-
 Design and Characterization of Yeast Protein–Polysaccharide Bioink Blends for 3D Printing
Design and Characterization of Yeast Protein–Polysaccharide Bioink Blends for 3D Printing -
 Chemically Modified Starch Films with Menthol or Sulfobetaine as Antimicrobial Agents for Active Packaging Applications
Chemically Modified Starch Films with Menthol or Sulfobetaine as Antimicrobial Agents for Active Packaging Applications -
 Shedding Light on Carob Seeds: A Non-Destructive Approach to Assess Dehusking Efficiency Using Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy and Kubelka–Munk Theory
Shedding Light on Carob Seeds: A Non-Destructive Approach to Assess Dehusking Efficiency Using Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy and Kubelka–Munk Theory -
 Wheat Hydrocolloids and Their Importance for Brewing
Wheat Hydrocolloids and Their Importance for Brewing -
 Gallic Acid Functionalization Improves the Pharmacological Profile of Fucoidan B: A Polysaccharide with Antioxidant Properties
Gallic Acid Functionalization Improves the Pharmacological Profile of Fucoidan B: A Polysaccharide with Antioxidant Properties
Journal Description
Polysaccharides
Polysaccharides
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on all aspects of the science of polysaccharides and their derivatives, published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within ESCI (Web of Science), Scopus, FSTA, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 36.4 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 4.5 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q1 (Polymer Science) / CiteScore - Q1 (Engineering (miscellaneous))
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- Journal Cluster of Polymer and Macromolecular Science: Polymers, Gels, Polysaccharides, Textiles, Macromol, Microplastics and Adhesives.
Impact Factor:
5.5 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
5.2 (2024)
Latest Articles
Development and Evaluation of Modified Dioscorea hispida Starch as a Sustainable Super-Disintegrant for Immediate-Release Tablets
Polysaccharides 2025, 6(4), 109; https://doi.org/10.3390/polysaccharides6040109 - 1 Dec 2025
Abstract
►
Show Figures
This study developed a sustainable super-disintegrant derived from Dioscorea hispida Dennst. var. hispida starch for use in immediate-release pharmaceutical tablets. Native starch (NS) was extracted and chemically modified via carboxymethylation to obtain carboxymethyl starch (CMS), followed by phosphate cross-linked to yield modified starch
[...] Read more.
This study developed a sustainable super-disintegrant derived from Dioscorea hispida Dennst. var. hispida starch for use in immediate-release pharmaceutical tablets. Native starch (NS) was extracted and chemically modified via carboxymethylation to obtain carboxymethyl starch (CMS), followed by phosphate cross-linked to yield modified starch (MS). Physicochemical properties demonstrated that MS exhibited superior water uptake, swelling, and viscosity compared to NS and CMS. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) revealed smaller and more uniform granules in MS, confirming enhanced structural modification. Preliminary tablet trials with dicalcium phosphate showed that 4% w/w MS achieved the fastest disintegration (16.5 s). In paracetamol tablets prepared by wet granulation, MS significantly improved hydration and disintegration performance relative to NS and CMS. Although commercial sodium starch glycolate (SSG) provided slightly faster disintegration, dissolution profiles of tablets containing MS and SSG were statistically equivalent (f1 = 7, f2 = 63), confirming comparable efficacy. Porosity analysis using synchrotron radiation X-ray tomography (SR-XTM) indicated that wet-granulated tablets possessed higher intra- and inter-granular porosity than direct compression tablets, facilitating rapid water penetration and disintegration. In contrast, denser direct compression tablets exhibited greater friability and lower mechanical integrity. Modified Dioscorea hispida starch demonstrated excellent disintegration efficiency, eco-friendliness, and local availability, presenting a promising natural alternative to synthetic super-disintegrants in immediate-release tablet formulations.
Full article
Open AccessReview
Polysaccharide-Based Drug Delivery Systems in Pediatrics: Addressing Age-Specific Challenges and Therapeutic Applications
by
Anđelka Račić, Biljana Gatarić, Valentina Topić Vučenović and Aneta Stojmenovski
Polysaccharides 2025, 6(4), 108; https://doi.org/10.3390/polysaccharides6040108 - 1 Dec 2025
Abstract
Pediatric drug delivery presents unique challenges due to physiological and pharmacological differences across age groups, requiring specialized formulation approaches beyond simple dose adjustments of adult medications. This review synthesizes recent advances in polysaccharide-based pediatric drug delivery and highlights novel findings that may accelerate
[...] Read more.
Pediatric drug delivery presents unique challenges due to physiological and pharmacological differences across age groups, requiring specialized formulation approaches beyond simple dose adjustments of adult medications. This review synthesizes recent advances in polysaccharide-based pediatric drug delivery and highlights novel findings that may accelerate clinical translation. It summarizes how chitosan, alginate, hyaluronic acid, dextran, modified starches, and other polysaccharides are engineered into nanoparticles, hydrogels, films, and orodispersible/mini-tablet formulations to improve stability, bioavailability, taste masking, and controlled release across neonates to adolescents. These systems can accommodate developmental variations in absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion processes across pediatric subpopulations, with particular emphasis on oral and alternative administration routes. Evidence supporting unexpectedly high acceptability of mini-tablets, successful integration of modified polysaccharides in 3D-printed personalized low-dose therapies, and the emergence of blood–brain barrier-penetrating and RGD-functionalized polysaccharide nanocarriers for pediatric oncology are emphasized as novel, clinically relevant trends. This review also addresses regulatory considerations, safety profiles, and future perspectives. By integrating developmental insights with innovative formulation strategies, polysaccharide polymers offer promising solutions to improve medication adherence, safety, and efficacy across the pediatric age spectrum.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Current Opinion in Polysaccharides)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessCommunication
GC-MS Analysis of Liposoluble Components from Six Kinds of Bast Fibers and Correlative Study on Their Antibacterial Activity
by
Xiang Zhou, Xiangyuan Feng, Lifeng Cheng, Guoguo Xi, Yuqin Hu, Si Tan, Wei Zhou, Zishu Chen, Zhenghong Peng, Shengwen Duan and Qi Yang
Polysaccharides 2025, 6(4), 107; https://doi.org/10.3390/polysaccharides6040107 - 29 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study systematically investigated the liposoluble components and their potential correlation with antibacterial activity in six bast fiber varieties—Apocynum venetum, Corchorus capsularis, Hibiscus cannabinus, Linum usitatissimum, Cannabis sativa, and Boehmeria nivea—using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). The
[...] Read more.
