Making the Connection Between PFASs and Agriculture Using the Example of Minnesota, USA: A Review
Abstract
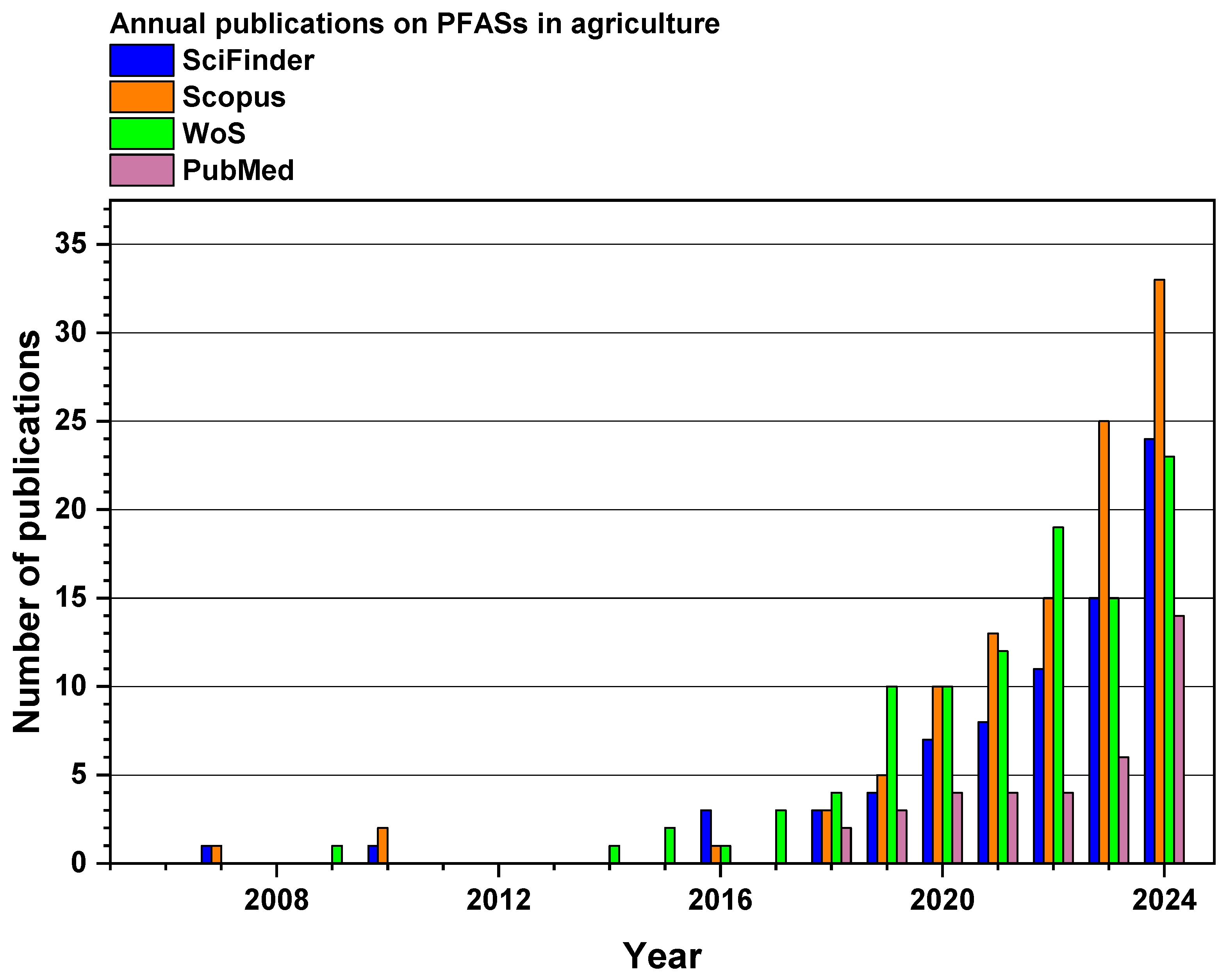
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. PFASs in Minnesota
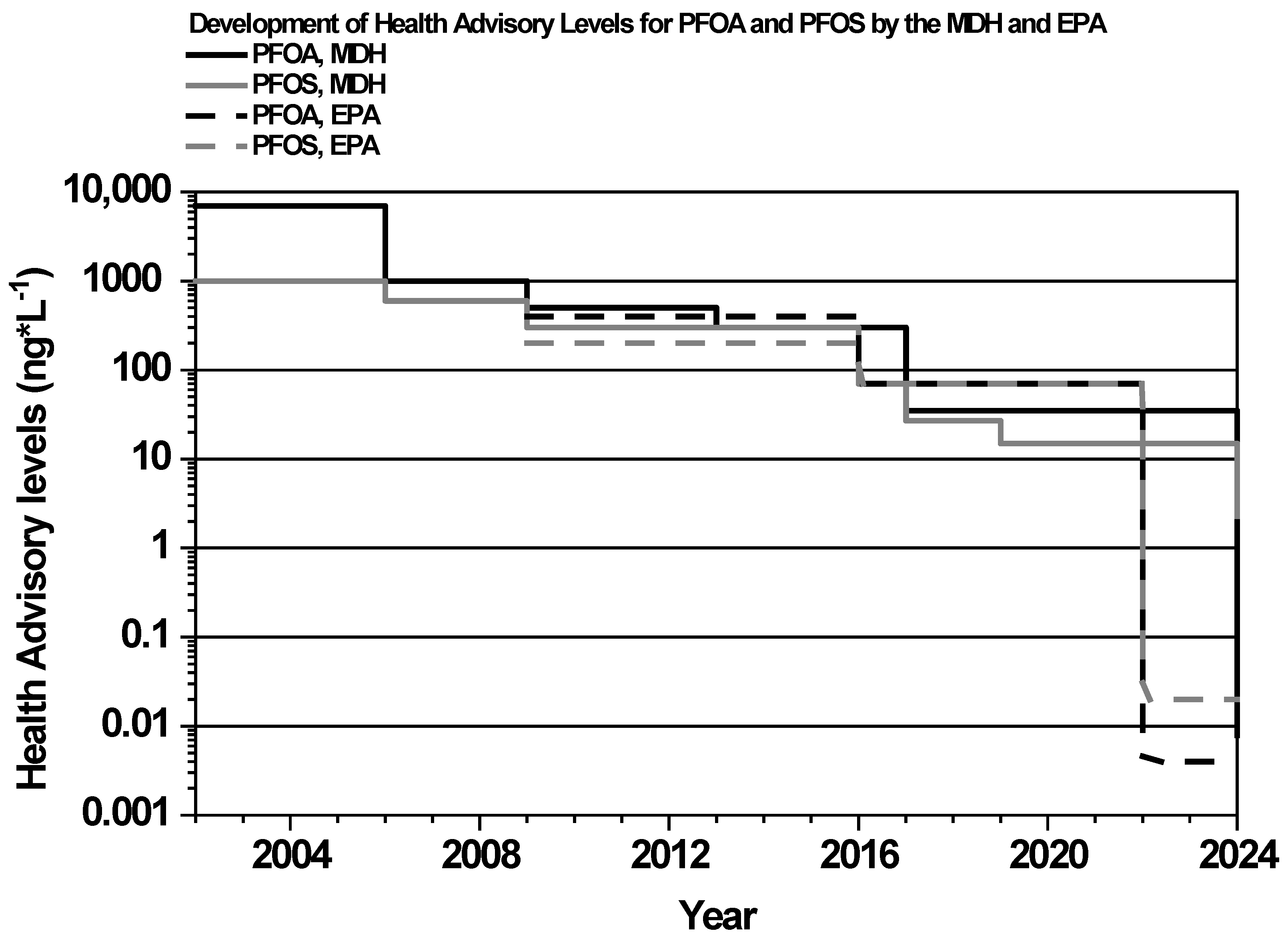
3.1.1. History of PFASs in Minnesota
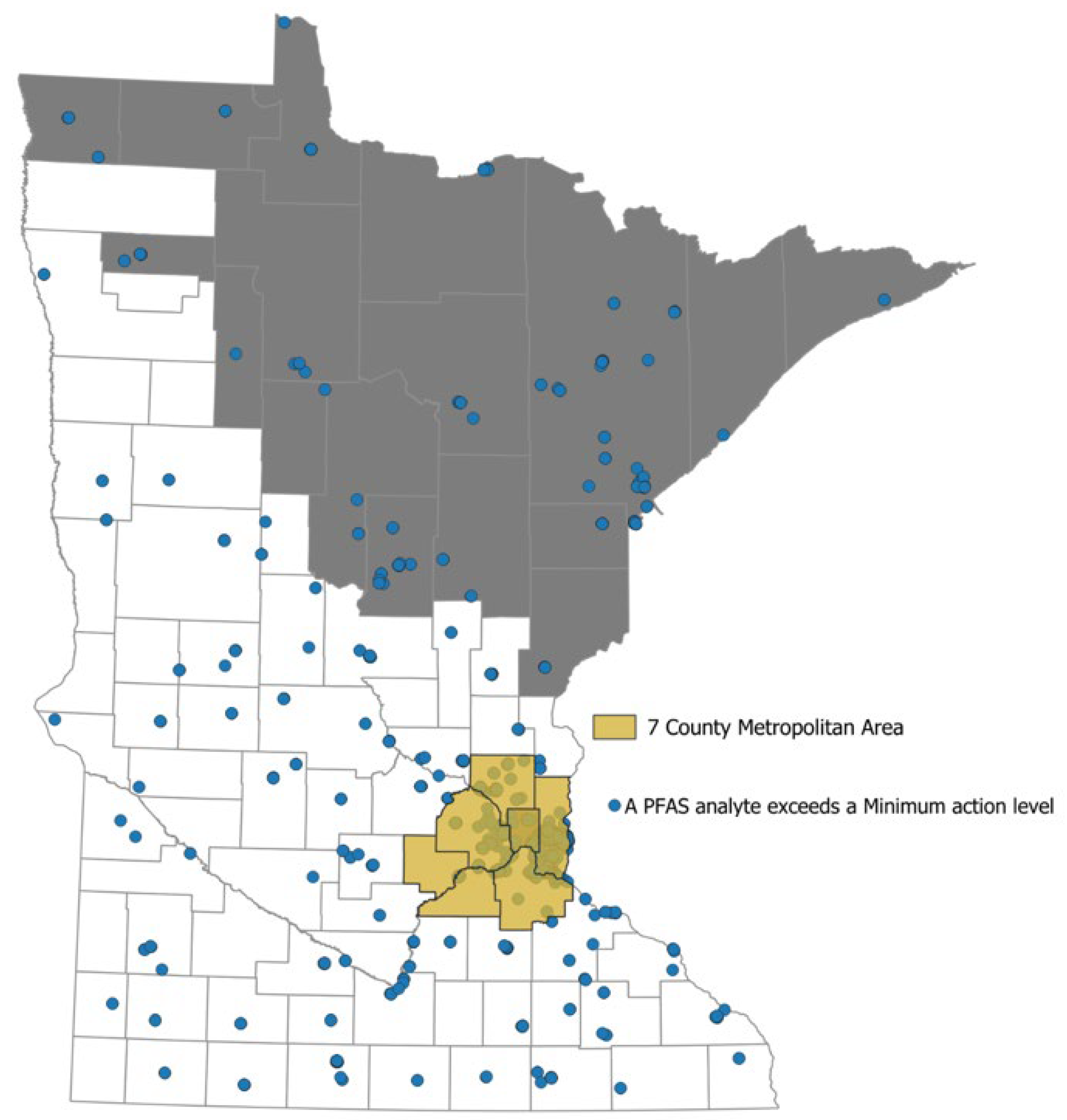
3.1.2. Contamination in Minnesota
Drinking Water Standards as a Guide
+ ([PFHxS])⁄(0.047 µg/L) + ([PFOA])⁄(0.035 µg/L) + ([PFOS])⁄(0.015 µg/L)
Air Pollution
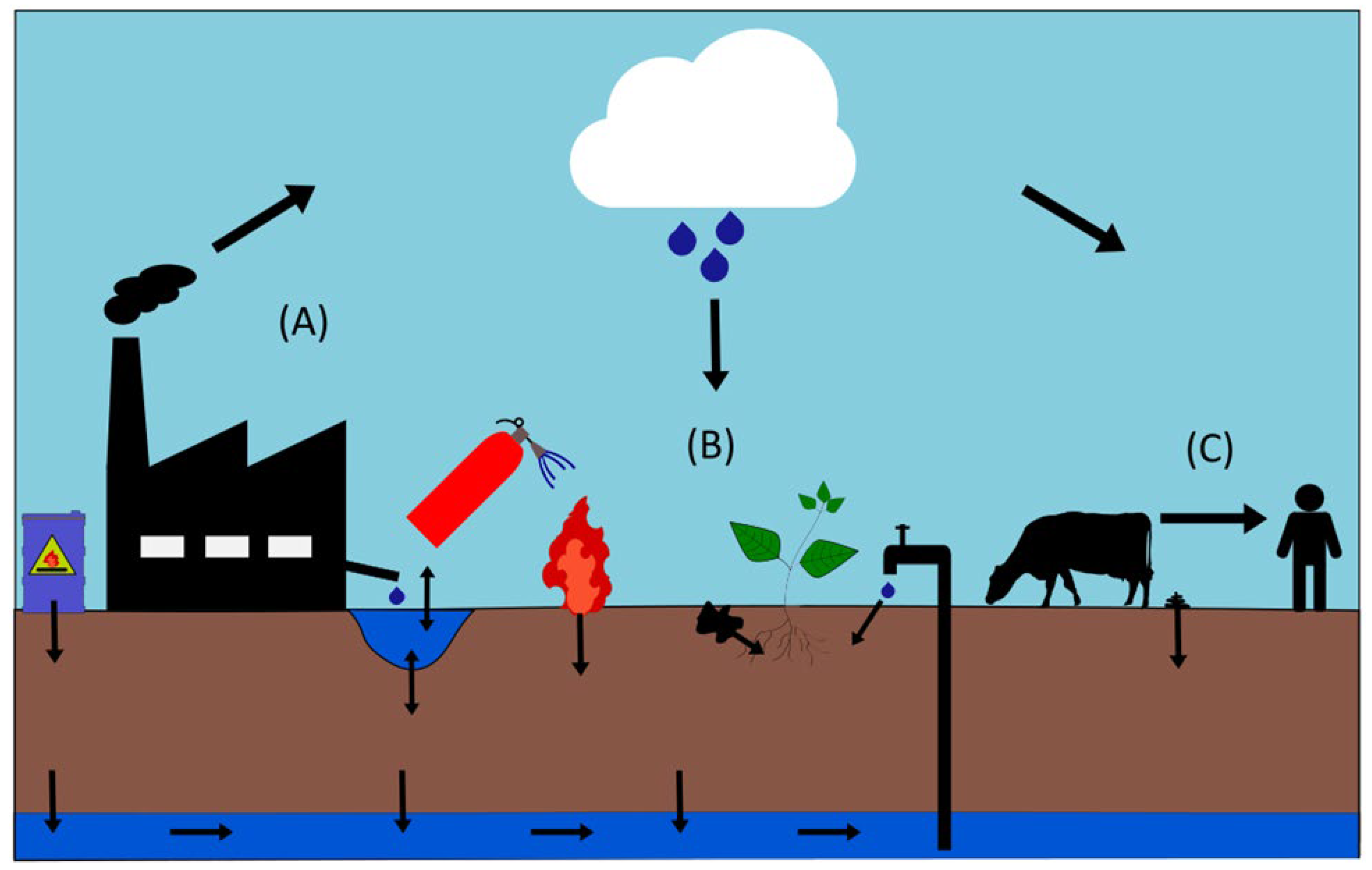
3.2. Significant Sources of PFASs in the Environment
3.2.1. Release of PFASs During Their Production, Use, and Disposal Phases
3.2.2. Aqueous Film-Forming Foam (AFFF)
3.2.3. Biosolids from Wastewater Treatment
3.2.4. PFASs in Pesticide Formulations
3.2.5. PFASs in Rural Versus Urban Communities
3.3. The Behavior and Transport of PFASs in the Agricultural Environment
3.3.1. PFASs in the Atmosphere
3.3.2. PFASs in Surface Water, Sediment, and Groundwater
3.3.3. Behavior and Uptake of PFASs in Soils
PFAS Sorption
PFAS Retention
PFASs in Agricultural and Rural Soils
3.4. PFASs in Plant and Animal Systems
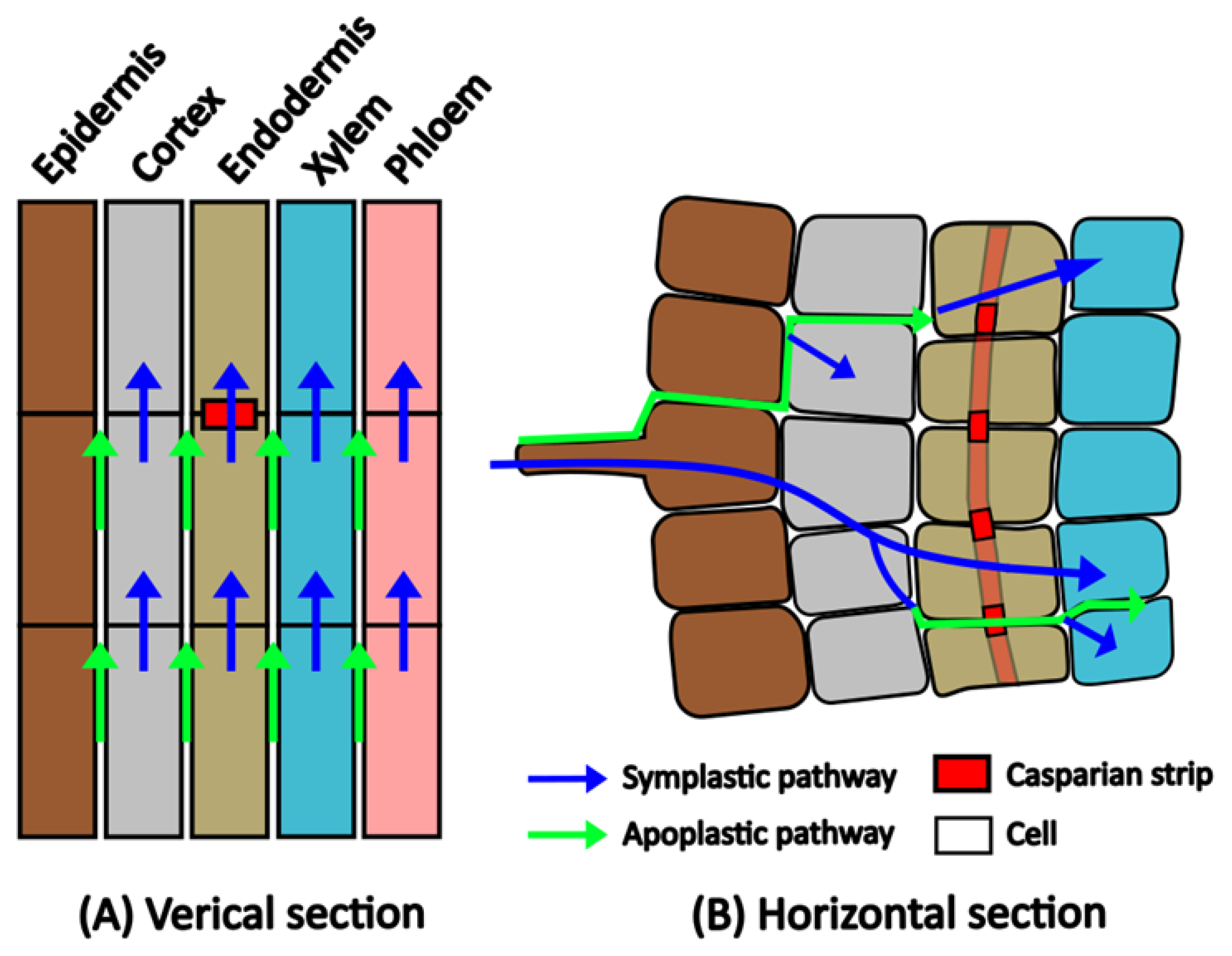
3.4.1. Plant Uptake of PFASs
PFAS Uptake Mechanisms in Plants
Uptake Rates of Different Crops
3.4.2. PFAS Contamination in Livestock
3.4.3. PFAS Transfer Through the Food Chain
3.5. Policy and Regulations
3.6. Future Research Recommendations and Challenges
3.6.1. Agricultural Challenges and Strategies for PFAS Mitigation
3.6.2. Strategies for PFAS Risk Reduction on Farms
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Buck, R.C.; Franklin, J.; Berger, U.; Conder, J.M.; Cousins, I.T.; Voogt, P.d.; Jensen, A.A.; Kannan, K.; Ma-bury, S.A.; van Leeuwen, S.P.J. Perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances in the environment: Terminology, classification, and origins. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2011, 7, 513–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Reconciling Terminology of the Universe of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances: Recommendations and Practical Guidance. Available online: https://www.oecd.org/en/publications/reconciling-terminology-of-the-universe-of-per-and-polyfluoroalkyl-substances_e458e796-en.html (accessed on 9 July 2024).
- EPA. PFAS Structures in DSSTox. Available online: https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/chemical-lists/PFASSTRUCT (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Rankin, K.; Mabury, S.A.; Jenkins, T.M.; Washington, J.W. A North American and global survey of perfluoroalkyl substances in surface soils: Distribution patterns and mode of occurrence. Chemosphere 2016, 161, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giesy, J.P.; Kannan, K. Global distribution of perfluorooctane sulfonate in wildlife. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 1339–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, J.-M.; Chen, D.; Han, F.