LiDAR-IMU Sensor Fusion-Based SLAM for Enhanced Autonomous Navigation in Orchards
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Simulation Experiment Design
2.1.1. Robot Platform and Sensor Modeling
2.1.2. Simulation Software and ROS Configuration
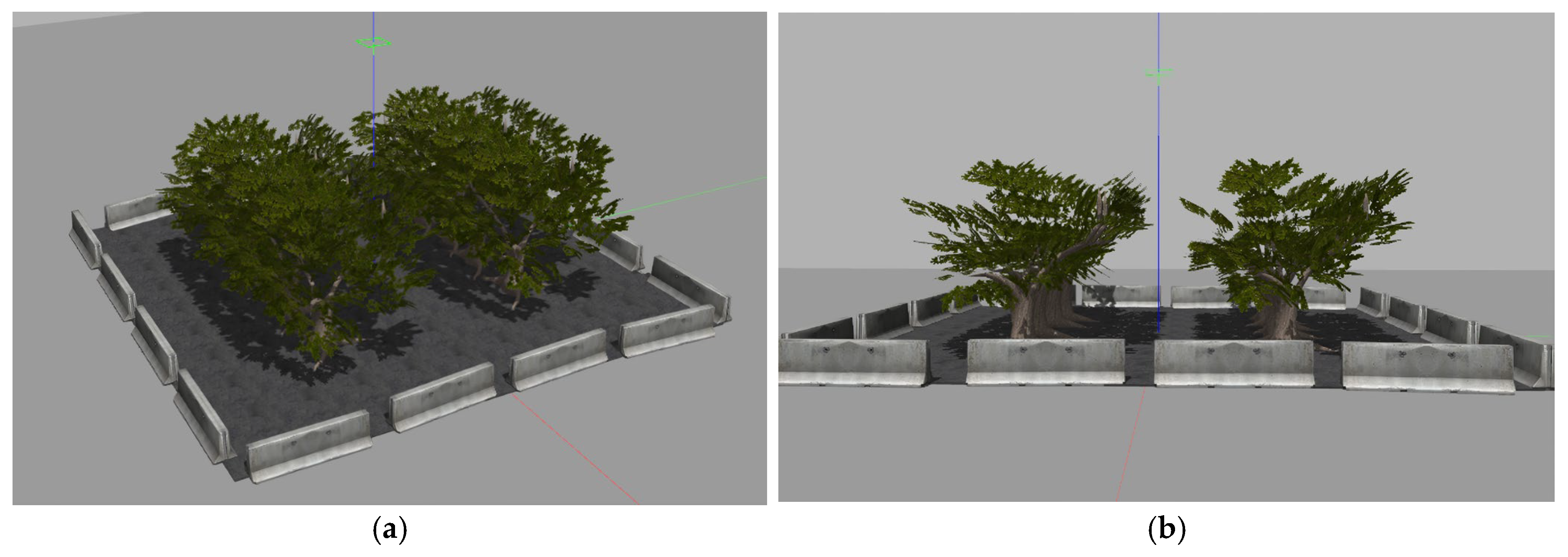
2.1.3. Simulation Environment Setup
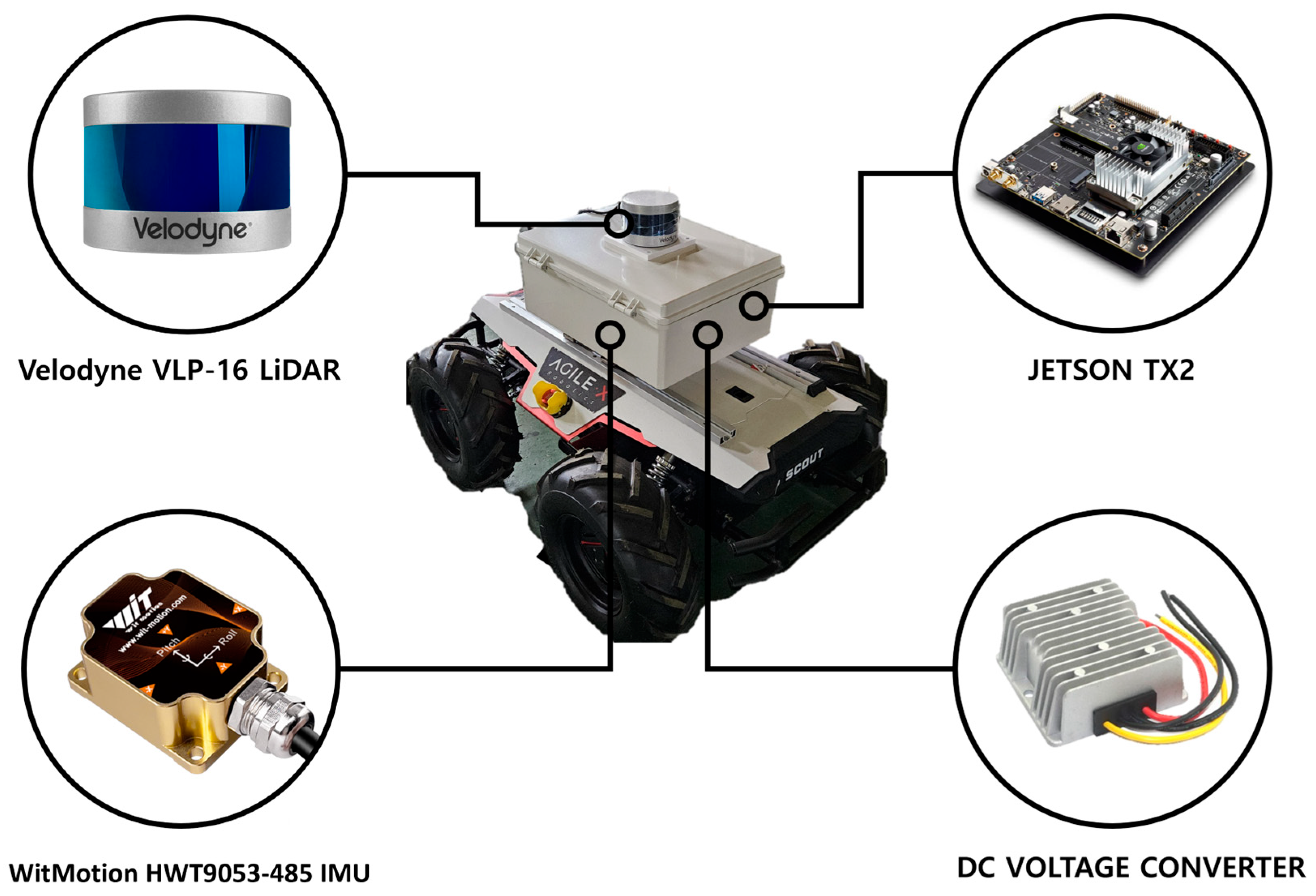
2.2. Hardware Configuration for Real-World Experiments
2.2.1. Robot Platform and Sensor Setup
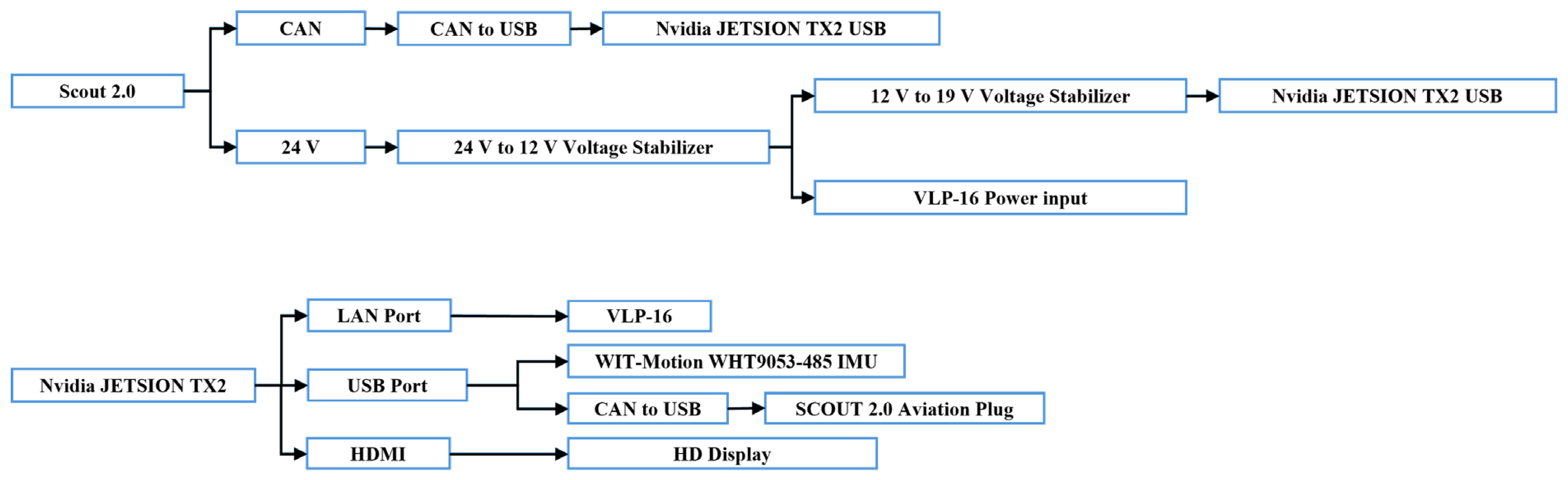
2.2.2. Electrical Wiring and Power Distribution
2.3. LiDAR–IMU Sensor Calibration
2.3.1. Frame Alignment and Data Filtering
2.3.2. Real-Time Tilt Compensation
2.3.3. LiDAR–IMU Calibration Workflow
2.4. Path Planning and Path Tracking
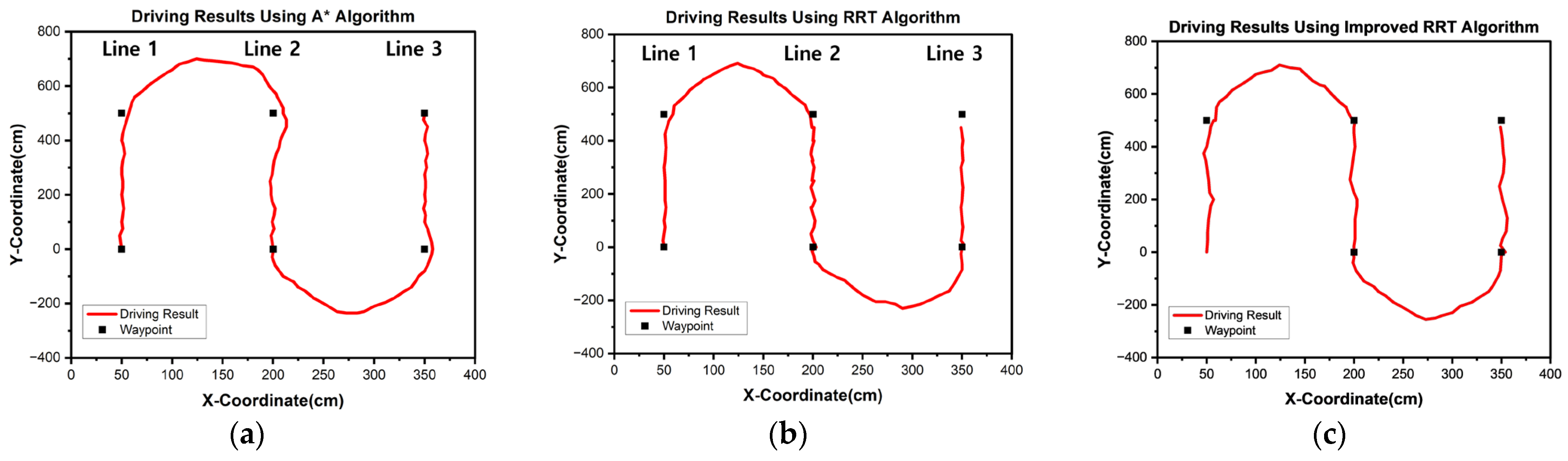
2.4.1. Path Planning with A*, RRT, and Improved RRT
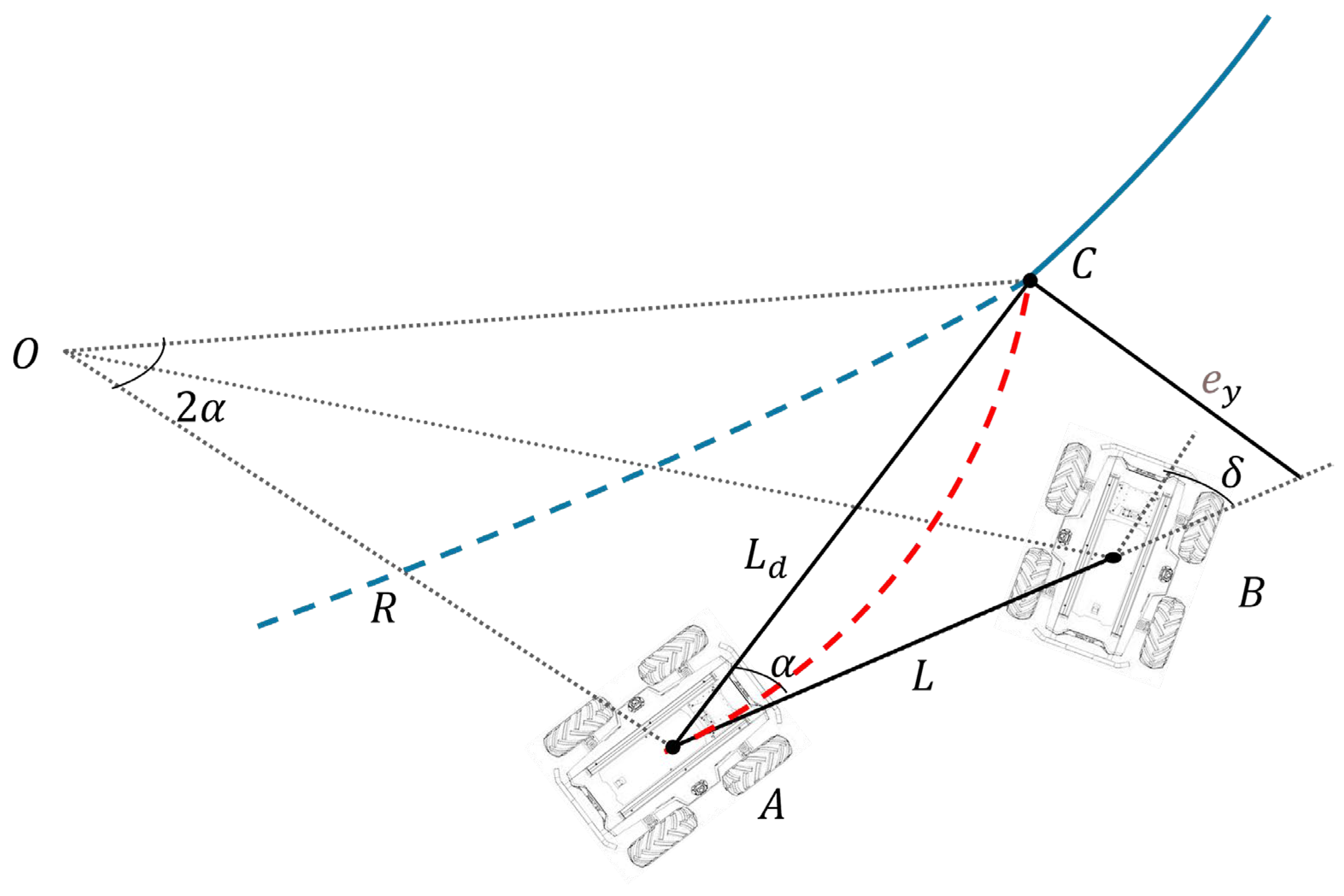
2.4.2. Path Tracking Algorithms
2.5. Mapping and Localization
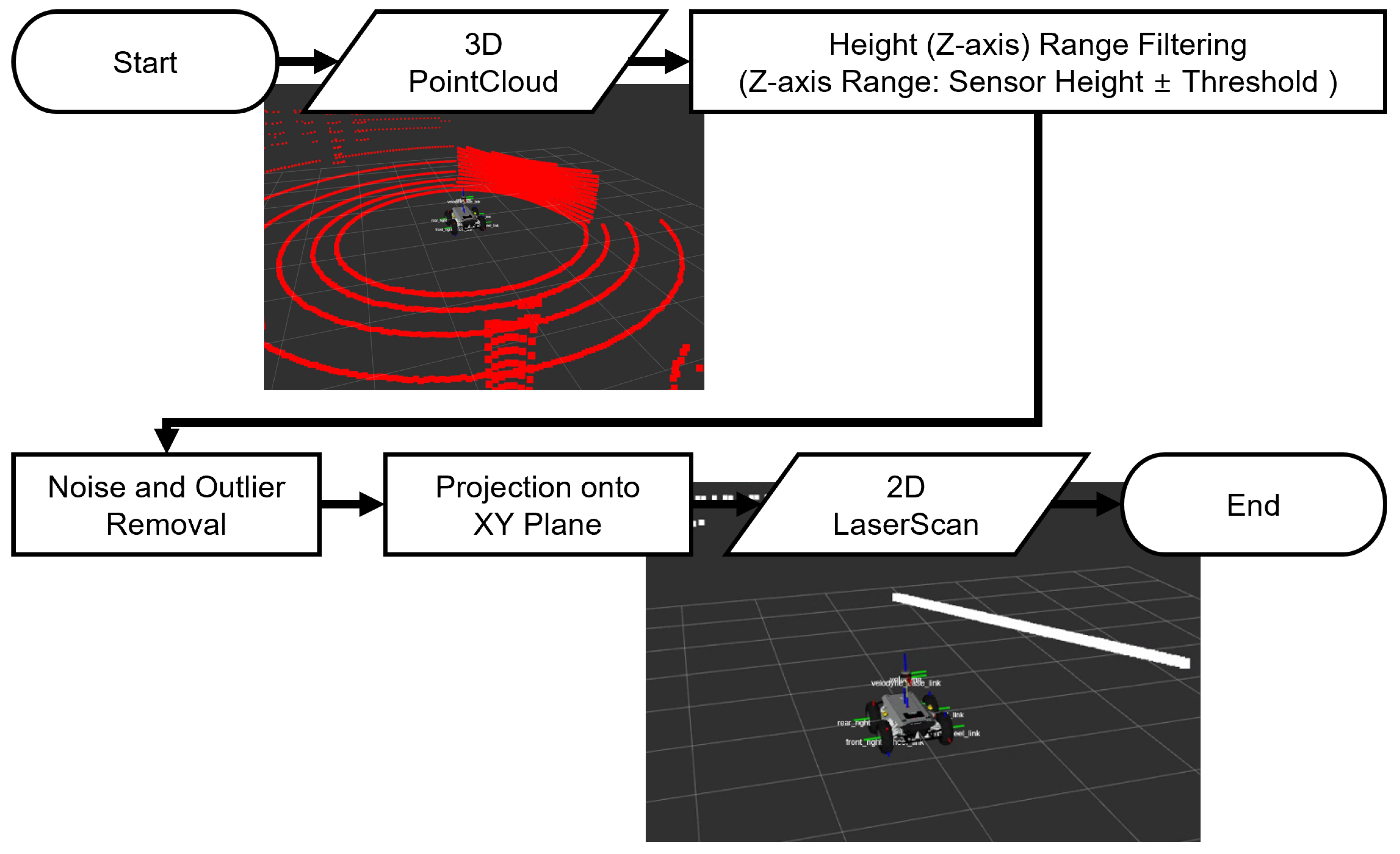
2.5.1. Point Cloud-to-Laser Scan Conversion
2.5.2. SLAM with Gmapping
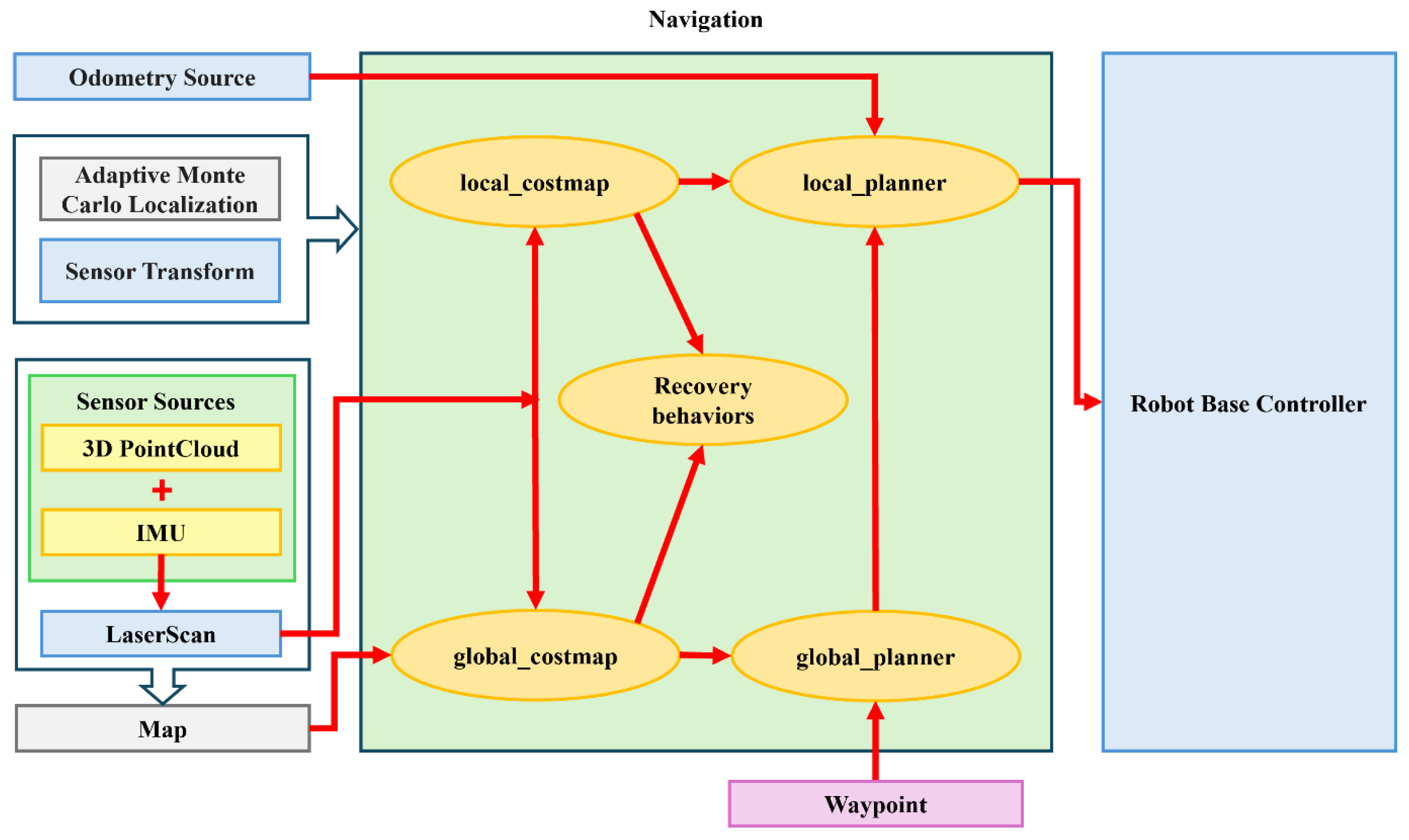
2.6. Integrated Navigation System
2.6.1. Global Planner Integration
2.6.2. Overall System Architecture
2.7. Baseline Experiment Design
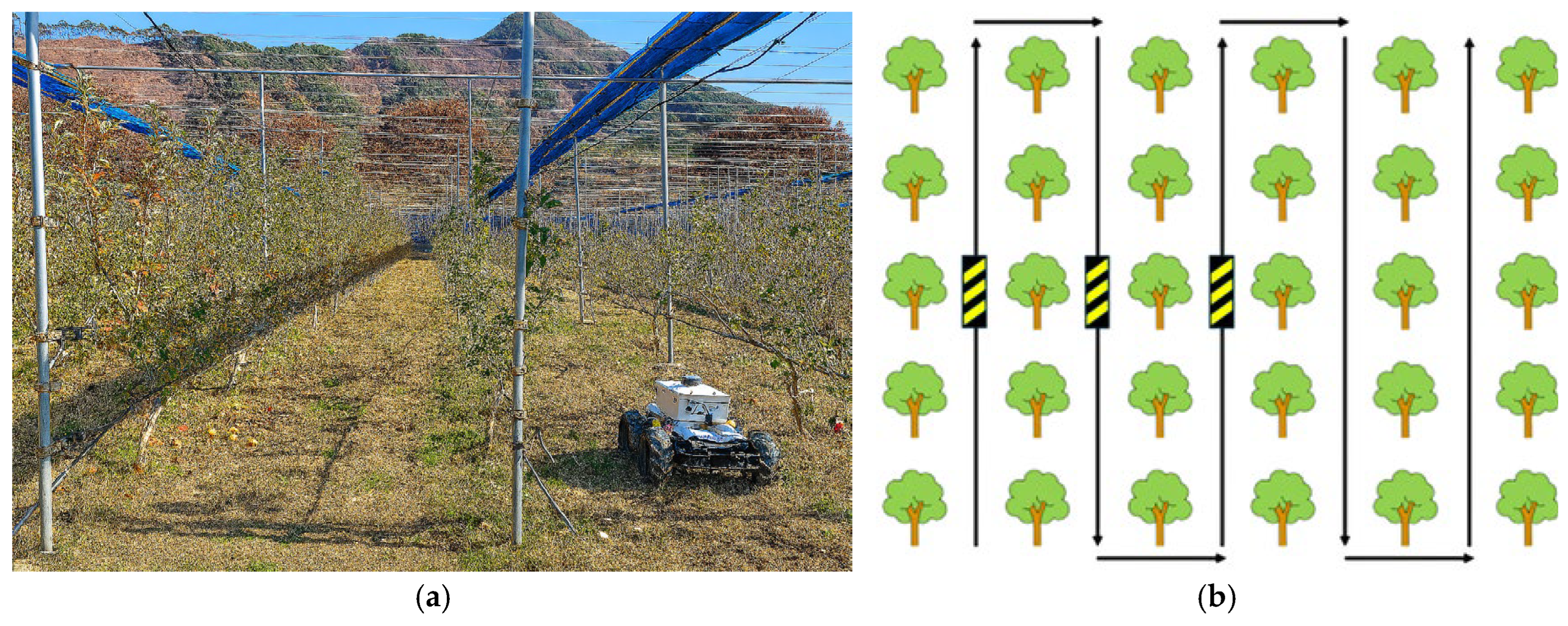
2.8. Orchard Experiment Design
3. Results
3.1. Simulation Experiment
3.2. Baseline Experiment
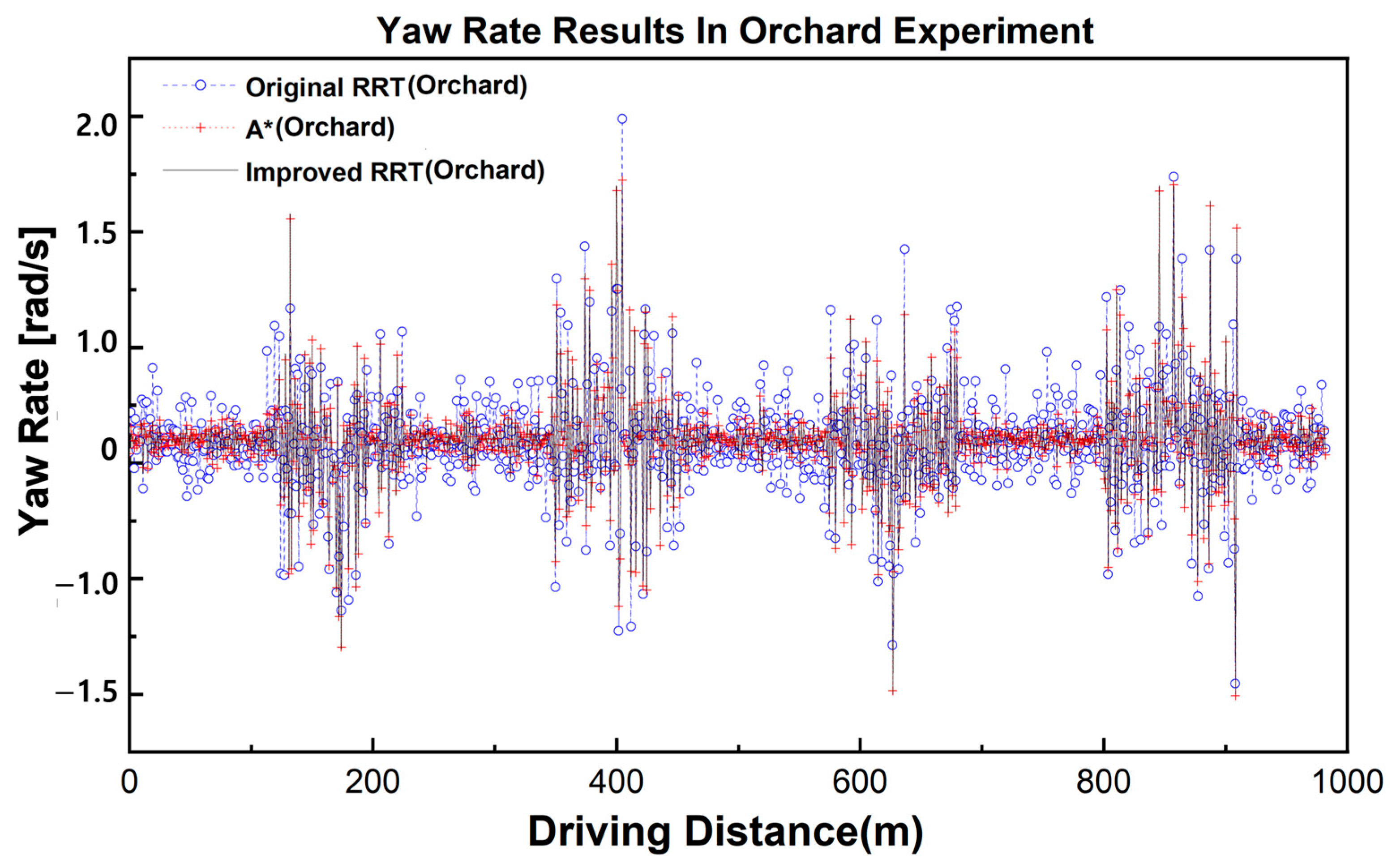
3.3. Orchard Experiment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RTK-GNSS | Real-Time Kinematic Global Navigation Satellite System |
| LiDAR | Light Detection and Ranging |
| SLAM | Simultaneous Localization and Mapping |
| IMU | Inertial Measurement Unit |
