-
 Synthesis of Novel Bismuth-Based Catalysts for the Degradation of Microplastics in Aquatic Matrices
Synthesis of Novel Bismuth-Based Catalysts for the Degradation of Microplastics in Aquatic Matrices -
 Assessing the Efficacy of Magnetic Micro-Nanoparticles in Water Treatment as a Potential Solution for Textile Microplastic Pollution
Assessing the Efficacy of Magnetic Micro-Nanoparticles in Water Treatment as a Potential Solution for Textile Microplastic Pollution -
 Characterization of Microplastics and 6-PPD Quinone in a Suburban Lake–Tributary System Impacted by Highway Runoff
Characterization of Microplastics and 6-PPD Quinone in a Suburban Lake–Tributary System Impacted by Highway Runoff -
 Investigating the Potential of Coagulants to Improve Microplastics Removal in Wastewater and Tap Water
Investigating the Potential of Coagulants to Improve Microplastics Removal in Wastewater and Tap Water -
 Microplastics in Lichen Thalli: A Photo or a Movie of Local Atmospheric Deposition?
Microplastics in Lichen Thalli: A Photo or a Movie of Local Atmospheric Deposition?
Journal Description
Microplastics
Microplastics
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on the science and technology of primary and secondary microplastics published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within ESCI (Web of Science), Scopus, EBSCO, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q1 (Environmental Sciences) / CiteScore - Q1 (Environmental Science (miscellaneous))
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 24.3 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 15.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review and reviewer names are published annually in the journal.
- Journal Cluster of Polymer and Macromolecular Science: Polymers, Gels, Polysaccharides, Textiles, Macromol, Microplastics and Adhesives.
Impact Factor:
5.1 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
5.2 (2024)
Latest Articles
Research Progress on the Effects of Combined Microplastics and Cadmium Pollution on Plants
Microplastics 2026, 5(1), 16; https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics5010016 - 21 Jan 2026
Abstract
►
Show Figures
The toxic effects of soil heavy metals and microplastics on plants have been extensively documented, with some researchers having conducted studies exploring the combination of these two factors. Preliminary findings indicate that their combined action can “reduce biomass, exacerbate oxidative stress, and inhibit
[...] Read more.
The toxic effects of soil heavy metals and microplastics on plants have been extensively documented, with some researchers having conducted studies exploring the combination of these two factors. Preliminary findings indicate that their combined action can “reduce biomass, exacerbate oxidative stress, and inhibit photosynthesis,” and the potential mechanisms of this combined toxicity are currently being explored. However, these combined effects remain unclear, with conflicting conclusions across studies. Research subjects are relatively fragmented, and systematic summaries are lacking. This paper systematically reviews current research findings on the combined toxic effects of microplastics and Cd on plants, specifically focusing on the following factors: (1) the mechanisms and influencing factors of Cd adsorption by microplastics: electrostatic adsorption is the primary mechanism, and soil environmental factors are significant influencers; (2) microplastics’ altering of the available Cd content in soil: soil environmental conditions can be modified to increase or decrease available Cd concentrations; (3) The “synergistic or antagonistic” toxic effects of microplastics and Cd on plants. Future research directions warranting in-depth investigation are also identified in this study.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Seasonal and Cross-Shore Assessment of Large and Small Microplastics Collected on the Ferrara Coast (Italy)
by
Joana Buoninsegni, Giorgio Anfuso, Umberto Tessari, Valentina Giro, Elena Marrocchino and Carmela Vaccaro
Microplastics 2026, 5(1), 15; https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics5010015 - 19 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Microplastic (MP) contamination along coastlines is a globally recognized environmental concern. This paper investigates the seasonal and cross-shore distribution of large and small microplastics (LMPs and SMPs) at four sites along the Ferrara coast in the northern Adriatic Sea (Italy). A combination of
[...] Read more.
Microplastic (MP) contamination along coastlines is a globally recognized environmental concern. This paper investigates the seasonal and cross-shore distribution of large and small microplastics (LMPs and SMPs) at four sites along the Ferrara coast in the northern Adriatic Sea (Italy). A combination of sampling and analytical approaches was employed to characterize the typology, morphology, and size of MPs. A subsample of LMPs was analyzed by Raman spectroscopy to determine polymers’ composition. The mean abundances recorded were 5.66 ± 13.15 LMPs/m2 and 2402.19 ± 1169.85 SMPs/m2. Among the LMPs, pellets and fragments, essentially cream and white in color, were dominant. The samples were predominantly composed of polyethylene, polypropylene, and polyethylene terephthalate. SMPs primarily consisted of black fibers. LMPs and SMPs displayed their lowest abundances in winter and cross-shore patterns indicated preferential accumulation at dune foot and crest. Since the study sites are located downstream of the Po and Reno river mouths, urban and riverine discharges, as well as emissions from plastic-processing industries, are likely major contributors to the observed MPs.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
From Antioxidant Defenses to Transcriptomic Signatures: Concentration-Dependent Responses to Polystyrene Nanoplastics in Reef Fish
by
Manuela Piccardo, Mirko Mutalipassi, Lucia Pittura, Rosa Maria Sepe, Pasquale De Luca, Laurence Besseau, Monia Renzi, Stefania Gorbi, Vincent Laudet, Alberto Pallavicini, Paolo Sordino and Antonio Terlizzi
Microplastics 2026, 5(1), 14; https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics5010014 - 16 Jan 2026
Abstract
Nanoplastics (NPs) pose significant risks due to their small size and ability to penetrate biological tissues. However, the molecular pathways and cellular mechanisms affected by NP exposure in marine teleosts remain poorly understood, especially in tropical reef fishes. This study examined the impact
[...] Read more.