-J.; Guo, Y.; Zeng, L.; Lu, X.; Wang, F. A short review on human exposure to and tissue distribution of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 1058–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.C.; Johns, L.E.; Meeker, J.D. Serum Biomarkers of Exposure to Perfluoroalkyl Substances in Relation to Serum Testosterone and Measures of Thyroid Function among Adults and Adolescents from NHANES 2011–2012. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 6098–6114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, F.; Nadal, M.; Navarro-Ortega, A.; Fàbrega, F.; Domingo, J.L.; Barceló, D.; Farré, M. Accumulation of perfluoroalkyl substances in human tissues. Environ. Int. 2013, 59, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunderland, E.M.; Hu, X.C.; Dassuncao, C.; Tokranov, A.K.; Wagner, C.C.; Allen, J.G. A Review of the Pathways of Human Exposure to Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) and Present Understanding of Health Effects. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2018, 29, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenton, S.E.; Ducatman, A.; Boobis, A.; DeWitt, J.C.; Lau, C.; Ng, C.; Smith, J.S.; Roberts, S.M. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substance Toxicity and Human Health Review: Current State of Knowledge and Strategies for Informing Future Research. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2020, 40, 606–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, G.W.; Burris, J.M.; Ehresman, D.J.; Froehlich, J.W.; Seacat, A.M.; Butenhoff, J.L.; Zobel, L.R. Half-life of Serum Elimination of Perfluorooctanesulfonate, Perfluorohexanesulfonate, and Perfluorooctanoate in Retired Fluorochemical Production Workers. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 1298–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; DeWitt, J.C.; Higgins, C.P.; Cousins, I.T. A Never-Ending Story of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Sub-stances (PFASs)? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 2508–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, I.; McDonough, J.; Miles, J.; Storch, P.; Kochunarayanan, P.T.; Kalve, E.; Hurst, J.; Dasgupta, S.S.; Burdick, J. A review of emerging technologies for remediation of PFASs. Remediat. J. 2018, 28, 101–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolan, N.; Sarkar, B.; Yan, Y.; Li, Q.; Wijesekara, H.; Kannan, K.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Schauerte, M.; Bosch, J.; Noll, H.; et al. Remediation of poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) contaminated soils—To mobilize or to immobilize or to degrade? J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glüge, J.; Scheringer, M.; Cousins, I.T.; DeWitt, J.C.; Goldenman, G.; Herzke, D.; Lohmann, R.; Ng, C.A.; Trier, X.; Wang, Z. An overview of the uses of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2020, 22, 2345–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meegoda, J.N.; Kewalramani, J.A.; Li, B.; Marsh, R.W. A Review of the Applications, Environmental Release, and Remediation Technologies of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EPA. Emerging Contaminants: Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) and Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA). Available online: https://semspub.epa.gov/work/HQ/100002767.pdf (accessed on 2 July 2024).
