Structures and Resources in GLAM Institutions -
 Human-AI Symbiotic Theory (HAIST): Development, Multi-Framework Assessment, and AI-Assisted Validation in Academic Research
Human-AI Symbiotic Theory (HAIST): Development, Multi-Framework Assessment, and AI-Assisted Validation in Academic Research -
 Explainable AI for Clinical Decision Support Systems: Literature Review, Key Gaps, and Research Synthesis
Explainable AI for Clinical Decision Support Systems: Literature Review, Key Gaps, and Research Synthesis -
 Federated Learning-Driven Cybersecurity Framework for IoT Networks with Privacy Preserving and Real-Time Threat Detection Capabilities
Federated Learning-Driven Cybersecurity Framework for IoT Networks with Privacy Preserving and Real-Time Threat Detection Capabilities -
 Federated Learning Spam Detection Based on FedProx and Multi-Level Multi-Feature Fusion
Federated Learning Spam Detection Based on FedProx and Multi-Level Multi-Feature Fusion
Journal Description
Informatics
Informatics
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on information and communication technologies, human–computer interaction, and social informatics, and is published monthly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, ESCI (Web of Science), dblp, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: CiteScore - Q1 (Communication)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 32.1 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 4.2 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Journal Cluster of Information Systems and Technology: Analytics, Applied System Innovation, Cryptography, Data, Digital, Informatics, Information, Journal of Cybersecurity and Privacy and Multimedia.
Impact Factor:
2.8 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
3.1 (2024)
Latest Articles
Depression Detection Method Based on Multi-Modal Multi-Layer Collaborative Perception Attention Mechanism of Symmetric Structure
Informatics 2026, 13(1), 8; https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics13010008 - 12 Jan 2026
Abstract
►
Show Figures
Depression is a mental illness with hidden characteristics that affects human physical and mental health. In severe cases, it may lead to suicidal behavior (for example, among college students and social groups). Therefore, it has attracted widespread attention. Scholars have developed numerous models
[...] Read more.
Depression is a mental illness with hidden characteristics that affects human physical and mental health. In severe cases, it may lead to suicidal behavior (for example, among college students and social groups). Therefore, it has attracted widespread attention. Scholars have developed numerous models and methods for depression detection. However, most of these methods focus on a single modality and do not consider the influence of gender on depression, while the existing models have limitations such as complex structures. To solve this problem, we propose a symmetric-structured, multi-modal, multi-layer cooperative perception model for depression detection that dynamically focuses on critical features. First, the double-branch symmetric structure of the proposed model is designed to account for gender-based variations in emotional factors. Second, we introduce a stacked multi-head attention (MHA) module and an interactive cross-attention module to comprehensively extract key features while suppressing irrelevant information. A bidirectional long short-term memory network (BiLSTM) module enhances depression detection accuracy. To verify the effectiveness and feasibility of the model, we conducted a series of experiments using the proposed method on the AVEC 2014 dataset. Compared with the most advanced HMTL-IMHAFF model, our model improves the accuracy by 0.0308. The results indicate that the proposed framework demonstrates superior performance.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
A Novel MBPSO–BDGWO Ensemble Feature Selection Method for High-Dimensional Classification Data
by
Nuriye Sancar
Informatics 2026, 13(1), 7; https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics13010007 - 12 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In a high-dimensional classification dataset, feature selection is crucial for improving classification performance and computational efficiency by identifying an informative subset of features while reducing noise, redundancy, and overfitting. This study proposes a novel metaheuristic-based ensemble feature selection approach by combining the complementary
[...] Read more.
In a high-dimensional classification dataset, feature selection is crucial for improving classification performance and computational efficiency by identifying an informative subset of features while reducing noise, redundancy, and overfitting. This study proposes a novel metaheuristic-based ensemble feature selection approach by combining the complementary strengths of Modified Binary Particle Swarm Optimization (MBPSO) and Binary Dynamic Grey Wolf Optimization (BDGWO). The proposed MBPSO–BDGWO ensemble method is specifically designed for high-dimensional classification problems. The performance of the proposed MBPSO–BDGWO ensemble method was rigorously evaluated through an extensive simulation study under multiple high-dimensional scenarios with varying correlation structures. The ensemble method was further validated on several real datasets. Comparative analyses were conducted against single-stage feature selection methods, including BPSO, BGWO, MBPSO, and BDGWO, using evaluation metrics such as accuracy, the F1-score, the true positive rate (TPR), the false positive rate (FPR), the AUC, precision, and the Jaccard stability index. Simulation studies conducted under various dimensionality and correlation scenarios show that the proposed ensemble method achieves a low FPR, a high TPR/Precision/F1/AUC, and strong selection stability, clearly outperforming both classical and advanced single-stage methods, even as dimensionality and collinearity increase. In contrast, single-stage methods typically experience substantial performance degradation in high-correlation and high-dimensional settings, particularly BPSO and BGWO. Moreover, on the real datasets, the ensemble method outperformed all compared single-stage methods and produced consistently low MAD values across repetitions, indicating robustness and stability even in ultra-high-dimensional genomic datasets. Overall, the findings indicate that the proposed ensemble method demonstrates consistent performance across the evaluated scenarios and achieves higher selection stability compared with the single-stage methods.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Second-Opinion Systems for Rare Diseases: A Scoping Review of Digital Workflows and Networks
by
Vinícius Lima, Mariana Mozini and Domingos Alves
Informatics 2026, 13(1), 6; https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics13010006 - 10 Jan 2026
Abstract
Introduction: Rare diseases disperse expertise across institutions and borders, making structured second-opinion systems a pragmatic way to concentrate subspecialty knowledge and reduce diagnostic delays. This scoping review mapped the design, governance, adoption, and impacts of such services across implementation scales. Objectives: To describe
[...] Read more.
