-
 State of the Art and Recent Advances on Ester and Ether Derivatives of Polysaccharides from Lignocellulose: Production and Technological Applications
State of the Art and Recent Advances on Ester and Ether Derivatives of Polysaccharides from Lignocellulose: Production and Technological Applications -
 Chitosan-Coated Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLCs) Incorporating Esters of Ferulic Acid with Photoprotective Activity
Chitosan-Coated Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLCs) Incorporating Esters of Ferulic Acid with Photoprotective Activity -
 A Review of Sterilization Methods and Their Commercial Impacts on Polysaccharide-Based Biomaterials
A Review of Sterilization Methods and Their Commercial Impacts on Polysaccharide-Based Biomaterials -
 RNA Polymerase II Activity and Nuclear Actin: Possible Roles of Nuclear Tropomyosin, Troponin and Ca2+ in Transcription in Striated Muscle Myocyte Nuclei
RNA Polymerase II Activity and Nuclear Actin: Possible Roles of Nuclear Tropomyosin, Troponin and Ca2+ in Transcription in Striated Muscle Myocyte Nuclei -
 Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate-Co-3-Hydroxyvalerate) Produced from Food-Related Wastes: Solid-State NMR Analysis
Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate-Co-3-Hydroxyvalerate) Produced from Food-Related Wastes: Solid-State NMR Analysis
Journal Description
Macromol
Macromol
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on all aspects of macromolecular research published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within ESCI (Web of Science), Scopus, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Polymer Science) / CiteScore - Q1 (Materials Science (miscellaneous))
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 23.3 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 4.7 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- Journal Cluster of Polymer and Macromolecular Science: Polymers, Gels, Polysaccharides, Textiles, Macromol, Microplastics and Adhesives.
Impact Factor:
4.4 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
4.6 (2024)
Latest Articles
Bioactive Potential of Peptide Fractions Derived from Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Chenopodium quinoa Proteins: Approach to Antihypertensive Activity
Macromol 2026, 6(1), 14; https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol6010014 - 15 Feb 2026
Abstract
►
Show Figures
Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa) is a promising source of plant proteins with the potential to produce bioactive peptides through enzymatic hydrolysis. This study aimed to extract quinoa protein and produce bioactive peptides using two microbial proteases: Alcalase (from Bacillus licheniformis) and
[...] Read more.
Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa) is a promising source of plant proteins with the potential to produce bioactive peptides through enzymatic hydrolysis. This study aimed to extract quinoa protein and produce bioactive peptides using two microbial proteases: Alcalase (from Bacillus licheniformis) and Flavourzyme (from Aspergillus oryzae). The protein was extracted through alkaline solubilization and isoelectric precipitation, achieving a 72% yield. Hydrolysis was conducted for 4 h, and enzymatic activity was measured using the TNBS method to determine the degree of hydrolysis, while SDS-PAGE was used to analyze protein breakdown. The reaction was performed at controlled pH and temperature (Alcalase: 9.5 and 55 °C; Flavourzyme: 7 and 37 °C). Both enzymes achieved maximum hydrolysis at 60 min. Consequently, the separation and inhibitory capacity of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE-I) were tested at the first four time points (0, 20, 40, and 60 min). A wider variety and higher concentration of peptides smaller than 2 kDa were found in hydrolysates treated with Flavourzyme, which is associated with antihypertensive activity. The ACE-I assay showed greater activity at the end of hydrolysis. Inhibition percentages of 87.5 ± 2.11 were observed in hydrolysates with Flavourzyme, and 94.1 ± 1.11 in those with Alcalase. These findings indicate that quinoa protein, hydrolyzed with microbial proteases, is a feasible source of peptides with potential antihypertensive effects for use in functional foods and nutraceuticals.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Replacing Brine with Chitosan Solution: A Sustainable, Low-Sodium Strategy for Table Olive Preservation
by
Vassilios K. Karabagias, Alexios Vardakas, Achilleas Kechagias, Nikolaos D. Andritsos, Ioannis K. Karabagias and Aris E. Giannakas
Macromol 2026, 6(1), 13; https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol6010013 - 14 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In response to the environmental and health concerns associated with high-sodium brine disposal and the sodium content in table olives, this study proposes a novel, sustainable preservation method that completely replaces traditional brine with chitosan solutions. Three food-grade chitosan solutions were formulated using
[...] Read more.