Nanoplastics (NPs) pose significant risks due to their small size and ability to penetrate biological tissues. However, the molecular pathways and cellular mechanisms affected by NP exposure in marine teleosts remain poorly understood, especially in tropical reef fishes. This study examined the impact of short-term (7 days) waterborne exposure of 100 nm-carboxyl-modified polystyrene NPs on the false clownfish (Amphiprion ocellaris) exposed at two daily concentrations: low (20 µg/L, environmentally relevant) and high (2000 µg/L). A multidisciplinary approach, including biochemical and transcriptomic analyses, was conducted to assess toxic effects. Biochemical assays revealed limited changes in antioxidant defenses (CAT, GR, GST, TOSC). However, the Integrated Biomarker Response index (IBRv2i) suggested a compromised physiological condition, supported by transcriptomic data. Transcriptomic profiling revealed 409 significantly differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in the high-concentration and 354 DEGs in the low-concentration groups, with 120 shared DEGs mostly upregulated and indicative of a core molecular response. Collectively, the transcriptional profile of the low-concentration group resembled an early-warning, energy-reallocation strategy aimed at preserving essential sensory functions while minimizing expendable functions. The high-concentration group amplified the shared stress signature and recruited an additional 289 unique genes, resulting in pronounced enrichment of Gene Ontology terms related to “muscle contraction”, “oxygen transport”, “hydrogen-peroxide catabolism”, and “extracellular-matrix”. This study demonstrates that PS-NP exposure can alter gene expression and physiology in juvenile reef fish, even at environmentally relevant concentrations. Molecular responses varied with concentrations highlighting the role of exposure level in influencing biological systems and potential long-term impacts of NP pollution in marine environments.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Micro- and Nanoplastics Beyond the Mainstream: Understudied Dimensions and Emerging Approaches)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Urban River Microplastics as Vectors for Pharmaceutical Contaminants in a Savannah Region (Caatinga Biome)
by
Yannice Tatiane da Costa Santos, Anderson Targino da Silva Ferreira, Lyndyanne Dias Martins, Hellen da Silva Sousa, Francisco Wedson Faustino, Maria Carolina Hernandez Ribeiro, Maria Kuznetsova, Anderson Zanardi de Freitas and Niklaus Ursus Wetter
Microplastics 2026, 5(1), 13; https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics5010013 - 16 Jan 2026
Abstract
The study investigates the presence of emerging contaminants in a river within a watershed located in the Brazilian semiarid region, specifically within the Caatinga biome, emphasizing the importance of environmental monitoring in areas that have historically been underrepresented in scientific research. The analysis
[...] Read more.
The study investigates the presence of emerging contaminants in a river within a watershed located in the Brazilian semiarid region, specifically within the Caatinga biome, emphasizing the importance of environmental monitoring in areas that have historically been underrepresented in scientific research. The analysis focused on the associations between microplastics and pharmaceutical compounds, demonstrating that the discharge of untreated domestic effluents and the low efficiency of sanitation systems increase water resource contamination and threaten water security. The interdependence between these variables underscores the need for integrated public policies for waste management, complemented by environmental education strategies and technological innovations. The work makes an unprecedented contribution to expanding knowledge about emerging pollutants in semiarid environments, highlighting the urgency of holistic approaches, continuous monitoring, and strengthening environmental governance to ensure the sustainability and resilience of ecosystems like the Caatinga in the face of the challenges posed by global environmental change, urban growth, and those outlined in the Sustainable Development Goals.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Microplastics in Freshwater Ecosystems)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Can Cigarette Butt-Derived Cellulose Acetate Nanoplastics Induce Toxicity in Allolobophora caliginosa? Immunological, Biochemical, and Histopathological Insights
by
Zeinab Bakr, Shimaa Mohamed Said, Naser A. Elshimy, Mohamed Abd El-Aal and Gehad N. Aboulnasr
Microplastics 2026, 5(1), 12; https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics5010012 - 15 Jan 2026
Abstract
Plastic pollution is a major global challenge, especially nanoplastics (NPs) emerging as harmful pollutants due to their small size, reactivity, and persistence in ecosystems. Among them, cigarette butts composed of cellulose acetate (CA) are one of the most widespread and hazardous sources of
[...] Read more.
