-
 Social Planning for eBRT Innovations: Multi-Criteria Evaluation of Societal Impacts
Social Planning for eBRT Innovations: Multi-Criteria Evaluation of Societal Impacts -
 Enabling Grid Services with Bidirectional EV Chargers: A Comparative Analysis of CCS2 and CHAdeMO Response Dynamics
Enabling Grid Services with Bidirectional EV Chargers: A Comparative Analysis of CCS2 and CHAdeMO Response Dynamics -
 Evaluating Unplug Incentives to Improve User Experience and Increase DC Fast Charger Utilization
Evaluating Unplug Incentives to Improve User Experience and Increase DC Fast Charger Utilization -
 EV and Renewable Energy Integration in Residential Buildings: A Global Perspective on Deep Learning, Strategies, and Challenges
EV and Renewable Energy Integration in Residential Buildings: A Global Perspective on Deep Learning, Strategies, and Challenges
Journal Description
World Electric Vehicle Journal
World Electric Vehicle Journal
(WEVJ) is the first international, peer-reviewed, open access journal that comprehensively covers all studies related to battery, hybrid, and fuel cell electric vehicles, published monthly online. It is the official journal of the World Electric Vehicle Association (WEVA) and its members, the E-Mobility Europe, Electric Drive Transportation Association (EDTA), and Electric Vehicle Association of Asia Pacific (EVAAP).
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, ESCI (Web of Science), Ei Compendex, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Engineering, Electrical and Electronic) / CiteScore - Q2 (Automotive Engineering)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 17.6 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.9 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Impact Factor:
2.6 (2024)
Latest Articles
Energy-Efficient Actuator Concept for Two-Speed Transmissions in Battery Electric Vehicles
World Electr. Veh. J. 2026, 17(1), 12; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj17010012 - 24 Dec 2025
Abstract
Two-speed transmissions can improve battery electric vehicle (BEV) drivetrain efficiency. However, the additional losses caused by shifting actuators offset these efficiency gains. Particularly hydraulic actuated wet running multi-plate clutches, which enable powershifts, typically require rotary feedthroughs. Commonly used rectangular sealing rings (RSR) demand
[...] Read more.
Two-speed transmissions can improve battery electric vehicle (BEV) drivetrain efficiency. However, the additional losses caused by shifting actuators offset these efficiency gains. Particularly hydraulic actuated wet running multi-plate clutches, which enable powershifts, typically require rotary feedthroughs. Commonly used rectangular sealing rings (RSR) demand continuous hydraulic power due to leakage and cause friction torque. This leads to high RSR temperatures, especially at high angular velocities of electric machines. This article introduces a two-speed BEV transmission concept using wet running multi-plate clutches actuated via a rotating 5/3-way valve that can shut off, i.e., lock up the actuating pressure directly in the rotating system. Consequently, the rotary feedthrough is depressurized and contactless gap seals are usable. This reduces supply pressure requirements and minimizes hydraulic and friction losses while retaining powershift capability. Component-level tests evaluate leakage, pressure shut off, actuator dynamics and power consumption. Results show that actuating pressure in a shut-off clutch is maintained for longer than 60 min and electrical actuator power consumption is less than 20 W. During overlapping gearshifts, gap seal leakage is less than 1 L/min at 10 bar and sufficient pressure dynamics are achieved. These findings confirm the feasibility of the proposed actuator for multi-plate clutches in two-speed BEV transmissions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Propulsion Systems and Components)
Open AccessArticle
A Hybrid Lagrangian Relaxation and Adaptive Sheep Flock Optimization to Assess the Impact of EV Penetration on Cost
by
Sridevi Panda, Sumathi Narra and Surender Reddy Salkuti
World Electr. Veh. J. 2026, 17(1), 11; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj17010011 - 24 Dec 2025
Abstract
The increasing penetration of electric vehicle (EV) fast-charging stations (FCSs) into distribution networks and microgrids poses considerable operational challenges, including voltage deviations, increased power losses, and peak load stress. This work proposes a novel hybrid optimization framework that integrates Lagrangian relaxation (LR) with
[...] Read more.
The increasing penetration of electric vehicle (EV) fast-charging stations (FCSs) into distribution networks and microgrids poses considerable operational challenges, including voltage deviations, increased power losses, and peak load stress. This work proposes a novel hybrid optimization framework that integrates Lagrangian relaxation (LR) with adaptive sheep flock optimization (ASFO) to address the resource scheduling issues when EVs are penetrated and their impact on net load demand, total cost. Besides the impact of EV uncertainty on energy exchange cost and operational costs, voltage profile deviations were also studied. LR is employed to decompose the original problem and manage complex operational constraints, while ASFO is employed to solve the relaxed subproblems by efficiently exploring the high-dimensional, non-convex solution space. The proposed method is tested on an IEEE 33-bus distribution system with integrated PV and BESS under 24 h dynamic load and renewable scenarios. Results establish that the hybrid LR-ASFO method significantly outperforms conventional methods. Compared to standalone metaheuristics, the proposed framework reduces total cost by 5.6%, improves voltage profile deviations by 2.4%, and minimizes total operational cost by 4.3%. Furthermore, it safeguards constraint feasibility while avoiding premature convergence, thereby accomplishing better global optimality and system reliability.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Vehicle Management)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Trajectory Tracking and Stability Control of Distributed-Drive Heavy Trucks on High-Speed Curves with Large Curvature
by
Zhi Li, Zhouquan Li, Huawei Wu and Zhen Liu
World Electr. Veh. J. 2026, 17(1), 10; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj17010010 - 23 Dec 2025
Abstract
To address the difficulty of balancing trajectory-tracking accuracy and yaw stability for distributed-drive four-axle heavy trucks under high-speed and large-curvature cornering conditions, this paper proposes a hierarchical cooperative control strategy. The upper layer employs Sliding Mode Control (SMC) to achieve precise trajectory tracking,
[...] Read more.
