-
 Seed Germination Ecology and Dormancy Release in Some Native and Underutilized Plant Species with Agronomic Pote
Seed Germination Ecology and Dormancy Release in Some Native and Underutilized Plant Species with Agronomic Pote -
 Manure Production Projections for Latvia: Challenges and Potential for Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Manure Production Projections for Latvia: Challenges and Potential for Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions -
 The European Charter for Sustainable Tourism (ECST) as a Tool for Development in Rural Areas: The Case of Vesuvius National Park (Italy)
The European Charter for Sustainable Tourism (ECST) as a Tool for Development in Rural Areas: The Case of Vesuvius National Park (Italy) -
 Nondestructive Quality Detection of Characteristic Fruits Based on Vis/NIR Spectroscopy: Principles, Systems, and Applications
Nondestructive Quality Detection of Characteristic Fruits Based on Vis/NIR Spectroscopy: Principles, Systems, and Applications
Journal Description
Agriculture
Agriculture
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal published semimonthly online.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubAg, AGRIS, RePEc, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q1 (Agronomy) / CiteScore - Q1 (Plant Science)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 18.8 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 1.9 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Companion journals for Agriculture include: Poultry, Grasses, Crops and AIPA.
Impact Factor:
3.6 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
3.8 (2024)
Latest Articles
Comparative Effectiveness of Kaolinite, Basal Powder, and Zeolite in Mitigating Heat Stress and Increasing Yield of Almond Trees (Prunus dulcis) Under Mediterranean Climate
Agriculture 2026, 16(2), 220; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture16020220 - 14 Jan 2026
Abstract
Heat and high-irradiance stress increasingly threaten almond production in Mediterranean environments, where rising temperatures and prolonged summer droughts impair photosynthetic performance and yield. This study evaluated the effectiveness of three mineral-based shielding materials: kaolin, basalt powder, and zeolite. We hypothesized that the foliar
[...] Read more.
Heat and high-irradiance stress increasingly threaten almond production in Mediterranean environments, where rising temperatures and prolonged summer droughts impair photosynthetic performance and yield. This study evaluated the effectiveness of three mineral-based shielding materials: kaolin, basalt powder, and zeolite. We hypothesized that the foliar application of reflective mineral materials would reduce leaf temperature, enhance photosynthetic efficiency, and improve yield without altering nut nutraceutical quality. A two-year field experiment (2024–2025) was conducted using a randomized block design with four materials (untreated control, kaolin, basalt powder, and zeolite). Physiological traits (gas exchange, chlorophyll fluorescence, leaf temperature, and SPAD index), morpho-biometric and biochemical parameters, and yield components were assessed. Kaolin and basalt powder significantly lowered leaf temperature (−1.6 to −1.8 °C), increased stomatal conductance and net photosynthesis, and improved photochemical efficiency (Fv′/Fm′) and electron transport rates. These treatments also enhanced drupe weight, kernel dry matter, and productive yield (up to +32% compared with the control). Zeolite produced positive but less prominent effects. No significant differences were detected in fatty acid profile, total polyphenols, or antioxidant capacity, indicating that the materials did not affect almond nutraceutical quality. Principal component analysis confirmed the strong association between kaolin and basalt powder and improved eco-physiological performance. Overall, mineral shielding materials, particularly kaolin and basalt powder, represent a promising, sustainable strategy for enhancing almond orchard resilience under Mediterranean climate change scenarios.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Crop Production)
Open AccessArticle
Modeling Moisture Content and Analyzing Water Infiltration in Coconut Coir Substrate Using RGB Image Recognition and Machine Learning
by
Xiaokun Feng, Ping Zou, Qingtao Wang, Haitao Wang, Xiangnan Li and Jiandong Wang
Agriculture 2026, 16(2), 219; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture16020219 - 14 Jan 2026
Abstract
Coconut coir, a key substrate in soilless cultivation, presents challenges for accurate moisture detection because of its complex internal structure, which limits the understanding of water infiltration and redistribution. This study employed RGB image recognition techniques combined with machine learning algorithms to systematically
[...] Read more.
Coconut coir, a key substrate in soilless cultivation, presents challenges for accurate moisture detection because of its complex internal structure, which limits the understanding of water infiltration and redistribution. This study employed RGB image recognition techniques combined with machine learning algorithms to systematically investigate the effects of initial moisture content (10%, 20%, and 30%), coarse-to-fine coir volume ratio (1:0, 1:1, and 0:1), and emitter discharge rate (1.0, 1.5, and 2.0 L h−1) on wetting front morphology, water transport dynamics, and moisture variation within coir substrates. Morphological features of the wetting front were extracted from images and incorporated into three machine learning models—Support Vector Regression (SVR), Random Forest (RF), and Polynomial Regression—to construct a predictive framework for coir moisture estimation. The results showed that the SVR model achieved the best predictive performance in coarse coir substrates (R2 = 0.89, RMSE = 3.37%), whereas Polynomial Regression performed best in mixed substrates (R2 = 0.861, RMSE = 4.34%). All models exhibited lower accuracy in fine coir, particularly at high moisture levels. Under the same irrigation volume, increasing the initial moisture content enhanced both the water transport rate and the wetting front extent, with the aspect ratio (AR) decreasing from approximately 2.0 to 1.3, indicating a morphological transition of the wetting front from a “thumb-shaped” to a “hemispherical” pattern. Coarse particles facilitated vertical infiltration, while fine particles exhibited stronger water retention. By integrating RGB image recognition with machine learning approaches, this study achieved reliable prediction of coir moisture content and proposed an optimal management strategy using mixed substrates with an initial moisture content of 20–30% to balance infiltration efficiency and water-holding capacity while minimizing percolation risk. These findings provide a robust technical pathway for precise water management in coir-based cultivation systems.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Agricultural Soils)
Open AccessArticle
Farmer-Friendly Approach for Table Grape Bunch Detection Using the Roboflow Platform
by
Francesco Vicino, Giovanni Popeo, Francesco Santoro, Simone Pascuzzi and Francesco Paciolla
Agriculture 2026, 16(2), 218; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture16020218 - 14 Jan 2026
Abstract
Accurate fruit detection and counting are fundamental requirements in the development of reliable computer vision applications for yield estimation. This work was conceived to provide farmers with a farmer-friendly approach for automatic grape bunch detection. This study exploits the free demo version of
[...] Read more.