Plastic pollution is a major global challenge, especially nanoplastics (NPs) emerging as harmful pollutants due to their small size, reactivity, and persistence in ecosystems. Among them, cigarette butts composed of cellulose acetate (CA) are one of the most widespread and hazardous sources of terrestrial NPs. In this study, the immunotoxic, biochemical, and histopathological effects of cellulose acetate nanoplastics (CA-NPs) derived from smoked cigarette butts (SCB-NPs), unsmoked cigarette butts (USCB-NPs), and commercial cellulose acetate (CCA-NPs) were evaluated on the earthworm Allolobophora caliginosa. Adult worms were exposed for 30 days to 100 mg/kg CA-NPs in artificial soil under controlled laboratory conditions. Results revealed that SCB-NPs induced the most pronounced alterations, including increased lysozyme and metallothionein levels, reduced phagocytic and peroxidase activities, and depletion of protein and carbohydrate reserves. Histological examination showed vacuoles in epithelial layer vacuolization, space between muscle fiber disruption, and degeneration in gut and body wall, especially under SCB-NP exposure. USCB-NPs and CCA-NPs caused milder but still significant effects. Taken together, these findings highlight that the high toxicity of SCB-NPs is due to the presence of combustion-derived toxicants (nicotine, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and heavy metals), which exacerbate oxidative stress, immune suppression, and tissue damage in soil invertebrates. This study underscores the ecological risk of cigarette butt-derived NPs and calls for urgent policy measures to mitigate their terrestrial impacts.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Micro- and Nanoplastics Beyond the Mainstream: Understudied Dimensions and Emerging Approaches)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Gaps and Pathways Towards Standardized, FAIR Microplastics Data Harmonization: A Systematic Review
by
Ebenezer S. Nyadjro, Just Cebrian, T. Erin Cox, Zhankun Wang, Yee H. Lau, Anastasia M. Konefal, Gray Turnage, Tia Offner, Rebecca Gilpin, Tim Boyer, Kirsten Larsen, Paul Mickle, Eric Sparks and Jennifer A. B. Webster
Microplastics 2026, 5(1), 11; https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics5010011 - 14 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The global proliferation of plastics and their degradation into microplastics (<5 mm) have created a pervasive environmental crisis with severe ecological and human health consequences. Despite the exponential growth in microplastic research over the past decade, standardized protocols are still lacking. The absence
[...] Read more.
The global proliferation of plastics and their degradation into microplastics (<5 mm) have created a pervasive environmental crisis with severe ecological and human health consequences. Despite the exponential growth in microplastic research over the past decade, standardized protocols are still lacking. The absence of consistent sampling, analysis, and reporting methods limits data comparability, interoperability, and harmonization across studies. This study conducted a systematic bibliographic review of 355 peer-reviewed articles published between 2010 and 2022 that investigated microplastics in freshwater as well as marine water and sediment environments. The goal was to evaluate methodological consistency, sampling instruments, measurement units, reported characteristics, and data-sharing practices to identify pathways toward harmonized and FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable) microplastic data. Results show that 80.6% of studies focused on marine environments, 18% on freshwater, and 1.4% on both. This highlights persistent data gaps in freshwater systems, which function as key transport pathways for plastics to the ocean. Most studies targeted water (59%) rather than sediment (41%) and were mostly based on single-time sampling, limiting long-term analyses. Surface layers (<1 m) were predominantly sampled, while deeper layers remain understudied. Nets, particularly Manta, neuston, and plankton nets were the dominant tools for water sampling, whereas grabs, corers, and metallic receptacles were used for sediments. However, variations in mesh size and sampling depth introduce substantial biases in particle size recovery and reduce comparability across studies. The most common units were counts/volume for water and counts/g dry weight for sediments, but more than ten unit expressions were identified, complicating conversions. Only 35% of studies reported all four key microplastic characteristics (color, polymer type, shape, and size), and less than 20% made datasets publicly available. To advance harmonization, we recommend the adoption of consistent measurement units, mandatory reporting of key metadata, and wider implementation of open data practices aligned with the FAIR principles. These insights provide a foundation for developing robust monitoring strategies and evidence-based management frameworks. This is especially important for freshwater systems, where data remain scarce, and policy intervention is urgently needed.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Sorption of Pyrene and Fluoranthene onto Common Microplastics Under Freshwater Conditions
by
Sara Exojo-Trujillo, Laura Higueras-Contreras, Pilar Hernández-Muñoz and Rafael Gavara
Microplastics 2026, 5(1), 10; https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics5010010 - 14 Jan 2026
Abstract
Microplastics (MPs) are recognised as emerging vectors for hydrophobic organic contaminants in aquatic environments due to their relatively large surface area and the diversity of their polymer chemistries compositions. This study investigates the sorption behaviour of two priority polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), pyrene
[...] Read more.