Introduction: Rare diseases disperse expertise across institutions and borders, making structured second-opinion systems a pragmatic way to concentrate subspecialty knowledge and reduce diagnostic delays. This scoping review mapped the design, governance, adoption, and impacts of such services across implementation scales. Objectives: To describe how second-opinion services for rare diseases are organized and governed, to characterize technological and workflow models, to summarize benefits and barriers, and to identify priority evidence gaps for implementation. Methods: Using a population–concept–context approach, we included peer-reviewed studies describing implemented second-opinion systems for rare diseases and excluded isolated case reports, purely conceptual proposals, and work outside this focus. Searches in August 2025 covered PubMed/MEDLINE, Scopus, Web of Science Core Collection, Cochrane Library, IEEE Xplore, ACM Digital Library, and LILACS without date limits and were restricted to English, Portuguese, or Spanish. Two reviewers screened independently, and the data were charted with a standardized, piloted form. No formal critical appraisal was undertaken, and the synthesis was descriptive. Results: Initiatives were clustered by scale (European networks, national programs, regional systems, international collaborations) and favored hybrid models over asynchronous and synchronous ones. Across settings, services shared reproducible workflows and provided faster access to expertise, quicker decision-making, and more frequent clarification of care plans. These improvements were enabled by transparent governance and dedicated support but were constrained by platform complexity, the effort required to assemble panels, uneven incentives, interoperability gaps, and medico-legal uncertainty. Conclusions: Systematized second-opinion services for rare diseases are feasible and clinically relevant. Progress hinges on usability, aligned incentives, and pragmatic interoperability, advancing from registries toward bidirectional electronic health record connections, alongside prospective evaluations of outcomes, equity, experience, effectiveness, and costs.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Health Informatics)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Visual Harmony Between Avatar Appearance and On-Avatar Text: Effects on Self-Expression Fit and Interpersonal Perception in Social VR
by
Yang Guang, Sho Sakurai, Takuya Nojima and Koichi Hirota
Informatics 2026, 13(1), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics13010005 - 7 Jan 2026
Abstract
In social virtual reality (VR) and metaverse platforms, users express their identity through both avatar appearance and on-avatar textual cues, such as speech balloons. However, little is known about how the harmony between these cues influences self-representation and social impressions. We propose that
[...] Read more.
In social virtual reality (VR) and metaverse platforms, users express their identity through both avatar appearance and on-avatar textual cues, such as speech balloons. However, little is known about how the harmony between these cues influences self-representation and social impressions. We propose that when avatar appearance and text design, including color, font, and tone, are consistent, users experience a stronger self-expression fit and elicit greater interpersonal affinity. A within-subject study (
(This article belongs to the Section Human-Computer Interaction)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
C-STEER: A Dynamic Sentiment-Aware Framework for Fake News Detection with Lifecycle Emotional Evolution
by
Ziyi Zhen and Ying Li
Informatics 2026, 13(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics13010004 - 5 Jan 2026
Abstract
The dynamic evolution of collective emotions across the news dissemination life-cycle is a powerful yet underexplored signal in affective computing. While phenomena like the spread of fake news depend on eliciting specific emotional trajectories, existing methods often fail to capture these crucial dynamic
[...] Read more.
The dynamic evolution of collective emotions across the news dissemination life-cycle is a powerful yet underexplored signal in affective computing. While phenomena like the spread of fake news depend on eliciting specific emotional trajectories, existing methods often fail to capture these crucial dynamic affective cues. Many approaches focus on static text or propagation topology, limiting their robustness and failing to model the complete emotional life-cycle for applications such as assessing veracity. This paper introduces C-STEER (Cycle-aware Sentiment-Temporal Emotion Evolution), a novel framework grounded in communication theory, designed to model the characteristic initiation, burst, and decay stages of these emotional arcs. Guided by Diffusion of Innovations Theory, C-STEER first segments an information cascade into its life-cycle phases. It then operationalizes insights from Uses and Gratifications Theory and Emotional Contagion Theory to extract stage-specific emotional features and model their temporal dependencies using a Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory (BiLSTM). To validate the framework’s descriptive and predictive power, we apply it to the challenging domain of fake news detection. Experiments on the Weibo21 and Twitter16 datasets demonstrate that modeling life-cycle emotion dynamics significantly improves detection performance, achieving F1-macro scores of 91.6% and 90.1%, respectively, outperforming state-of-the-art baselines by margins of 1.6% to 2.4%. This work validates the C-STEER framework as an effective approach for the computational modeling of collective emotion life-cycles.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Practical Applications of Sentiment Analysis)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Clustering Approach to Identify Risk Perception on Social Networks: A Study of Peruvian Children and Adolescents
by
Yasiel Pérez Vera, Richart Smith Escobedo Quispe and Patrick Andrés Ramírez Santos
Informatics 2026, 13(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics13010003 - 4 Jan 2026
Abstract
The excessive and inappropriate use of the internet by children and young people increases their exposure to risky situations, especially since the COVID-19 pandemic. This study analyzes risky situations on social media among children and adolescents. The objective of this work was to
[...] Read more.