To address the difficulty of balancing trajectory-tracking accuracy and yaw stability for distributed-drive four-axle heavy trucks under high-speed and large-curvature cornering conditions, this paper proposes a hierarchical cooperative control strategy. The upper layer employs Sliding Mode Control (SMC) to achieve precise trajectory tracking, while the lower layer integrates a sliding-mode-based Direct Yaw Moment Control (DYC) and a differential braking allocation strategy to enhance vehicle stability. TruckSim–Simulink co-simulation results demonstrate that, under large-curvature scenarios such as S-shaped paths, sharp lane changes, and single-lane transitions, the proposed strategy outperforms the conventional SMC method. Specifically, the maximum lateral deviation is reduced by 19.23–23.02%, the peak heading angle error decreases from 5.3° to 3.5°, the maximum yaw rate drops from 12.6°/s to 4.6°/s (a 63.49% reduction), and the peak sideslip angle at the vehicle’s center of mass converges from 4.6° to 3.8° (a 17.39% decrease). The results indicate that the proposed strategy achieves coordinated optimization of trajectory tracking and yaw stability under high-speed, large-curvature cornering conditions, providing both theoretical support and engineering value for high-dynamic control of distributed-drive heavy trucks.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Propulsion Systems and Components)
Open AccessArticle
A Novel Reduced-Ripple Average Torque Control Technique for Light Electric Vehicle Switched Reluctance Motors
by
Mahmoud Hamouda, Ameer L. Saleh, Ahmed Elsanabary and Mohammad A. Abido
World Electr. Veh. J. 2026, 17(1), 9; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj17010009 (registering DOI) - 23 Dec 2025
Abstract
The switched reluctance motors (SRMs) are an attractive solution for electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs). However, the main drawbacks of SRMs are their highly nonlinear magnetic characteristics, complicated control algorithms, and the inherent torque ripples. This paper presents a simple
[...] Read more.
The switched reluctance motors (SRMs) are an attractive solution for electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs). However, the main drawbacks of SRMs are their highly nonlinear magnetic characteristics, complicated control algorithms, and the inherent torque ripples. This paper presents a simple structure average torque control (ATC) technique with a better ability to reduce torque ripples. Based on the detailed analysis of an inductance profile, this paper introduces a novel current compensation mechanism (CCM) that has the ability to profile the phase current and, hence, reduce the torque ripple. The proposed CCM is meant for the minimum inductance zone (MIZ) to profile the current of the ongoing phase. Over the MIZ, the inductance is independent of the phase current that helps to simplify the deduced mathematical formulations and provides a simple structure ATC with a lower computational burden, making it a feasible solution for real-time implementations and future developments. A series of experimental results are achieved to show the feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed ATC technique. The results show the superior performance of the proposed ATC, providing better torque profiles and reducing the torque ripples with an average value of 30% compared to conventional ATC.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Propulsion Systems and Components)
Open AccessArticle
Real-Time Energy Management of a Dual-Stack Fuel Cell Hybrid Electric Vehicle Based on a Commercial SUV Platform Using a CompactRIO Controller
by
Mircea Raceanu, Nicu Bizon, Mariana Iliescu, Elena Carcadea, Adriana Marinoiu and Mihai Varlam
World Electr. Veh. J. 2026, 17(1), 8; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj17010008 - 22 Dec 2025
Abstract
This study presents the design, real-time implementation, and full-scale experimental validation of a rule-based Energy Management Strategy (EMS) for a dual-stack Fuel Cell Hybrid Electric Vehicle (FCHEV) developed on a Jeep Wrangler platform. Unlike previous studies, predominantly focused on simulation-based analysis or single-stack
[...] Read more.
This study presents the design, real-time implementation, and full-scale experimental validation of a rule-based Energy Management Strategy (EMS) for a dual-stack Fuel Cell Hybrid Electric Vehicle (FCHEV) developed on a Jeep Wrangler platform. Unlike previous studies, predominantly focused on simulation-based analysis or single-stack architectures, this work provides comprehensive vehicle-level experimental validation of a deterministic real-time EMS applied to a dual fuel cell system in an SUV-class vehicle. The control algorithm, deployed on a National Instruments CompactRIO embedded controller, ensures deterministic real-time energy distribution and stable hybrid operation under dynamic load conditions. Simulation analysis conducted over eight consecutive WLTC cycles shows that both fuel cell stacks operate predominantly within their optimal efficiency range (25–35 kW), achieving an average DC efficiency of 68% and a hydrogen consumption of 1.35 kg/100 km under idealized conditions. Experimental validation on the Wrangler FCHEV demonstrator yields a hydrogen consumption of 1.67 kg/100 km, corresponding to 1.03 kg/100 km·m2 after aerodynamic normalization (Cd·A = 1.624 m2), reflecting real-world operating constraints. The proposed EMS promotes fuel-cell durability by reducing current cycling amplitude and maintaining operation within high-efficiency regions for the majority of the driving cycle. By combining deterministic real-time embedded control with vehicle-level experimental validation, this work strengthens the link between EMS design and practical deployment and provides a scalable reference framework for future hydrogen powertrain control systems.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Advances in Electric Vehicle Charging Systems and Vehicle-to-Grid Technology)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Obstacle Avoidance for Vehicle Platoons in I-VICS: A Safety-Centric Approach Using an Improved Potential Field Method
by
Du Chigan, Jianbei Liu, Yang Zhao and Jianyou Zhao
World Electr. Veh. J. 2026, 17(1), 7; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj17010007 - 22 Dec 2025
Abstract
Based on an enhanced artificial potential field approach, this paper presents a control method for obstacle avoidance in vehicle platoons within Intelligent Vehicle-Infrastructure Cooperative Systems (I-VICS). To enhance safety during maneuvers, an inter-vehicle obstacle avoidance potential field model is established. By integrating virtual
[...] Read more.