Microplastics (MPs) are recognised as emerging vectors for hydrophobic organic contaminants in aquatic environments due to their relatively large surface area and the diversity of their polymer chemistries compositions. This study investigates the sorption behaviour of two priority polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), pyrene (PYR) and fluoranthene (FLU), onto six common MPs: poly(m-xylene adipamide) (PA-MXD6), high- and low-density polyethylene (HDPE, LDPE), polypropylene (PP), polyethylene terephthalate (PET), and polylactic acid (PLA). Sorption isotherms and kinetics were evaluated under simulated freshwater conditions at environmentally relevant concentrations (1–50 µg·L−1). Despite the low MP concentration used (0.2 g·L−1), over 80% of the initial PAH content was removed by polyolefins, and more than 50% by all other MPs. Sorption capacity was strongly dependent on particle surface area. Langmuir, Henry, and Freundlich isotherms models were fitted, with linear behaviour prevailing at low concentrations. Analysis using the Dubini–-Radushkevich model confirmed that sorption involves chemisorption contributions, mainly through π–π interactions and hydrophobic interactions (polyolefins). Mechanistically, molecular diffusion within the MP matrix was not governing the sorption process, as diffusion coefficients varied with particle size instead of polymer chemistry. Instead, sorption appears to be governed by PAH diffusion through the hydrodynamic boundary layer and subsequent retention on the MP surface. Empirically, kinetic data fitted the pseudo-second-order model, further supporting that the sorption process involves chemisorption. These findings highlight the role of MPs as vectors for PAHs in freshwater systems and their potential application in contaminant removal. Expressing sorption per unit surface area is recommended for accurate assessment. This work contributes to understanding the environmental behaviour of MPs and their implications for pollutant transport and toxicity.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Microplastics in Freshwater Ecosystems)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessEditorial
Microplastics—Four Years of Publications on the Environmental Challenges and Adverse Health Effects of Microplastics
by
Nicolas Kalogerakis
Microplastics 2026, 5(1), 9; https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics5010009 - 13 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Microplastics is a new, open access, peer-reviewed journal from MDPI that has just completed its fourth year of publication (2025) [...]
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Microplastics and Human Health: A Comprehensive Review on Exposure Pathways, Toxicity, and Emerging Risks
by
Nayak Snehamayee, Sephalika Somya, Sahoo Chinmaya Kumar, Mohanty Niranjan, Sahu Bikash Ranjan and Mohakud Nirmal Kumar
Microplastics 2026, 5(1), 8; https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics5010008 - 13 Jan 2026
Abstract
Microplastics (MPs) are considered to be dominant agents responsible for serious contamination in environmental and biological systems. Despite a huge increase in research on these contaminants, there are still considerable uncertainties and progress to be made on the exposure pathways of biological systems,
[...] Read more.
Microplastics (MPs) are considered to be dominant agents responsible for serious contamination in environmental and biological systems. Despite a huge increase in research on these contaminants, there are still considerable uncertainties and progress to be made on the exposure pathways of biological systems, modes of detection, and toxicity assessments. Therefore, developing a critical review of MPs is crucial due to growing evidence of their harmful effects on human health. In the current review, we aim to emphasize the potential toxic effects of MPs on different biological systems in humans, the mechanisms of their toxic effects, and gaps in our knowledge on risk assessment. Importantly, we focus on the risks posed by MPs for fetuses and child health. To ensure methodological rigor, the current review follows the PRISMA guidelines, explicitly detailing the literature search strategy and inclusion/exclusion criteria. The present review summarizes potential sources of MP generation, exposure pathways, quantitative analyses of dietary exposure, estimated daily intake, particle/leachate toxicity evidence, detection in different human organs, and potential toxic effects. MPs cause toxicity in several biological systems in humans, such as the gastrointestinal, nervous, hepatic, endocrine, respiratory, and reproductive systems. In addition, these particles are known to cause oxidative stress, alter metabolism, and affect gut microflora and gastrointestinal functions. Importantly, the current review also discusses the challenges encountered in conducting risk assessments for MPs and the approaches for counteracting these challenges. Finally, the review concludes by recommending future research directions in terms of counteracting the toxic effects of MPs on human health.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Microplastics and Human Health: Impact, Challenges and Interaction Mechanisms)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Impact of Microplastics on Copper Electrodeposition: Morphological and Electrochemical Insights
by
Claudia Giovani, Walter Giurlani, Monica Tonelli, Laura Sforzi, Massimo Bonini, Alessandra Cincinelli, Tania Martellini and Massimo Innocenti
Microplastics 2026, 5(1), 7; https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics5010007 - 9 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Microplastics (MPs) have been attracting considerable interest in recent years due to their ubiquitous existence and accumulation within different systems and ecosystems. Moreover, their presence in electroplating baths involves a more serious challenge considering that the electroplating industry is progressing towards the electroplating
[...] Read more.