| RRT | Rapidly-Exploring Random Tree |
| RRT* | Rapidly-Exploring Random Tree Star |
| XACRO | XML Macros |
| URDF | Unified Robot Description Format |
| ROS | Robot Operating System |
| DWA | Dynamic Window Approach |
| AMCL | Adaptive Monte Carlo Localization |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
| GPS | Global Positioning System |
| EKF | Extended Kalman Filter |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
References
- Fuglie, K.; Wang, S.L. Productivity Growth in Global Agriculture Shifting to Developing Countries. Choices 2012, 27, 1–7. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/10.2307/choices.27.4.09 (accessed on 12 September 2024).
- Chávez, R.X.; Lombeida, E.D.; Pazmiño, Á.M.; Vasconez, F.D.C. Innovation in the agricultural sector: Experiences in Latin America. Cienc. Investig. Agrar. 2015, 42, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiaensen, L.; Rutledge, Z.; Taylor, J.E. The Future of Work in Agriculture: Some Reflections. World Bank Policy Research Working Paper 2020. No. 9193. pp. 1–27. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3560626 (accessed on 4 June 2025).
- Alston, M.; Kent, J. Generation X-pendable: The social exclusion of rural and remote young people. J. Sociol. 2009, 45, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulcher, A.; Rihn, A.L.; Warner, L.A.; Lebude, A.V.; Schexnayder, S.; Altland, J.E.; Bumgarner, N.; Marble, S.C.; Nackley, L.; Palma, M.; et al. Overcoming the nursery industry labor shortage: A survey of strategies to adapt to a reduced workforce and automation and mechanization technology adoption levels. Hortscience 2023, 58, 