This study systematically investigated the liposoluble components and their potential correlation with antibacterial activity in six bast fiber varieties—Apocynum venetum, Corchorus capsularis, Hibiscus cannabinus, Linum usitatissimum, Cannabis sativa, and Boehmeria nivea—using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). The analysis identified a range of compounds including alkanes, phenols, sterols, esters, and triterpenoids, with notable compositional differences among the fibers. Tetracontane was predominant in A. venetum (40.39%) and H. cannabinus (22.47%), while γ-sitosterol was highest in C. capsularis (12.80%). L. usitatissimum was rich in n-hexadecanoic acid (9.16%), C. sativa in heptacosanal (8.96%), and B. nivea in both tetracontane (45.42%) and tetracosane (10.09%). Based on existing literature, components such as 2,4-di-tert-butylphenol, γ-sitosterol, n-hexadecanoic acid, lupeol, and betulin were inferred as key antibacterial constituents. A comprehensive review of reported antimicrobial activities revealed distinct antibacterial spectra and intensities across the varieties, aligning with their unique liposoluble profiles. This study provides a systematic chemical profile of bast fibers and offers a predictive assessment of their antibacterial potential. The findings lay a chemical foundation for future targeted research and development of antibacterial materials derived from specific bast fiber varieties.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Advances in Succinoglycan-Based Biomaterials: Structural Features, Functional Derivatives, and Multifunctional Applications
by
Kyungho Kim, Jae-pil Jeong and Seunho Jung
Polysaccharides 2025, 6(4), 106; https://doi.org/10.3390/polysaccharides6040106 - 28 Nov 2025
Abstract
Succinoglycan (SG), a rhizobial exopolysaccharide produced by Sinorhizobium meliloti, has attracted increasing attention as a sustainable biomaterial due to its unique molecular structure and versatile physicochemical properties. Over the past decade, an expanding number of studies have explored SG in biomedical, pharmaceutical,
[...] Read more.
Succinoglycan (SG), a rhizobial exopolysaccharide produced by Sinorhizobium meliloti, has attracted increasing attention as a sustainable biomaterial due to its unique molecular structure and versatile physicochemical properties. Over the past decade, an expanding number of studies have explored SG in biomedical, pharmaceutical, and materials-science contexts; however, a comprehensive understanding linking its biosynthetic mechanisms, structural features, chemical modifications, and functional performances has not yet been systematically summarized. This review therefore aims to bridge this gap by providing an integrated overview of recent advances in SG research from biosynthesis and molecular design to emerging multifunctional applications, while highlighting the structure, property, and function correlations that underpin its material performance. This review summarizes recent advances in SG biosynthesis, structural characterization, chemical modification, and multifunctional applications. Progress in oxidation, succinylation, and phenolic grafting has yielded derivatives with remarkably enhanced rheological stability, antioxidant capacity, antibacterial activity, and multi-stimuli responsiveness. These developments have supported the creation of biodegradable and bioactive smart films possessing superior barrier, mechanical, and optical properties, thereby extending their potential use in bio-medical and biotechnological applications such as food packaging and wound dressings. In parallel, SG-based hydrogels exhibit self-healing, adhesive, and injectable characteristics with tunable multi-stimuli responsiveness, offering innovative platforms for con-trolled drug delivery and tissue engineering. Despite these advances, industrial translation remains hindered by challenges including the need for scalable fermentation, reproducible quality control, and standardized modification protocols to ensure batch-to-batch consistency. Overall, the structural tunability and multifunctionality of SG highlight its promise as a next-generation platform for polysaccharide-based biomaterials.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Current Opinion in Polysaccharides)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Optimization of Mono- and Disaccharide Extraction from Cocoa pod Husk
by
Edna Elena Suárez-Patlán, Teodoro Espinosa-Solares, José Enrique Herbert-Pucheta, Holber Zuleta-Prada and Emanuel Hernández-Núñez
Polysaccharides 2025, 6(4), 105; https://doi.org/10.3390/polysaccharides6040105 - 25 Nov 2025
Abstract
Cocoa pod husk (CPH) is a potential material to produce value-added products. The objective of this study was to optimize the microwave-assisted hydrothermal pretreatment (MA-HTP) of CPH and CPH hemicellulose (HMC-CPH) using only water as the extraction medium, in combination with response surface
[...] Read more.