The excessive and inappropriate use of the internet by children and young people increases their exposure to risky situations, especially since the COVID-19 pandemic. This study analyzes risky situations on social media among children and adolescents. The objective of this work was to identify the risks associated with the use of social media. A comparative analysis of five clustering algorithms was applied to a dataset developed by eBiz Latin America in collaboration with La Salle University of Arequipa and the Institute of Christian Schools of the De La Salle Brothers of the Bolivia-Peru district. Among the results, it was shown that children around 11 years old display a high prevalence of digital risk behaviors such as adding strangers, followed by pretending to be someone else; adults around 43 years old exhibit a tendency to follow strangers and, even more so, to take photographs without permission; adolescents with an average age of 11 show a heavy use of YouTube, TikTok, and Instagram. It is concluded that among digital risks in children and adults, the clusters highlight shared vulnerabilities, such as the addition of strangers and exposure to requests for personal data, which persist throughout the life stages but intensify in early adulthood. These findings emphasize the urgency of preventive policies addressing generational differences in social network use to promote proactive responses to digital harassment.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Machine Learning)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
AIMarkerFinder: AI-Assisted Marker Discovery Based on an Integrated Approach of Autoencoders and Kolmogorov–Arnold Networks
by
Pavel S. Demenkov, Timofey V. Ivanisenko and Vladimir A. Ivanisenko
Informatics 2026, 13(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics13010002 - 24 Dec 2025
Abstract
In modern bioinformatics, the analysis of high-dimensional data (genomic, metabolomic, etc.) remains a critical challenge due to the “curse of dimensionality,” where feature redundancy reduces classification efficiency and model interpretability. This study introduces a novel method, AIMarkerFinder (v0.1.0), for analyzing metabolomic data to
[...] Read more.
In modern bioinformatics, the analysis of high-dimensional data (genomic, metabolomic, etc.) remains a critical challenge due to the “curse of dimensionality,” where feature redundancy reduces classification efficiency and model interpretability. This study introduces a novel method, AIMarkerFinder (v0.1.0), for analyzing metabolomic data to identify key biomarkers. The method is based on a denoising autoencoder with an attention mechanism (DAE), enabling the extraction of informative features and the elimination of redundancy. Experiments on glioblastoma and adjacent tissue metabolomic data demonstrated that AIMarkerFinder reduces dimensionality from 446 to 4 key features while improving classification accuracy. Using the selected metabolites (Malonyl-CoA, Glycerophosphocholine, SM(d18:1/22:0 OH), GC(18:1/24:1)), the Random Forest and Kolmogorov–Arnold Networks (KAN) models achieved accuracies of 0.904 and 0.937, respectively. The analytical formulas derived by the KAN provide model interpretability, which is critical for biomedical research. The proposed approach is applicable to genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and the study of exogenous factors on biological processes. The study’s results open new prospects for personalized medicine and early disease diagnosis.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Machine Learning)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
SAFE-GUARD: Semantic Access Control Framework Employing Generative User Assessment and Rule Decisions
by
Nastaran Farhadighalati, Luis A. Estrada-Jimenez, Sepideh Kalateh, Sanaz Nikghadam-Hojjati and Jose Barata
Informatics 2026, 13(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics13010001 - 19 Dec 2025
Abstract
Healthcare faces a critical challenge: protecting sensitive medical data while enabling necessary clinical access. Evolving user behaviors, dynamic clinical contexts, and strict regulatory requirements demand adaptive access control mechanisms. Despite strict regulations, healthcare remains the most breached industry, consistently facing severe security risks
[...] Read more.