Microplastics (MPs) have been attracting considerable interest in recent years due to their ubiquitous existence and accumulation within different systems and ecosystems. Moreover, their presence in electroplating baths involves a more serious challenge considering that the electroplating industry is progressing towards the electroplating of plastic materials. Contaminated baths can lead to surface defects, poor adhesion, corrosion, and inconsistent deposit thicknesses. Despite these issues, the interactions between pollutant MPs and heavy metal ions in electroplating environments are still underexplored. The present study aims to investigate the behavior of self-produced “Nylon PA” MPs dispersed in acid copper electroplating baths and their interactions with copper ions in solution. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) reveals several surface defects in copper deposits caused by MPs in the bath. Additionally, cyclic voltammetry and chronoamperometry indicate significant changes in nucleation and growth mechanisms, with MPs showing suppressant-like effects on copper deposition. These results shed light on the impact of MPs on copper electrodeposition, emphasizing the urgent need for further research and mitigation strategies to address this emerging issue in the electroplating industry.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Sticking Efficiency of Microplastic Particles in Terrestrial Environments Determined with Atomic Force Microscopy
by
Robert M. Wheeler and Steven K. Lower
Microplastics 2026, 5(1), 6; https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics5010006 - 9 Jan 2026
Abstract
Subsurface deposition determines whether soils, aquifers, or ocean sediment represent a sink or temporary reservoir for microplastics. Deposition is generally studied by applying the Smoluchowski–Levich equation to determine a particle’s sticking efficiency, which relates the number of particles filtered by sediment to the
[...] Read more.
Subsurface deposition determines whether soils, aquifers, or ocean sediment represent a sink or temporary reservoir for microplastics. Deposition is generally studied by applying the Smoluchowski–Levich equation to determine a particle’s sticking efficiency, which relates the number of particles filtered by sediment to the probability of attachment occurring from an interaction between particles and sediment. Sticking efficiency is typically measured using column experiments or estimated from theory using the Interaction Force Boundary Layer (IFBL) model. However, there is generally a large discrepancy (orders of magnitude) between the values predicted from IFBL theory and the experimental column measurements. One way to bridge this gap is to directly measure a microparticle’s interaction forces using Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM). Herein, an AFM method is presented to measure sticking efficiency for a model polystyrene microparticle (2 μm) on a model geomaterial surface (glass or quartz) in environmentally relevant, synthetic freshwaters of varying ionic strength (de-ionized water, soft water, hard water). These data, collected over nanometer length scales, are compared to sticking efficiencies determined through traditional approaches. Force measurement results show that AFM can detect extremely low sticking efficiencies, surpassing the sensitivity of column studies. These data also demonstrate that the 75th to 95th percentile, rather than the mean or median force values, provides a better approximation to values measured in model column experiments or field settings. This variability of the methods provides insight into the fundamental mechanics of microplastic deposition and suggests AFM is isolating the physicochemical interactions, while column experiments also include physical interactions like straining. Advantages of AFM over traditional column/field experiments include high throughput, small volumes, and speed of data collection. For example, at a ramp rate of 1 Hz, 60 sticking efficiency measurements could be made in only a minute. Compared to column or field experiments, the AFM requires much less liquid (μL volume) making it effortless to examine the impact of solution chemistry (temperature, pH, ionic strength, valency of dissolved ions, presence of organics, etc.). Potential limitations of this AFM approach are presented alongside possible solutions (e.g., baseline correction, numerical integration). If these challenges are successfully addressed, then AFM would provide a completely new approach to help elucidate which subsurface minerals represent a sink or temporary storage site for microparticles on their journey from terrestrial to oceanic environments.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Microplastics in Freshwater Ecosystems)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Toxic Impact of Polystyrene Microplastics (PS-MPs) on Freshwater Mussel Lamellidens marginalis
by
Nishigandha Muduli, Sthitaprajna Nath Sharma, Smruti Prajna Pradhan, Pratyusha Nayak, Subhashree Nayak and Lipika Patnaik
Microplastics 2026, 5(1), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics5010005 - 9 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Microplastics are among the most emerging environmental micro-threats to aquatic ecosystems. Bivalves are filter-feeding benthic organisms and are often considered excellent bioindicators of contamination in aquatic bodies. This study focuses on the toxic effects of fibrous polystyrene microplastics (1 mg/L) on biochemical parameters
[...] Read more.