Accurate fruit detection and counting are fundamental requirements in the development of reliable computer vision applications for yield estimation. This work was conceived to provide farmers with a farmer-friendly approach for automatic grape bunch detection. This study exploits the free demo version of the Roboflow 3.0 platform to train five state-of-the-art computer vision models with RGB images of white and red grape bunches, acquired with a smartphone in the field, and compares their performance. The results were evaluated both quantitatively, in terms of precision, recall, and AP@50 calculated on the validation set, and qualitatively on the test set. The models that achieved the best performances, also in the presence of overlapping clusters, were Roboflow 3.0 Object Detection and YOLOv11, reaching precisions of 86.6% and 88%, respectively, for the detection of white bunches, and of 85.7% and 89.9% for red bunches. This study highlights the possibility of developing highly accurate computer vision models for table grape bunch detection using the Roboflow platform, offering an accessible and user-friendly tool for non-expert users, including farmers.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Application of Smart Technologies in Orchard Management)
Open AccessArticle
The Relationship Between Economic Performance, Sustainability, and Agricultural Productivity: Empirical Evidence from the European Union
by
Anca Antoaneta Vărzaru
Agriculture 2026, 16(2), 217; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture16020217 - 14 Jan 2026
Abstract
Agriculture in the European Union operates in a context where productivity, output growth, and sustainability increasingly shape policy priorities and economic choices. This research explores how these elements have interacted and influenced one another from 2000 to 2024, focusing on the dynamic relationships
[...] Read more.
Agriculture in the European Union operates in a context where productivity, output growth, and sustainability increasingly shape policy priorities and economic choices. This research explores how these elements have interacted and influenced one another from 2000 to 2024, focusing on the dynamic relationships among economic performance, sustainability, labor productivity, and agricultural output across EU member states. The methodology is straightforward: it starts with factor analysis to uncover the fundamental structures linking key variables and to clarify connections that are often hidden in aggregated data. Building on these insights, a General Linear Model provides a clearer picture of how economic performance and sustainability affect changes in labor productivity and agricultural output, revealing the mechanisms through which these factors promote or hinder agricultural progress. To enhance understanding, cluster analysis groups EU countries according to shared patterns, enabling interpretation of national differences within broader structural trends rather than as isolated cases. The findings show that countries with stronger economies and more consistent sustainability initiatives tend to achieve higher productivity and output, while the clusters identified demonstrate significant differences that explain the diverse development paths within the Union.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainable Farming Intensification: Balancing Productivity and Resilience)
Open AccessArticle
Astragalus Straw Inhibited Methane Emissions by Regulating Ruminal Fermentation Parameters and Microbial Community Dynamics in Lanzhou Fat-Tailed Sheep
by
Juanshan Zheng, Wangmei Feng, Chi Ma, Xiang Pan, Tong Wang, Honghe Li, Junsong Zhang, Xiaofang Feng, Na Jiao, Siqiu Yang and Penghui Guo
Agriculture 2026, 16(2), 216; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture16020216 - 14 Jan 2026
Abstract
Methane (CH4), a significant greenhouse gas, ranks second only to carbon dioxide in its contribution to global warming. The application of Chinese herbs as a strategy to mitigate CH4 emissions in ruminants has shown promise. However, there is limited information
[...] Read more.
Methane (CH4), a significant greenhouse gas, ranks second only to carbon dioxide in its contribution to global warming. The application of Chinese herbs as a strategy to mitigate CH4 emissions in ruminants has shown promise. However, there is limited information regarding the efficacy of Chinese herb straw in reducing CH4 emissions in ruminants. This research aimed to investigate the beneficial effects of varying levels of Astragalus straw supplementation on methane emissions and to elucidate the underlying molecular mechanisms. The study examined the effects of different supplementation levels (0%, 5%, 10%, 15%, 20%) on in vitro rumen fermentation, CH4 emissions, and ruminal microbial community in Lanzhou fat-tailed sheep using an in vitro fermentation method. The findings indicated that IVDMD, gas production, and CH4 production significantly decreased with increasing levels of Astragalus straw supplementation (p < 0.05). Simultaneously, the lowest levels of AA, AA/PA, and NH3-N, along with the highest concentrations of PA, BA, and MCP, were observed in the 20% supplementation group after 48 h of fermentation. In addition, supplementation with Astragalus straw resulted in an increased abundance of Bacteroidota, Spirochaetota, and Actinobacteriota, while decreasing the abundance of Firmicutes, Fibrobacterota, and Verrucomicrobiota. At the genus level, there was an observed increase in the abundance of Prevotella and Streptococcus, accompanied by a decrease in Rikenellaceae_RC9_gut_group. In conclusion, the supplementation of Astragalus straw has the potential to reduce CH4 production by altering ruminal fermentation patterns, fermentation parameters, and microbial dynamics.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Alternative Approaches to Feed Selection and Animal Performance in Ruminants)
►▼
Show Figures
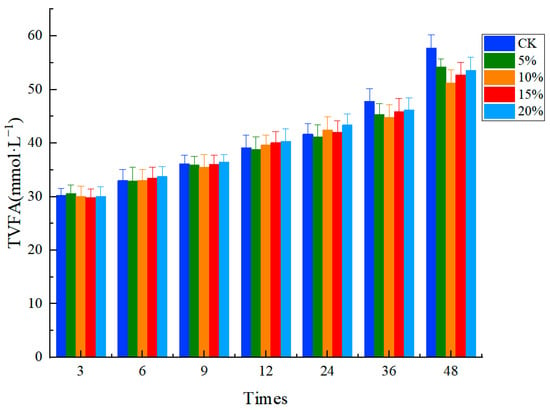
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Intelligent Evaluation of Rice Resistance to White-Backed Planthopper (Sogatella furcifera) Based on 3D Point Clouds and Deep Learning
by
Yuxi Zhao, Huilai Zhang, Wei Zeng, Litu Liu, Qing Li, Zhiyong Li and Chunxian Jiang
Agriculture 2026, 16(2), 215; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture16020215 - 14 Jan 2026
Abstract
Accurate assessment of rice resistance to Sogatella furcifera (Horváth) is essential for breeding insect-resistant cultivars. Traditional assessment methods rely on manual scoring of damage severity, which is subjective and inefficient. To overcome these limitations, this study proposes an automated resistance evaluation approach based
[...] Read more.