In response to the environmental and health concerns associated with high-sodium brine disposal and the sodium content in table olives, this study proposes a novel, sustainable preservation method that completely replaces traditional brine with chitosan solutions. Three food-grade chitosan solutions were formulated using acetic acid, vinegar, and vinegar neutralized with baking soda as alternative liquid media for preserving Kalamata olives. Over a five-month storage period with a one-year endpoint, these solutions were evaluated against a conventional 8% NaCl brine control. The chitosan-based systems demonstrated effective microbial control, maintaining significantly lower total viable counts for most of the storage period, while yeast and mold populations were comparable to or slightly higher than the control over extended storage. Notably, they reduced the medium’s salinity by 75–85%, directly addressing the issue of high sodium content. The chitosan solutions also provided superior pH stability and color maintenance in the olives. A key finding was the distinct nature of the interaction between the olives and the chitosan medium compared to brine: while antioxidant activity within the olive flesh declined, the chitosan solutions themselves exhibited high and stable intrinsic antioxidant capacity (>78%), acting as an active antioxidant reservoir—a dynamic not observed with traditional brine. This research successfully validates chitosan solution as a viable, low-sodium, brine-free preservation medium, offering a novel strategy for sustainable olive processing that valorizes seafood waste and aligns with circular economy principles.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Efficient Chitin Derivatization Methods Using Ionic Liquids and Deep Eutectic Solvents
by
Masayasu Totani and Jun-ichi Kadokawa
Macromol 2026, 6(1), 12; https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol6010012 - 11 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Ionic liquids (ILs) and deep eutectic solvents (DESs) have emerged as effective solvents for poorly soluble materials such as natural polysaccharides, including chitin. This review describes recently developed efficient chitin derivatization methods that harness the solubilizing power of ILs and DESs. It covers
[...] Read more.
Ionic liquids (ILs) and deep eutectic solvents (DESs) have emerged as effective solvents for poorly soluble materials such as natural polysaccharides, including chitin. This review describes recently developed efficient chitin derivatization methods that harness the solubilizing power of ILs and DESs. It covers chitin acylation approaches, including acylation and mixed ester formation, as well as chitin etherification protocols. For example, the ILs 1-allyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide (AMIMBr) and 1-allyl-2,3-dimethylimidazolium bromide serve as effective media for chitin acylation and etherification, respectively, yielding single esters and benzyl derivatives with high degrees of substitution (DS). The use of DESs comprising AMIM chloride (AMIMCl) as a hydrogen bond acceptor and several hydrogen bond donors for chitin acylation are presented. In an optimized system, acylation using acyl chlorides proceeded smoothly without additives, such as a base/catalyst, in a DES comprising AMIMCl and 1,1,3,3-tetramethylguanidine, affording high-DS ester derivatives. The method was extended to the synthesis of mixed chitin esters bearing both long and bulky acyl substituents at appropriate substitution ratios, which exhibit thermoplasticity.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Globulins from a New Brazilian Chickpea Cultivar GB Cappuccino: Insights into Compositional, Digestibility, and Bio-Functional Potential of Their Hydrolysates
by
Lara Campos Borim, Sarah Cristina de Oliveira Dias, Taiara de Fátima Lucio, Beatriz de Cassia Garcia Silva, Amanda Teodoro de Moura, Raissa Leite Coelho, Maria Teresa Bertoldo Pacheco and Olga Luisa Tavano
Macromol 2026, 6(1), 11; https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol6010011 - 9 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study presents the first characterization of the globulin fraction from a newly registered chickpea cultivar, which represents the first desi-type cultivar (GB Cappuccino) released in Brazil. Although desi chickpeas are widely consumed in other countries, they have not been part of the
[...] Read more.
This study presents the first characterization of the globulin fraction from a newly registered chickpea cultivar, which represents the first desi-type cultivar (GB Cappuccino) released in Brazil. Although desi chickpeas are widely consumed in other countries, they have not been part of the Brazilian dietary pattern, and this introduction may represent an opportunity for changing this scenario. Characterizing its proteins is essential, given that legumes are recognized as important protein sources. In this study, globulins were confirmed as the predominant protein fraction, with the legumin-like fraction accounting for more than 80% of the total globulins. Its electrophoretic and amino acid profiles were highly distinctive and strongly influenced by this major fraction. In addition to the expected solubilization in saline solution, under in vitro pepsin–pancreatin digestion conditions designed to assess maximum hydrolysis potential, the globulin fraction was partially hydrolyzed, indicating a degree of protein digestibility while simultaneously releasing peptides that exhibited antioxidant activity and angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory potential. Overall, these results highlight the nutritional relevance of this new cultivar and, based on the preliminary bioactivity screening performed, suggest that its globulin-rich protein composition may represent a promising source of bioactive peptides.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Innovations in Tannin-Based Phenolic Foams: A Review of the Research
by
António G. Abreu, Joana J. Costa, P. Filipe Santos, Abel J. Duarte, Elizabeth S. Vieira and Felismina T. C. Moreira
Macromol 2026, 6(1), 10; https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol6010010 - 6 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Research on tannin-based foams has shown promising results. However, all developments in this field have not been addressed from different perspectives, in a systematic way, and with an emphasis on sustainability. This work discusses different formulations, emphasizing their bio-based components and how modifications
[...] Read more.