Based on an enhanced artificial potential field approach, this paper presents a control method for obstacle avoidance in vehicle platoons within Intelligent Vehicle-Infrastructure Cooperative Systems (I-VICS). To enhance safety during maneuvers, an inter-vehicle obstacle avoidance potential field model is established. By integrating virtual forces and a consistency control strategy into the control law, the proposed method effectively handles obstacle avoidance for vehicles operating at large inter-vehicle distances (80–110 m). Experimental validation using real-world trajectory data shows a 34% improvement in trajectory smoothness, as quantified by a proposed Vehicle Trajectory Stability (VTS) metric, leading to significantly safer avoidance maneuvers. A coordinated multi-vehicle obstacle avoidance strategy is further devised using a rotating potential field method, enabling collaborative and safe overall motion planning. Moreover, a path tracking strategy based on virtual force design is introduced to enhance platoon stability and reliability. Future work will focus on collision avoidance for vehicle platoons with varying inter-vehicle distances and will extend the consistency control and cooperative avoidance strategies to longer vehicle platoon to further improve overall traffic safety.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Automated and Connected Vehicles)
Open AccessArticle
Electric BRT Readiness and Impacts in Athens, Greece: A Gradient Boosting-Based Decision Support Framework
by
Parmenion Delialis, Orfeas Karountzos, Konstantia Kontodimou, Christina Iliopoulou and Konstantinos Kepaptsoglou
World Electr. Veh. J. 2026, 17(1), 6; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj17010006 - 20 Dec 2025
Abstract
The integration of electric buses into urban transportation networks is a priority for policymakers aiming to promote sustainable public mobility. Among available technologies, electric Bus Rapid Transit (eBRT) systems offer an environmentally friendly and operationally effective alternative to conventional modes. This study introduces
[...] Read more.
The integration of electric buses into urban transportation networks is a priority for policymakers aiming to promote sustainable public mobility. Among available technologies, electric Bus Rapid Transit (eBRT) systems offer an environmentally friendly and operationally effective alternative to conventional modes. This study introduces a Machine Learning Decision Support Framework designed to assess the feasibility of deploying eBRT systems in urban environments. Using a dataset of 28 routes in the Athens Metropolitan Area, the framework integrates diverse variables such as land use, population coverage, proximity to public transport, points of interest, road characteristics, and safety indicators. The XGBoost model demonstrated strong predictive performance, outperforming traditional approaches and highlighting the significance of points of interest, land use diversity, green spaces, and roadway infrastructure in forecasting travel times. Overall, the proposed framework provides urban planners and policymakers with a robust, data-driven tool for evaluating the practical and environmental viability of eBRT systems.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Zero Emission Buses for Public Transport)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Evaluating the Potential of Sodium-Ion Batteries for Low Voltage Mobility
by
Alexander Fandakov, Brahim Soltani, Sébastien Sallard, Oliver Nolte, Johannes Werfel, Karsten Mueller and Marc Sens
World Electr. Veh. J. 2026, 17(1), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj17010005 - 19 Dec 2025
Abstract
The automotive industry is under pressure to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. While the growth of electric vehicles is crucial, optimizing low-voltage batteries for conventional powertrain architecture (12–48 V) can help reduce carbon dioxide emissions. Currently, lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries dominate the low-voltage
[...] Read more.
The automotive industry is under pressure to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. While the growth of electric vehicles is crucial, optimizing low-voltage batteries for conventional powertrain architecture (12–48 V) can help reduce carbon dioxide emissions. Currently, lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries dominate the low-voltage battery market due to their stability, safety, and ecological benefits as replacement to lead-acid. However, sodium-ion batteries (SIB) are emerging as a promising alternative to LFP, offering advantages in power, lifespan, cold temperature performance, integration, cost, material availability, and sustainability. These advantages of sodium-ion batteries make them a perfect candidate for fulfilling the requirements typically associated with 48 V applications as well. This contribution evaluates low-voltage SIB prototypes developed by the company IAV GmbH and its partners and explores their potential for automotive applications, aiming to share insights and assess future prospects.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue EVS38—International Electric Vehicle Symposium and Exhibition (Gothenburg, Sweden))
►▼
Show Figures
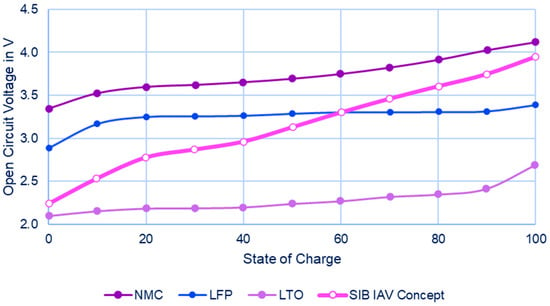
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Study on a Dual-Dimensional Compensation Mechanism and Bi-Level Optimization Approach for Real-Time Electric Vehicle Demand Response in Unified Build-and-Operate Communities
by
Shuang Hao and Guoqiang Zu
World Electr. Veh. J. 2026, 17(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj17010004 - 19 Dec 2025
Abstract
With the rapid growth of residential electric vehicles, synchronized charging during peak periods can induce severe load ramping and exceed distribution network capacity limits. To mitigate these issues, governments have promoted a unified build-and-operate community model that enables centralized coordination of community charging
[...] Read more.