Healthcare faces a critical challenge: protecting sensitive medical data while enabling necessary clinical access. Evolving user behaviors, dynamic clinical contexts, and strict regulatory requirements demand adaptive access control mechanisms. Despite strict regulations, healthcare remains the most breached industry, consistently facing severe security risks related to unauthorized access. Traditional access control models cannot handle contextual variations, detect credential compromise, or provide transparent decision rationales. To address this, SAFE-GUARD (Semantic Access Control Framework Employing Generative User Assessment and Rule Decisions) is proposed as a two-layer framework that combines behavioral analysis with policy enforcement. The Behavioral Analysis Layer uses Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) to detect contextual anomalies by comparing current requests against historical patterns. The Rule-Based Policy Evaluation Layer independently validates organizational procedures and regulatory requirements. Access is granted only when behavioral consistency and both organizational and regulatory policies are satisfied. We evaluate SAFE-GUARD using simulated healthcare scenarios with three LLMs (GPT-4o, Claude 3.5 Sonnet, and Gemini 2.5 Flash) achieving an anomaly detection accuracy of 95.2%, 94.1%, and 91.3%, respectively. The framework effectively identifies both compromised credentials and insider misuse by detecting deviations from established behavioral patterns, significantly outperforming conventional RBAC and ABAC approaches that rely solely on static rules.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Health Data Management in the Age of AI)
►▼
Show Figures
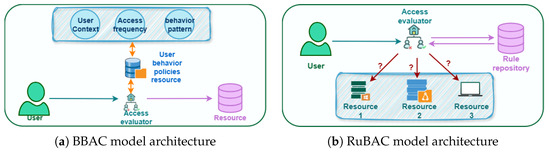
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Combining Fuzzy Cognitive Maps and Metaheuristic Algorithms to Predict Preeclampsia and Intrauterine Growth Restriction
by
María Paula García, Jesús David Díaz-Meza, Kenia Hoyos, Bethia Pacheco, Rodrigo García and William Hoyos
Informatics 2025, 12(4), 141; https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics12040141 - 15 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Preeclampsia (PE) and intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) are obstetric complications associated with placental dysfunction, which represent a public health problem due to high maternal and fetal morbidity and mortality. Early detection is crucial for timely interventions. Therefore, this study proposes the development of
[...] Read more.
Preeclampsia (PE) and intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) are obstetric complications associated with placental dysfunction, which represent a public health problem due to high maternal and fetal morbidity and mortality. Early detection is crucial for timely interventions. Therefore, this study proposes the development of models based on fuzzy cognitive maps (FCM) optimized with metaheuristic algorithms (particle swarm optimization (PSO) and genetic algorithms (GA)) for the prediction of PE and IUGR. The results showed that FCM-PSO applied to the PE dataset achieved excellent performance (accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-Score = 1.0). The FCM-GA model excelled in predicting IUGR with an accuracy and F1-Score of 0.97. Our proposed models outperformed those reported in the literature to predict PE and IUGR. Analysis of the relationships between nodes allowed for the identification of influential variables such as sFlt-1, sFlt-1/PlGF, and uterine Doppler parameters, in accordance with the pathophysiology of placental disorders. FCM optimized with PSO and GA offer a viable clinical alternative as a medical decision support system due to their ability to explore nonlinear relationships and interpretability of variables. In addition, they are suitable for scenarios where low computational resource consumption is required.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Vertebra Segmentation and Cobb Angle Calculation Platform for Scoliosis Diagnosis Using Deep Learning: SpineCheck
by
İrfan Harun İlkhan, Halûk Gümüşkaya and Firdevs Turgut
Informatics 2025, 12(4), 140; https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics12040140 - 11 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study presents SpineCheck, a fully integrated deep-learning-based clinical decision support platform for automatic vertebra segmentation and Cobb angle (CA) measurement from scoliosis X-ray images. The system unifies end-to-end preprocessing, U-Net-based segmentation, geometry-driven angle computation, and a web-based clinical interface within a single
[...] Read more.
This study presents SpineCheck, a fully integrated deep-learning-based clinical decision support platform for automatic vertebra segmentation and Cobb angle (CA) measurement from scoliosis X-ray images. The system unifies end-to-end preprocessing, U-Net-based segmentation, geometry-driven angle computation, and a web-based clinical interface within a single deployable architecture. For secure clinical use, SpineCheck adopts a stateless “process-and-delete” design, ensuring that no radiographic data or Protected Health Information (PHI) are permanently stored. Five U-Net family models (U-Net, optimized U-Net-2, Attention U-Net, nnU-Net, and UNet3++) are systematically evaluated under identical conditions using Dice similarity, inference speed, GPU memory usage, and deployment stability, enabling deployment-oriented model selection. A robust CA estimation pipeline is developed by combining minimum-area rectangle analysis with Theil–Sen regression and spline-based anatomical modeling to suppress outliers and improve numerical stability. The system is validated on a large-scale dataset of 20,000 scoliosis X-ray images, demonstrating strong agreement with expert measurements based on Mean Absolute Error, Pearson correlation, and Intraclass Correlation Coefficient metrics. These findings confirm the reliability and clinical robustness of SpineCheck. By integrating large-scale validation, robust geometric modeling, secure stateless processing, and real-time deployment capabilities, SpineCheck provides a scalable and clinically reliable framework for automated scoliosis assessment.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Multimodal Large Language Models vs. Human Authors: A Comparative Study of Chinese Fairy Tales for Young Children
by
Jing Du, Wenhao Liu, Dibin Zhou, Seongku Hong and Fuchang Liu
Informatics 2025, 12(4), 139; https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics12040139 - 9 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In the realm of children’s education, multimodal large language models (MLLMs) are already being utilized to create educational materials for young learners. But how significant are the differences between image-based fairy tales generated by MLLMs and those crafted by human authors? This paper
[...] Read more.