1513–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Shivandu, S.K. Integrating artificial intelligence and internet of things (IOT) for enhanced crop monitoring and management in precision agriculture. Sens. Int. 2024, 5, 100292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshram, A.T.; Vanalkar, A.V.; Kalambe, K.B.; Badar, A.M. Pesticide Spraying Robot for Precision Agriculture: A Categorical Literature Review and Future Trends. J. Field Robot. 2021, 38, 1467–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Jin, Y.; Faheem, M.; Gao, W.; Liu, J.; Jiang, H.; Cai, L.; Li, Y. Research Progress of Autonomous Navigation Technology for Multi-Agricultural Scenes. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 205, 107963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, J.; Yan, Y.; Tian, G.; Gu, B. Recent Developments and Applications of Simultaneous Localization and Mapping in Agriculture. J. Field Robot. 2022, 39, 956–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.-M.; Park, J.-W.; Lee, J.-S.; Han, S.-K. Assessment of the GNSS-RTK for Application in Precision Forest Operations. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, O.; Uusitalo, J.; Pietarinen, J.; Lajunen, A. Evaluation of Forest Features Determining GNSS Positioning Accuracy of a Novel Low-Cost, Mobile RTK System Using LiDAR and TreeNet. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Wang, D. A Review of Three-Dimensional Vision Techniques in Food and Agriculture Applications. Smart Agric. Technol. 2023, 5, 100259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Jia, W.; Ou, M.; Dong, X.; Dai, S. A Review of Environmental Sensing Technologies for Targeted Spraying in Orchards. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Fu, H.; Xiao, L.; Fan, Y.; Zhao, D.; Dai, B. Traversability Analysis for Autonomous Driving in Complex Environment: A LiDAR-Based Terrain Modeling Approach. J. Field Robot. 2023, 40, 1779–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Huang, H.-Z.; Zeng, Q.; Huang, P. A robust 2D Lidar SLAM method in complex environment. Photon. Sens. 2022, 12, 220416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Mo, Z.; Yang, X.; Liu, W.; Imran, M. Obstacle Detection and Avoidance Methods for Mobile Robot in Indoor Environment. Preprints 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Wang, H.; Qin, W.; Wang, Q.; Liu, H.; Yin, Y.; Song, Z.; Meng, Z. Design and Test of Obstacle Detection and Harvester Pre-Collision System Based on 2D Lidar. Agronomy 2023, 13, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Valente, J.; Kooistra, L.; Guo, L.; Wang, W. Orchard management with small unmanned aerial vehicles: A survey of sensing and analysis approaches. Precis. Agric. 2021, 22, 2007–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsadik, B.; Karam, S. The simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM): An overview. Surv. Geospat. Eng. J. 2021, 2, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Zhao, X.; Zeng, L.; Liu, L.; Liu, S.; Sun, L.; Li, Z.; Chen, H.; Liu, G.; Qiao, Z.; et al. A review of research on slam technology based on the fusion of lidar and vision. Sensors 2025, 25, 1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaltenthaler, J.; Lauterbach, H.A.; Borrmann, D.; Nüchter, A. Pose estimation and mapping based on IMU and LiDAR. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2022, 55, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, S.; Zhuang, Y.; Yan, F. Deep sensor fusion between 2D laser scanner and IMU for mobile robot localization. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 21, 8501–8509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Cao, S.S.; Bai, T.; Kong, F.T.; Sun, W. Research progress and prospect of multi-robot collaborative SLAM in complex agricultural scenarios. Smart Agric. 2024, 6, 23–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiozzo Fasiolo, D.; Scalera, L.; Maset, E.; Lesquerré-Caudebez, B.; Fusiello, A.; Beinat, A.; Gasparetto, A. A Navigation Approach for Autonomous Mobile Robots in Sustainable Agriculture. In Proceedings of the I4SDG Workshop 2025–IFToMM for Sustainable Development Goals (I4SDG 2025), Lamezia Terme, Italy, 9–11 June 2025; Mechanisms and Machine Science Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; Volume 179, pp. 399–408. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Y.; Ma, R.; Li, C.; Shao, C.; Huang, J.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, Y. Three-dimensional localization and mapping of multi-agricultural scenes via hierarchically-coupled LiDAR–inertial odometry. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 227, 109487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-G.; Lee, H.-M.; Lee, S.-H. A new covariance intersection based integrated SLAM framework for 3D outdoor agricultural applications. Electron. Lett. 2024, 60, e13206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, H.; Yu, H.; Xie, Q.; Dong, J.; Sun, X.; Liu, H.; Sun, C.; Li, B.; Zheng, F. SLAM