Research on tannin-based foams has shown promising results. However, all developments in this field have not been addressed from different perspectives, in a systematic way, and with an emphasis on sustainability. This work discusses different formulations, emphasizing their bio-based components and how modifications influence key properties. It examines life cycle assessment (LCA) studies through a sustainability lens and identifies major commercial phenolic products to highlight the practical use of tannin foams for thermal insulation. The type of tannins, as well as their sources, influences the key properties of these foams. The replacement of formaldehyde, a crosslinking agent known for its health risks, is possible, particularly through more sustainable alternatives that allow for foams with better properties than those obtained with formaldehyde. Substitution of diethyl ether with less hazardous alternatives results in foams with improved thermal and mechanical performance. The elimination of the blowing agent—the green alternative—also leads to foams with good performance. The presence of additives (surfactants, plasticizers, and fillers), some of which are sustainable, improves the mechanical properties of the foams. The performance in fire-related applications, already promising, is also enhanced by the presence of additives. An increase in understanding, combined with the sustainable nature of the various alternatives, makes tannin-based foams promising candidates for next-generation insulation and structural materials in construction.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Catabolite Repression and Substrate Induction as Strategies for Protease Production in Edible Mushrooms
by
Giovanna Lima-Silva, Walter J. Martínez-Burgos, Daiane B. Pereira, Larissa B. N. Soares, Aldenora S. Vasconcelos, Vítor A. Pessoa, Ceci Sales-Campos and Larissa R. Chevreuil
Macromol 2026, 6(1), 9; https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol6010009 - 5 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Edible mushrooms are an underexplored source of industrial proteases, whose synthesis is highly dependent on the cultivation substrate. This study investigated the effect of nine culture media on the proteolytic profiles of Auricularia sp., Lentinus sp., Macrocybe sp., and Grifola frondosa. Fungi
[...] Read more.
Edible mushrooms are an underexplored source of industrial proteases, whose synthesis is highly dependent on the cultivation substrate. This study investigated the effect of nine culture media on the proteolytic profiles of Auricularia sp., Lentinus sp., Macrocybe sp., and Grifola frondosa. Fungi were cultivated on diverse media (e.g., Czapek, Malt, Soy Flour). We analyzed total protein, specific activities (total, cysteine, serine proteases) using a biochemical assay, and protein secondary structure via FTIR, with metabolic patterns identified by PCA. A dissociation was found between total protein yield (highest in MFI/Casein media) and specific activity (highest in maltose media), suggesting catabolite repression. Distinct metabolic strategies emerged: Grifola frondosa specialized in serine protease production in the minimal Czapek medium (catabolic derepression), while Macrocybe sp. maximized cysteine protease production on soy flour (substrate induction). FTIR confirmed this, revealing a β-sheet-dominant (75.5%) structure for Grifola extract versus a random-coil-dominant (60.8%) structure for Macrocybe. This study provides a framework for mechanism-based bioprocess design, enabling the tailored production of serine proteases from G. frondosa (Czapek medium) or cysteine proteases from Macrocybe sp. (soy medium) for customized biotechnological applications.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Biopolymers and Biocomposites for Additive Manufacturing of Optical Frames
by
Beatriz Carvalho, Fátima Santos, Juliana Araújo, Bruna Santos, João Alhada Lourenço, Pedro Ramos and Telma Encarnação
Macromol 2026, 6(1), 8; https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol6010008 - 21 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Optical frames are used worldwide to correct visual impairments, protect from UV damage, or simply for fashion purposes. Optical frames are often made of poorly biodegradable and fossil-based materials, with designs not targeted to everyone’s tastes and requirements. Additive manufacturing processes allow personalisation
[...] Read more.
Optical frames are used worldwide to correct visual impairments, protect from UV damage, or simply for fashion purposes. Optical frames are often made of poorly biodegradable and fossil-based materials, with designs not targeted to everyone’s tastes and requirements. Additive manufacturing processes allow personalisation of optical frames and the use of new sustainable biomaterials to replace fossil-based ones. This comprehensive review combines an extensive survey of the scientific literature, market trends, and information from other relevant sources, analysing the biomaterials currently used in additive manufacturing and identifying biomaterials (biopolymers, natural fibres, and natural additives) with the potential to be developed into biocomposites for printing optical frames. Requirements for optical devices were carefully considered, such as standards, regulations, and demands for manufacturing materials. By comparing with fossil-based analogues and by discussing the chemical, physical, and mechanical properties of each biomaterial, it was found that combining various materials in biocomposites is promising for achieving the desirable properties for printing optical frames. The advantages of the various techniques of this cutting-edge technology were also analysed and discussed for optical industry applications. This study aims to answer the central research question: which biopolymers and biocomposite constituents (natural fibres, plasticisers, and additives) have the ideal mechanical, thermal, physical, and chemical properties for combining into a biomaterial suitable for producing sustainable, customisable, and inclusive optical frames on demand, using additive manufacturing techniques.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Effective Control of Poly(L-lactide-co-ε-caprolactone) Chain Microstructure Through Polymerization with Different Catalysts and Delayed Co-Monomer Addition
by
Evgeniy Anokhin, Nikita Sedush, Alexander Buzin, Artem Bakirov, Sergei Korolev and Sergei Chvalun
Macromol 2026, 6(1), 7; https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol6010007 - 19 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Poly(L-lactide-co-ε-caprolactones) (PLCL) are promising biodegradable polymers with tunable properties for various biomedical applications. Along with the composition, the microstructure of PLCL chain is an important factor affecting its properties, crystallinity, and degradation profile. In this study, to find effective ways for tailoring the
[...] Read more.