In the realm of children’s education, multimodal large language models (MLLMs) are already being utilized to create educational materials for young learners. But how significant are the differences between image-based fairy tales generated by MLLMs and those crafted by human authors? This paper addresses this question through the design of multi-dimensional human evaluation and actual questionnaire surveys. Specifically, we conducted studies on evaluating MLLM-generated stories and distinguishing them from human-written stories involving 50 undergraduate students in education-related majors, 30 first-grade students, 81 second-grade students, and 103 parents. The findings reveal that most undergraduate students with an educational background, elementary school students, and parents perceive stories generated by MLLMs as being highly similar to those written by humans. Through the evaluation of primary school students and vocabulary analysis, it is further shown that, unlike human-authored stories, which tend to exceed the vocabulary level of young students, MLLM-generated stories are able to control vocabulary complexity and are also very interesting for young readers. Based on the results of the above experiments, we further discuss the following question: Can MLLMs assist or even replace humans in writing Chinese children’s fairy tales based on pictures for young children? We approached this question from both a technical perspective and a user perspective.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
AI-Enabled Intelligent System for Automatic Detection and Classification of Plant Diseases Towards Precision Agriculture
by
Gujju Siva Krishna, Zameer Gulzar, Arpita Baronia, Jagirdar Srinivas, Padmavathy Paramanandam and Kasharaju Balakrishna
Informatics 2025, 12(4), 138; https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics12040138 - 8 Dec 2025
Abstract
Technology-driven agriculture, or precision agriculture (PA), is indispensable in the contemporary world due to its advantages and the availability of technological innovations. Particularly, early disease detection in agricultural crops helps the farming community ensure crop health, reduce expenditure, and increase crop yield. Governments
[...] Read more.
Technology-driven agriculture, or precision agriculture (PA), is indispensable in the contemporary world due to its advantages and the availability of technological innovations. Particularly, early disease detection in agricultural crops helps the farming community ensure crop health, reduce expenditure, and increase crop yield. Governments have mainly used current systems for agricultural statistics and strategic decision-making, but there is still a critical need for farmers to have access to cost-effective, user-friendly solutions that can be used by them regardless of their educational level. In this study, we used four apple leaf diseases (leaf spot, mosaic, rust and brown spot) from the PlantVillage dataset to develop an Automated Agricultural Crop Disease Identification System (AACDIS), a deep learning framework for identifying and categorizing crop diseases. This framework makes use of deep convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and includes three CNN models created specifically for this application. AACDIS achieves significant performance improvements by combining cascade inception and drawing inspiration from the well-known AlexNet design, making it a potent tool for managing agricultural diseases. AACDIS also has Region of Interest (ROI) awareness, a crucial component that improves the efficiency and precision of illness identification. This feature guarantees that the system can quickly and accurately identify illness-related areas inside images, enabling faster and more accurate disease diagnosis. Experimental findings show a test accuracy of 99.491%, which is better than many state-of-the-art deep learning models. This empirical study reveals the potential benefits of the proposed system for early identification of diseases. This research triggers further investigation to realize full-fledged precision agriculture and smart agriculture.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Machine Learning)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Mapping the AI Surge in Higher Education: A Bibliometric Study Spanning a Decade (2015–2025)
by
Mousin Omarsaib, Sara Bibi Mitha, Anisa Vahed and Ghulam Masudh Mohamed
Informatics 2025, 12(4), 137; https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics12040137 - 8 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
There has recently been a pronounced global escalation in scholarly output concerning Artificial Intelligence (AI) within the context of higher education (HE). However, the precise locus of this growth remains ambiguous, thereby hindering the systematic integration of critical AI trends into HE practices.
[...] Read more.
There has recently been a pronounced global escalation in scholarly output concerning Artificial Intelligence (AI) within the context of higher education (HE). However, the precise locus of this growth remains ambiguous, thereby hindering the systematic integration of critical AI trends into HE practices. To address this opacity, the present study adopts a rigorous and impartial analytical approach by synthesizing datasets from the Web of Science (WoS) and Scopus through the Biblioshiny platform. In addition, independent examinations of WoS and Scopus data were conducted using co-occurrence network analyses in VOSviewer, which revealed comparable patterns of cluster strength across both datasets. Complementing these methods, Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) was employed to extract and interpret thematic structures within locally cited references, thereby providing deeper insights into the extant research discourse. Findings revealed significant acceleration patterns from 2023 concerning publication trends, annual growth patterns, cited references, top authors, leading journals, and leading countries. Patterns of strengths from co-occurrence networks in VOSviewer revealed growing interest in generative AI tools, AI ethics, and concerns about AI integration into the curriculum in HE. The LDA analysis identified two dominant themes: the pedagogical integration of generative AI tools and broader academic discourse on AI ethics that correlated with the VOSviewer findings. This enhanced the credibility, reliability, and validity of the bibliometric techniques applied in the study. Recommendations and future directions offer valuable insights for policymakers and stakeholders to address pedagogical integration of generative AI tools in HE. The development of frameworks and ethical guidelines are important to address fair and transparent adoption of AI in HE. Further, global inequalities in adoption, aligning with UNESCO’s Sustainable Development Goals, are crucial to ensure equitable and responsible AI integration in HE.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
CLFF-NER: A Cross-Lingual Feature Fusion Model for Named Entity Recognition in the Traditional Chinese Festival Culture Domain
by
Shenghe Yang, Kun He, Wei Li and Yingying He
Informatics 2025, 12(4), 136; https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics12040136 - 5 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
With the rapid development of information technology, there is an increasing demand for the digital preservation of traditional festival culture and the extraction of relevant knowledge. However, existing research on Named Entity Recognition (NER) for Chinese traditional festival culture lacks support from high-quality
[...] Read more.