Cocoa pod husk (CPH) is a potential material to produce value-added products. The objective of this study was to optimize the microwave-assisted hydrothermal pretreatment (MA-HTP) of CPH and CPH hemicellulose (HMC-CPH) using only water as the extraction medium, in combination with response surface analysis (RSA), Box–Behnken design (BBD), and proton nuclear magnetic resonance identification and quantification (1H NMR Qu) to provide an efficient protocol for the extraction of mono- and disaccharides, as a novel method for which no precedent was found. The methodology consisted of 15 CPH MA-HTPs and 15 HMC-CPH MA-HTPs (triplicate) designed by RSA-BBD; the experimental variables were time, temperature, and power, and the response was the concentration of extraction products. Glucose, sucrose, and fructose were identified as products of the extractions by 1H NMR. With 95% confidence, higher sucrose content was determined for CPH (45.62%) compared to HMC-CPH (17.34%), high fructose content for both CPH and HMC-CPH (37.88% and 35.37%, respectively), and minimal glucose concentrations were obtained in both CPH and HMC-CPH (4.57% and 0.93%, respectively). Using RSA-BBD, optimal temperature, power, and time points were predicted for glucose CPH: 135.4 °C, 180.6 W, and 5.8 min; sucrose: 154.3 °C, 256.3 W, and 20. 2 min; fructose 129.5 °C, 173.8 W, and 5.27 min. For HMC-CPH, the optimal conditions were as follows: glucose: 142.2 °C, 204.4 W, and 10.5 min; sucrose: 148.8 °C, 215.6 W, and 14.3 min; fructose: 151.6 °C, 231.6 W, and 13 min.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Bioactive Polysaccharides)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessSystematic Review
Hydroxypropyl Cellulose Research over Two Decades (2005–2024): A Systematic Review with Bibliometric Analysis and Translational Insights
by
Derina Paramitasari, Okta Amelia, Karjawan Pudjianto, Musa Musa, Banon Rustiaty, Arni Supriyanti, Dyah Primarini Meidiawati, Okta Nama Putra, Yanuar Sigit Pramana, Yassaroh Yassaroh, Frita Yuliati, Jatmiko Eko Witoyo and Untia Kartika Sari
Polysaccharides 2025, 6(4), 104; https://doi.org/10.3390/polysaccharides6040104 - 14 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC) is a versatile cellulose ether with two standardized forms: highly substituted (H-HPC), which is water-soluble and thermoresponsive, and low-substituted (L-HPC), which is insoluble but swellable. This systematic review with bibliometric analysis aimed to map the global HPC research landscape (2005–2024),
[...] Read more.
Hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC) is a versatile cellulose ether with two standardized forms: highly substituted (H-HPC), which is water-soluble and thermoresponsive, and low-substituted (L-HPC), which is insoluble but swellable. This systematic review with bibliometric analysis aimed to map the global HPC research landscape (2005–2024), focusing on publication trends, research impact, and thematic directions. Original research articles and conference proceedings indexed in Scopus were included, while reviews and non-research items were excluded. The database was searched on 7 July 2025 using predefined strategies and analyzed using Excel for descriptive statistics and VOSviewer for network visualization. Risk of bias assessment was not applicable; data accuracy was ensured through duplicate removal and the use of standardized bibliometric indicators. A total of 1273 H-HPC and 92 L-HPC publications were analyzed. H-HPC research dominates multidisciplinary applications in drug delivery, 3D printing, thermochromic, and energy materials, whereas L-HPC remains focused on pharmaceutical disintegration and binding. Nevertheless, the field is constrained by reliance on commercial grades and a narrow application focus, leaving broader material innovations underexplored. HPC is positioned as a strategic polysaccharide derivative with expanding translational potential. Future studies should emphasize greener synthesis, advanced functionalization, and industrial scale-up. Funding: Supported by BRIN. Systematic review registration: INPLASY202590019.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Chemically Modified Starch Films with Menthol or Sulfobetaine as Antimicrobial Agents for Active Packaging Applications
by
Pedro Francisco Muñoz-Gimena, Anselmo del Prado, Alejandro Aragón-Gutiérrez, Laura Peponi and Daniel López
Polysaccharides 2025, 6(4), 103; https://doi.org/10.3390/polysaccharides6040103 - 12 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study aims to develop a modified starch with menthol (M) or sulfobetaine (S) using 1,6-hexamethyl diisocyanate (HMDI) as a linker to create biodegradable antibacterial materials for active packaging applications. The modification of potato starch is performed in a two-step reaction. First, the