Microplastics are among the most emerging environmental micro-threats to aquatic ecosystems. Bivalves are filter-feeding benthic organisms and are often considered excellent bioindicators of contamination in aquatic bodies. This study focuses on the toxic effects of fibrous polystyrene microplastics (1 mg/L) on biochemical parameters of the freshwater bivalve Lamellidens marginalis after exposure periods of 7, 10, and 15 days (Experimental groups I, II, and III, respectively). Biochemical analysis showed reduced protein, ACP, and ALP activities in all tissues except for a significant increase in ACP in the mantle and foot of group III. AST activity increased in the gill and hepatopancreas but declined in the mantle and foot. ALT activity consistently decreased across all experimental tissues relative to the control. The Integrated Biomarker Response Index increased over time for gill, mantle, and foot tissue. For the hepatopancreas, the values were 11, 8.82, and 9.02 for Experimental groups I, II, and III, respectively. From Biomarker Response Index values, group I gill tissue (2.2) was most severely altered. Major alterations occurred in the hepatopancreas, mantle, and foot of groups II and III. Hepatopancreas generally acts as a site of detoxification, digestion, and absorption, and exposure to microplastics can lead to the accumulation in hepatopancreas.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Microplastic Contamination of Surface Water and Sediments in Lake Kotokel (Eastern Cisbaikalia)
by
Selmeg V. Bazarsadueva, Elena P. Nikitina, Yulia A. Frank, Vasilii V. Taraskin, Liubov A. Konovalova and Endon Zh. Garmaev
Microplastics 2026, 5(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics5010004 - 7 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Lake Kotokel is one of the largest lakes along the eastern shore of Lake Baikal. Increasing anthropogenic pressure combined with climate variability led to a sharp decline in its ecological condition, culminating in an outbreak of Gaff disease in 2009. Moreover, Lake Kotokel
[...] Read more.
Lake Kotokel is one of the largest lakes along the eastern shore of Lake Baikal. Increasing anthropogenic pressure combined with climate variability led to a sharp decline in its ecological condition, culminating in an outbreak of Gaff disease in 2009. Moreover, Lake Kotokel may serve as a source of pollutants to Lake Baikal due to its hydrological connection via a system of rivers. In light of these factors, ongoing research seeks to identify the drivers of ecological degradation in the lake ecosystem and provide a comprehensive assessment of its current environmental status and potential adverse processes. In this study, we report, for the first time, the occurrence of microplastic particles in the surface water and sediments of Lake Kotokel. Mean microplastic concentrations were 0.59 ± 0.25 items/m3 in water and 280 ± 162 items/kg dry weight in sediments, with corresponding average microplastic masses of 2.6 ± 1.4 μg/m3 in water and 1.33 ± 1.21 mg/kg dry weight in sediments. In surface waters, microplastic were predominantly 1–3 mm in size, whereas sediments were dominated by 0.1–1 mm particles. Fibers were the most abundant morphological form, comprising 79.5% and 82.8% of particles in water and sediments, respectively. Five polymer types were identified, with polyethylene terephthalate being the most prevalent. Based on particle abundance and polymer composition, the ecological risk of microplastic in Lake Kotokel was assessed as low to moderate.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Plastic Particles and Female Fertility: Pathways, Toxicity, and Analytical Challenges
by
Vanda Rísová, Lívia Gajdošová, Rami Saade, Olia El Hassoun Sečanská, Martin Kopáni and Štefan Polák
Microplastics 2026, 5(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics5010003 - 1 Jan 2026
Abstract
Microplastics (MPs) and nanoplastics (NPs) are widespread environmental contaminants with documented impacts on human health, particularly on the female reproductive system. Defined as polymeric fragments smaller than 5 mm, MPs (typically ranging from 1 µm to 5 mm) and NPs (smaller than 1
[...] Read more.