Poly(L-lactide-co-ε-caprolactones) (PLCL) are promising biodegradable polymers with tunable properties for various biomedical applications. Along with the composition, the microstructure of PLCL chain is an important factor affecting its properties, crystallinity, and degradation profile. In this study, to find effective ways for tailoring the microstructure of PLCL chain, kinetic patterns of L-lactide/ε-caprolactone (75:25) ring-opening copolymerization in the presence of two different catalysts were evaluated. The kinetic studies, accompanied by the assessment of the evolution of PLCL microstructure over the reaction course, provided the optimal regimes for synthesis of PLCL with a fixed composition (LA:CL = 75:25) and different chain microstructure. This was achieved by employing two types of catalysts (tin(II) 2-ethylhexanoate and zirconium(IV) acetylacetonate) and delayed co-monomer addition approach. The control of average LA block length (lLA) was achieved in a wide range from 4 to 14 monomeric units. Differential scanning calorimetry and wide-angle X-ray scattering revealed a pronounced effect of lLA on glass transition temperature, melting temperature, and crystallinity.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Microbial Biosurfactants: Antimicrobial Agents Against Pathogens
by
Albert D. Luong, Maruthapandi Moorthy and John HT Luong
Macromol 2026, 6(1), 6; https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol6010006 - 14 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Microbial biosurfactants (mBSs) are bioactive molecules with diverse applications, notably as antimicrobial agents against antibiotic-resistant pathogens. Produced by bacteria and yeasts, mBSs are classified as glycolipids, lipopeptides, polymeric, and particulate types. The global rise in multidrug-resistant organisms, such as Escherichia coli, Klebsiella
[...] Read more.
Microbial biosurfactants (mBSs) are bioactive molecules with diverse applications, notably as antimicrobial agents against antibiotic-resistant pathogens. Produced by bacteria and yeasts, mBSs are classified as glycolipids, lipopeptides, polymeric, and particulate types. The global rise in multidrug-resistant organisms, such as Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Salmonella typhimurium, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Acinetobacter baumannii, underscores the urgent need for new antimicrobial strategies. mBSs disrupt microbial growth by interacting with the lipid components of pathogens, offering promising alternatives to conventional antibiotics. This review highlights the sources, chemical structures, and properties of mBSs, their antimicrobial activities, synergistic effects with antibiotics, and structure–activity relationships. Special emphasis is placed on surfactant modification, where targeted changes—such as valine substitution in surfactin—significantly lower critical micelle concentrations (CMC) and enhance antimicrobial potency. Such rational engineering demonstrates how biosurfactants can be tailored for improved biomedical performance while minimizing cytotoxicity. In parallel, artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms, including artificial neural networks and genetic algorithms, optimize yields, predict substrate suitability from agricultural residues, and guide microbial strain engineering. AI models can predict interfacial behavior and synchronize fermentation with purification. Advancing the understanding of mBS interactions with microbial membranes, combined with modification strategies and AI-guided optimization, is essential for developing targeted therapies against resistant infections. Future research should integrate these approaches to engineer novel derivatives, reduce costs, and validate clinical potential through comprehensive in vivo studies.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Fibrous Polycaprolactone-Based Composite Materials with the Addition of Hardystonite: Haemostatic Potential, Antioxidant Activity, and Biocompatibility Assessment
by
Anna Kaczmarek, Marcin H. Kudzin, Michał Juszczak, Katarzyna Woźniak, Paulina Król, César I. Hernández Vázquez, Zdzisława Mrozińska and Jerzy J. Chruściel
Macromol 2026, 6(1), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol6010005 - 13 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Fibrous polycaprolactone-based composite materials with the addition of hardystonite (1, 3, and 5 wt.%) were developed using the electrospinning method. The obtained PCL and PCL-HT nonwovens were evaluated in terms of their physiochemical properties (SEM, EDS, BET, and zeta potential). Furthermore, the antioxidant
[...] Read more.
Fibrous polycaprolactone-based composite materials with the addition of hardystonite (1, 3, and 5 wt.%) were developed using the electrospinning method. The obtained PCL and PCL-HT nonwovens were evaluated in terms of their physiochemical properties (SEM, EDS, BET, and zeta potential). Furthermore, the antioxidant potential [measured by thiobarbituric acid reactive substance (TBARS) levels], blood plasma coagulation parameters, and cyto- and genotoxicity towards PBM and Hs68 cells were assessed to determine the biochemical activity of the composites. The conducted experiments confirmed that hardystonite was successfully incorporated into the PCL matrix. No substantial changes in the fibres’ surface morphology and the structure of the composites were observed. Similarly, the specific surface area, total pore volume, and average pore size did not change significantly. The addition of hardystonite to the polymer solution resulted in a shift in zeta potential toward less negative values. With regard to plasma coagulation parameters, no significant changes were observed in the aPTT, PT, or TT, likely due to the counterbalancing effect of Zn2+ and Ca2+ ions. Furthermore, the PCL-HT composites exhibited a lowered TBARS level, suggesting antioxidant properties, which could be attributed to the presence of zinc in hardystonite. The PCL and PCL-HT composites demonstrated no cytotoxic or genotoxic effects on the tested blood or skin cell types, suggesting their safety.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Study on Mechanical Properties of Natural Rubber Composites Reinforced with Agave lechuguilla Fibers
by
J. A. Maldonado-Torres, E. Rocha-Rangel, C. A. Calles-Arriaga, W. Pech-Rodriguez, J. López-Hernández, U. A. Macías-Castillo, M. C. Kantún-Uicab, A. Jiménez-Rosales, L. F. Martínez-Mosso and J. A. Castillo-Robles
Macromol 2026, 6(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol6010004 - 12 Jan 2026
Abstract
Agave lechuguilla fibers exhibit high tensile strength, low density and durability, but their use in natural rubber composites is underexplored. This study investigates alkaline-treated fibers (149–180 µm) as reinforcements for natural latex. Fibers were pretreated with a methanol–acetone mixture, followed by immersion in
[...] Read more.