With the rapid growth of residential electric vehicles, synchronized charging during peak periods can induce severe load ramping and exceed distribution network capacity limits. To mitigate these issues, governments have promoted a unified build-and-operate community model that enables centralized coordination of community charging and ensures real-time responsiveness to grid dispatch signals. Targeting this emerging operational paradigm, a dual-dimensional compensation mechanism for real-time electric vehicle (EV) demand response is proposed. The mechanism integrates two types of compensation: power regulation compensation, which rewards users for providing controllable power flexibility, and state-of-charge (SoC) loss compensation, which offsets energy deficits resulting from demand response actions. This dual-layer design enhances user willingness and long-term engagement in community-level coordination. Based on the proposed mechanism, a bi-level optimization framework is developed to realize efficient real-time regulation: the upper level maximizes the active response capacity under budget constraints, while the lower level minimizes the aggregator’s total compensation cost subject to user response behavior. Simulation results demonstrate that, compared with conventional fair-share curtailment and single-compensation approaches, the proposed mechanism effectively increases active user participation and reduces incentive expenditures. The study highlights the mechanism’s potential for practical deployment in unified build-and-operate communities and discusses limitations and future research directions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Charging Infrastructure and Grid Integration)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Approaches for Lifetime Prediction of Vehicle Traction Battery Systems During a Technical Inspection: A Systematic Review
by
Markus Gregor, Maximilian Bauder, Aline Kirsten Vidal de Oliveira, Pascal Mast, Ricardo Rüther and Hans-Georg Schweiger
World Electr. Veh. J. 2026, 17(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj17010003 - 19 Dec 2025
Abstract
Creating trust in society for new technologies, such as a new types of powertrains, and making them marketable requires transparent, neutral, and independent technical verification. This is crucial for the acceptance and success of electrified vehicles in the used car markets. A key
[...] Read more.
Creating trust in society for new technologies, such as a new types of powertrains, and making them marketable requires transparent, neutral, and independent technical verification. This is crucial for the acceptance and success of electrified vehicles in the used car markets. A key component of electric vehicles is the traction battery, whose current and future condition, particularly regarding aging, determines its residual value and safe operation. This review aims to identify and evaluate methods for predicting the lifetime of onboard traction batteries, focusing on their applicability in technical inspections. A systematic literature and patent review was conducted using targeted keywords, yielding 22 patents and 633 publications. From these, 150 distinct lifetime prediction methods were extracted and categorized into a four-level mind map. These methods are summarized, cited, and structured in detailed tables. The relationships between approaches are explained to clarify the current research landscape. Long Short-Term Memory, Convolutional Neural Networks, and Particle Filters were identified as the most frequently used techniques. However, no methods were found suitable for predicting the lifetime of traction batteries during technical vehicle inspections, which operate under short test durations, limited data access, and diverse real-world operating conditions. Most studies focused on cell-level testing and did not address complete battery systems in operational vehicles. This gap highlights the need for applied research and the development of practical methods to support battery assessment in real-world conditions. Advancing this field is essential to foster confidence in battery systems and enable a sustainable transition to electromobility.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Energy Supply and Sustainability)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessCommunication
Physics-Informed Temperature Prediction of Lithium-Ion Batteries Using Decomposition-Enhanced LSTM and BiLSTM Models
by
Seyed Saeed Madani, Yasmin Shabeer, Michael Fowler, Satyam Panchal, Carlos Ziebert, Hicham Chaoui and François Allard
World Electr. Veh. J. 2026, 17(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj17010002 - 19 Dec 2025
Abstract
Accurately forecasting the operating temperature of lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) is essential for preventing thermal runaway, extending service life, and ensuring the safe operation of electric vehicles and stationary energy-storage systems. This work introduces a unified, physics-informed, and data-driven temperature-prediction framework that integrates mathematically
[...] Read more.