Accurate assessment of rice resistance to Sogatella furcifera (Horváth) is essential for breeding insect-resistant cultivars. Traditional assessment methods rely on manual scoring of damage severity, which is subjective and inefficient. To overcome these limitations, this study proposes an automated resistance evaluation approach based on multi-view 3D reconstruction and deep learning–based point cloud segmentation. Multi-view videos of rice materials with different resistance levels were collected over time and processed using Structure from Motion (SfM) and Multi-View Stereo (MVS) to reconstruct high-quality 3D point clouds. A well-annotated “3D Rice WBPH Damage” dataset comprising 174 samples (15 rice materials, three replicates each, 45 pots) was established, where each sample corresponds to a reconstructed 3D point cloud from a video sequence. A comparative study of various point cloud semantic segmentation models, including PointNet, PointNet++, ShellNet, and PointCNN, revealed that the PointNet++ (MSG) model, which employs a Multi-Scale Grouping strategy, demonstrated the best performance in segmenting complex damage symptoms. To further accurately quantify the severity of damage, an adaptive point cloud dimensionality reduction method was proposed, which effectively mitigates the interference of leaf shrinkage on damage assessment. Experimental results demonstrated a strong correlation (R2 = 0.95) between automated and manual evaluations, achieving accuracies of 86.67% and 93.33% at the sample and material levels, respectively. This work provides an objective, efficient, and scalable solution for evaluating rice resistance to S. furcifera, offering promising applications in crop resistance breeding.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Crop Protection, Diseases, Pests and Weeds)
Open AccessArticle
Mapping Women’s Role in Agriculture 4.0: A Bibliometric Analysis and Conceptual Framework
by
Roberta Guglielmetti Mugion, Veronica Ungaro, Laura Di Pietro, Atifa Amin and Federica Bisceglia
Agriculture 2026, 16(2), 214; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture16020214 - 14 Jan 2026
Abstract
The agricultural sector is predominantly male, with approximately 30% of farms in the EU operated by women. The European Union Rural Pact, the Agri-Food Pact for Skills, and the Common Agricultural Policy have catalysed an increase in agricultural 4.0 research, with the role
[...] Read more.
The agricultural sector is predominantly male, with approximately 30% of farms in the EU operated by women. The European Union Rural Pact, the Agri-Food Pact for Skills, and the Common Agricultural Policy have catalysed an increase in agricultural 4.0 research, with the role of women emerging as a subfield of sustainable agriculture. The primary objective of this paper is to evaluate the current literature on women’s roles in smart agriculture, examining the advantages of their participation as a digitally competent workforce that could catalyse improvements in productivity and resilience in rural areas and promote women’s empowerment. A bibliometric study was conducted utilising the Scopus database to fulfil the research objective. This led to the incorporation of 253 articles into the sample. The records were examined using performance analysis and bibliographic coupling (science mapping), facilitated by Biblioshiny 5.0 and VOSviewer 1.6.20 software. The primary findings elucidate essential concepts, predominant study themes, and the temporal progression of the research domain. The identification of numerous women’s role and socio-economic constraints affecting women, which are overlooked in the creation and implementations of technology advancements . Additionally, a research agenda was developed, alongside practical implications for managers and policymakers, to aid the formulation of inclusive agriculture 4.0 projects.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Agricultural Economics, Policies and Rural Management)
Open AccessArticle
Glucose and Lignin Differentially Drive Phosphorus Fractions to Vary in Mollisols (WRB) and Fluvo-Aquic Soil (Chinese Soil Taxonomy) via Microbial Community Shifts
by
Xue Li, Fuyue Dai, Shuo Chen, Hongyuan Wang, Shuxia Wu, Bingqian Fan and Hongbin Liu
Agriculture 2026, 16(2), 213; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture16020213 - 14 Jan 2026
Abstract
Carbon (C) is crucial for nutrient cycling and the assembly of microbial populations in the soil. However, it is still unclear how the C-source utilization characteristics of microbes in distinct types of soils respond to changes in soil phosphorus (P) activity. This study
[...] Read more.