[...] Read more.
This study aims to develop a modified starch with menthol (M) or sulfobetaine (S) using 1,6-hexamethyl diisocyanate (HMDI) as a linker to create biodegradable antibacterial materials for active packaging applications. The modification of potato starch is performed in a two-step reaction. First, the starch modifiers are synthesized through an equimolar reaction between HMDI and menthol or the sulfobetaine precursor. Next, the synthesized HMDI derivative is dissolved in a bio-based solvent (methyl-THF) with starch and K2CO3 (1:1 weight ratio) to chemically modify the starch. The chemical and thermal properties of the modified starch are analyzed. Starch films containing 25 wt.% glycerol and low amounts (0.5, 1, and 3% wt.) of M- or S-modified starch were successfully produced by extrusion. Although most film properties remain similar to the control, adding 3% of S-modified starch resulted in a 149% increase in Elastic Modulus and a 29% decrease in water vapor permeability. Additionally, just 0.5 wt.% of either M- or S-modified starch effectively inhibits S. aureus growth, indicating its potential as a bioactive compound for active packaging.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
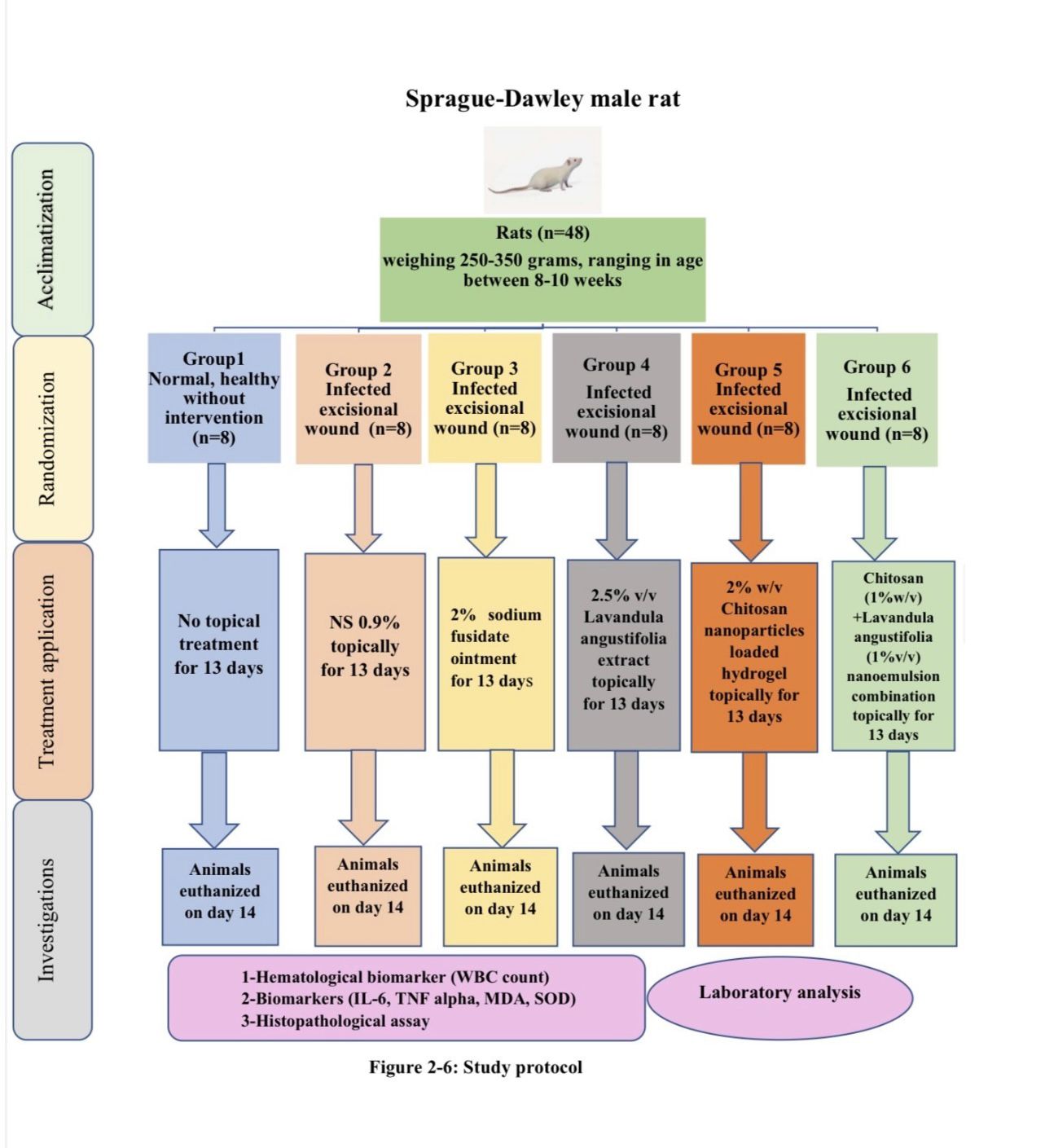
The Effect of Chitosan Nanoparticle-Loaded Hydrogel and Lavandula Angustifolia Extract on Staphylococcus Aureus-Infected Wounds in a Rat Model: An Animal Study
by
Farah Faraedon Mohidden Zardawi and Mohammed Qasim Yahya Malallah A. Al Atrakji
Polysaccharides 2025, 6(4), 102; https://doi.org/10.3390/polysaccharides6040102 - 11 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background: Chitosan and Lavandula angustifolia (lavender) exhibit antibacterial, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory effects, making them potential candidates for managing infected wounds. This study investigated the therapeutic efficacy of a chitosan nanoparticle-loaded hydrogel, lavender extract, and their combination in treating Staphylococcus aureus-infected wounds in
[...] Read more.
Background: Chitosan and Lavandula angustifolia (lavender) exhibit antibacterial, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory effects, making them potential candidates for managing infected wounds. This study investigated the therapeutic efficacy of a chitosan nanoparticle-loaded hydrogel, lavender extract, and their combination in treating Staphylococcus aureus-infected wounds in rats. Methods: Forty-eight male Sprague-Dawley rats (250–350 g, 8–10 weeks) were divided into six groups: healthy control, infected untreated, Fucidin, lavender extract, chitosan hydrogel, and chitosan–lavender combination. Wound healing was evaluated on days 3, 7, and 14 using clinical assessment, histopathology, and biochemical markers. Non-parametric statistical tests were applied, with significance set at p < 0.05. Results: The chitosan–lavender group showed the most pronounced healing response, with significantly reduced WBC counts, lower levels of TNF-α, IL-6, and MDA, and enhanced SOD activity (p < 0.05). Histological analysis confirmed superior re-epithelialization, granulation tissue development, collagen deposition, and wound contraction in chitosan-based treatments, particularly their combination, compared to lavender or Fucidin alone (p < 0.001). Inflammatory infiltrates, angiogenesis, necrosis, and hemorrhage were also notably reduced across treated groups. Conclusion: Combining chitosan hydrogel with lavender extract exerts synergistic antibacterial and wound healing effects, offering a promising alternative therapy for infected wounds.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Bioactive Polysaccharides)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Design and Characterization of Yeast Protein–Polysaccharide Bioink Blends for 3D Printing
by
Or Peleg-Evron, Noy Hen, Maya Davidovich-Pinhas, Shulamit Levenberg and Havazelet Bianco-Peled
Polysaccharides 2025, 6(4), 101; https://doi.org/10.3390/polysaccharides6040101 - 10 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Yeast protein (YP) offers nutritional and sustainable benefits; however, its poor gelation properties limit its use in soft material formulations. This study investigates the rheological behavior and the formation of crosslinked networks using YP–polysaccharide mixtures for extrusion-based 3D printing. Binary bioink blends with
[...] Read more.