Agave lechuguilla fibers exhibit high tensile strength, low density and durability, but their use in natural rubber composites is underexplored. This study investigates alkaline-treated fibers (149–180 µm) as reinforcements for natural latex. Fibers were pretreated with a methanol–acetone mixture, followed by immersion in 10% NaOH at 70 °C for 1 h, removing lignin and hemicellulose as confirmed by FTIR and SEM. Thermogravimetric analysis showed three weight-loss stages: moisture/volatiles (9.4%), hemicellulose (peak at 341 °C), and cellulose/lignin (peak at 482 °C), with <3% residue above 500 °C. Treated composites exhibited enhanced tensile strength (4.68 ± 1.2 MPa vs. 1.3 ± 0.8 MPa for untreated) and elongation at break (530 ± 51% vs. 452 ± 32%). Hardness increased from 21.8 (neat latex) to 30.3, and compression resistance was improved. Optical microscopy revealed strong fiber–matrix adhesion with uniform dispersion. Alkaline treatment enhances interfacial bonding and mechanical performance, making A. lechuguilla fibers a sustainable reinforcement for eco-friendly composites in automotive, construction, and packaging sectors.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Starch and Lignocellulosic-Based Materials)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effect of Low-Temperature Storage of Kefir Grains and Trehalose Addition on the Production of the Exopolysaccharide Kefiran
by
Lydia Arsou, Stylianos Exarhopoulos, Athanasios Goulas and Georgia Dimitreli
Macromol 2026, 6(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol6010003 - 8 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Kefiran, the extracellular polysaccharide produced by Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) bacteria found in kefir grains, is a promising biopolymer with multiple applications in agri-food and biomedical fields. Besides its characteristics and potential applications, the factors that affect its production remain a prime
[...] Read more.
Kefiran, the extracellular polysaccharide produced by Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) bacteria found in kefir grains, is a promising biopolymer with multiple applications in agri-food and biomedical fields. Besides its characteristics and potential applications, the factors that affect its production remain a prime subject of interest. Lactic acid bacteria synthesize polysaccharides to protect their cells from adverse conditions. Therefore, low-temperature storage (4 °C) of kefir grains inoculated into Ultra-High-Temperature (UHT) milk at two different concentrations (5% and 30%) was studied as a factor for increasing kefiran production in the medium. The cryoprotectant disaccharide trehalose, which comprises a carbon and energy source for many microorganisms, was also evaluated for its effectiveness in enhancing kefiran production. The pH, the increase in kefir grain mass, the amount of kefiran produced, and the rheological properties of the acidified milk were determined during two distinct storage periods, depending on kefir grain concentration. For comparison, kefir grains were also fermented at 25 °C and 30 °C. Low-temperature storage at a kefir grain concentration of 30% resulted in an increase in the amount of polysaccharide produced beyond that obtained through fermentation. Fermentation of a 5% grain inoculum at 30 °C resulted in the lowest kefiran production. In the presence of trehalose, prolonged low-temperature storage favored an increase in the biosynthesis of kefiran, especially at a 30% kefir grain inoculum. Trehalose, however, was not a significant factor in the fermentation experiments. Proper selection of low-temperature storage time is required to avoid a reduction in kefiran concentration due to the metabolic activity of the microorganisms in kefir grains. The acidified milk (low-temperature storage) and kefir (fermentation) samples both exhibited increased elasticity and apparent viscosity with increasing kefir grain concentration. However, the rheological behavior of acidified milk was greatly affected by protein degradation during low-temperature storage. As shown by the findings of the present study, low-temperature storage (4 °C) of a 30% kefir grain inoculum in the presence of trehalose (3% w/w) until a final pH of 4.2 proves to favor kefiran production in the medium the most.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Phase Separation in Gelatin/Zein Films: Structure–Property Correlation and Multi-Criteria Decision Making Evaluation for Food Packaging
by
Ainun Zulfikar, Peifu Kong and Toshiharu Enomae
Macromol 2026, 6(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol6010002 - 26 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Protein-based films are attractive candidates for biodegradable packaging, yet their performance is often compromised by phase separation when combining components with contrasting hydrophilicity. In this study, gelatin/zein films were used as a model system to elucidate how phase separation governs multifunctional properties. FTIR,
[...] Read more.