Carbon (C) is crucial for nutrient cycling and the assembly of microbial populations in the soil. However, it is still unclear how the C-source utilization characteristics of microbes in distinct types of soils respond to changes in soil phosphorus (P) activity. This study investigated how the addition of different C sources with different decomposition rates (glucose, hemicellulose, and lignin) affects P transformation in two distinct agricultural soils (i.e., Mollisols and Fluvo-aquic soil). Results revealed that the short-term glucose addition to soil induced rapid acidification and microbial biomass accumulation, thereby significantly increasing labile P (NaHCO3-Pi, NaOH-Po) content in Fluvo-aquic soil. Lignin amendment promoted gradual HCl-P release in Mollisols, reflecting differential microbial utilization strategies. Glucose stimulated phosphatase activity (2.5–3.0× control) and phoD gene abundance (4.8×) in Fluvo-aquic soil in the early stage, favoring the growth of Pseudomonas and Burkholderia, whereas lignin sustained the mineralization of fungal-associated P in Mollisols (1.8–2.3× phosphatase activity) by enhancing the abundance of Streptomyces and Bradyrhizobium. Soil type dictated P mobilization efficiency. The Fluvo-aquic soil exhibited rapid but transient P release via bacterial dominance, while Mollisols retained slower yet persistent P availability through specialized microbial consortia. Notably, glucose enhanced organic P mineralization by stimulating C decomposition by microbes, particularly in C-rich Mollisols. Lignin increased P availability in Mollisols via Fe/Al-P desorption. However, in Fluvo-aquic soil, lignin reduced the availability of P through microbial immobilization. These findings highlight that C source degradability and soil properties interactively govern microbial-mediated P cycling in soil. Therefore, organic amendments in contrasting agroecosystems need to be optimized.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Phosphorus Utilization and Management in Agricultural Soil Systems)
Open AccessArticle
Utilisation of Woody Waste from Wine Production for Energy Purposes Depending on the Place of Cultivation
by
Magdalena Kapłan, Grzegorz Maj, Kamila E. Klimek, Richard Danko, Mojmir Baroň and Radek Sotolář
Agriculture 2026, 16(2), 212; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture16020212 - 14 Jan 2026
Abstract
Orchard crops generate substantial quantities of diverse biomass each year, with grapevines being among the most economically significant species worldwide. Considering the scale of this biomass, there is a growing need to explore rational strategies for its utilisation, for example, for energy production
[...] Read more.
Orchard crops generate substantial quantities of diverse biomass each year, with grapevines being among the most economically significant species worldwide. Considering the scale of this biomass, there is a growing need to explore rational strategies for its utilisation, for example, for energy production or other value-added applications. Such approaches may contribute to improving resource efficiency and reducing the environmental burden associated with agricultural waste. The aim of this study was to examine the energy potential of woody post-production waste from wine processing, with particular emphasis on grape stems of four cultivars—Chardonnay, Riesling, Merlot, and Zweigelt—grown in two contrasting climatic regions: south-eastern Poland and Moravia (Czech Republic). The results demonstrated that both the grape variety and cultivation site significantly influenced the majority of bunch biometric traits, including bunch and berry weight, berry number, and stem dimensions. A moderately warm climate promoted the development of larger and heavier bunches as well as more robust stems across all examined cultivars. Energy analyses indicated that Zweigelt stems produced under moderately warm conditions and Chardonnay stems from a temperate climate exhibited the most favourable combustion properties. Nonetheless, certain constraints were identified, such as increased ash (12.20%) and moisture content (11.51%) in Chardonnay grown in warmer conditions, and elevated CO and CO2 emissions observed for Zweigelt (1333.26 kg·mg−1). Overall, the findings confirm that grape stems constitute a promising local source of bioenergy, with their energy performance determined predominantly by varietal characteristics and climatic factors. Their utilisation aligns with circular-economy principles and may help reduce the environmental impacts associated with traditional viticultural waste management.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Agricultural Technology)
►▼
Show Figures
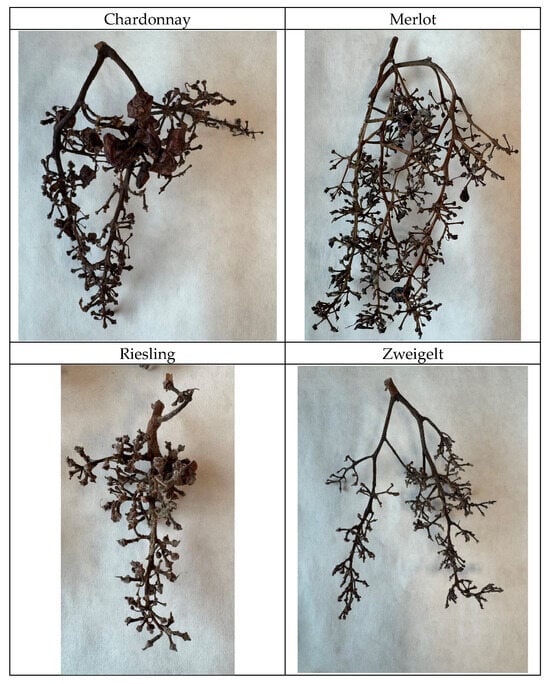

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Characterization of PpZCP11 as a Key Regulator of Primordium Formation in Pleurotus pulmonarius
by
Chunxia Wang, Zhaopeng Ge, Wenchao Li, Chao Li, Liudan Wang, Mengfei Chen, Yining Li and Suyue Zheng
Agriculture 2026, 16(2), 211; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture16020211 - 14 Jan 2026
Abstract
Pleurotus pulmonarius is a high-value, commercially cultivated edible fungus whose primordium formation is a critical phase for yield and commercial value. To better understand the developmental processes of P. pulmonarius, samples from four key developmental stages were collected and subjected to transcriptome
[...] Read more.