Algorithm for Mobile Robots Based on Improved LVI-SAM in Complex Environments. Sensors 2024, 24, 7214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, C.; Wang, L.; Chi, R.; Su, T.; Ma, Y. A Camera–LiDAR–IMU fusion method for real-time extraction of navigation line between maize field rows. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 223, 109114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Dou, H.; Gao, Y.; Zhai, C.; Wang, X.; Zou, W. Research on an orchard row centreline multipoint autonomous navigation method based on LiDAR. Artif. Intell. Agric. 2025, 15, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikder, C.; Zhang, W.; Chen, X.; Li, F.; Zuo, Z.; Tan, X. Soft Computing Techniques Applied to Adaptive Hybrid Navigation Methods for Tethered Robots in Dynamic Environments. J. Field Robot. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Han, S.I. Adaptive Bi-directional RRT algorithm for three-dimensional path planning of unmanned aerial vehicles in complex environments. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 23748–23767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Li, J.; Li, P. Improving path planning for mobile robots in complex orchard environments: The continuous bidirectional Quick-RRT* algorithm. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1337638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Wen, J.; Yao, L.; Yang, Z.; Xu, L.; Yao, L. Agricultural machinery path tracking with varying curvatures based on an improved pure-pursuit method. Agriculture 2025, 15, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Pan, W.; Hou, X.; Liu, Z. Autonomous trajectory tracking control method for an agricultural robotic vehicle. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2024, 17, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazate-Burgos, P.; Torres-Torriti, M.; Aguilera-Marinovic, S.; Arévalo, T.; Huang, S.; Cheein, F.A. Robust 2D Lidar-Based SLAM in Arboreal Environments Without IMU/GNSS. arXiv, 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Qin, J.; Huang, D.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Yang, F. Integrated navigation method for orchard-dosing robot based on LiDAR/IMU/GNSS. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








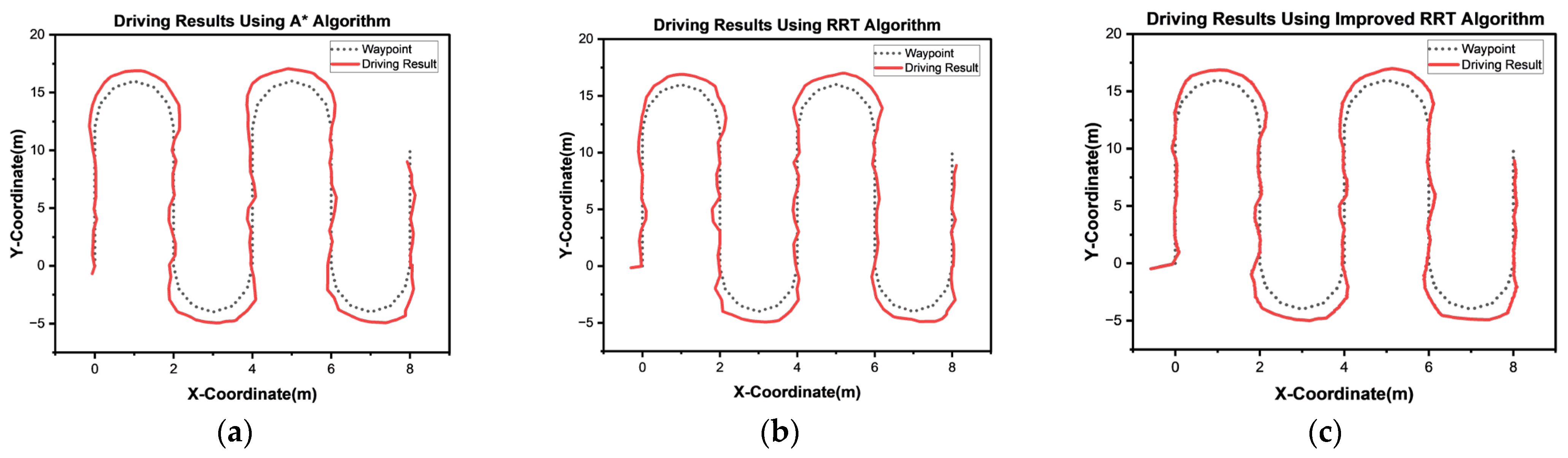
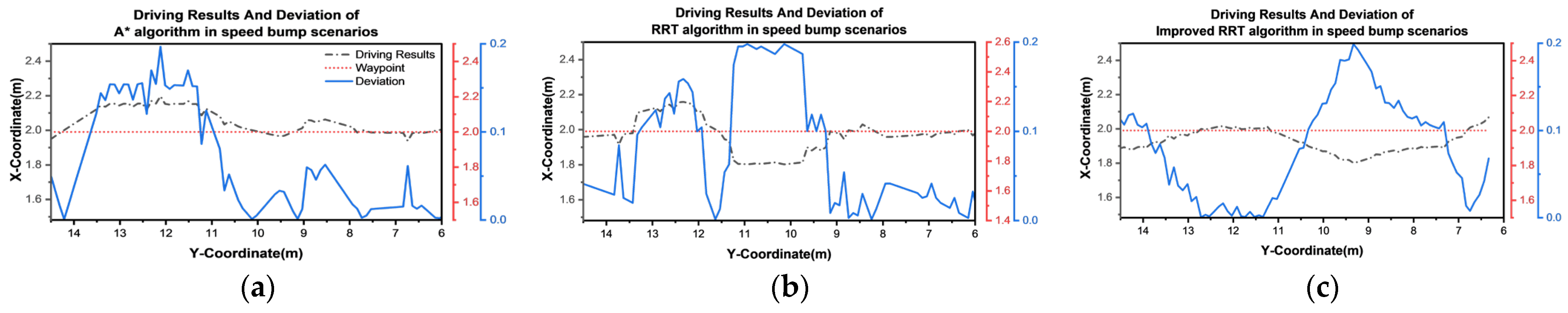
| Algorithm | A* | RRT | Improved A* | Improved RRT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time to Destination (s) | 88.318 ± 0.521 | 92.634 ± 0.613 | 89.762 ± 0.476 | 90.814 ± 0.501 |
| Driving distance (m) | 64.341 ± 0.215 | 66.561 ± 0.308 | 57.480 ± 0.182 | 56.826 ± 0.197 |
| RMSE (cm) | 3.600 ± 0.200 | 5.400 ± 0.300 | 2.900 ± 0.200 | 2.300 ± 0.100 |
| Maximum Yaw Rate (rad·s−1) | 1.037 ± 0.024 | 0.950 ± 0.018 | 0.907 ± 0.015 | 0.905 ± 0.012 |
| Average Yaw Rate (rad·s−1) | 0.305 ± 0.013 | 0.376 ± 0.012 | 0.352 ± 0.011 | 0.349 ± 0.009 |
| Algorithm | Path | RMSE (cm) | Average RMSE (cm) | Time Consumption (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A* | Line 1 | 2.3 | 3.4 ± 0.3 | 63.078 |
| Line 2 | 4.3 | |||
| Line 3 | 3.8 | |||
| RRT | Line 1 | 3.3 | 3.7 ± 0.4 | 69.265 |
| Line 2 | 3.6 | |||
| Line 3 | 4.2 | |||
| Improved RRT | Line 1 | 2.1 | 2.2 ± 0.2 | 76.428 |
| Line 1 | 2.4 | |||
| Line 2 | 2.2 |
