- Article
A Novel Bioactive Emulgel with Phlomis kurdica: Antioxidant Potential, Enzyme Inhibition and Permeation Kinetics
- Tuğba Buse Şentürk,
- Timur Hakan Barak and
- Zafer Ömer Özdemir
- + 3 authors
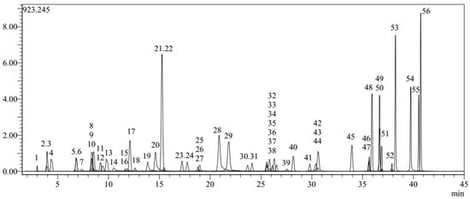
Phlomis L., with more than 100 species belonging to the Lamiaceae family, is a genus encompassing a diverse group of plants known for their rich phytochemical profiles and important medicinal properties. Phlomis kurdica Rech. fil. is a member of this genus widely distributed in the Middle East, especially in Iran, Iraq and Türkiye. In traditional medicine, Phlomis species have been employed in the treatment of various disorders, particularly skin conditions such as wound healing, as well as diabetes, hemorrhoids, inflammation, and gastric ulcers. The purpose of this study was to investigate the biological activities of Phlomis kurdica on skin-related enzymes and to evaluate its phytochemical properties using HPTLC, LC-MS/MS. Additionally, an emulgel formulation was developed with methanolic extract of the plant and characterized in terms of spreadability, textural profile analysis, pH, viscosity, and content quantification determination. In vitro release and rheology studies were carried out following the characterization investigations. According to our investigations, P. kurdica may be a useful component of wrinkle prevention and skin-regenerating products.
13 March 2026