Protein-based films are attractive candidates for biodegradable packaging, yet their performance is often compromised by phase separation when combining components with contrasting hydrophilicity. In this study, gelatin/zein films were used as a model system to elucidate how phase separation governs multifunctional properties. FTIR, XRD, TGA, and SEM analyses confirmed heterogeneous domains arising from immiscibility, which strongly influenced mechanical, heat-sealing, barrier, and optical behaviors. Zein incorporation improved tensile strength, water resistance, and UV-blocking capacity, while it simultaneously compromised heat-sealing strength, transparency, and gas barrier uniformity. To rationalize these trade-offs, a Multi-Criteria Decision-Making (MCDM) framework integrating the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) and Technique for Order of Preference by Similarity to the Ideal Solution (TOPSIS) was applied, revealing that gelatin/zein blends performed worse overall than pure films. These findings demonstrate that phase separation can improve individual attributes without generating synergistic effects, emphasizing the importance of compatibility control and holistic evaluation in the rational design of biodegradable packaging materials.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Influence of Aggressive Liquid Media on the Properties of Swelling Rubbers Filled with Carboxymethylated Cellulose
by
Abdirakym Nakyp, Elena Cherezova, Yulia Karaseva, Aida Dauylbek and Rakhymzhan Turmanov
Macromol 2026, 6(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol6010001 - 25 Dec 2025
Abstract
The stability of physical and mechanical properties of highly filled swelling rubbers in polar and nonpolar liquids (oil, mineralized water) was studied. Nitrile butadiene rubber of BNKS-28 AMN grade served as the elastomer matrix, with sodium salt of carboxymethylcellulose (NaCMC) as the swelling
[...] Read more.
The stability of physical and mechanical properties of highly filled swelling rubbers in polar and nonpolar liquids (oil, mineralized water) was studied. Nitrile butadiene rubber of BNKS-28 AMN grade served as the elastomer matrix, with sodium salt of carboxymethylcellulose (NaCMC) as the swelling filler. Oxal T-92, a mixture of dioxane alcohols (10–50 phr, step 10 phr), was used as a plasticizer due to its good thermodynamic miscibility with rubber (confirmed by Scatchard–Hildebrand calculations). Adding Oxal T-92 to NaCMC-filled compounds markedly reduced Mooney viscosity, improving processing through increased macromolecule mobility, without significantly affecting vulcanization kinetics—indicating chemical inertness toward crosslinking centers. Increasing Oxal T-92 from 10 to 50 phr reduced tensile strength from 4.1 MPa to 2.9 MPa. Swelling in aqueous solutions of varying mineralization was evaluated via volume and mass change. The optimal plasticizer content for high swelling with acceptable strength is 20–30 phr. After 3 days in oil and formation water, NaCMC-filled rubbers retained stable physical and mechanical properties.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Future Trends in Polymer Science: Materials, Design, and Advanced Applications)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate-Co-3-Hydroxyvalerate) Produced from Food-Related Wastes: Solid-State NMR Analysis
by
Atanu Biswas, Huai N. Cheng and John C. Edwards
Macromol 2025, 5(4), 61; https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol5040061 - 9 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Poly(hydroxyalkanoates) (PHAs) have garnered significant attention due to their biodegradable and biocompatible properties, making them promising alternatives to conventional petroleum-based plastics. As microbial-derived polyesters, PHAs offer a sustainable solution to plastic waste accumulation and microplastics because they can be produced from renewable resources,
[...] Read more.
Poly(hydroxyalkanoates) (PHAs) have garnered significant attention due to their biodegradable and biocompatible properties, making them promising alternatives to conventional petroleum-based plastics. As microbial-derived polyesters, PHAs offer a sustainable solution to plastic waste accumulation and microplastics because they can be produced from renewable resources, including food-related waste. Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV), a copolymer in the PHA family, exhibits improved mechanical flexibility and thermal properties compared to poly(3-hydroxybutyrate), thereby broadening its potential applications. In this work, eight samples of PHBV, including those made from food waste and municipal waste streams, were studied by solid-state NMR. Information obtained includes the copolymer composition, chemical shifts due to crystalline lattices, crystallinity, and polymer chain mobility. The composition matches the results from the fatty acid feed and solution NMR analysis. The samples appear to be about 62–70% crystalline. No significant differences in mobility are observed from NMR relaxation data. These results indicate that PHBV materials generated from different food-related waste sources, despite their compositional differences, possess similar crystallinity and molecular mobility, suggesting their suitability as biobased semi-crystalline plastics.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Design of Experiments Methodology for Fused Filament Fabrication of Silicon-Carbide-Particulate-Reinforced Polylactic Acid Composites
by
Andrew P. Gyekenyesi, Meelad Ranaiefar, Michael C. Halbig and Mrityunjay Singh
Macromol 2025, 5(4), 60; https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol5040060 - 8 Dec 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) is an additive manufacturing technique that constructs parts by extruding material layer by layer. It offers advantages such as rapid prototyping, cost-effectiveness, and the ability to produce complex geometries. This study investigates the mechanical behavior of a composite filament
[...] Read more.
Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) is an additive manufacturing technique that constructs parts by extruding material layer by layer. It offers advantages such as rapid prototyping, cost-effectiveness, and the ability to produce complex geometries. This study investigates the mechanical behavior of a composite filament composed of silicon carbide (SiC) ceramic particulates embedded in a polylactic acid (PLA) matrix, fabricated via FFF. Pure PLA specimens were also printed and tested to serve as a baseline. A Design of Experiments (DOE) methodology was employed to evaluate the influence of key printing parameters on mechanical properties, including Young’s modulus, yield strength, and ultimate strength. Microstructural analysis was performed on printed specimens using scanning electron microscopy (SEM). For compression testing, the parameters studied were infill percentage, number of shells, and print orientation. For tensile testing, the parameters included layer height, number of shells, and infill angle. Results indicated that infill percentage had the most significant impact on compressive properties, while layer height was the dominant factor in tensile performance. These findings provide insights into optimizing FFF process parameters for ceramic-particulate-reinforced polymer composites.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Antioxidant, Photoprotective, and In Vitro Antiaging Assessment of Optimized Water/Oil Emulsions of Selenized Chickpea Glutelin with Rosehip Oil or Grapeseed Oil
by
Ada Keila Milán-Noris, Ángel R. Rábago-Monzón, Maritza G. Castro-Quintero, Marilena Antunes-Ricardo, Álvaro Montoya-Rodríguez, Julio Montes-Ávila, Cuauhtémoc Reyes-Moreno and Daniela Guardado-Félix
Macromol 2025, 5(4), 59; https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol5040059 - 4 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The selenized glutelin (Se-G) from Se-enriched chickpea sprouts has demonstrated high antioxidant potential. In this study, the response surface methodology was employed to optimize Se-G content (1–4%) and grape or rosehip oils (10–40%) for the preparation of W/O emulsions with strong antioxidant activity.
[...] Read more.
The selenized glutelin (Se-G) from Se-enriched chickpea sprouts has demonstrated high antioxidant potential. In this study, the response surface methodology was employed to optimize Se-G content (1–4%) and grape or rosehip oils (10–40%) for the preparation of W/O emulsions with strong antioxidant activity. In the optimal emulsions (Se-GG with grape oil and Se-GR with rosehip oil), antioxidant, photoprotective, and antiaging properties were evaluated. Non-Se glutelin was used in the control emulsions. The optimal conditions determined (4.0% Se-G/10.0% rosehip oil and 3.39% Se-G/12.50% grape oil) allowed for the preparation of emulsions with higher antioxidant capacity. The Se-GR with rosehip oil had greater antioxidant capacity than the Se-GG with grape oil. The optimal emulsions with Se, compared to their Se-free controls, had significantly higher antioxidant activity. The zeta potential value increased with the presence of Se. A positive effect on the inhibition of ROS production and lipid peroxidation was observed, as well as the inhibition of collagenase, elastase, and hyaluronidase activity, mainly due to the presence of selenium. Se-G represents a powerful tool for preventing damage to the skin caused by UV exposure.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
From Nature to Science: A Review of the Applications of Pectin-Based Hydrogels
by
Karla Nohemi Rubio-Martin del Campo, María Fernanda Rivas-Gastelum, Luis Eduardo Garcia-Amezquita, Maricruz Sepulveda-Villegas, Edgar R. López-Mena, Jorge L. Mejía-Méndez and Angélica Lizeth Sánchez-López
Macromol 2025, 5(4), 58; https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol5040058 - 2 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Pectin is widely used in different areas like biomedical, pharmaceutical, food, and environmental industries thanks to its gelling properties. Pectin hydrogels are of great interest because of their wide biomedical applications in drug delivery, tissue engineering, wound healing, the food industry, agriculture, and
[...] Read more.
Pectin is widely used in different areas like biomedical, pharmaceutical, food, and environmental industries thanks to its gelling properties. Pectin hydrogels are of great interest because of their wide biomedical applications in drug delivery, tissue engineering, wound healing, the food industry, agriculture, and cosmetic products because of their biocompatibility, biodegradability, and non-toxic nature. This review provides an understanding of pectin-based hydrogels and their applications in various industrial areas. In addition, an overview of emerging technologies and recent applications of pectin hydrogels is provided, including the controlled and targeted release of bioactive compounds or drugs. They are used as a scaffold for cell growth, as a wound dressing to promote healing, as a fat replacer in food, and as a texturizer in skin-care products. It also serves as a coating for seeds to improve their germination and growth. This paper also identifies knowledge gaps and future research direction for optimizing pectin hydrogels.