With the rapid development of information technology, there is an increasing demand for the digital preservation of traditional festival culture and the extraction of relevant knowledge. However, existing research on Named Entity Recognition (NER) for Chinese traditional festival culture lacks support from high-quality corpora and dedicated model methods. To address this gap, this study proposes a Named Entity Recognition model, CLFF-NER, which integrates multi-source heterogeneous information. The model operates as follows: first, Multilingual BERT is employed to obtain the contextual semantic representations of Chinese and English sentences. Subsequently, a Multiconvolutional Kernel Network (MKN) is used to extract the local structural features of entities. Then, a Transformer module is introduced to achieve cross-lingual, cross-attention fusion of Chinese and English semantics. Furthermore, a Graph Neural Network (GNN) is utilized to selectively supplement useful English information, thereby alleviating the interference caused by redundant information. Finally, a gating mechanism and Conditional Random Field (CRF) are combined to jointly optimize the recognition results. Experiments were conducted on the public Chinese Festival Culture Dataset (CTFCDataSet), and the model achieved 89.45%, 90.01%, and 89.73% in precision, recall, and F1 score, respectively—significantly outperforming a range of mainstream baseline models. Meanwhile, the model also demonstrated competitive performance on two other public datasets, Resume and Weibo, which verifies its strong cross-domain generalization ability.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Enhancing Intuitive Decision-Making and Reliance Through Human–AI Collaboration: A Review
by
Gerui Xu, Shruthi Venkatesha Murthy and Bochen Jia
Informatics 2025, 12(4), 135; https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics12040135 - 5 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
As AI decision support systems play a growing role in high-stakes decision making, ensuring effective integration of human intuition with AI recommendations is essential. Despite advances in AI explainability, challenges persist in fostering appropriate reliance. This review explores AI decision support systems that
[...] Read more.
As AI decision support systems play a growing role in high-stakes decision making, ensuring effective integration of human intuition with AI recommendations is essential. Despite advances in AI explainability, challenges persist in fostering appropriate reliance. This review explores AI decision support systems that enhance human intuition through the analysis of 84 studies addressing three questions: (1) What design strategies enable AI systems to support humans’ intuitive capabilities while maintaining decision-making autonomy? (2) How do AI presentation and interaction approaches influence trust calibration and reliance behaviors in human–AI collaboration? (3) What ethical and practical implications arise from integrating AI decision support systems into high-risk human decision making, particularly regarding trust calibration, skill degradation, and accountability across different domains? Our findings reveal four key design strategies: complementary role architectures that amplify rather than replace human judgment, adaptive user-centered designs tailoring AI support to individual decision-making styles, context-aware task allocation dynamically assigning responsibilities based on situational factors, and autonomous reliance calibration mechanisms empowering users’ control over AI dependence. We identified that visual presentations, interactive features, and uncertainty communication significantly influence trust calibration, with simple visual highlights proving more effective than complex presentation and interactive methods in preventing over-reliance. However, a concerning performance paradox emerges where human–AI combinations often underperform the best individual agent while surpassing human-only performance. The research demonstrates that successful AI integration in high-risk contexts requires domain-specific calibration, integrated sociotechnical design addressing trust calibration and skill preservation simultaneously, and proactive measures to maintain human agency and competencies essential for safety, accountability, and ethical responsibility.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
MCD-Temporal: Constructing a New Time-Entropy Enhanced Dynamic Weighted Heterogeneous Ensemble for Cognitive Level Classification
by
Yuhan Wu, Long Zhang, Bin Li and Wendong Zhang
Informatics 2025, 12(4), 134; https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics12040134 - 2 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Accurate classification of cognitive levels in instructional dialogues is essential for personalized education and intelligent teaching systems. However, most existing methods predominantly rely on static textual features and a shallow semantic analysis. They often overlook dynamic temporal interactions and struggle with class imbalance.
[...] Read more.