Microplastics (MPs) and nanoplastics (NPs) are widespread environmental contaminants with documented impacts on human health, particularly on the female reproductive system. Defined as polymeric fragments smaller than 5 mm, MPs (typically ranging from 1 µm to 5 mm) and NPs (smaller than 1 µm, often <100 nm) originate either from primary sources—intentionally manufactured for specific industrial applications—or from secondary sources through physical, chemical, or biological degradation of macroplastics. Human exposure occurs via multiple routes, including ingestion, inhalation, dermal absorption, and iatrogenic introduction, with growing evidence that these particles can accumulate in the ovaries, oocytes, and placental tissue. Experimental studies in rodents demonstrate that MPs and NPs induce oxidative stress, trigger inflammatory responses, and promote granulosa cell apoptosis, ultimately diminishing ovarian reserve and impairing folliculogenesis. Clinical and pilot human studies have confirmed the presence of MPs in placentas, umbilical cord blood, and meconium, indicating exposure from the earliest stages of development. Moreover, MPs and NPs may disrupt the hypothalamic–pituitary–ovarian axis, contributing to endocrine dysregulation and hormonal imbalance. Analytical methods such as Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy, and scanning electron microscopy enable detection of these particles in biological samples, although methodological standardization remains insufficient. This paper summarizes current evidence on the exposure pathways, toxicological effects, and reproductive consequences of MPs and NPs in women. It further highlights existing research gaps and evaluates available analytical approaches to support future studies and develop strategies aimed at mitigating their detrimental impact on women’s reproductive health and fertility.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Microplastics and Human Health: Impact, Challenges and Interaction Mechanisms)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Detection and Identification of Non-Labeled Polystyrene Nanoplastics in Rodent Tissues Using Asymmetric Flow Field-Flow Fractionation (AF4) Combined with UV–Vis, Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) Detectors and Offline Pyrolysis–GCMS (Pyro-GCMS)
by
Gurmit Singh, Ligia Velasquez, Chris Mason, Michal Scur, Kristen A. Marcellus and Santokh Gill
Microplastics 2026, 5(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics5010002 - 1 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Microplastic pollution is a growing global environmental and public health concern, driven by the increasing production and use of plastics. Due to their ubiquitous presence in the environment, humans and animals may be exposed to micro- and nanoplastics via several possible routes. For
[...] Read more.
Microplastic pollution is a growing global environmental and public health concern, driven by the increasing production and use of plastics. Due to their ubiquitous presence in the environment, humans and animals may be exposed to micro- and nanoplastics via several possible routes. For micro- and nanoplastics, the development of standardized and validated methods remains an important area of progress to support human health risk assessments. In order to monitor micro/nanoplastics’ occurrence in organisms and the environment, it is necessary to develop accurate and reliable methods to quantify and characterize micro/nanoplastics from various biological and environmental matrices. In this study, an analytical, multi-platform approach was established to characterize and quantify polystyrene nanoplastics in biological samples through a combination of sample pre-concentration, asymmetric flow field-flow fractionation, ultraviolet–visible light, dynamic light scattering detectors and pyrolysis–gas chromatography–mass spectroscopy. Several digestion methods on various rodent tissues were tested and modified, and these led to the development of tissue-specific protocols to maximize yield. These digestion protocols were then combined with a new method of concentrating and retaining plastics to prevent the loss of submicron particles. For identification and quantification, known amounts of polystyrene nanoplastics were spiked into rodent tissues (intestine, kidney and liver). This was followed up by a mouse in vivo study consisting of a single dose of PS-NPs, followed by tissue collection, digestion and analysis. Polystyrene particles were detected in the liver and kidney, but not reliably in the intestinal tissues.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Mechanisms and Perspectives of Microplastic Biodegradation by Insects and Their Associated Microorganisms
by
Feroz Ahmad, Huarui Zhang, Chao Sun, Abrar Muhammad and Yongqi Shao
Microplastics 2026, 5(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics5010001 - 23 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Plastic pollution, particularly the widespread presence of microplastics, has emerged as a global environmental threat. Conventional plastics are highly resistant to degradation and can persist in ecosystems for decades, posing a serious long-term risk to wildlife, habitats, and human health. Increasing evidence suggests
[...] Read more.
Plastic pollution, particularly the widespread presence of microplastics, has emerged as a global environmental threat. Conventional plastics are highly resistant to degradation and can persist in ecosystems for decades, posing a serious long-term risk to wildlife, habitats, and human health. Increasing evidence suggests that insects and their gut microbiota may play a significant role in the degradation of these plastics. This review examines the mechanisms by which insects and their associated microorganisms contribute to microplastic biodegradation. Plastivorous insect larvae such as Spodoptera frugiperda, Galleria mellonella, Tenebrio molitor and Zophobas atratus have demonstrated the ability to ingest and partially degrade diverse polymers. The initial mechanical breakdown caused by insect mandibles increases the surface area, which allows gut microbes to colonize the material. Once these microbes are established, they form biofilms that help with adhesion, create localized redox environments, and concentrate degradative enzymes at the polymer interface. The enzymatic machinery of insect-associated microbes plays a crucial role in breaking down polymers. Oxidative enzymes, including DyP-type peroxidases, multicopper oxidases, alkane monooxygenases, and laccases, initiate the oxidation of polymers, while hydrolases and esterases further break down the resulting fragments. Co-metabolic processes and microbial consortia improve degradation efficiency by primary degraders by producing oxidized intermediates, which are then consumed and mineralized by secondary fermenters. Despite significant progress, the complete biochemical pathways of microplastic mineralization remain unclear. Degradation rates are slow, and scalability challenges hinder practical applications, with incomplete mineralization in insect biodegradation potentially causing secondary microplastics. Understanding these mechanisms will lay the groundwork for developing insect-microbe systems as potential biotechnological solutions to mitigate plastic pollution in terrestrial environments.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Nanoplastic Contamination Across Common Beverages and Infant Food: An Assessment of Packaging Influence
by
Roser Salvia, Carlos Soriano, Irene Casanovas, Marc Sorigué, Emily Evans, Julia Gala de Pablo, Michael D. Ward and Jordi Petriz
Microplastics 2025, 4(4), 108; https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4040108 - 18 Dec 2025
Abstract
The widespread presence of nanoplastics (NPs) in the environment creates a significant and growing concern for global health, with ingestion, inhalation, and dermal contact identified as primary exposure pathways. Despite their documented presence in various environmental matrices and human tissues, robust quantitative data
[...] Read more.