Pleurotus pulmonarius is a high-value, commercially cultivated edible fungus whose primordium formation is a critical phase for yield and commercial value. To better understand the developmental processes of P. pulmonarius, samples from four key developmental stages were collected and subjected to transcriptome analysis. A total of 6530 DEGs were identified, including 50 transcription factors from 10 families. Among these, the PpZCP11 gene, encoding a Zn2Cys6 transcription factor, was found to be specifically highly expressed during the primordium stage. We cloned PpZCP11 gene and confirmed its nuclear localization. The OE-PpZCP11 strains produced abundant primordia, while primordium formation in the RNAi-PpZCP11 strains was severely suppressed. Moreover, RNA-seq and yeast-one-hybrid analysis suggested that PpZCP11 may regulate cell wall synthesis. These findings indicate that the PpZCP11 transcription factor acts as a positive regulator of primordium formation by regulating the expression of cell wall-related genes. This study provides a theoretical reference for elucidating the molecular mechanism underlying primordium formation in P. pulmonarius.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Edible and Medicinal Mushrooms: Molecular Biology, Cultivation, Active Compounds, Preservation and Processing)
►▼
Show Figures
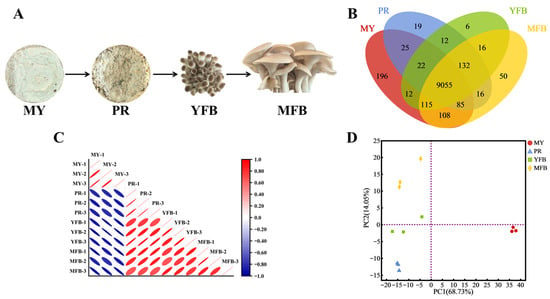
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Effect of Straw Management and Nitrogen Fertilisation on Soil Properties During 50 Years of Continuous Spring Barley Cropping
by
Magdaléna Koubová, Jan Křen, Markéta Mayerová, Vladimír Smutný, Tamara Dryšlová and Mikuláš Madaras
Agriculture 2026, 16(2), 210; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture16020210 - 13 Jan 2026
Abstract
This study is based on a long-term field trial with spring barley monoculture that was established in 1970 on Gleyic Fluvisol in the Žabčice, Czech Republic. The aim was to clarify the long-term impact of straw management and mineral nitrogen (N) application on
[...] Read more.
This study is based on a long-term field trial with spring barley monoculture that was established in 1970 on Gleyic Fluvisol in the Žabčice, Czech Republic. The aim was to clarify the long-term impact of straw management and mineral nitrogen (N) application on grain yields and soil aggregate stability (SAS), and to determine the mineralogical and geochemical properties crucial for soil aggregate stability changes. Variants of the experiment included a combination of incorporated and harvested straw with doses of 0, 30, 60, and 90 kg N ha−1 in the form of ammonium sulphate (NH4)2SO4. The incorporated straw variants had a higher average grain yield of 0.51 t ha−1. The SAS values were in the range 54–64% and increased in all variants with N application compared to the 0N control. Ammonium sulphate fertilisation caused soil acidification, which was not reduced even by the incorporation of straw. SAS increased with decreasing pH value, although cation exchange capacity and exchangeable Ca2+ decreased, and the soil organic carbon content was similar in all variants. The relatively high content of Fe- and Al-(oxo)hydroxides extracted with ammonium oxalate (Feox and Alox) in all samples caused an increase in SAS due to decreasing pH in the N fertilised variants compared to the control. SAS should be considered in relation to other soil properties when evaluating soil quality and fertility.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Effects of Crop Rotation and Continuous Cropping on Soil Health and Crop Yields)
Open AccessArticle
Cassava Response to Weather Variability in Eastern Africa
by
Zsuzsanna Bacsi and Dawit Dandano Jarso
Agriculture 2026, 16(2), 209; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture16020209 - 13 Jan 2026
Abstract
Cassava is one of the most important crops in global food security. It is the second most important staple crop in Africa. Its significance is enhanced by the fact that it very well tolerates droughts, and therefore it may be a prospective response
[...] Read more.
Cassava is one of the most important crops in global food security. It is the second most important staple crop in Africa. Its significance is enhanced by the fact that it very well tolerates droughts, and therefore it may be a prospective response to climate change in hot and dry areas. The potentials of cassava are under-utilized in Eastern Africa, and there is a lack of research studies regarding climate impacts on cassava yields in this region. The present research focuses on cassava production in Eastern Africa, analyzing the relationship of cassava yields, harvested areas, temperature, and precipitation from 1961 to 2023. The statistical analysis applies panel regression for the 63 years of time series, for the 15 most important cassava producing countries of Eastern Africa. Findings show that while the impacts of rainfall are insignificant on yields, the effects of temperature are significantly positive, indicating yield and area increases with warming climate. An expansion of the cassava growing area and the expanding rural population contributed to decreasing yields, probably because of the expansion of smallholder subsistence farming, suffering from to limitations in other farming resources. Therefore, even if climate change may benefit cassava production, other factors create severe limitations on improving yields. However, the positive response of the crop to rising temperatures is a clear sign that it is a useful choice for food security under climate change and would deserve more support from agricultural policymakers in Eastern Africa.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Ecosystem, Environment and Climate Change in Agriculture)
►▼
Show Figures
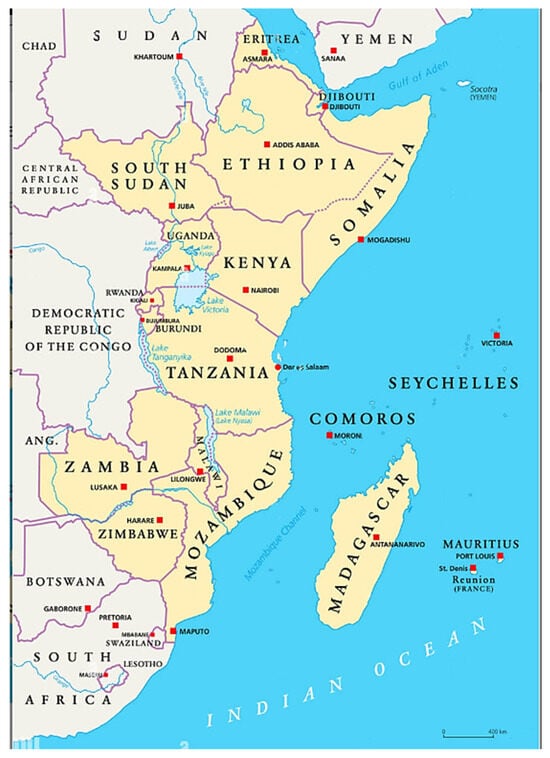
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Research on Confined Compression and Breakage Behaviour as Well as Stress Evolution of Rice Under Framework of Cohesion Zone Model
by
Xianle Li, Mengyuan Wang, Yanlong Han, Anqi Li, Xinlei Wang, Haonan Gao and Tianyi Wang
Agriculture 2026, 16(2), 208; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture16020208 - 13 Jan 2026
Abstract
Agricultural materials frequently undergo fragmentation due to high-stress conditions during processing, storage, and transportation. Throughout these processes, the spatial arrangement and morphology of particles continuously evolve, rendering the breakage behaviour of particle groups particularly complex. Thus, an in-depth understanding of the fracture processes
[...] Read more.