- Barlow, C.A.; Boyd, C.A.; Kemp, M.J.; Hoppe Parr, K.A. PFAS Toxicology: What is Driving Variation in Drinking Water Standards? 2019. Available online: https://portal.ct.gov/-/media/DEEP/PFASTaskForce/HHCBarlowBoydKempHoppeParr2019PFASToxicologypdf.pdf (accessed on 17 June 2024).
- Carey, G.R.; Hakimabadi, S.G.; Singh, M.; McGregor, R.; Woodfield, C.; van Geel, P.J.; Pham, A.L.-T. Longevity of colloidal activated carbon for in situ PFAS remediation at AFFF-contaminated airport sites. Remediat. J. 2022, 33, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmer, R.W.; Reeves, D.M.; Cassidy, D.P. Per- and Polyfluorinated Alkyl Substances (PFAS) cycling within Michigan: Contaminated sites, landfills and wastewater treatment plants. Water Res. 2022, 210, 117983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, G.R. PFAS in soil and groundwater following historical land application of biosolids. Water Res. 2022, 211, 118035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatore, D.; Mok, K.; Garrett, K.K.; Poudrier, G.; Brown, P.; Birnbaum, L.S.; Goldenman, G.; Miller, M.F.; Patton, S.; Poehlein, M.; et al. Presumptive Contamination: A New Approach to PFAS Contamination Based on Likely Sources. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2022, 9, 983–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.O.d.; Armitage, J.M.; Bruton, T.A.; Dassuncao, C.; Heiger-Bernays, W.; Hu, X.C.; Kärrman, A.; Kelly, B.; Ng, C.; Robuck, A.; et al. PFAS Exposure Pathways for Humans and Wildlife: A Synthesis of Current Knowledge and Key Gaps in Understanding. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2020, 40, 631–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klenow, S.; Heinemeyer, G.; Brambilla, G.; Dellatte, E.; Herzke, D.; Voogt, P.d. Dietary exposure to selected perfluoroalkyl acids (PFAAs) in four European regions. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2013, 30, 2141–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, J.; Ehlers, S.; Oberhausen, A.; Tischer, M.; Fürst, P.; Schafft, H.; Lahrssen-Wiederholt, M. Absorption, Distribution, and Milk Secretion of the Perfluoroalkyl Acids PFBS, PFHxS, PFOS, and PFOA by Dairy Cows Fed Naturally Contaminated Feed. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 2903–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, J.; Ehlers, S.; Fürst, P.; Schafft, H.; Lahrssen-Wiederholt, M. Transfer of Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) and Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) from Contaminated Feed into Milk and Meat of Sheep: Pilot Study. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2012, 63, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treat, S.A. With a Second Farm Shuttered Due to Massive PFAS Contamination, Maine Legislators Weigh Easing Access to the Courts. Available online: https://www.iatp.org/blog/202007/second-farm-shuttered-due-massive-pfas-contamination-maine-legislators-weigh-easing (accessed on 11 July 2024).
