- Article
Operationalising CTT and IRT in Spreadsheets: A Methodological Demonstration for Classroom Assessment
- António Faria and
- Guilhermina Lobato Miranda
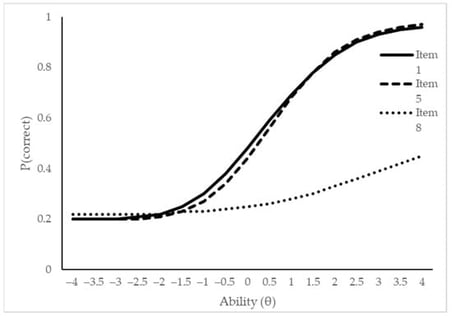
The evaluation of student performance often relies on basic spreadsheet outputs that provide limited insight into item functioning. This study presents a methodological demonstration showing how widely available spreadsheet software can be transformed into a practical environment for psychometric analysis. Using a simulated dataset of 40 students responding to 20 dichotomous items, spreadsheet formulas were developed to compute descriptive statistics and Classical Test Theory (CTT) indices, including item difficulty, discrimination, and corrected item–total correlations. The demonstration was extended to Item Response Theory (IRT) through the implementation of 1PL, 2PL, and 3PL logistic models using forward-calculated item parameters. A smaller dataset of 10 students and 10 items was used to illustrate the interpretability of the indices and the generation of Item Characteristic Curves (ICCs). Results show that spreadsheets can support teachers in in-terpreting test data beyond total scores, enabling the identification of weak items, refinement of distractors, and construction of small-scale item banks aligned with competence-based curricula. The approach contributes to Sustainable Development Goal 4 (SDG 4) by promoting accessible, equitable, and high-quality assessment practices. Limitations include the instability of IRT parameter estimation in small samples and the need for teacher training. Future research should apply the approach to real classroom data, explore automation within spreadsheet environments, and examine the integration of artificial intelligence for adaptive assessment.
24 February 2026



![Generating FGDPs from a doctor’s notes (adapted from [25]).](https://mdpi-res.com/cdn-cgi/image/w=281,h=192/https://mdpi-res.com/analytics/analytics-05-00011/article_deploy/html/images/analytics-05-00011-g001-550.jpg)