Agricultural materials frequently undergo fragmentation due to high-stress conditions during processing, storage, and transportation. Throughout these processes, the spatial arrangement and morphology of particles continuously evolve, rendering the breakage behaviour of particle groups particularly complex. Thus, an in-depth understanding of the fracture processes and breakage mechanisms within particle beds holds significant research value. This study systematically investigates the breakage behaviour of rice particle groups under confined compression through an integrated methodology combining experimental testing, X-ray CT imaging, and finite element modelling (FEM) based on the cohesive zone model (CZM). Results demonstrate that, at the granular assembly scale, external loads are transmitted through force chains and progressively attenuate. As compression proceeds, stress disseminates toward peripheral particle regions. At the individual particle level, particle breakage results from the intricate interaction between coordination number (CN) and localized contact stress, with tensile stress playing a predominant role in the fracture process. An increase in coordination number promotes a more uniform stress distribution and inhibits breakage, thereby exhibiting a “protective effect”. These findings provide valuable insights for the design and optimization of grain processing equipment, contributing to a deeper comprehension of particle breakage characteristics.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Innovations in Grain Storage, Handling, and Processing)
►▼
Show Figures
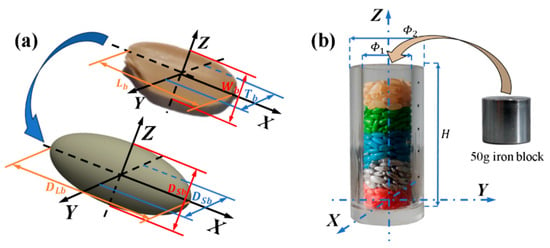
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Multi-Source Monitoring of High-Temperature Heat Damage During Summer Maize Flowering Period Based on Machine Learning
by
Xiaofei Wang, Hongwei Tian, Lin Cheng, Fangmin Zhang and Lizhu Xing
Agriculture 2026, 16(2), 207; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture16020207 - 13 Jan 2026
Abstract
With the intensification of global climate change, high temperatures have emerged as a major abiotic stressor adversely affecting summer maize yields in North China. This study presents a high-resolution monitoring framework for Henan Province. First, an hourly, high-resolution (0.02° × 0.02°) near-surface air
[...] Read more.
With the intensification of global climate change, high temperatures have emerged as a major abiotic stressor adversely affecting summer maize yields in North China. This study presents a high-resolution monitoring framework for Henan Province. First, an hourly, high-resolution (0.02° × 0.02°) near-surface air temperature dataset was generated by fusing Himawari-8 satellite observations, ERA5 reanalysis data, and ground-based measurements through a machine learning approach. Among the tested algorithms (support vector regression, random forest, and XGBoost), XGBoost achieved the best performance (R2 = 0.933 and RMSE = 0.841 °C). Second, a High-Temperature Damage Index (HTDI) was constructed using hourly temperature thresholds of 32 °C and 35 °C, respectively. The index exhibited a statistically significant but modest negative correlation with ear grain number (R2 = 0.054 and p = 0.0007). Spatial assessment revealed intensified heat damage in 2024 (average HTDI = 0.51; over 67% of the area experienced moderate or worse damage) compared to 2023 (average HTDI = 0.22), with severe damage concentrated in south–central and east–central Henan. This approach surpasses the limitations of conventional daily scale assessments by enabling refined, hourly monitoring of high-temperature heat stress. It not only advances the deep integration of remote sensing and machine learning in agricultural meteorology but also provides technical support for addressing food security challenges under climate change.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Advances in Smart Agriculture with Remote Sensing as the Core and Its Applications in Crops Field)
Open AccessArticle
Whole-Process Agricultural Production Chain Management and Land Productivity: Evidence from Rural China
by
Qilin Liu, Guangcai Xu, Jing Gong and Junhong Chen
Agriculture 2026, 16(2), 206; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture16020206 - 13 Jan 2026
Abstract
As agricultural labor shifted toward non-farm sectors and the farming population aged, innovative production arrangements became essential to sustain land productivity. While partial agricultural production chain management (PAPM) was widespread, the productivity impact of whole-process agricultural production chain management (WAPM)—a comprehensive model integrating
[...] Read more.
As agricultural labor shifted toward non-farm sectors and the farming population aged, innovative production arrangements became essential to sustain land productivity. While partial agricultural production chain management (PAPM) was widespread, the productivity impact of whole-process agricultural production chain management (WAPM)—a comprehensive model integrating all production stages—remained empirically underexplored. Using nationally representative panel data from the China Labor-force Dynamics Survey (CLDS, 2014–2018) for grain-producing households, this study estimates the differential impacts of WAPM and PAPM with a two-way fixed-effects (TWFE) model, supplemented by propensity score matching (PSM) as a robustness check. The results show that WAPM significantly enhanced land productivity. Notably, the effect size of WAPM (coefficient: 0.486) is substantially larger than that of PAPM (coefficient: 0.214), indicating that systematic integration of service chains offers superior efficiency gains over fragmented outsourcing. Mechanism analysis suggests that WAPM improves productivity primarily by alleviating labor constraints and mitigating the disadvantages of small-scale farming. Furthermore, heterogeneity analysis demonstrated that these benefits are amplified in major grain-producing regions and hilly areas. These findings support policies that facilitate a transition from single-link outsourcing toward whole-process integrated service provision.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Agricultural Economics, Policies and Rural Management)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Calibration of Discrete Element Method Parameters for Cabbage Stubble–Soil Interface Using In Situ Pullout Force
by
Wentao Zhang, Zhi Li, Qinzhou Cao, Wen Li and Ping Jiang
Agriculture 2026, 16(2), 205; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture16020205 - 13 Jan 2026
Abstract
Cabbage stubble left in fields after harvest forms a mechanically complex stubble–soil composite that hinders subsequent tillage and crop establishment. Although the Discrete Element Method (DEM) is widely used to model soil-root systems, calibrated contact parameters for taproot-dominated vegetables like cabbage remain unreported.