Accurate classification of cognitive levels in instructional dialogues is essential for personalized education and intelligent teaching systems. However, most existing methods predominantly rely on static textual features and a shallow semantic analysis. They often overlook dynamic temporal interactions and struggle with class imbalance. To address these limitations, this study proposes a novel framework for cognitive-level classification. This framework integrates time entropy-enhanced dynamics with a dynamically weighted, heterogeneous ensemble strategy. Specifically, we reconstruct the original Multi-turn Classroom Dialogue (MCD) dataset by introducing time entropy to quantify teacher–student speaking balance and semantic richness features based on Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency (TF-IDF), resulting in an enhanced MCD-temporal dataset. We then design a Dynamic Weighted Heterogeneous Ensemble (DWHE), which adjusts weights based on the class distribution. Our framework achieves a state-of-the-art macro-F1 score of 0.6236. This study validates the effectiveness of incorporating temporal dynamics and adaptive ensemble learning for robust cognitive level assessment, offering a more powerful tool for educational AI applications.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Fuzzy Ontology Embeddings and Visual Query Building for Ontology Exploration
by
Vladimir Zhurov, John Kausch, Kamran Sedig and Mostafa Milani
Informatics 2025, 12(4), 133; https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics12040133 - 1 Dec 2025
Abstract
Ontologies play a central role in structuring knowledge across domains, supporting tasks such as reasoning, data integration, and semantic search. However, their large size and complexity—particularly in fields such as biomedicine, computational biology, law, and engineering—make them difficult for non-experts to navigate. Formal
[...] Read more.
Ontologies play a central role in structuring knowledge across domains, supporting tasks such as reasoning, data integration, and semantic search. However, their large size and complexity—particularly in fields such as biomedicine, computational biology, law, and engineering—make them difficult for non-experts to navigate. Formal query languages such as SPARQL offer expressive access but require users to understand the ontology’s structure and syntax. In contrast, visual exploration tools and basic keyword-based search interfaces are easier to use but often lack flexibility and expressiveness. We introduce FuzzyVis, a proof-of-concept system that enables intuitive and expressive exploration of complex ontologies. FuzzyVis integrates two key components: a fuzzy logic-based querying model built on fuzzy ontology embeddings, and an interactive visual interface for building and interpreting queries. Users can construct new composite concepts by selecting and combining existing ontology concepts using logical operators such as conjunction, disjunction, and negation. These composite concepts are matched against the ontology using fuzzy membership-based embeddings, which capture degrees of membership and support approximate, concept-level similarity search. The visual interface supports browsing, query composition, and partial search without requiring formal syntax. By combining fuzzy semantics with embedding-based reasoning, FuzzyVis enables flexible interpretation, efficient computation, and exploratory learning. A usage scenario demonstrates how FuzzyVis supports subtle information needs and helps users uncover relevant concepts in large, complex ontologies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Human-Computer Interaction)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Reducing AI-Generated Misinformation in Australian Higher Education: A Qualitative Analysis of Institutional Responses to AI-Generated Misinformation and Implications for Cybercrime Prevention
by
Leo S. F. Lin, Geberew Tulu Mekonnen, Mladen Zecevic, Immaculate Motsi-Omoijiade, Duane Aslett and Douglas M. C. Allan
Informatics 2025, 12(4), 132; https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics12040132 - 28 Nov 2025
Abstract
Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) has transformed Australian higher education, amplifying online harms such as misinformation, fraud, and image-based abuse, with significant implications for cybercrime prevention. Combining a PRISMA-guided systematic review with MAXQDA-driven analysis of Australian university policies, this research evaluates institutional strategies against
[...] Read more.
Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) has transformed Australian higher education, amplifying online harms such as misinformation, fraud, and image-based abuse, with significant implications for cybercrime prevention. Combining a PRISMA-guided systematic review with MAXQDA-driven analysis of Australian university policies, this research evaluates institutional strategies against national frameworks, such as the Cybersecurity Strategy 2023–2030. Analyzing data from academic literature, we identify three key themes: educational strategies, alignment with national frameworks, and policy gaps and development. As the first qualitative analysis of 40 Australian university policies, this study uncovers systemic fragmentation in governance frameworks, with only 12 institutions addressing data privacy risks and none directly targeting AI-driven disinformation threats like deepfake harassment—a critical gap in global AI governance literature. This study provides actionable recommendations to develop the National GenAI Governance Framework, co-developed by TEQSA/UA and DoE, enhanced cyberbullying policies, and behavior-focused training to enhance digital safety and prevent cybercrime in Australian higher education. Mandatory annual CyberAI Literacy Module for all students and staff to ensure awareness of cybersecurity risks, responsible use of artificial intelligence, and digital safety practices within the university community.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Generative AI in Higher Education: Applications, Implications, and Future Directions)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Hierarchical Fake News Detection Model Based on Multi-Task Learning and Adversarial Training
by
Yi Sun and Dunhui Yu
Informatics 2025, 12(4), 131; https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics12040131 - 27 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The harmfulness of online fake news has brought widespread attention to fake news detection by researchers. Most existing methods focus on improving the accuracy and early detection of fake news, while ignoring the frequent cross-topic issues faced by fake news in online environments.
[...] Read more.
