- Article
Modeling Street-Level Energy and Emissions: The Role of Vehicle Traffic
- Miguel Campino,
- Luís Sousa and
- Gonçalo O. Duarte
- + 1 author
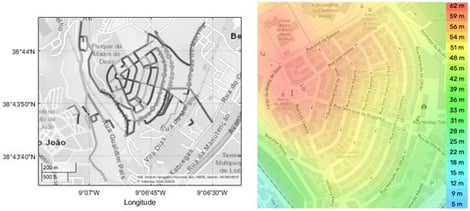
The transportation sector accounts for 25% of CO2 global emissions. Europe aims for carbon neutrality by 2050 through new light-duty vehicle technologies and stricter regulations, though these efforts may be insufficient. This work aims to assess a small neighborhood by analyzing over 19,500 routes to calculate an indicator that identifies streets with the highest impacts to evaluate the individual impacts of various light-duty vehicle technologies and examines how different combinations of technologies, based on traffic distribution, influence overall energy and emissions outcomes. The results highlight how uphill steep roads increase energy use, while downhill sections allow for energy recovery. A Street VSP Impact Factor (SVIF) was developed to identify streets with high energy use and emissions, offering insights into targeted urban planning strategies. The findings suggest that promoting BEV adoption and optimizing street infrastructure are key to reducing energy consumption and emissions in cities.
8 February 2026