- Leigh, V. There Are No Tears Left Arundel Dairy Farmer Devastated by PFAS Fights for State Help, 2022. Available online: https://www.newscentermaine.com/article/tech/science/environment/pfas/there-are-no-tears-left-arun-del-dairy-farmer-devastated-by-pfas-fights-for-state-help-maine-agriculture/97-1d7f1b97-84f5-4dd3-8f51-90f36e72af6e (accessed on 14 April 2024).
- Miller, K. More Than 50 Maine Farms Impacted by PFAS, but State Officials See ‘Glimmer of Hope’. Available online: https://www.mainepublic.org/environment-and-outdoors/2023-02-01/more-than-50-maine-farms-impacted-by-pfas-but-state-officials-see-glimmer-of-hope (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- O’Brien, K. ‘Forever Chemicals’ Upended a Maine Farm—And Point to Larger Problem. The Washington Post, April 11, 2022. Available online: https://www.washingtonpost.com/nation/2022/04/11/pfas-forever-chemicals-maine-farm/ (accessed on 14 April 2023).
- Kolpin, D.W.; Hubbard, L.E.; Cwiertny, D.M.; Meppelink, S.M.; Thompson, D.A.; Gray, J.L. A Comprehensive Statewide Spatiotemporal Stream Assessment of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in an Agricultural Region of the United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2021, 8, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, H.; Roser, M. Land Use, 2019. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/land-use#:~:text=Almost%20half%20(44%25)%20of,land%20is%20used%20for%20agriculture.&text=In%20total%20it%20is%20an,size%20of%20the%20United%20States (accessed on 26 March 2024).
- 3M. Perfluorochemical Release at the 3M–Cottage Grove Facility, 2005. Available online: https://www.health.state.mn.us/communities/environment/hazardous/docs/sites/washington/3mcg0205.pdf (accessed on 19 July 2024).
- Nordby, G.L.; Luck, J.M. Perfluorooctanoic acid interactions with human serum albumin. J. Biol. Chem. 1955, 219, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rich, N. The Lawyer Who Became DuPont’s Worst Nightmare. Available online: https://www.nytimes.com/2016/01/10/magazine/the-lawyer-who-became-duponts-worst-nightmare.html (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- 3M. Fluorochemical Use, Distribution and Release Overview, 1999. Available online: https://www.regulations.gov/document/EPA-HQ-OPPT-2002-0051-0003 (accessed on 19 July 2023).
- Oliaei, F.; Kriens, D.; Weber, R.; Watson, A. PFOS and PFC releases and associated pollution from a PFC production plant in Minnesota (USA). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 1977–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State of Minnesota. Settlement Agreement and Consent Order, 2007. Available online: https://www.pca.state.mn.us/sites/default/files/c-pfc2-11c.pdf (accessed on 19 July 2024).
- Oliaei, F.; Kriens, D.; Kessler, K. Investigation of Perfluorochemical (PFC) Contamination in Minnesota: Phase One, 2006. Available online: https://www.leg.mn.gov/archive/leg/minutes/database/84-s-1261-0-20060227-a.pdf (accessed on 18 April 2024).
- MPCA. PFAS Air and Deposition Monitoring Report, 2022. Available online: https://www.pca.state.mn.us/sites/default/files/tdr-g1-23.pdf (accessed on 26 April 2023).
- MPCA. 2007 MPCA Metro Lakes PFC Fish Data—First 10 of 30 Lakes, 2007. Available online: https://www.pca.state.mn.us/sites/default/files/pfc-metro-lakes-fish.pdf (accessed on 27 April 2024).
- MPCA. Update: Urban Lakes PFCs Study, 2008. Available online: https://www.pca.state.mn.us/sites/default/files/pfc-fishdata.pdf (accessed on 27 April 2024).
- MPCA. 2005–2008 Perfluorochemical Evaluation at Solid Waste Facilities in Minnesota Technical Evaluation and Regulatory Management Approach, 2010. Available online: https://www.pca.state.mn.us/sites/default/files/c-pfc4-01.pdf (accessed on 27 April 2023).
- Wood. Site Investigation Report: Investigation of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances at Select Source Separated Organic Material and Yard Waste Sites, Minnesota, 2019. Available online: https://www.pca.state.mn.us/sites/default/files/w-sw4-37.pdf (accessed on 26 April 2024).
- Sunding, D.L. Damage to Minnesota’s Matural Resources Resulting from 3M’s Disposal of PFCs in Washington County, MN, 2017. Available online: https://minnesotareformer.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/David-Sunding-Expert-Witness-Report-1.pdf (accessed on 20 August 2024).
- Olsen, G.W.; Mair, D.C.; Reagen, W.K.; Ellefson, M.E.; Ehresman, D.J.; Butenhoff, J.L.; Zobel, L.R. Preliminary evidence of a decline in perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) concentrations in American Red Cross blood donors. Chemosphere 2007, 68, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MPCA. East Metro | 3M PFAS Contamination. Available online: https://www.pca.state.mn.us/local-sites-and-projects/east-metro-3m-pfas-contamination#:~:text=The%203M%20chemicals%20that%20contain,its%20Cottage%20Grove%20manufacturing%20facility (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- 3M. 3M to Exit PFAS Manufacturing by the End of 2025. Available online: https://news.3m.com/2022-12-20-3M-to-Exit-PFAS-Manufacturing-by-the-End-of-2025 (accessed on 2 July 2024).
- MPCA. PFAS Testing of Minnesota Community Water Systems, 2024. Available online: https://mdh.maps.arcgis.com/apps/MapSeries/index.html?appid=63515695237f425ea7120d1aac1fd09a (accessed on 17 July 2024).
- EWG. PFAS Contamination in the U.S., 2022. Available online: https://www.ewg.org/interactive-maps/pfas_contamination/?gad_source=1&gad_campaignid=6485693431&gbraid=0AAAAAD_iHo6be2j_2aLgTUlOTJIBAEKZ5&gclid=Cj0KCQjws4fEBhD-ARIsACC3d28k9wrjaaB2hMNQt9HOFImLVuqwiSSrl2GoX8vsxrUehvXpYhoGklsaAnq3EALw_wcB (accessed on 26 April 2024).
- MDH. History of MDH Activities—Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS), 2024. Available online: https://www.health.state.mn.us/communities/environment/hazardous/topics/history.html (accessed on 17 November 2024).
- Croll, H.; Capelle, R. Cottage Grove Pilot Study Final Report, 2022. Available online: https://3msettlement.state.mn.us/sites/3msettlement/files/2023-02/c-pfc3-22.pdf (accessed on 28 April 2024).
- Minnesota Geospatial Commons. Minnesota Groundwater Contamination Atlas. Available online: https://gisdata.mn.gov/dataset/env-mn-gw-contamination-atlas (accessed on 8 July 2024).
- Young, C.J.; Mabury, S.A. Atmospheric Perfluorinated Acid Precursors: Chemistry, Occurrence, and Impacts. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 208, 1–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valsecchi, S.; Rusconi, M.; Mazzoni, M.; Viviano, G.; Pagnotta, R.; Zaghi, C.; Serrini, G.; Polesello, S. Occurrence and sources of perfluoroalkyl acids in Italian river basins. Chemosphere 2015, 129, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lu, Y.; Song, X.; Jones, K.; Sweetman, A.J.; Johnson, A.C.; Zhang, M.; Lu, X.; Su, C. Multiple crop bioaccumulation and human exposure of perfluoroalkyl substances around a mega fluorochemical industrial park, China: Implication for planting optimization and food safety. Environ. Int. 2019, 127, 671–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neely, N.; Gillespie, D.; Schauf, F.; Walsh, J. Remedial Actions at Hazardous Waste Sites: Survey and Case studies, 1981. Available online: https://nepis.epa.gov/Exe/ZyPDF.cgi/9101OX8Y.PDF?Dockey=9101OX8Y.PDF (accessed on 21 August 2024).