The harmfulness of online fake news has brought widespread attention to fake news detection by researchers. Most existing methods focus on improving the accuracy and early detection of fake news, while ignoring the frequent cross-topic issues faced by fake news in online environments. A hierarchical fake news detection method (HAMFD) based on multi-task learning and adversarial training is proposed. Through the multi-task learning task at the event level, subjective and objective information is introduced. A subjectivity classifier is used to capture sentiment shift within events, aiming to improve in-domain performance and generalization ability of fake news detection. On this basis, textual features and sentiment shift features are fused to perform event-level fake news detection and enhance detection accuracy. The post-level loss and event-level loss are weighted and summed for backpropagation. Adversarial perturbations are added to the embedding layer of the post-level module to deceive the detector, enabling the model to better resist adversarial attacks and enhance its robustness and topic adaptability. Experiments are conducted on three real-world social media datasets, and the results show that the proposed method improves performance in both in-domain and cross-topic fake news detection. Specifically, the model attains accuracies of 91.3% on Twitter15, 90.4% on Twitter16, and 95.7% on Weibo, surpassing advanced baseline methods by 1.6%, 1.5%, and 1.1%, respectively.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Explainable Artificial Intelligence for Workplace Mental Health Prediction
by
Tsholofelo Mokheleli, Tebogo Bokaba and Elliot Mbunge
Informatics 2025, 12(4), 130; https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics12040130 - 26 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The increased prevalence of mental health issues in the workplace affects employees’ well-being and organisational success, necessitating proactive interventions such as employee assistance programmes, stress management workshops, and tailored wellness initiatives. Artificial intelligence (AI) techniques are transforming mental health risk prediction using behavioural,
[...] Read more.
The increased prevalence of mental health issues in the workplace affects employees’ well-being and organisational success, necessitating proactive interventions such as employee assistance programmes, stress management workshops, and tailored wellness initiatives. Artificial intelligence (AI) techniques are transforming mental health risk prediction using behavioural, environmental, and workplace data. However, the “black-box” nature of many AI models hinders trust, transparency, and adoption in sensitive domains such as mental health. This study used the Open Sourcing Mental Illness (OSMI) secondary dataset (2016–2023) and applied four ML classifiers, Random Forest (RF), xGBoost, Support Vector Machine (SVM), and AdaBoost, to predict workplace mental health outcomes. Explainable AI (XAI) techniques, SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) and Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations (LIME), were integrated to provide both global (SHAP) and instance-level (LIME) interpretability. The Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique (SMOTE) was applied to address class imbalance. The results show that xGBoost and RF achieved the highest cross-validation accuracy (94%), with xGBoost performing best overall (accuracy = 91%, ROC AUC = 90%), followed by RF (accuracy = 91%). SHAP revealed that sought_treatment, past_mh_disorder, and current_mh_disorder had the most significant positive impact on predictions, while LIME provided case-level explanations to support individualised interpretation. These findings show the importance of explainable ML models in informing timely, targeted interventions, such as improving access to mental health resources, promoting stigma-free workplaces, and supporting treatment-seeking behaviour, while ensuring the ethical and transparent integration of AI into workplace mental health management.
Full article

Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Informatics Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Electronics, Informatics, JCP, Future Internet, Mathematics, Sensors, Remote Sensing
Recent Advances in Artificial Intelligence for Security and Security for Artificial Intelligence
Topic Editors: Tao Zhang, Xiangyun Tang, Jiacheng Wang, Chuan Zhang, Jiqiang LiuDeadline: 28 February 2026
Topic in
Computers, Informatics, Information, Logistics, Mathematics, Algorithms
Decision Science Applications and Models (DSAM)
Topic Editors: Daniel Riera Terrén, Angel A. Juan, Majsa Ammuriova, Laura CalvetDeadline: 30 June 2026
Topic in
AI, Algorithms, BDCC, Computers, Data, Future Internet, Informatics, Information, MAKE, Publications, Smart Cities
Learning to Live with Gen-AI
Topic Editors: Antony Bryant, Paolo Bellavista, Kenji Suzuki, Horacio Saggion, Roberto Montemanni, Andreas Holzinger, Min ChenDeadline: 31 August 2026
Topic in
World, Informatics, Information
The Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Tourism
Topic Editors: Angelica Lo Duca, Jose BerengueresDeadline: 30 September 2026

Special Issues
Special Issue in
Informatics
Generative AI in Higher Education: Applications, Implications, and Future Directions
Guest Editors: Amir Ghapanchi, Reza Ghanbarzadeh, Purarjomandlangrudi AfroozDeadline: 28 February 2026
Special Issue in
Informatics
Practical Applications of Sentiment Analysis
Guest Editors: Patricia Anthony, Jing ZhouDeadline: 31 March 2026
Special Issue in
Informatics
Real-World Applications and Prototyping of Information Systems for Extended Reality (VR, AR, and MR)
Guest Editors: Kitti Puritat, Kannikar Intawong, Wirapong ChansanamDeadline: 31 March 2026
Special Issue in
Informatics
Health Data Management in the Age of AI
Guest Editors: Brenda Scholtz, Hanlie SmutsDeadline: 30 May 2026