Yeast protein (YP) offers nutritional and sustainable benefits; however, its poor gelation properties limit its use in soft material formulations. This study investigates the rheological behavior and the formation of crosslinked networks using YP–polysaccharide mixtures for extrusion-based 3D printing. Binary bioink blends with alginate (Alg) or xanthan gum (XG) showed enhanced viscosity and exhibited shear-thinning properties. However, a high concentration of Alg negatively affected the material’s thixotropic recovery. On the other hand, YP–XG bioink displayed more pronounced elastic behavior and demonstrated thixotropic recovery, though they lacked the capacity for ionic crosslinking. A triple bioink formulation consisting of 8% (w/v) YP, 2% (w/v) Alg, and 0.5% (w/v) XG effectively combined the advantages of both polysaccharides. Alg provided structural stability through calcium crosslinking, while XG offered rheological flexibility. These bioinks were successfully printed using embedded 3D printing and maintained their shape fidelity after printing. The crosslinked triple hydrogel exhibited good mechanical strength, volume retention after crosslinking, structural integrity under compression of up to 70%, and recovery after deformation that indicates high structural stability. This research presents an effective strategy to enhance the application of yeast-derived proteins in sustainable, animal-free 3D printed food products and other soft biomaterials.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Understanding Forage Palm Mucilage Behavior: Harnessing Plackett–Burman Screening for Tailoring Formulation and Process
by
Sander Moreira Rodrigues, Kaliston Aurélio Lomba, Tatiane Monteiro dos Santos, Gabrielly de Fátima Rodrigues das Neves, Maria Laura Gomes Vieira, Nathalia de Andrade Neves, César Alberto Roldan Cruz, Giselle Pereira Cardoso, Silvia Leticia Rivero Meza, Polyanna Mara de Oliveira, Larissa de Oliveira Ferreira Rocha, Monalisa Pereira Dutra Andrade, Vivian Machado Benassi, Tatiana Nunes Amaral, Irene Andressa, Maria Teresa Pedrosa Silva Clerici and Marcio Schmiele
Polysaccharides 2025, 6(4), 100; https://doi.org/10.3390/polysaccharides6040100 - 9 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The rheological and textural behavior of a highly viscous solution containing forage palm mucilage (FPM) was investigated using the Plackett–Burman (PB) design and multivariate analysis. The influence of carbohydrates (xanthan gum (XG), carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC), and sucrose), proteins (soy, egg, and whey), and
[...] Read more.
The rheological and textural behavior of a highly viscous solution containing forage palm mucilage (FPM) was investigated using the Plackett–Burman (PB) design and multivariate analysis. The influence of carbohydrates (xanthan gum (XG), carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC), and sucrose), proteins (soy, egg, and whey), and salts (NaCl and CaCl2), as well as pH and temperature, on FPM formulations was evaluated (α < 0.10 and R2 > 0.75). The flow curves indicate that gels fitted to the Ostwald-de Waele model and presented pseudoplastic behavior. Apparent viscosity at 10 s−1 showed results between 0.05 and 36.16 Pa·s, affected by XG, FPM and egg albumin. Hysteresis (–1138 to 3950 Pa·s) was reduced with increasing pH (p = 0.041), indicating the formation of more stable three-dimensional networks. Significant effects on firmness (0.114–0.434 N), consistency (1.286–3.397 N·s), cohesiveness (0.047–0.167 N), and viscosity index (0.067–0.810 N·s) were observed for sucrose, salts, and temperature (p < 0.100). Chemometric analysis confirmed the influence of these factors on the evaluated responses but revealed no correlation between rheological and textural parameters.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Chondroitin 4-Sulfate Disaccharide-Based Inhibitors of Cathepsin S
by
Alexis David, Roxane Domain, Florian Surback, Aude Vibert, Pierre Buisson, Martyna Maszota-Zieleniak, Ludovic Landemarre, Marie Schuler, Gilles Lalmanach, Sergey A. Samsonov, Chrystel Lopin-Bon and Fabien Lecaille
Polysaccharides 2025, 6(4), 99; https://doi.org/10.3390/polysaccharides6040099 - 5 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Cathepsin S (Cat S) is a cysteine protease involved in several human diseases (i.e., autoimmune, inflammatory and cardiovascular disorders, cancer, and psoriasis) and is an important target in drug development. Emerging evidence highlights the potential of inhibiting Cat S by glycosaminoglycans, particularly chondroitin
[...] Read more.
Cathepsin S (Cat S) is a cysteine protease involved in several human diseases (i.e., autoimmune, inflammatory and cardiovascular disorders, cancer, and psoriasis) and is an important target in drug development. Emerging evidence highlights the potential of inhibiting Cat S by glycosaminoglycans, particularly chondroitin sulfates (CSs), as a promising therapeutic strategy. Given the limited and heterogeneous GAG materials from animal sources, a series of synthetic biotinylated non- or sulfated chondroitin oligomers were synthesized and assessed for their ability to inhibit Cat S. The biotinylated disaccharide C4S displayed in vitro potent inhibitory activity toward Cat S with IC50 value in the micromolar range and showed selectivity over cathepsins K and L. Molecular modeling studies suggested that only C4S dp2 but not C6S, C4,6S or non-sulfated chondroitin binds selectively to the active site of Cat S. In addition, a synthetic multivalent C4S dp2 glycosylated BSA was shown to be more efficient towards Cat S inhibition (nanomolar range) than the monovalent parent C4S dp2. Our findings also indicated that this new neoglycoconjugate displayed selectivity for Cat S vs. cysteine cathepsins expressed by differentiated THP-1 cells. This study reports a new approach for designing selective and potent inhibitors of Cat S using multivalent C4S derivatives as a molecular scaffold.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Characterization of Pectin Extracted from the Peel of Dragon Fruit (Selenicereus cf. guatemalensis ‘Queen Purple’)
by
Victoria Carpio-Rivas, Rosendo Balois-Morales, Verónica Alhelí Ochoa-Jiménez, Juan Esteban Bello-Lara, Julio César Tafolla-Arellano and Guillermo Berumen-Varela
Polysaccharides 2025, 6(4), 98; https://doi.org/10.3390/polysaccharides6040098 - 3 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The dragon fruit (Selenicereus sp.) peel is a viable plant source for the extraction of polysaccharides such as pectin, the demand for which has increased significantly in the food and pharmaceutical industries. In Nayarit, Mexico, the Queen Purple variety of dragon fruit
[...] Read more.