[...] Read more.
Cabbage stubble left in fields after harvest forms a mechanically complex stubble–soil composite that hinders subsequent tillage and crop establishment. Although the Discrete Element Method (DEM) is widely used to model soil-root systems, calibrated contact parameters for taproot-dominated vegetables like cabbage remain unreported. This study addresses this gap by calibrating a novel DEM framework that couples the JKR model and the Bonding V2 model to represent adhesion and mechanical interlocking at the stubble–soil interface. Soil intrinsic properties and contact parameters were determined through triaxial tests and angle-of-repose experiments. Physical pullout tests on ‘Zhonggan 21’ cabbage stubble yielded a mean peak force of 165.5 N, used as the calibration target. A three-stage strategy—factor screening, steepest ascent, and Box–Behnken design (BBD)—identified optimal interfacial parameters: shear stiffness per unit area = 4.40 × 108 N·m−3, normal strength = 6.26 × 104 Pa, and shear strength = 6.38 × 104 Pa. Simulation predicted a peak pullout force of 162.0 N, showing only a 2.1% deviation from experiments and accurately replicating the force-time trend. This work establishes the first validated DEM framework for cabbage stubble–soil interaction, enabling reliable virtual prototyping of residue management implements and supporting low-resistance, energy-efficient tillage tool development for vegetable production.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Intelligent Agriculture: Perception Technologies and Agricultural Equipment for Crop Production Processes)
Open AccessEditorial
Economic Development of Rural Areas in Border Territories: Threats and Opportunities
by
Francisco Javier Castellano-Álvarez, Paulo Ferreira, Luís Loures and Rafael Robina-Ramírez
Agriculture 2026, 16(2), 204; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture16020204 - 13 Jan 2026
Abstract
Given the focus of this publication, most of the works included are case studies that address different issues related to the development of border areas: energy transition, food sufficiency, tourism development, social capital, the balance between innovation and tradition in primary production systems,
[...] Read more.
Given the focus of this publication, most of the works included are case studies that address different issues related to the development of border areas: energy transition, food sufficiency, tourism development, social capital, the balance between innovation and tradition in primary production systems, digital economy, etc. [...]
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Economic Development of Rural Areas in Border Territories: Threats and Opportunities)
Open AccessArticle
Ecosystem Service-Based Eco-Efficiency of Cultivated Land Use in Plateau Lake Regions: Spatial Dynamics and Nonlinear Drivers
by
Ruijia Wang, Qiuchen Hong, Zonghan Zhang, Shuyu Zhou, Jinmin Hao and Dong Ai
Agriculture 2026, 16(2), 203; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture16020203 - 13 Jan 2026
Abstract
Plateau lake regions face escalating conflicts between food production and ecosystem conservation under rapid urbanization and strict ecological regulation. However, existing evaluations often overlook the positive ecosystem services generated by cultivated land and fail to capture the nonlinear mechanisms shaping eco-efficiency of cultivated
[...] Read more.
Plateau lake regions face escalating conflicts between food production and ecosystem conservation under rapid urbanization and strict ecological regulation. However, existing evaluations often overlook the positive ecosystem services generated by cultivated land and fail to capture the nonlinear mechanisms shaping eco-efficiency of cultivated land use (ECLU). This study develops an ecosystem service-based framework to assess the ECLU of Kunming, a typical plateau lake-basin city in southwest China, from 2005 to 2022. Ecosystem service value (ESV) is incorporated as a desirable output within a super-efficiency SBM model, and an XGBoost–SHAP approach is applied to identify the intensity, nonlinear thresholds and interaction mechanisms. Results show an average ECLU of 1.12 with a fluctuating downward trend and widening spatial disparities. High-efficiency zones cluster in central–southern regions, while urbanizing cores experience ecological function degradation despite productivity gains. Cultivated land fragmentation is the dominant barrier, with a critical threshold of 31.90 mu, and fertilizer intensity turns detrimental beyond 0.19 t/ha. Urbanization exhibits an inverted-U pattern—initially suppressive (<35%), promotional (35–55%), and suppressive again (>55%)—with the promotion phase weakened by approximately 67% under severe fragmentation. Globally, threshold-based zoning and fragmentation mitigation must precede fertilizer optimization to ensure synergistic benefits.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Ecosystem, Environment and Climate Change in Agriculture)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Electron Transfer-Mediated Heavy Metal(loid) Bioavailability, Rice Accumulation, and Mitigation in Paddy Ecosystems: A Critical Review
by
Zheng-Xian Cao, Zhuo-Qi Tian, Hui Guan, Yu-Wei Lv, Sheng-Nan Zhang, Tao Song, Guang-Yu Wu, Fu-Yuan Zhu and Hui Huang
Agriculture 2026, 16(2), 202; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture16020202 - 13 Jan 2026
Abstract
Electron transfer (ET) is a foundational biogeochemical process in paddy soils, distinctively molded by alternating anaerobic-aerobic conditions from flooding-drainage cycles. Despite extensive research on heavy metal(loid) (denoted as “HM”, e.g., As, Cd, Cr, Hg) dynamics in paddies, ET has not been systematically synthesized
[...] Read more.