- Wu, Y.; Romanak, K.; Bruton, T.; Blum, A.; Venier, M. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in paired dust and carpets from childcare centers. Chemosphere 2020, 251, 126771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schellenberger, S.; Liagkouridis, I.; Awad, R.; Khan, S.; Plassmann, M.; Peters, G.; Benskin, J.P.; Cousins, I.T. An Outdoor Aging Study to Investigate the Release of Per- And Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) from Functional Textiles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 3471–3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EPA. National Overview: Facts and Figures on Materials, Wastes and Recycling. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/facts-and-figures-about-materials-waste-and-recycling/national-overview-facts-and-figures-materials (accessed on 4 July 2024).
- Lang, J.R.; Allred, B.M.; Field, J.A.; Levis, J.W.; Barlaz, M.A. National Estimate of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substance (PFAS) Release to U.S. Municipal Landfill Leachate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 2197–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, D.; Soong, T.-Y.; Tian, S. Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Landfills: Occurrence, Transformation and Treatment. Waste Manag. 2023, 155, 162–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huset, C.A.; Barlaz, M.A.; Barofsky, D.F.; Field, J.A. Quantitative determination of fluorochemicals in municipal landfill leachates. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 1380–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Cousins, I.T.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, Q. Perfluoroalkyl acids in municipal landfill leachates from China: Occurrence, fate during leachate treatment and potential impact on groundwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 524–525, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozzi, S.L.; Leang, A.L.; Rodenburg, L.A.; Chandramouli, B.; Delistraty, D.A.; Carter, C.H. PFAS in municipal landfill leachate: Occurrence, transformation, and sources. Chemosphere 2023, 334, 138924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MPCA. PFAS and Closed Landfills. Available online: https://www.pca.state.mn.us/air-water-land-climate/pfas-and-closed-landfills (accessed on 22 July 2024).
- Hamid, H.; Li, L.Y.; Grace, J.R. Review of the fate and transformation of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in landfills. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzen-Hanson, K.A.; Roberts, S.C.; Choyke, S.; Oetjen, K.; McAlees, A.; Riddell, N.; McCrindle, R.; Ferguson, P.L.; Higgins, C.P.; Field, J.A. Discovery of 40 Classes of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Historical Aqueous Film-Forming Foams (AFFFs) and AFFF-Impacted Groundwater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 2047–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, C.A.; Field, J.A. Perfluorinated Surfactants and the Environmental Implications of Their Use in Fire-Fighting Foams. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 3864–3870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding-Marjanovic, K.C.; Houtz, E.F.; Yi, S.; Field, J.A.; Sedlak, D.L.; Alvarez-Cohen, L. Aerobic Biotransformation of Fluorotelomer Thioether Amido Sulfonate (Lodyne) in AFFF-Amended Microcosms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 7666–7674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.; Harding-Marjanovic, K.C.; Houtz, E.F.; Gao, Y.; Lawrence, J.E.; Nichiporuk, R.V.; Iavarone, A.T.; Zhuang, W.-Q.; Hansen, M.; Field, J.A.; et al. Biotransformation of AFFF Component 6:2 Fluorotelomer Thioether Amido Sulfonate Generates 6:2 Fluorotelomer Thioether Carboxylate under Sulfate-Reducing Conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2018, 5, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collivignarelli, M.C.; Canato, M.; Abbà, A.; Miino, M.C. Biosolids: What are the different types of reuse? J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 238, 117844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uggetti, E.; Ferrer, I.; Nielsen, S.; Arias, C.; Brix, H.; García, J. Characteristics of biosolids from sludge treatment wetlands for agricultural reuse. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 40, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellsing, M.S.; Josefsson, S.; Hughes, A.V.; Ahrens, L. Sorption of perfluoroalkyl substances to two types of minerals. Chemosphere 2016, 159, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, R.L.; Anschutz, A.J.; Smolen, J.M.; Simcik, M.F.; Penn, R.L. The Adsorption of Perfluorooctane Sulfonate onto Sand, Clay, and Iron Oxide Surfaces. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2007, 52, 1165–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Oliver, D.P.; Kookana, R.S. A critical analysis of published data to discern the role of soil and sediment properties in determining sorption of per and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 628–629, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvaniti, O.S.; Stasinakis, A.S. Review on the occurrence, fate and removal of perfluorinated compounds during wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 524–525, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenka, S.P.; Kah, M.; Padhye, L.P. A review of the occurrence, transformation, and removal of poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in wastewater treatment plants. Water Res. 2021, 199, 117187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredriksson, F.; Eriksson, U.; Kärrman, A.; Yeung, L.W.Y. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in sludge from wastewater treatment plants in Sweden—First findings of novel fluorinated copolymers in Europe including temporal analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 846, 157406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifan, H.; Bagheri, M.; Wang, D.; Burken, J.G.; Higgins, C.P.; Liang, Y.; Liu, J.; Schaefer, C.E.; Blotevogel, J. Fate and transport of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in the vadose zone. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 771, 145427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Zeng, J.; Brusseau, M.L. A Mathematical Model for the Release, Transport, and Retention of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in the Vadose Zone. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2019WR026667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivaram, A.K.; Lee, E.; Curnow, A.; Surapaneni, A.; Kannan, K.; Megharaj, M. Uptake, accumulation, and toxicity of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in Allium cepa grown in soils amended with biosolids. Environ. Chall. 2023, 10, 100670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, M.C.S.; Lee, L.S. Sources, Fate, and Plant Uptake in Agricultural Systems of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2020, 10, 799–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisi, R.; Vamerali, T.; Manzetti, S. Accumulation of perfluorinated alkyl substances (PFAS) in agricultural plants: A review. Environ. Res. 2019, 169, 326–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Simcik, M.F.; Halbach, T.R.; Gulliver, J.S. Perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) in soils and groundwater of a U.S. metropolitan area: Migration and implications for human exposure. Water Res. 2015, 72, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Death, C.; Bell, C.; Champness, D.; Milne, C.; Reichman, S.; Hagen, T. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in livestock and game species: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 774, 144795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindstrom, A.B.; Strynar, M.J.; Delinsky, A.D.; Nakayama, S.F.; McMillan, L.; Libelo, E.L.; Neill, M.; Thomas, L. Application of WWTP biosolids and resulting perfluorinated compound contamination of surface and well water in Decatur, Alabama, USA. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 8015–8021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA. Basic Infromation About Biosolids. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/biosolids/basic-information-about-biosolids (accessed on 16 July 2024).
- Venkatesan, A.K.; Halden, R.U. National inventory of perfluoroalkyl substances in archived U.S. biosolids from the 2001 EPA National Sewage Sludge Survey. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 252–253, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moavenzadeh Ghaznavi, S.; Zimmerman, C.; Shea, M.E.; MacRae, J.D.; Peckenham, J.M.; Noblet, C.L.; Apul, O.G.; Kopec, A.D. Management of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS)-laden wastewater sludge in Maine: Perspectives on a wicked problem. Biointerphases 2023, 18, 041004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Geological Survey. One Hundred Small Streams in the Midwest Were Tested for Pesticides During the 2013 Growing Season and Found to Contain, on Average, 52 Pesticides per Stream. Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/news/national-news-release/pesticides-prevalent-midwestern-streams#:~:text=%E2%80%9CAbout%20150%20million%20pounds%20of,lead%20scientist%20for%20the%20study (accessed on 16 July 2024).
- Gaines, L.G.T. Historical and current usage of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS): A literature review. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2023, 66, 353–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasee, S.; McDermett, K.; Kumar, N.; Guelfo, J.; Payton, P.; Yang, Z.; Anderson, T.A. Targeted analysis and Total Oxidizable Precursor assay of several insecticides for PFAS. J. Hazard. Mater. Lett. 2022, 3, 100067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; French, D. Verification Analysis for PFAS in Pesticide Products, 2023. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/system/files/documents/2023-05/BEAD%20PFAS%20Study%20Results%202023.pdf (accessed on 23 July 2024).
- Guida, Y.; Torres, F.B.M.; Barizon, R.R.M.; Assalin, M.R.; Rosa, M.A. Confirming sulfluramid (EtFOSA) application as a precursor of perfluorooctanesulfonic acid (PFOS) in Brazilian agricultural soils. Chemosphere 2023, 325, 138370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNEP. SC-4/17: Listing of Perfluorooctane Sulfonic Acid, Its Salts and Perfluorooctane Sulfonyl Fluoride, 2009. Available online: http://www.pops.int/Portals/0/download.aspx?d=UNEP-POPS-COP.4-SC-4-17.English.pdf (accessed on 23 July 2024).