The dragon fruit (Selenicereus sp.) peel is a viable plant source for the extraction of polysaccharides such as pectin, the demand for which has increased significantly in the food and pharmaceutical industries. In Nayarit, Mexico, the Queen Purple variety of dragon fruit (Selenicereus cf. guatemalensis) is commonly cultivated. The peel is typically discarded, while only the pulp is utilized for direct consumption or processed into derivative products. The objective of this study was to characterize the properties of pectin extracted from the peel of dragon fruit (Selenicereus cf. guatemalensis ‘Queen Purple’). The yield, molecular weight, anhydrouronic acid content, betalain content, antioxidant capacity, and phenolic compounds were determined using gravimetric, volumetric, spectrophotometric, and colorimetric techniques, among others. Furthermore, the functional groups and degree of esterification of the pectin were identified using Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy. The pectin presented a yield of 12.8%, esterification degree of 49.85%, molecular weight of 645 kDa, anhydrouronic acid, phenolic acid and betalain content of 98.27%, 195.7 mg EAG/100 gDW and 4.26 mg/100 gDW respectively and an antioxidant capacity of 149.6, 192.76 and 20.5 mg EAA/100 gDW by the DPPH, ABTS and FRAP methods respectively, classified as high-purity, low-methoxyl, intermediate-molecular-weight, with an important betalain content and antioxidant capacity. Based on these findings, the extracted pectin complies with the Food and Agriculture Organization specifications and shows promise as a functional ingredient in the food industry.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Symbiotic Culture of Bacteria and Yeast (SCOBY) in the Food Sector as a Source of Polysaccharides and Other Applications in the Food Sector
by
Rosa Maria Santiago-Santiago, Mariela R. Michel, Raúl Rodríguez-Herrera, Pedro Aguilar-Zárate, Juan Alberto Ascacio-Valdés and Adriana C. Flores-Gallegos
Polysaccharides 2025, 6(4), 97; https://doi.org/10.3390/polysaccharides6040097 - 21 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The SCOBY (Symbiotic Culture of Bacteria and Yeast) is a microbial consortium composed of a diverse range of bacteria and yeasts that coexist symbiotically. The most commonly identified microorganisms include Gluconobacter, Acetobacte, Saccharomyces and Zygosaccharomyces. Its primary objective is to utilize
[...] Read more.
The SCOBY (Symbiotic Culture of Bacteria and Yeast) is a microbial consortium composed of a diverse range of bacteria and yeasts that coexist symbiotically. The most commonly identified microorganisms include Gluconobacter, Acetobacte, Saccharomyces and Zygosaccharomyces. Its primary objective is to utilize sucrose as a substrate. SCOBY requires specific conditions for its multiplication, such as temperature, pH, and a suitable carbon source. Through its microbial dynamics and proper management, this consortium develops functional properties that are beneficial to health. This microbial consortium has been the subject of numerous studies due to the wide range of benefits it can offer through fermentation-derived products. Among the most frequently mentioned are organic acids, phenolic compounds, and a high concentration of probiotics. Originally, the SCOBY was used as a started culture in the production of the beverage “Kombucha”. However, due to the growing public interest, its use has diversified into fruit-based, dairy-based, and cereal-based beverages. Furthermore, its application has expanded to unconventional substrates. Its potential uses in other fields, such as medicine, as well as its antimicrobial activity, should also be noted.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessEditorial
Updating the Scope of Polysaccharides
by
Karin Stana Kleinschek
Polysaccharides 2025, 6(4), 96; https://doi.org/10.3390/polysaccharides6040096 - 21 Oct 2025
Abstract
Polysaccharides was launched in 2020, aiming to provide an advanced forum for studies related to polysaccharides and their derivatives, from basics to applications [...]
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Shedding Light on Carob Seeds: A Non-Destructive Approach to Assess Dehusking Efficiency Using Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy and Kubelka–Munk Theory
by
Rui Guerra, António Brázio, Sandra Gonçalves, Anabela Romano and Bruno Medronho
Polysaccharides 2025, 6(4), 95; https://doi.org/10.3390/polysaccharides6040095 - 20 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The carob tree (Ceratonia siliqua L.) is receiving growing attention for its agro-industrial potential, particularly due to its seeds, which are the source of locust bean gum (LBG), a galactomannan-rich polysaccharide with wide applications in food and pharmaceutical industries. Efficient dehusking of
[...] Read more.