Electron transfer (ET) is a foundational biogeochemical process in paddy soils, distinctively molded by alternating anaerobic-aerobic conditions from flooding-drainage cycles. Despite extensive research on heavy metal(loid) (denoted as “HM”, e.g., As, Cd, Cr, Hg) dynamics in paddies, ET has not been systematically synthesized as a unifying regulatory mechanism, and the trade-offs of ET-based mitigation strategies remain unclear. These critical gaps have drastically controlled HMs’ mobility, which further modulates bioavailability and subsequent accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L., a staple sustaining half the global population), posing substantial food safety risks. Alongside progress in electroactive microorganism (EAM) research, extracellular electron transfer (EET) mechanism delineation, and soil electrochemical monitoring, ET’s role in orchestrating paddy soil HM dynamics has garnered unparalleled attention. This review explicitly focuses on the linkage between ET processes and HM biogeochemistry in paddy ecosystems: (1) elucidates core ET mechanisms in paddy soils (microbial EET, Fe/Mn/S redox cycling, organic matter-mediated electron shuttling, rice root-associated electron exchange) and their acclimation to flooded conditions; (2) systematically unravels how ET drives HM valence transformation (e.g., As(V) to As(III), Cr(VI) to Cr(III)), speciation shifts (e.g., exchangeable Cd to oxide-bound Cd), and mobility changes; (3) expounds on ET-regulated HM bioavailability by modulating soil retention capacity and iron plaque formation; (4) synopsizes ET-modulated HM accumulation pathways in rice (root uptake, xylem/phloem translocation, grain sequestration); (5) evaluates key factors (water management, fertilization, straw return) impacting ET efficiency and associated HM risks. Ultimately, we put forward future avenues for ET-based mitigation strategies to uphold rice safety and paddy soil sustainability.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue From Agricultural Soils to Human Health: Exposure Sources, Intake Pathways, and Accumulation of Heavy Metals)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Rice Yield Prediction Model at Pixel Level Using Machine Learning and Multi-Temporal Sentinel-2 Data in Valencia, Spain
by
Rubén Simeón, Alba Agenjos-Moreno, Constanza Rubio, Antonio Uris and Alberto San Bautista
Agriculture 2026, 16(2), 201; https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture16020201 - 13 Jan 2026
Abstract
Rice yield prediction at high spatial resolution is essential to support precision management and sustainable intensification in irrigated systems. While many remote sensing studies provide yield estimates at the field scale, pixel-level predictions are required to characterize within-field variability. This study assesses the
[...] Read more.
Rice yield prediction at high spatial resolution is essential to support precision management and sustainable intensification in irrigated systems. While many remote sensing studies provide yield estimates at the field scale, pixel-level predictions are required to characterize within-field variability. This study assesses the potential of multitemporal Sentinel-2 imagery and machine learning to estimate rice yield at pixel level in the Albufera rice area (Valencia, Spain). Yield data from combine harvester maps were collected for ‘JSendra’ and ‘Bomba’ Japonica varieties over five growing seasons (2020–2024) and linked to 10 m Sentinel-2 bands in the visible, near-infrared (NIR) and short-wave infrared (SWIR) regions. Random Forest (RF) and XGBoost (XGB) models were trained with 2020–2023 data and independently validated in 2024. XGB systematically outperformed RF, achieving at 110 and 130 DAS (days after showing), R2 values of 0.74 and 0.85 and RMSE values of 0.63 and 0.28 t·ha−1 for ‘JSendra’ and ‘Bomba’. Prediction accuracy increased as the season progressed, and models using all spectral bands clearly outperformed configurations based only on spectral indices, confirming the dominant contribution of NIR reflectance. Spatial error analysis revealed errors at field edges and headlands, while central pixels were more accurately predicted. Overall, the proposed approach provides accurate, spatially explicit rice yield maps that capture within-field variability and support both end-of-season yield estimation and early season forecasting, enabling the identification of potentially low-yield zones to support targeted management decisions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Artificial Intelligence and Digital Agriculture)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Agriculture Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Agriculture, Agronomy, Crops, Plants, IJMS, IJPB
Plant Responses and Tolerance to Salinity Stress, 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Ricardo Aroca, Pablo CornejoDeadline: 15 January 2026
Topic in
Agriculture, Remote Sensing, Sustainability, Water, Hydrology, Limnological Review, Earth
Water Management in the Age of Climate Change
Topic Editors: Yun Yang, Chong Chen, Hao SunDeadline: 31 January 2026
Topic in
Agriculture, Agronomy, Crops, Horticulturae, Microorganisms, Plants, Agrochemicals
Applications of Biotechnology in Food and Agriculture
Topic Editors: Edgar Omar Rueda-Puente, Bernardo Murillo-AmadorDeadline: 1 February 2026
Topic in
Agrochemicals, Agronomy, Insects, IJMS, Marine Drugs, Toxins, Agriculture, Biology
Research on Natural Bioactive Product-Based Pesticidal Agents—2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Min Lv, Hui XuDeadline: 28 February 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Agriculture
Animal Source Foods: Novel Approaches in Safety and Quality
Guest Editors: Tomislav Mikuš, Zeljka CvrtilaDeadline: 15 January 2026
Special Issue in
Agriculture
Functional Analysis of Insect Pest Genomes and Gut Microbiome for Crop Protection
Guest Editor: Lijun LiuDeadline: 15 January 2026
Special Issue in
Agriculture
Crop Microbiome and Stress: Interactions, Mechanisms, and Applications
Guest Editors: Soon-Jae Lee, Li WangDeadline: 15 January 2026
Special Issue in
Agriculture
Phytochemical Changes in Vegetables and Fruits During Post-Harvest Storage and Processing
Guest Editor: Marek SzmigielskiDeadline: 15 January 2026