- Löfstedt Gilljam, J.; Leonel, J.; Cousins, I.T.; Benskin, J.P. Is Ongoing Sulfluramid Use in South America a Significant Source of Perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS)? Production Inventories, Environmental Fate, and Local Occurrence. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T. Results of EPA’s Analytical Chemistry Branch Laboratory Study of PFAS Leaching from Fluorinated HDPE Containers, 2022. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/system/files/documents/2022-09/EPA%20PFAS%20Container%20Leaching%20Study%2008122022_0.pdf (accessed on 26 July 2024).
- Ratcliffe, M.; Burd, C.; Holder, K.; Fields, A. Defining Rural at the U.S. Census Bureau, 2016. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Michael-Ratcliffe-2/publication/311533270_Defining_Rural_at_the_US_Census_Bureau/links/584aad3708aeb19dcb758910/Defining-Rural-at-the-US-Census-Bureau.pdf (accessed on 22 August 2024).
- Simcik, M.F.; Dorweiler, K.J. Ratio of Perfluorochemical Concentrations as a Tracer of Atmospheric Deposition to Surface Waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 8678–8683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MnDOT. Minnesota Airports. Available online: https://www.dot.state.mn.us/aero/operations/minnesotaairports.html (accessed on 30 July 2024).
- Ahrens, L.; Bundschuh, M. Fate and effects of poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances in the aquatic environment: A review. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2014, 33, 1921–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.W.; Mabury, S.A.; Solomon, K.R.; Muir, D.C.G. Bioconcentration and tissue distribution of perfluorinated acids in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2002, 22, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, L.; Taniyasu, S.; Yeung, L.W.Y.; Yamashita, N.; Lam, P.K.S.; Ebinghaus, R. Distribution of polyfluoroalkyl compounds in water, suspended particulate matter and sediment from Tokyo Bay, Japan. Chemosphere 2010, 79, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidu, R.; Nadebaum, P.; Fang, C.; Cousins, I.; Pennell, K.; Conder, J.; Newell, C.J.; Longpré, D.; Warner, S.; Crosbie, N.D.; et al. Per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFAS): Current status and research needs. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 19, 100915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, L. Polyfluoroalkyl compounds in the aquatic environment: A review of their occurrence and fate. J. Environ. Monit. 2011, 13, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallenborn, R.; Berger, U.; Järnberg, U. Perfluorinated Alkylated Substances (PFAS) in the Nordic Environment; Nordic Council of Ministers’ Publishing House: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2004; ISBN 9789289310512. [Google Scholar]
- Kwok, K.Y.; Yamazaki, E.; Yamashita, N.; Taniyasu, S.; Murphy, M.B.; Horii, Y.; Petrick, G.; Kallerborn, R.; Kannan, K.; Murano, K.; et al. Transport of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) from an arctic glacier to downstream locations: Implications for sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 447, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prevedouros, K.; Cousins, I.T.; Buck, R.C.; Korzeniowski, S.H. Sources, Fate and Transport of Perfluorocarboxylates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, K.Y.; Taniyasu, S.; Yeung, L.W.Y.; Murphy, M.B.; Lam, P.K.S.; Horii, Y.; Kannan, K.; Petrick, G.; Sinha, R.K.; Yamashita, N. Flux of Perfluorinated Chemicals through Wet Deposition in Japan, the United States, And Several Other Countries. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 7043–7049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Jin, Y.; Quan, X.; Sasaki, K.; Saito, N.; Nakayama, S.F.; Sato, I.; Tsuda, S. Perfluorosulfonates and perfluorocarboxylates in snow and rain in Dalian, China. Environ. Int. 2009, 35, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, L.; Li, M.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Munoz, G.; Sun, H. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in precipitation from mainland China: Contributions of unknown precursors and short-chain (C2-C3) perfluoroalkyl carboxylic acids. Water Res. 2019, 153, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahrens, L.; Yamashita, N.; Yeung, L.W.Y.; Taniyasu, S.; Horii, Y.; Lam, P.K.S.; Ebinghaus, R. Partitioning behavior of per- and polyfluoroalkyl compounds between pore water and sediment in two sediment cores from Tokyo Bay, Japan. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 6969–6975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zheng, H.; Wang, T.; Cai, M.; Wang, P. Perfluoroalkyl acids in surface seawater from the North Pacific to the Arctic Ocean: Contamination, distribution and transportation. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 238, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Lee, L.S. Solubility and Sorption by Soils of 8:2 Fluorotelomer Alcohol in Water and Cosolvent Systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 7535–7540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, C.P.; Luthy, R.G. Sorption of Perfluorinated Surfactants on Sediments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 7251–7256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigus, P.; Tobiszewski, M.; Namieśnik, J. Historical records of organic pollutants in sediment cores. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 78, 26–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Zheng, M.; Liang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gao, W.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, G. Legacy and emerging per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in sediments from the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea: Occurrence, source apportionment and environmental risk assessment. Chemosphere 2021, 282, 131042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, K.; Silva, M.R.; Klaper, R. Distribution and effects of branched versus linear isomers of PFOA, PFOS, and PFHxS: A review of recent literature. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 139186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sammut, G.; Sinagra, E.; Sapiano, M.; Helmus, R.; Voogt, P.d. Perfluoroalkyl substances in the Maltese environment—(II) sediments, soils and groundwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 682, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pétré, M.-A.; Genereux, D.P.; Koropeckyj-Cox, L.; Knappe, D.R.U.; Duboscq, S.; Gilmore, T.E.; Hopkins, Z.R. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substance (PFAS) Transport from Groundwater to Streams near a PFAS Manufacturing Facility in North Carolina, USA. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 5848–5856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, K.; Alygizakis, N.; Androulakakis, A.; Galani, A.; Aalizadeh, R.; Thomaidis, N.S.; Slobodnik, J. Target and suspect screening of 4777 per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in river water, wastewater, groundwater and biota samples in the Danube River Basin. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 436, 129276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepburn, E.; Madden, C.; Szabo, D.; Coggan, T.L.; Clarke, B.; Currell, M. Contamination of groundwater with per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) from legacy landfills in an urban re-development precinct. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 248, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Jiao, X.-C.; Gai, N.; Li, X.-J.; Wang, X.-C.; Lu, G.-H.; Piao, H.-T.; Rao, Z.; Yang, Y.-L. Perfluorinated compounds in soil, surface water, and groundwater from rural areas in eastern China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 211, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, K.L.; Aucoin, M.D.; Larsen, B.S.; Kaiser, M.A.; Hartten, A.S. Transport of ammonium perfluorooctanoate in environmental media near a fluoropolymer manufacturing facility. Chemosphere 2007, 67, 2011–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lu, Y.; Wang, T.; Wang, P.; Li, Q.; Johnson, A.C.; Sarvajayakesavalu, S.; Sweetman, A.J. Risk assessment and source identification of perfluoroalkyl acids in surface and ground water: Spatial distribution around a mega-fluorochemical industrial park, China. Environ. Int. 2016, 91, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Liu, S.; Zhou, J.L.; Zheng, C.; Weifeng, J.; Chen, B.; Zhang, T.; Qiu, W. PFAS and their substitutes in groundwater: Occurrence, transformation and remediation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 412, 125159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.-M.; Vieira, V.M.; Ryan, P.B.; Detwiler, R.; Sanders, B.; Steenland, K.; Bartell, S.M. Environmental Fate and Transport Modeling for Perfluorooctanoic Acid Emitted from the Washington Works Facility in West Virginia. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 1435–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.M.; Bharat, G.K.; Tayal, S.; Larssen, T.; Bečanová, J.; Karásková, P.; Whitehead, P.G.; Futter, M.N.; Butterfield, D.; Nizzetto, L. Perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in river and ground/drinking water of the Ganges River basin: Emissions and implications for human exposure. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 208, 704–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Szostek, B.; McCausland, P.K.; Wolstenholme, B.W.; Lu, X.; Wang, N.; Buck, R.C. 6:2 and 8:2 Fluorotelomer Alcohol Anaerobic Biotransformation in Digester Sludge from a WWTP under Methanogenic Conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 4227–4235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Lu, X.; Wang, N.; Buck, R.C. Biotransformation potential of 6:2 fluorotelomer sulfonate (6:2 FTSA) in aerobic and anaerobic sediment. Chemosphere 2016, 154, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebert, S.; Burke, J.; Faures, J.M.; Frenken, K.; Hoogeveen, J.; Döll, P.; Portmann, F.T. Groundwater use for irrigation—A global inventory. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 14, 1863–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokranov, A.K.; LeBlanc, D.R.; Pickard, H.M.; Ruyle, B.J.; Barber, L.B.; Hull, R.B.; Sunderland, E.M.; Vecitis, C.D. Surface-water/groundwater boundaries affect seasonal PFAS concentrations and PFAA precursor transformations. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2021, 23, 1893–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tombácz, E.; Szekeres, M. Surface charge heterogeneity of kaolinite in aqueous suspension in comparison with montmorillonite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2006, 34, 105–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qafoku, N.P.; van Ranst, E.; Noble, A.; Baert, G. Variable Charge Soils: Their Mineralogy, Chemistry and Management. Adv. Agron. 2004, 84, 159–215. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Chorover, J. Adsorption of perfluorooctanoic acid and perfluorooctanesulfonic acid to iron oxide surfaces as studied by flow-through ATR-FTIR spectroscopy. Environ. Chem. 2012, 9, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Deng, S.; Bei, Y.; Huang, Q.; Wang, B.; Huang, J.; Yu, G. Adsorption behavior and mechanism of perfluorinated compounds on various adsorbents: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 274, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Munoz, G.; Vo Duy, S.; Sauvé, S.; Liu, J. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances in Contaminated Soil and Groundwater at Airports: A Canadian Case Study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 885–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washington, J.W.; Yoo, H.; Ellington, J.J.; Jenkins, T.M.; Libelo, E.L. Concentrations, Distribution, and Persistence of Perfluoroalkylates in Sludge-Applied Soils near Decatur, Alabama, USA. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 8390–8396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baduel, C.; Mueller, J.F.; Rotander, A.; Corfield, J.; Gomez-Ramos, M.-J. Discovery of novel per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) at a fire fighting training ground and preliminary investigation of their fate and mobility. Chemosphere 2017, 185, 1030–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickerson, A.; Rodowa, A.E.; Adamson, D.T.; Field, J.A.; Kulkarni, P.R.; Kornuc, J.J.; Higgins, C.P. Spatial Trends of Anionic, Zwitterionic, and Cationic PFASs at an AFFF-Impacted Site. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, H.; Washington, J.W.; Ellington, J.J.; Jenkins, T.M.; Neill, M.P. Concentrations, Distribution, and Persistence of Fluorotelomer Alcohols in Sludge-Applied Soils near Decatur, Alabama, USA. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 8397–8402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Szostek, B.; Buck, R.C.; Folsom, P.W.; Sulecki, L.M.; Gannon, J.T. 8-2 fluorotelomer alcohol aerobic soil biodegradation: Pathways, metabolites, and metabolite yields. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejia-Avendaño, S.; Vo Duy, S.; Sauvé, S.; Liu, J. Generation of Perfluoroalkyl Acids from Aerobic Biotransformation of Quaternary Ammonium Polyfluoroalkyl Surfactants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 9923–9932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, L.; Yeung, L.W.Y.; Taniyasu, S.; Lam, P.K.S.; Yamashita, N. Partitioning of perfluorooctanoate (PFOA), perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctane sulfonamide (PFOSA) between water and sediment. Chemosphere 2011, 85, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-C.; Lo, S.-L.; Li, N.-H.; Lee, Y.-C.; Kuo, J. Sorption of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) onto wetland soils. Desalination Water Treat. 2013, 51, 7469–7475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, C.; Yu, Y.; Han, J. Sorption of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) on marine sediments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 902–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Fang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Liao, X.; Zou, J.; Yuan, B.; Sun, W. Adsorption of perfluorinated acids onto soils: Kinetics, isotherms, and influences of soil properties. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milinovic, J.; Lacorte, S.; Vidal, M.; Rigol, A. Sorption behaviour of perfluoroalkyl substances in soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 511, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, C.; Jia, C.; Pan, G. Effect of salinity and sediment characteristics on the sorption and desorption of perfluorooctane sulfonate at sediment-water interface. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 1343–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, W.; Navarro, D.A.; Du, J.; Ying, G.; Yang, B.; McLaughlin, M.J.; Kookana, R.S. Increasing ionic strength and valency of cations enhance sorption through hydrophobic interactions of PFAS with soil surfaces. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 817, 152975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, Y.; Brusseau, M.L.; Chen, W.; Yan, N.; Fu, X.; Lin, X. Adsorption of PFOA at the Air—Water Interface during Transport in Unsaturated Porous Media. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 7745–7753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brusseau, M.L. Assessing the potential contributions of additional retention processes to PFAS retardation in the subsurface. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613–614, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter Anderson, R.; Adamson, D.T.; Stroo, H.F. Partitioning of poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances from soil to groundwater within aqueous film-forming foam source zones. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2019, 220, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gellrich, V.; Stahl, T.; Knepper, T.P. Behavior of perfluorinated compounds in soils during leaching experiments. Chemosphere 2012, 87, 1052–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guelfo, J.L.; Higgins, C.P. Subsurface Transport Potential of Perfluoroalkyl Acids at Aqueous Film-Forming Foam (AFFF)-Impacted Sites. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 4164–4171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatton, J.; Holton, C.; DiGuiseppi, B. Occurrence and behavior of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances from aqueous film-forming foam in groundwater systems. Remediat. J. 2018, 28, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechner, M.; Knapp, H. Carryover of Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) and Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) from Soil to Plant and Distribution to the Different Plant Compartments Studied in Cultures of Carrots (Daucus carota ssp. Sativus), Potatoes (Solanum tuberosum), and Cucumbers (Cucumis sativus). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 11011–11018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, B.; Li, L.; Zhang, H.; Ma, Y.; Shan, X.-Q.; Zhang, S. Field study on the uptake and translocation of perfluoroalkyl acids (PFAAs) by wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) grown in biosolids-amended soils. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 184, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, T.; Heyn, J.; Thiele, H.; Hüther, J.; Failing, K.; Georgii, S.; Brunn, H. Carryover of Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) and Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) from Soil to Plants. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2009, 57, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Tevlin, A.G.; Mabury, S.A.; Mabury, S.A. Fate of Polyfluoroalkyl Phosphate Diesters and Their Metabolites in Biosolids-Applied Soil: Biodegradation and Plant Uptake in Greenhouse and Field Experiments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Ren, C.; Wang, B.; Sun, H.; Alder, A.C.; Kannan, K. Multimedia Distribution and Transfer of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) Surrounding Two Fluorochemical Manufacturing Facilities in Fuxin, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 8263–8271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, C.; Fryer, M.; Grosso, A. Plant Uptake of Non-Ionic Organic Chemicals. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, G.; Wei, M.; Zhu, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y. Concentration profiles and spatial distribution of perfluoroalkyl substances in an industrial center with condensed fluorochemical facilities. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 490, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvesitadze, E.; Sadunishvili, T.; Kvesitadze, G. Mechanisms of Organic Contaminants Uptake and Degradation in Plants. Int. J. Biol. Biomol. Agric. Food Biotechnol. Eng. 2009, 2009, 361–371. [Google Scholar]
- Briskin, D.P. Membranes and Transport Systems in Plants: An Overview. Weed Sci. 1994, 42, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, B.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Hu, X.; Huang, H.; Zhang, S. The roles of protein and lipid in the accumulation and distribution of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) in plants grown in biosolids-amended soils. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 216, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, H.; Wang, Q.; Chen, H.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Alder, A.C. Uptake mechanisms of perfluoroalkyl acids with different carbon chain lengths (C2-C8) by wheat (Triticum acstivnm L.). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 654, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, W.; Sun, H.; Song, M.; Jiang, L.; Li, Y.; Lu, W.; Ying, G.-G.; Luo, C.; Zhang, G. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in the soil-plant system: Sorption, root uptake, and translocation. Environ. Int. 2021, 156, 106642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaine, A.C.; Rich, C.D.; Sedlacko, E.M.; Hundal, L.S.; Kumar, K.; Lau, C.; Mills, M.A.; Harris, K.M.; Higgins, C.P. Perfluoroalkyl Acid Distribution in Various Plant Compartments of Edible Crops Grown in Biosolids-Amended Soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 7858–7865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, C.E.; LeFevre, G.H.; Timofte, A.E.; Hussain, F.A.; Sattely, E.S.; Luthy, R.G. Competing mechanisms for perfluoroalkyl acid accumulation in plants revealed using an Arabidopsis model system. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2015, 35, 1138–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.Q.; Wang, M.; He, Q.; Niu, X.; Liang, Y. Distribution of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in aquatic plant-based systems: From soil adsorption and plant uptake to effects on microbial community. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 257, 113575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesmeister, L.; Lange, F.T.; Breuer, J.; Biegel-Engler, A.; Giese, E.; Scheurer, M. Extending the knowledge about PFAS bioaccumulation factors for agricultural plants: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 766, 142640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krippner, J.; Falk, S.; Brunn, H.; Georgii, S.; Schubert, S.; Stahl, T. Accumulation Potentials of Perfluoroalkyl Carboxylic Acids (PFCAs) and Perfluoroalkyl Sulfonic Acids (PFSAs) in Maize (Zea mays). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 3646–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krippner, J.; Brunn, H.; Falk, S.; Georgii, S.; Schubert, S.; Stahl, T. Effects of chain length and pH on the uptake and distribution of perfluoroalkyl substances in maize (Zea mays). Chemosphere 2014, 94, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, B.; Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Hu, X.; Shan, X.-Q.; Zhang, S. Mechanistic studies of perfluorooctane sulfonate, perfluorooctanoic acid uptake by maize (Zea mays L. cv. TY2). Plant Soil 2013, 370, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, E.R.; Bräunig, J.; Janik, L.J.; Navarro, D.A.; Kookana, R.S.; Mueller, J.F.; McLaughlin, M.J. An investigation into the long-term binding and uptake of PFOS, PFOA and PFHxS in soil—Plant systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 404, 124065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ateia, M.; Maroli, A.; Tharayil, N.; Karanfil, T. The overlooked short- and ultrashort-chain poly- and perfluorinated substances: A review. Chemosphere 2019, 220, 866–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusseau, M.L.; Anderson, R.H.; Guo, B. PFAS concentrations in soils: Background levels versus contaminated sites. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 140017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sun, J.; Li, P. Exposure routes, bioaccumulation and toxic effects of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) on plants: A critical review. Environ. Int. 2022, 158, 106891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeWitt, J.C. Toxicological Effects of Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; ISBN 978-3-319-15518-0. [Google Scholar]
- Pizzurro, D.M.; Seeley, M.; Kerper, L.E.; Beck, B.D. Interspecies differences in perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) toxicokinetics and application to health-based criteria. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 106, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ylinen, M.; Auriola, S. Tissue Distribution and Elimination of Perfluorodecanoic Acid in the Rat after Single Intraperitoneal Administration. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1990, 66, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, P.D.; Hu, W.; Coen, W.d.; Newsted, J.L.; Giesy, J.P. Binding of perfluorinated fatty acids to serum proteins. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2003, 22, 2639–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drew, R.; Hagen, T.G.; Champness, D. Accumulation of PFAS by livestock—Determination of transfer factors from water to serum for cattle and sheep in Australia. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2021, 38, 1897–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seacat, A.M.; Thomford, P.J.; Hansen, K.J.; Olsen, G.W.; Case, M.T.; Butenhoff, J.L. Subchronic toxicity studies on perfluorooctanesulfonate potassium salt in cynomolgus monkeys. Toxicol. Sci. 2002, 68, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlouskova, V.; Hradkova, P.; Poustka, J.; Brambilla, G.; Filipps, S.P.d.; D’Hollander, W.; Bervoets, L.; Herzke, D.; Huber, S.; Voogt, P.d.; et al. Occurrence of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in various food items of animal origin collected in four European countries. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2013, 30, 1918–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasecnaja, E.; Bartkevics, V.; Zacs, D. Occurrence of selected per- and polyfluorinated alkyl substances (PFASs) in food available on the European market—A review on levels and human exposure assessment. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesfin Tefera, Y.; Gaskin, S.; Mitchell, K.; Springer, D.; Mills, S.; Pisaniello, D. Food grown on fire stations as a potential pathway for firefighters’ exposure to per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). Environ. Int. 2022, 168, 107455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Cui, Q.; Sheng, N.; Yeung, L.W.Y.; Guo, Y.; Sun, Y.; Dai, J. First Report on the Occurrence and Bioaccumulation of Hexafluoropropylene Oxide Trimer Acid: An Emerging Concern. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 9553–9560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brendel, S.; Fetter, É.; Staude, C.; Vierke, L.; Biegel-Engler, A. Short-chain perfluoroalkyl acids: Environmental concerns and a regulatory strategy under REACH. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2018, 30, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA. Perfluoroalkylated substances in food: Occurrence and dietary exposure. EFSA J. 2012, 10, 2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances National Primary Drinking Water Regulation. Available online: https://www.regulations.gov/document/EPA-HQ-OW-2022-0114-0027 (accessed on 16 July 2024).
- Ramírez Carnero, A.; Lestido-Cardama, A.; Vazquez Loureiro, P.; Barbosa-Pereira, L.; Rodríguez Ber-naldo de Quirós, A.; Sendón, R. Presence of Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Food Contact Materials (FCM) and Its Migration to Food. Foods 2021, 10, 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DACF. PFAS Response, 2021. Available online: https://www.maine.gov/dacf/ag/pfas/pfas-response.shtml (accessed on 3 April 2024).
- Schrenk, D.; Bignami, M.; Bodin, L.; Chipman, J.K.; Del Mazo, J.; Grasl-Kraupp, B.; Hogstrand, C.; Hoo-genboom, L.R.; Leblanc, J.-C.; Nebbia, C.S.; et al. Risk to human health related to the presence of perfluoroalkyl substances in food. EFSA J. 2020, 18, e06223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MDA. Products with Added PFAS, 2023. Available online: https://www.mda.state.mn.us/environment-sustainability/products-added-pfas (accessed on 3 April 2024).
- MPCA. Minnesota’s PFAS Blueprint, 2021. Available online: https://www.pca.state.mn.us/sites/default/files/p-gen1-22.pdf (accessed on 8 August 2024).
- EPA. PFAS Strategic Roadmap: EPA’s Commitments to Action 2021–2024. 2021. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/system/files/documents/2021-10/pfas-roadmap_final-508.pdf (accessed on 3 May 2024).
- DEED. Food & Agriculture: We Hope You’re Hungry. There’s a Lot to Take in. Available online: https://mn.gov/deed/joinusmn/key-industries/food-agriculture/ (accessed on 17 July 2024).
- Evich, M.G.; Davis, M.J.B.; McCord, J.P.; Acrey, B.; Awkerman, J.A.; Knappe, D.R.U.; Lindstrom, A.B.; Speth, T.F.; Tebes-Stevens, C.; Strynar, M.J.; et al. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in the environment. Science 2022, 375, eabg9065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MPCA. PFAS Use Prohibitions, 2023. Available online: https://www.pca.state.mn.us/air-water-land-climate/pfas-use-prohibitions (accessed on 8 April 2024).
- DACF. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS), 2023. Available online: https://www.maine.gov/dep/spills/topics/pfas/ (accessed on 8 April 2024).
- University of Maine. Cooperative Extension: Agriculture: Guide to Investigating PFAS Risk on Your Farm, 2022. Available online: https://extension.umaine.edu/agriculture/guide-to-investigating-pfas-risk-on-your-farm/ (accessed on 3 April 2024).
- Hu, X.C.; Andrews, D.Q.; Lindstrom, A.B.; Bruton, T.A.; Schaider, L.A.; Grandjean, P.; Lohmann, R.; Carignan, C.C.; Blum, A.; Balan, S.A.; et al. Detection of Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in U.S. Drinking Water Linked to Industrial Sites, Military Fire Training Areas, and Wastewater Treatment Plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2016, 3, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Name | Abbreviation | Chemical Formula | Structural Formulas |
|---|---|---|---|
| Perfluorobutanoic acid | PFBA | C4HF7O2 | 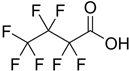 |
| Perfluorobutanesulfonic acid | PFBS | C4HF9O3S | 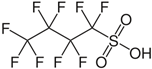 |
| Perfluorohexanoic acid | PFHxA | C6HF11O2 | 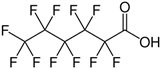 |
| Perfluorohexanesulfonic acid | PFHxS | C6HF13O3S | 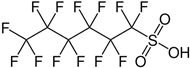 |
| Perfluorooctanoic acid | PFOA | C8HF15O2 | 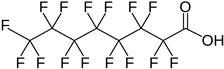 |
| Perfluorooctanesulfonic acid | PFOS | C8HF17O3S | 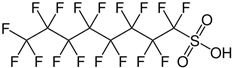 |
| 6:2-Fluorotelomersulfonic acid | 6:2 FTS | C8H5F13O3S |  |
| Hexafluoropropylene oxide dimer acid * | HFPO-DA * | C6HF11O3 | 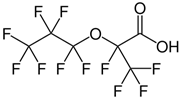 |
| 6:2 chlorinated polyfluoroalkyl ether sulfonate | F-53B | C8ClF16KO4S | 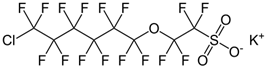 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reetz, S.; Tallaksen, J.; Larson, J.; Wetter, C. Making the Connection Between PFASs and Agriculture Using the Example of Minnesota, USA: A Review. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1676. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15151676
Reetz S, Tallaksen J, Larson J, Wetter C. Making the Connection Between PFASs and Agriculture Using the Example of Minnesota, USA: A Review. Agriculture. 2025; 15(15):1676. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15151676
Chicago/Turabian StyleReetz, Sven, Joel Tallaksen, John Larson, and Christof Wetter. 2025. "Making the Connection Between PFASs and Agriculture Using the Example of Minnesota, USA: A Review" Agriculture 15, no. 15: 1676. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15151676
APA StyleReetz, S., Tallaksen, J., Larson, J., & Wetter, C. (2025). Making the Connection Between PFASs and Agriculture Using the Example of Minnesota, USA: A Review. Agriculture, 15(15), 1676. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15151676