Accurately forecasting the operating temperature of lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) is essential for preventing thermal runaway, extending service life, and ensuring the safe operation of electric vehicles and stationary energy-storage systems. This work introduces a unified, physics-informed, and data-driven temperature-prediction framework that integrates mathematically governed preprocessing, electrothermal decomposition, and sequential deep learning architectures. The methodology systematically applies the governing relations to convert raw temperature measurements into trend, seasonal, and residual components, thereby isolating long-term thermal accumulation, reversible entropy-driven oscillations, and irreversible resistive heating. These physically interpretable signatures serve as structured inputs to machine learning and deep learning models trained on temporally segmented temperature sequences. Among all evaluated predictors, the Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory (BiLSTM) network achieved the highest prediction fidelity, yielding an RMSE of 0.018 °C, a 35.7% improvement over the conventional Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) (RMSE = 0.028 °C) due to its ability to simultaneously encode forward and backward temporal dependencies inherent in cyclic electrochemical operation. While CatBoost exhibited the strongest performance among classical regressors (RMSE = 0.022 °C), outperforming Random Forest, Gradient Boosting, Support Vector Regression, XGBoost, and LightGBM, it remained inferior to BiLSTM because it lacks the capacity to represent bidirectional electrothermal dynamics. This performance hierarchy confirms that LIB thermal evolution is not dictated solely by historical load sequences; it also depends on forthcoming cycling patterns and entropic interactions, which unidirectional and memoryless models cannot capture. The resulting hybrid physics-data-driven framework provides a reliable surrogate for real-time LIB thermal estimation and can be directly embedded within BMS to enable proactive intervention strategies such as predictive cooling activation, current derating, and early detection of hazardous thermal conditions. By coupling physics-based decomposition with deep sequential learning, this study establishes a validated foundation for next-generation LIB thermal-management platforms and identifies a clear trajectory for future work extending the methodology to module- and pack-level systems suitable for industrial deployment.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Vehicle Management)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Research and Design of a Single-Switch Wireless Power Transfer System with Misalignment-Tolerant Characteristics
by
Chuan Yang, Liguo Zhang, Wenge Huang, Yi Yang and Ke Guo
World Electr. Veh. J. 2026, 17(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj17010001 - 19 Dec 2025
Abstract
To address the issue that the output voltage and power of medium- and low-power wireless power transfer (WPT) systems cannot remain constant under coil misalignment, this paper proposes a single-switch WPT system with misalignment-tolerant characteristics. Based on a single-switch topology, the system combines
[...] Read more.
To address the issue that the output voltage and power of medium- and low-power wireless power transfer (WPT) systems cannot remain constant under coil misalignment, this paper proposes a single-switch WPT system with misalignment-tolerant characteristics. Based on a single-switch topology, the system combines the LCC-S and S-S compensation networks through an input-series and output-series connection, forming a simplified hybrid-compensated single-switch WPT topology. By exploiting the complementary output characteristics of the two compensation networks, a stable output voltage is achieved under varying mutual inductance conditions. To further enhance misalignment adaptability, a grid-type flat spiral (GFSP) coil is designed for the magnetic coupler. This coil configuration avoids magnetic flux cancelation during lateral displacement, while maintaining a consistent mutual inductance variation trend between the dual windings, thereby exhibiting strong tolerance to misalignment along the X-axis. The proposed system is validated through MATLAB/Simulink simulations and experiments on a 50 W prototype. The results demonstrate that the system maintains resonance and achieves zero-voltage switching (ZVS) of the power device under ±60 mm X-axis misalignment, with output voltage fluctuation below 4% and efficiency fluctuation below 3%, verifying the proposed system’s effectiveness in misalignment tolerance.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Charging Infrastructure and Grid Integration)
►▼
Show Figures
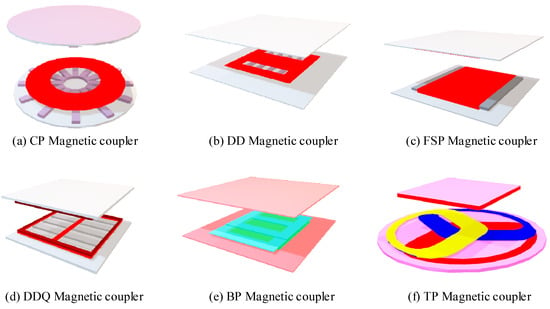
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Energy Harvesting Devices for Extending the Lifespan of Lithium-Polymer Batteries: Insights for Electric Vehicles
by
David Gutiérrez-Rosales, Omar Jiménez-Ramírez, Daniel Aguilar-Torres, Juan Carlos Paredes-Rojas, Eliel Carvajal-Quiroz and Rubén Vázquez-Medina
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(12), 682; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16120682 - 18 Dec 2025
Abstract
This study rigorously evaluated the integration of energy-harvesting systems within electric vehicles to prolong battery service life. A laboratory-scale system was configured utilizing a scale electric vehicle with a 12.6 V lithium-polymer (Li-Po) battery alongside an automated control platform to precisely estimate the
[...] Read more.
This study rigorously evaluated the integration of energy-harvesting systems within electric vehicles to prolong battery service life. A laboratory-scale system was configured utilizing a scale electric vehicle with a 12.6 V lithium-polymer (Li-Po) battery alongside an automated control platform to precisely estimate the real-time State of Charge (SoC) through monitoring of current, voltage, and temperature of the vehicle battery under three distinct driving conditions: (A) constant velocity at 30 km/h, (B) variable velocities exhibiting a sawtooth profile, and (C) random speed variations. Wind energy was harvested employing Savonius rotor microturbines, with assessments conducted on efficiency losses and drag coefficients to determine the net power yield for each operational profile, which was found to be marginally positive. Considering the energy consumption of electric vehicles based on 2017 U.S. EPA fuel economy data, the maximal recovered energy corresponded to 0.0833% of auxiliary system demand, while the minimal recovery was 0.0398%. These results substantiated the necessity for continued research into sustainable energy management frameworks for electric vehicles. They emphasized the critical importance of optimizing the incorporation of renewable energy technologies to mitigate the environmental ramifications of the transportation sector.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Advances in Electric Vehicle Charging Systems and Vehicle-to-Grid Technology)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Sustainable Port Horizontal Transportation: Environmental and Economic Optimization of Mobile Charging Stations Through Carbon-Efficient Recharging
by
Jie Qiu, Wenxuan Zhao, Hanlei Tian, Minhui Li and Wei Han
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(12), 681; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16120681 - 18 Dec 2025
Abstract
Electrifying port horizontal transportation is constrained by downtime and deadheading from fixed charging/swapping systems, large battery sizes, and the lack of integrated decision tools for life-cycle emissions. This study develops a carbon-efficiency-centered bi-objective optimization framework benchmarking Mobile Charging Stations (MCSs) against Fixed Charging
[...] Read more.
