- Article
Optimization Research on Torque Ripple of Built-In V-Shaped Permanent Magnet Motor with Magnetic Isolation Holes
- Junhong Dong,
- Hongbin Yin and
- Xiaojun Wang
- + 2 authors
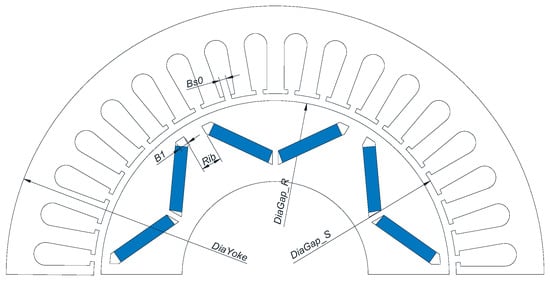
The built-in V-shaped permanent magnet motor can effectively utilize reluctance torque to improve torque density, but there is also a problem of large torque ripple causing high vibration noise. This article proposes a rotor structure with four magnetic isolation holes to reduce torque ripple in V-shaped built-in permanent magnet motors. Firstly, a finite element analysis model of the built-in V-shaped permanent magnet motor is established. The influence of slot width, rotor rib width, and magnetic bridge parameters on the torque of the permanent magnet motor was studied through parameterized scanning, and an optimization scheme was selected. Then, the position and size of the magnetic hole were optimized through an adaptive single-objective algorithm. Compared with the ordinary built-in V-shaped structure, the torque ripple of the built-in V-shaped permanent magnet motor with four magnetic isolation holes is reduced from 17.7% to 6.7%. The proposed internal V-shaped rotor structure with magnetic isolation holes and the optimization method can effectively reduce torque ripple, thus effectively solving the problem of vibration noise caused by torque ripple.
21 January 2026