Full article
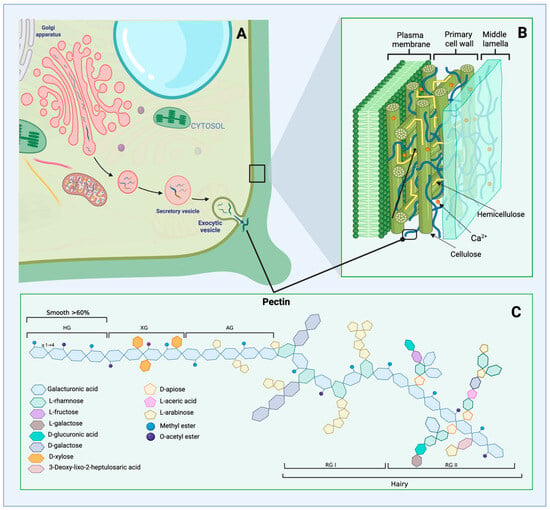
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Investigating Swelling and Bending Response of pH-Sensitive Chitosan-Based Hydrogels
by
Jafar Arash Mehr and Hamed Hatami-Marbini
Macromol 2025, 5(4), 57; https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol5040057 - 27 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Biocompatible electroactive hydrogels with bidirectional pH-responsive bending are important for the creation of biomedical actuators. This study developed chitosan/carboxymethylcellulose (CS/CMC) semi-interpenetrating networks (SIPNs) with different volume ratios, which were crosslinked with glutaraldehyde. The swelling and bending behaviors of SPINs were systematically characterized as
[...] Read more.
Biocompatible electroactive hydrogels with bidirectional pH-responsive bending are important for the creation of biomedical actuators. This study developed chitosan/carboxymethylcellulose (CS/CMC) semi-interpenetrating networks (SIPNs) with different volume ratios, which were crosslinked with glutaraldehyde. The swelling and bending behaviors of SPINs were systematically characterized as a function of the pH of the solution and the magnitude of the applied electric field. The hydrogels exhibited pH-dependent bidirectional actuation, with the maximum swelling of 4.67–6.00 at pH ≈ 3.9 and minimum swelling of 1.58–2.53 at pH ≈ 5.7. The SPINs with CS/CMC = 1:1 composition achieved the highest bending angle of 77° at pH ≈ 5.7, while cathodic bending up to an angle of −13.7° was observed in basic conditions. The electromechanical response was significantly enhanced by decreasing the electrode distance and increasing the applied voltage. The observed correlation between the composition, swelling behavior, and bending performance was explained in terms of the electrostatic interactions between NH3+ and COO− groups present in the CS/CMC mixtures. These findings provided novel insight into the ongoing efforts for the development of non-toxic electroactive hydrogels with tailored electromechanical bending behavior necessary for use as artificial muscles and biomedical actuators.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
RNA Polymerase II Activity and Nuclear Actin: Possible Roles of Nuclear Tropomyosin, Troponin and Ca2+ in Transcription in Striated Muscle Myocyte Nuclei
by
Amelia J. Koopman, Alexandra J. Martin, Lauren G. Moore, Michelle Rodriguez and Prescott Bryant Chase
Macromol 2025, 5(4), 56; https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol5040056 - 13 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) polymerases are macromolecular machines that catalyze the synthesis of RNA macromolecules, the sequences of which are coded for by the sequences of regions of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) macromolecules in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells, or nuclei in the case of
[...] Read more.
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) polymerases are macromolecular machines that catalyze the synthesis of RNA macromolecules, the sequences of which are coded for by the sequences of regions of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) macromolecules in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells, or nuclei in the case of many mature striated muscle cells, or myocytes, which are in many cases polynucleated. Herein, we review the evidence that transcription, the activity of RNA polymerases that is an essential step in gene expression, and processes related to maturation of eukaryotic RNA can be influenced by the macromolecule actin and its macromolecular complex of filamentous actin and its association with actin-binding proteins in the nucleus. We furthermore hypothesize that the macromolecular complexes of troponin (Tn) and tropomyosin (Tm), which bind actin filaments in the cytoplasm of striated muscle myocytes to form thin filaments and which are also found in the nuclei of striated muscle myocytes and some cancerous cells, could modulate that influence of nuclear actin on transcription when present in a nucleus. Interestingly, troponin and tropomyosin could confer Ca2+ dependence to transcriptional modulation by nuclear actin, a mechanism that would complement Ca2+-dependent modulation of post-translational modifications that influence gene expression.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
IJMS, JFB, Macromol, Materials, J. Compos. Sci., Polymers
Recent Advances in Composite Biomaterials
Topic Editors: Diego Romano Perinelli, Florentina LupascuDeadline: 30 November 2026
Topic in
Applied Nano, Macromol, Nanomaterials, Polymers, Gels
Future Trends in Polymer Science: Materials, Design, and Advanced Applications
Topic Editors: Emi Haladjova, Olya StoilovaDeadline: 30 January 2027

Special Issues
Special Issue in
Macromol
Advances in Starch and Lignocellulosic-Based Materials
Guest Editor: Valentina SessiniDeadline: 28 February 2026
Special Issue in
Macromol
Editorial Board Members’ Collection Series: Advances in Cellulose-Based Materials
Guest Editors: John H.T. Luong, Zhaobin QiuDeadline: 31 May 2026
Special Issue in
Macromol
Recent Trends in Carbohydrate-Based Therapeutics
Guest Editor: Rajendra RohokaleDeadline: 31 May 2026
Special Issue in
Macromol
Chitosan-Based Materials for Biomedical Applications: Derivatives and Composites
Guest Editors: Maria Bonferoni, Sara PerteghellaDeadline: 31 August 2026