Electrifying port horizontal transportation is constrained by downtime and deadheading from fixed charging/swapping systems, large battery sizes, and the lack of integrated decision tools for life-cycle emissions. This study develops a carbon-efficiency-centered bi-objective optimization framework benchmarking Mobile Charging Stations (MCSs) against Fixed Charging Stations (FCSs) and Battery Swapping Stations (BSWSs). The framework integrates operational parameters such as charging power, range, dispatch, and non-operational mileage, along with grid carbon intensity, battery embodied emissions, and carbon-market factors. It generates Pareto fronts using the NSGA-II algorithm with real port data. Port horizontal transportation refers to the movement of goods within the port area, typically involving the use of specialized vehicles to transport containers short distances across the terminal. Results show that MCSs can reuse idle windows to reduce deadheading and infrastructure demand, yielding significant economic improvements. The trade-off between emissions and profitability is context-dependent: at low-to-moderate reuse levels, low-carbon and profitable solutions coexist; beyond a threshold of approximately 0.5–0.75, the Pareto fronts shift to high emissions and high profits, highlighting the context-specific advantages of MCSs for port-infrastructure planning. MCSs thus provide context-dependent advantages over FCSs and BSWSs, offering practical guidance for port infrastructure planning and carbon-informed policy design.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Contribution of Electric Vehicles to Realization of Dual Carbon Goal)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Optimized Design of a Permanent Magnet Machine for Golf Carts Under Multiple Operating Conditions
by
Wenye Wu, Donghui Li and Weifeng Wang
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(12), 680; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16120680 - 18 Dec 2025
Abstract
In response to the growing demand for efficient and eco-friendly golf carts, this paper presents an optimized design of a permanent magnet synchronous machine (PMSM) for multiple operating conditions. The application scenarios of the golf cart were first analyzed, identifying the power requirements
[...] Read more.
In response to the growing demand for efficient and eco-friendly golf carts, this paper presents an optimized design of a permanent magnet synchronous machine (PMSM) for multiple operating conditions. The application scenarios of the golf cart were first analyzed, identifying the power requirements under three driving conditions such as unloaded on flat roads, fully loaded on flat roads, and fully loaded on slopes. Then, a 36-slot 8-pole interior PMSM is developed, and a systematic two-stage optimization strategy using a Multi-Objective Genetic Algorithm (MOGA) is applied to enhance both no-load and rated-load performance. By adjusting key rotor parameters to balance competing objectives, the optimized machine demonstrates notable improvements in cogging torque reduction, output torque, torque ripple minimization, and operational efficiency. Specifically, the results show that the optimized machine achieves a cogging torque reduction of over 60%, an increase in maximum output torque by 7.3%, and a peak efficiency improvement of 1.2 percentage points under high-load conditions. Experimental results validate the effectiveness of the design and confirm its suitability for the complex operating conditions of golf carts.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Propulsion Systems and Components)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Attack Detection of Federated Learning Model Based on Attention Mechanism Optimization in Connected Vehicles
by
Lanying Liu, Fujun Wang and Ning Du
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(12), 679; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16120679 - 18 Dec 2025
Abstract
To address the problem of decreased model accuracy and poor global aggregation performance among existing methods in non-independent and identically distributed (non-IID) data backgrounds, the author proposes a method for attack detection in the Internet of Vehicles based on the attention mechanism optimization
[...] Read more.
To address the problem of decreased model accuracy and poor global aggregation performance among existing methods in non-independent and identically distributed (non-IID) data backgrounds, the author proposes a method for attack detection in the Internet of Vehicles based on the attention mechanism optimization of federated learning models. The author uses a combination of CNN and LSTM as the basic detection framework, integrating self-attention modules to optimize the spatiotemporal feature modeling effect. At the same time, an adaptive aggregation algorithm based on attention weights was designed in the federated aggregation stage, providing the model with stronger stability and generalization ability when dealing with data differences among nodes. In order to comprehensively evaluate the performance of the model, the experimental part is based on real datasets such as CICDDoS2019. The experimental results show that the federated learning model based on attention mechanism optimization proposed by the author demonstrates significant advantages in the task of detecting vehicle networking attacks. Compared with traditional methods, the new model improves attack detection accuracy by more than 5% in non-IID data environments, accelerates aggregation convergence speed, reduces aggregation epochs by more than 20%, and achieves stronger data privacy protection and real-time defense capabilities. Conclusion: This method not only improves the adaptability of the model in complex vehicle networking environments, but also effectively reduces the overall computational and communication overhead of the system.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Automated and Connected Vehicles)
►▼
Show Figures
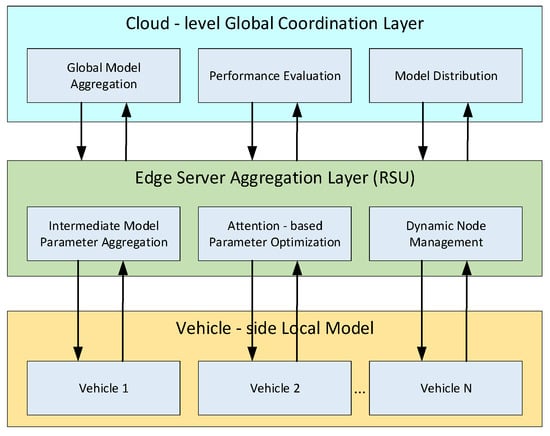
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Enhancing Object Detection for Autonomous Vehicles in Low-Resolution Environments Using a Super-Resolution Transformer-Based Preprocessing Framework
by
Mokhammad Mirza Etnisa Haqiqi, Ajib Setyo Arifin and Arief Suryadi Satyawan
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(12), 678; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16120678 - 17 Dec 2025
Abstract
Low-resolution (LR) imagery poses significant challenges to object detection systems, particularly in autonomous and resource-constrained environments where bandwidth and sensor quality are limited. To address this issue, this paper presents an integrated framework that enhances object detection performance by incorporating a Super-Resolution (SR)
[...] Read more.