The carob tree (Ceratonia siliqua L.) is receiving growing attention for its agro-industrial potential, particularly due to its seeds, which are the source of locust bean gum (LBG), a galactomannan-rich polysaccharide with wide applications in food and pharmaceutical industries. Efficient dehusking of carob seeds is critical to maximize LBG purity and yield, yet current industrial methods pose environmental concerns and lack robust quality control tools. In this study, we demonstrate the use of Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy (DRS) and Kubelka–Munk (KM) modeling as a rapid, non-destructive technique to assess dehusking efficiency. By combining spectral data from four complementary spectrometers (450–1800 nm), we identified key reflectance and absorbance features capable of distinguishing raw, industrially treated, and laboratory-dehusked seeds. Notably, our laboratory-treated seeds exhibited a considerably lower reflectance in the NIR plateau (800–1400 nm) compared to raw and industry-treated seeds, and their KM-reconstructed skin showed enhanced absorption bands at 960, 1200, and 1400 nm, consistent with more complete husk removal and improved light penetration. Principal Component Analysis revealed tighter clustering and lower variability in lab-processed seeds, indicating superior process reproducibility. These results establish DRS as a scalable, green analytical tool to support quality control and optimization in carob processing.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Wheat Hydrocolloids and Their Importance for Brewing
by
Kristina Habschied, Marija Kovačević Babić, Daniela Horvat, Krešimir Dvojković, Vinko Krstanović and Krešimir Mastanjević
Polysaccharides 2025, 6(4), 94; https://doi.org/10.3390/polysaccharides6040094 - 13 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Wheat is often used as a raw material in the brewing of special styles of beer. Hydrocolloids naturally present in wheat are called pentosans. They constitute approximately 2% of wheat flour. Arabinoxylans (pentosanes) and β-glucan are common compounds in wheat and are mostly
[...] Read more.
Wheat is often used as a raw material in the brewing of special styles of beer. Hydrocolloids naturally present in wheat are called pentosans. They constitute approximately 2% of wheat flour. Arabinoxylans (pentosanes) and β-glucan are common compounds in wheat and are mostly found in the cell wall. Hydrocolloids are commonly used to retain moisture in bread and baked goods. Besides the moisture content, they affect the texture and retrogradation enthalpy of starch molecules. In the baking industry, they can be useful and improve the dough properties, but in the brewing industry, they are commonly designated as problematic compounds. Namely, to a certain extent, they can improve the foam stability; however, they can hinder the filtration process. This review paper aims to give an overview of non-starch compounds and their properties and to emphasize the significance of these macromolecules in the malting and brewing industries, especially in wheat varieties. The objective of this review is to gather information by searching different databases with scientific papers to broaden knowledge on arabinoxylans and β-glucans in brewing.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Development and Evaluation of Hyaluronic Acid-Chitosan Coated Liposomes for Enhanced Delivery of Resveratrol to Breast Cancer Cells
by
Yin Yin Myat, Khin Khin Gyi, Pornthida Riangjanapatee, Chuda Chittasupho, Songyot Anuchapreeda and Siriporn Okonogi
Polysaccharides 2025, 6(4), 93; https://doi.org/10.3390/polysaccharides6040093 - 10 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Resveratrol (RES), a naturally occurring polyphenolic compound with well-documented anticancer potential, is limited in clinical application due to its poor aqueous solubility and low bioavailability. This study aimed to develop RES-loaded liposomes coated sequentially with chitosan (CS) and hyaluronic acid-chitosan (HA) (RES-HA-CS-Lip) to
[...] Read more.
Resveratrol (RES), a naturally occurring polyphenolic compound with well-documented anticancer potential, is limited in clinical application due to its poor aqueous solubility and low bioavailability. This study aimed to develop RES-loaded liposomes coated sequentially with chitosan (CS) and hyaluronic acid-chitosan (HA) (RES-HA-CS-Lip) to enhance RES stability, delivery, and anticancer efficacy in breast cancer cells. HA-CS-coated liposomes were prepared using a thin-film hydration technique. Their physicochemical characteristics were thoroughly investigated through dynamic light scattering, transmission electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and differential scanning calorimetry. The optimized RES-HA-CS-Lip exhibited spherical morphology with an average particle size of 212 nm, a narrow polydispersity index (<0.4), a zeta potential of +9.04 ± 1.0 mV, and high entrapment efficiency of 82.16%. Stability studies demonstrated superior retention of size, surface charge, and encapsulation efficiency over 28 days at both 4 °C and 25 °C. In vitro release profiles at physiological and acidic pH revealed sustained drug release, with enhanced release under acidic conditions mimicking the tumor microenvironment. Antioxidant activity, assessed via DPPH and ABTS radical-scavenging assays, indicated that RES retained its radical-scavenging potential upon encapsulation. Cytotoxicity assays demonstrated markedly improved anticancer activity against MCF-7 breast cancer cells, with an IC50 of 13.08 μg/mL at 48 h, while maintaining high biocompatibility toward normal HaCaT keratinocytes. RES-HA-CS-Lip demonstrated excellent stability against degradation and aggregation. Overall, these findings highlight HA-CS-coated liposomes as a promising polysaccharide-based nanocarrier that enhances stability, bioactivity, and therapeutic efficacy of RES, representing a potential strategy for targeted breast cancer therapy.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Tailoring Rheological, Viscoelastic, and Starch Structural Properties in Plant-Based Beverages via Homolactic Fermentation of Quinoa and Chickpea Flour Blends
by
John Hurtado-Murillo, Wendy Franco and Ingrid Contardo
Polysaccharides 2025, 6(4), 92; https://doi.org/10.3390/polysaccharides6040092 - 10 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study investigated the effects of homolactic fermentation on the rheological, viscoelastic, and starch structural properties of quinoa–chickpea flour-based beverages. Three formulations with increasing proportions of chickpea flour (10, 25, and 50%) were fermented for 10 h with Lactobacillus acidophilus LA-5. Apparent viscosity,
[...] Read more.