| Line Segment | A* RMSE (m) | RRT RMSE (m) | Improved RRT RMSE (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Line 1 | 0.914 | 0.962 | 0.959 |
| Line 2 | 0.896 | 0.817 | 0.834 |
| Line 3 | 0.937 | 0.107 | 0.978 |
| Line 4 | 0.801 | 0.702 | 0.790 |
| Average RMSE | 0.894 | 0.887 | 0.890 |
| Algorithm | Straight with Bumps (RMSE; cm) | Rotation (RMSE; cm) |
|---|---|---|
| A* | 8.900 | 27.600 |
| RRT | 14.300 | 27.500 |
| Improved RRT | 8.500 | 24.100 |
| Metric (rad·s−1) | A* | RRT | Improved RRT |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 0.156 | 0.173 | 0.174 |
| Std | 0.378 | 0.357 | 0.355 |
| Min | −1.665 | −1.757 | −1.745 |
| Max | 2.598 | 2.134 | 2.080 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, S.; Han, X.; Chang, E.; Jeong, H. LiDAR-IMU Sensor Fusion-Based SLAM for Enhanced Autonomous Navigation in Orchards. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1899. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15171899
Choi S, Han X, Chang E, Jeong H. LiDAR-IMU Sensor Fusion-Based SLAM for Enhanced Autonomous Navigation in Orchards. Agriculture. 2025; 15(17):1899. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15171899
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Seulgi, Xiongzhe Han, Eunha Chang, and Haetnim Jeong. 2025. "LiDAR-IMU Sensor Fusion-Based SLAM for Enhanced Autonomous Navigation in Orchards" Agriculture 15, no. 17: 1899. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15171899
APA StyleChoi, S., Han, X., Chang, E., & Jeong, H. (2025). LiDAR-IMU Sensor Fusion-Based SLAM for Enhanced Autonomous Navigation in Orchards. Agriculture, 15(17), 1899. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15171899