Low-resolution (LR) imagery poses significant challenges to object detection systems, particularly in autonomous and resource-constrained environments where bandwidth and sensor quality are limited. To address this issue, this paper presents an integrated framework that enhances object detection performance by incorporating a Super-Resolution (SR) preprocessing stage prior to detection. Specifically, a Dense Residual Connected Transformer (DRCT) is employed to reconstruct high-resolution (HR) images from LR inputs, effectively restoring fine-grained structural and textural information essential for accurate detection. The reconstructed HR images are subsequently processed by a YOLOv11 detector without requiring architectural modifications. Experimental evaluations demonstrate consistent improvements across multiple scaling factors, with an average increase of 13.4% in Mean Average Precision (mAP)@50 at ×2 upscaling and 9.7% at ×4 compared with direct LR detection. These results validate the effectiveness of the proposed SR-based preprocessing approach in mitigating the adverse effects of image degradation. The proposed method provides an improved yet computationally challenging solution for object detection.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Automated and Connected Vehicles)
►▼
Show Figures
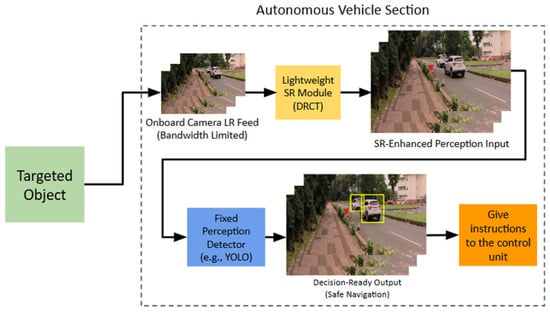
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Four-Wheel Steering Control for Mining X-by-Wire Chassis Based on AUKF State Estimation
by
Qiang Ji, Yueqi Bi, Mingrui Hao, Jiaran Li and Long Chen
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(12), 677; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16120677 - 17 Dec 2025
Abstract
To address the challenges to driving stability caused by large-curvature steering of wire-controlled mining vehicles in narrow tunnels, a fused four-wheel steering (4WS) control strategy based on real-time estimation of vehicle state parameters is proposed. A comprehensive longitudinal–lateral–yaw dynamics model for 4WS is
[...] Read more.
To address the challenges to driving stability caused by large-curvature steering of wire-controlled mining vehicles in narrow tunnels, a fused four-wheel steering (4WS) control strategy based on real-time estimation of vehicle state parameters is proposed. A comprehensive longitudinal–lateral–yaw dynamics model for 4WS is established, and a comparative study is conducted on three control methods: proportional feedforward control, yaw rate feedback control, and fused control. Expressions for steady-state yaw rate gain under different control modes are derived, and the stability differences in 4WS characteristics among these strategies are thoroughly analyzed. To overcome the difficulty in directly acquiring state information for chassis steering control, a vehicle state parameter estimator based on the unscented Kalman filter (UKF) is designed. To enhance the robustness to noise and computational real-time performance of vehicle state estimation in complex environments, a method for real-time estimation of noise covariance matrices using innovative sequences is adopted, improving the estimation accuracy of the algorithm. To validate the effectiveness of the control strategies, a co-simulation platform integrating Carsim and Matlab/Simulink is developed to simulate the performance of the three 4WS control methods under step steering and sinusoidal steering input conditions. The results show that, under low-speed conditions, 4WS strategies increase the yaw rate by approximately 50% and reduce the turning radius by over 45%, significantly enhancing steering maneuverability. Under medium-high speed conditions, 4WS strategies decrease the yaw rate by up to 68% and increase the turning radius by 17–29%, effectively suppressing oversteering tendencies to comprehensively improve stability, with the integrated control strategy demonstrating the best performance. Under both test conditions, the fused feedforward and feedback control strategy reduces the steady-state yaw rate by approximately 12.7% and 48.7%, respectively, compared to other control strategies, demonstrating superior stability.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advanced Design Theory and Methods of Intelligent Electric Vehicle Chassis)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Research on Mobile Robot Path Planning Using Improved Whale Optimization Algorithm Integrated with Bird Navigation Mechanism
by
Zhijun Guo, Tong Zhang, Hao Su, Shilei Jie, Yanan Tu and Yixuan Li
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(12), 676; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16120676 - 17 Dec 2025
Abstract
In order to solve the problems of slow convergence speed, insufficient accuracy, and easily falling into the local optimum of the traditional whale optimization algorithm (WOA) in mobile robot path planning, an improved whale optimization algorithm (IWOA) combined with the bird navigation mechanism
[...] Read more.