This study investigated the effects of homolactic fermentation on the rheological, viscoelastic, and starch structural properties of quinoa–chickpea flour-based beverages. Three formulations with increasing proportions of chickpea flour (10, 25, and 50%) were fermented for 10 h with Lactobacillus acidophilus LA-5. Apparent viscosity, deformation capacity, storage modulus (G′), and pasting behavior were measured along with FTIR-based analysis of the starch molecular structure. All fermented samples reached pH values < 4.5 and exhibited improved rheological properties with significant increases in viscosity and storage modulus (G′), particularly in the 50:50 blend. These enhancements were attributed to the synergistic effects of homolactic fermentation and inherent properties of chickpea starch, particularly its high amylose content, large granule size, and long amylopectin chains. FTIR analysis revealed that the short-range molecular order of starches was preserved after fermentation in all beverages, except for the 50:50 blend, as evidenced by the increased degree of order (DO) and double helix (DD) ratios. Overall, these findings demonstrate that integrating chickpea flour and controlled homolactic fermentation is an effective strategy for tailoring the viscosity and stability of plant-based probiotic beverages, providing a theoretical basis for the development of clean-label and functional fermented plant-based systems.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Methylcellulose Bionanocomposite Films Incorporated with Zein Nanoparticles Containing Propolis and Curcumin for Functional Packaging
by
Michael Ramos Nunes, Cleonice Gonçalves da Rosa, Gabriel Salvador, Sarah Cardoso de Oliveira Teixeira, Maria Clara Marinho da Costa, Aline da Rosa Almeida, Vanessa Valgas dos Santos, Ana Emília Siegloch, Fernando Domingo Zinger, Jaqueline Suave and Dachamir Hotza
Polysaccharides 2025, 6(4), 91; https://doi.org/10.3390/polysaccharides6040091 - 9 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The increasing demand for sustainable alternatives to non-biodegradable plastic packaging is driving the development of active packaging based on biopolymers such as methylcellulose. In this study, innovative methylcellulose nanocomposite films incorporating zein nanoparticles loaded with propolis and curcumin were developed for active packaging
[...] Read more.
The increasing demand for sustainable alternatives to non-biodegradable plastic packaging is driving the development of active packaging based on biopolymers such as methylcellulose. In this study, innovative methylcellulose nanocomposite films incorporating zein nanoparticles loaded with propolis and curcumin were developed for active packaging applications. The zein nanoparticles revealed excellent physicochemical properties, with a zeta potential above 30 mV, suggesting adequate stability. Transmission electron microscopy confirmed nanoparticles containing curcumin and propolis with uniform sizes ranging from approximately 130 to 140 nm with low polydispersity. Release studies revealed that approximately 25% of the curcumin and 35% of the propolis were released from the nanoparticles within 24 h. The release mechanism was best described by the Korsmeyer–Peppas model, suggesting a sustained release profile. The nanoparticles reduced the hydrophobicity and rigidity of the films, as evidenced by a lower elastic modulus and higher percentage elongation, thereby suggesting greater flexibility. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) analysis revealed the incorporation of bioactive compounds in the polymer matrix. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) revealed the thermal parameters of the synthesized films. Furthermore, the films exhibited antibacterial and antioxidant activities, making them highly suitable for use as biodegradable active packaging.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Adsorption of Pharmaceutical Compounds from Water on Chitosan/Glutaraldehyde Hydrogels: Theoretical and Experimental Analysis
by
Billy Alberto Ávila Camacho, Miguel Andrés Rojas Pabón, Norma Aurea Rangel Vázquez, Edgar A. Márquez Brazón, Hilda Elizabeth Reynel Ávila, Didilia Ileana Mendoza Castillo and Yectli A. Huerta
Polysaccharides 2025, 6(4), 90; https://doi.org/10.3390/polysaccharides6040090 - 9 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Chitosan-based hydrogels are used in the adsorption of pharmaceutical compounds from water. The adsorption process of diclofenac and naproxen on chitosan hydrogels cross-linked with glutaraldehyde has been studied theoretically and experimentally. According to the thermodynamic properties, the adsorption processes were spontaneous and endothermic,
[...] Read more.
Chitosan-based hydrogels are used in the adsorption of pharmaceutical compounds from water. The adsorption process of diclofenac and naproxen on chitosan hydrogels cross-linked with glutaraldehyde has been studied theoretically and experimentally. According to the thermodynamic properties, the adsorption processes were spontaneous and endothermic, due to the negative values of Gibbs free energy, and the enthalpies of formation were positive. Furthermore, the different systems were studied by electrostatic potential maps, where the functional groups (amino and hydroxyl) represented the active sites of the hydrogel. The maximum adsorption capacity obtained for diclofenac and naproxen was 108.85 and 97.22 mg/g, respectively, at a temperature of 308.15 K. On the other hand, the adsorbent was characterized by FTIR (Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy) and XRD (X-ray Diffraction) before and after the adsorption of the drugs to confirm the binding of the adsorbates on the surface of the material.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Polysaccharides
Recent Progress on Lignocellulosic-Based Materials
Guest Editors: Adrian C. Puiţel, Mircea Teodor NechitaDeadline: 30 December 2025
Special Issue in
Polysaccharides
Nanocellulose-Based Materials: Sustainable and Smart Platforms for Biomedical and Functional Applications
Guest Editor: Tamilselvan MohanDeadline: 31 July 2026
Special Issue in
Polysaccharides
Polysaccharides in Advanced Packaging: Active Coatings, Safe Additives, and Green Processing
Guest Editors: Lidija Fras Zemljič, Klementina Pušnik ČrešnarDeadline: 31 July 2026
Special Issue in
Polysaccharides
New Insights into Polysaccharide-Based Scaffolds: Design, Production and Applications
Guest Editor: Antonio LaezzaDeadline: 1 August 2026
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Polysaccharides
Current Opinion in Polysaccharides
Collection Editors: Cédric Delattre, Paolina Lukova, Guillaume Pierre