In order to solve the problems of slow convergence speed, insufficient accuracy, and easily falling into the local optimum of the traditional whale optimization algorithm (WOA) in mobile robot path planning, an improved whale optimization algorithm (IWOA) combined with the bird navigation mechanism was proposed. Specific improvement measures include using logical chaos mapping to initialize the population to enhance the randomness and diversity of the initial solution, designing a nonlinear convergence factor to prevent the algorithm from prematurely entering the shrinking surround phase and extending the global search time, introducing an adaptive spiral shape constant to dynamically adjust the search range to balance exploration and development capabilities, optimizing the individual update strategy in combination with the bird navigation mechanism, and optimizing the algorithm through companion position information, thereby improving the stability and convergence speed of the algorithm. Path planning simulations were performed on 30 × 30 and 50 × 50 grid maps. The results show that compared with WOA, MSWOA, and GA, in the 30 × 30 map, the path length of IWOA is shortened by 3.23%, 7.16%, and 6.49%, respectively; in the 50 × 50 map, the path length is shortened by 4.88%, 4.53%, and 28.37%, respectively. This study shows that IWOA has significant advantages in the accuracy and efficiency of path planning, which verifies its feasibility and superiority.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Research on Intelligent Vehicle Path Planning Algorithm)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Research on the Supply–Demand Evaluation and Configuration Optimization of Urban Residential Public Charging Facilities Based on Collaborative Service Networks: A Case Study of Hongshan District, Wuhan
by
Yanyan Huang, Yunfang Zha, You Zou, Xudong Jia, Zaiyu Fan, Hangyi Ren, Yilun Wei and Daoyuan Chen
World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16(12), 675; https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16120675 - 17 Dec 2025
Abstract
The rapid growth of electric vehicles has intensified the spatial mismatch between the layout of charging infrastructure and user demand, resulting in a structural contradiction in which “local oversupply” and “local shortages” coexist. To systematically diagnose and optimize this issue, this study develops
[...] Read more.
The rapid growth of electric vehicles has intensified the spatial mismatch between the layout of charging infrastructure and user demand, resulting in a structural contradiction in which “local oversupply” and “local shortages” coexist. To systematically diagnose and optimize this issue, this study develops an innovative analytical framework for a “residential area–charging infrastructure” collaborative service network and conducts an empirical analysis using Hongshan District in Wuhan as a case study. The framework integrates actual facility utilization data, complex network analysis, and spatial clustering methods. The findings reveal that the collaborative service network in the study area is overall sparse, exhibiting a distinct “core–periphery” structure, with noticeable patterns of resource concentration and isolation. Residential areas can be categorized into three types based on their supply–demand characteristics: efficient-collaborative, transitional-mixed, and low-demand peripheral areas. The predominance of the transitional-mixed type indicates that most areas are currently in an unstable state of supply–demand adjustment. A key systemic mechanism identified in this study is the significant “collaborative reinforcement effect” between facility utilization rates and network centrality. Building on these insights, we propose a hierarchical optimization strategy consisting of “overall network optimization—local cluster coordination—individual facility enhancement.” This ultimately forms a comprehensive decision-support framework for “assessment—diagnosis—optimization,” providing scientific evidence and new solutions for the precise planning and efficient operation of urban charging infrastructure.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Charging Infrastructure and Grid Integration)
►▼
Show Figures
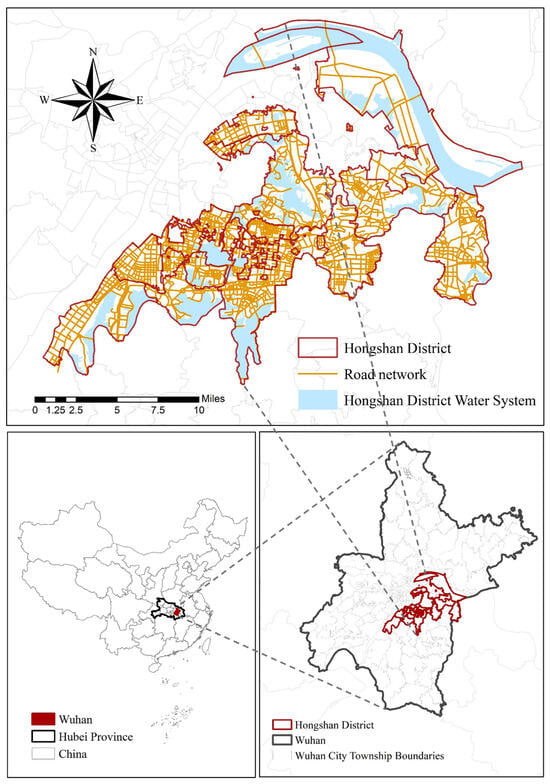
Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- WEVJ Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
WEVJ
Vehicle System Dynamics and Intelligent Control for Electric Vehicles
Guest Editors: Leilei Zhao, Liguo Zang, Yuewei Yu, Jian WangDeadline: 31 December 2025
Special Issue in
WEVJ
New Trends in Electrical Drives for EV Applications
Guest Editors: Ayman Abdel-Khalik, Mohamed AbdelrahemDeadline: 31 December 2025
Special Issue in
WEVJ
Vehicle-to-Grid in Coordinated Power and Transportation Systems: Challenges and Development
Guest Editors: Qinran Hu, Tao QianDeadline: 31 December 2025
Special Issue in
WEVJ
Recent Advances in Intelligent Vehicle
Guest Editors: Biao Yu, Jiajia Chen, Xiang DongDeadline: 31 December 2025