The widespread presence of nanoplastics (NPs) in the environment creates a significant and growing concern for global health, with ingestion, inhalation, and dermal contact identified as primary exposure pathways. Despite their documented presence in various environmental matrices and human tissues, robust quantitative data on NP levels remains scarce. This study addresses this critical gap by employing a novel and rapid flow cytometry technique to quantify nanoplastic concentrations in commercial waters, common beverages and infant food, with special focus in packaging influence. Pyrogen-free water was analyzed to establish the negative control for NP concentration, yielding 5.24 ± 2.02 events/µL. Ten commercial waters from natural springs in Spain and France showed NP levels ranging from 1.75 NP/µL to 67.94 NP/µL (mean: 19.90 ± 14.53 NP/µL), where three of those brands showed significantly higher NP numbers than the pyrogen-free water control. Compared to pyrogen-free water, infant formula and cereal porridge showed very low NP concentrations, with values of 10.27 ± 6.85 and 6.78 ± 2.27 events/µL, respectively, following triplicate analyses of six samples. Additional analyses comparing three similar soft drinks across different packaging (can, plastic bottle, or glass bottle) found no significant differences in NP concentration attributable to the container type. NPs, as ubiquitous contaminants, can be ingested by organisms through food and drink. Potential NP contamination in commercial water may be due to factors such as source water contamination, filtration and packaging. The presence of very low concentrations of NPs in infant foods suggests rigorous and effective quality control. Finally, the presence of NP in soft drinks was not affected by the type of packaging. Although soft drinks have higher NP levels than water, the type of packaging had no effect on the presence of NP in these soft drinks. Despite all plastic bottles being made of polyethylene terephthalate, variation in NP accumulation implies that material quality, storage condition, and substantially, water treatment and filtering processes contribute to NP contamination. This research gives evidence for widespread nanoplastic accumulation in bottled water, common beverages and infant formula and sets the stage for demanding research to further investigate sources, health effects, and development into effective quality control and preventive measures for public health.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Feature Papers in Microplastics)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Nature-Based Solutions for Removal of Microplastics from Wastewater: Technologies, Challenges, and Prospects
by
Casper Boongaling Agaton
Microplastics 2025, 4(4), 107; https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4040107 - 16 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Microplastic pollution has emerged as a serious societal concern, posing risks to the environment, human health, and economies. Conventional wastewater treatment processes remove microplastics at various levels from physical removal (primary), biological degradation (secondary), and contaminant-specific removal (tertiary treatment). Nature-based solutions (NbSs) offer
[...] Read more.
Microplastic pollution has emerged as a serious societal concern, posing risks to the environment, human health, and economies. Conventional wastewater treatment processes remove microplastics at various levels from physical removal (primary), biological degradation (secondary), and contaminant-specific removal (tertiary treatment). Nature-based solutions (NbSs) offer an ecologically friendly alternative that utilizes nature to remove microplastics from wastewater. Recent reviews either focus broadly on NBSs for wastewater, technological solutions for microplastics, or NbSs for microplastics, but rarely connect them systematically. This review presents an integrated review of the sources and impacts of microplastic pollution, NbS technologies for the removal of microplastics, challenges and prospects in utilizing NbSs, and the knowledge gaps. Primary sources of microplastics are intentionally produced at microscopic sizes, while secondary sources originate from the disintegration of larger plastic debris. Among the NbS technologies are constructed wetlands (horizontal subsurface flow, vertical flow, surface flow, microbial fuel cells, multistage) with up to 100% efficiency; green infrastructures (bioretention systems, green walls, permeable pavements, retention ponds) with up to 99% efficiency; macrophytes and microphytes with up to 94% microplastic removal rate. Despite the ecosystem services provided by NbSs, they are challenged by the decrease in efficiency in removing other contaminants, detection and evaluation of NbS performance, and non-technical factors (operations and maintenance, public acceptance, climate risks, and financing). The findings present insights on further research and policy recommendations aimed at facilitating the integration of NbSs into existing frameworks for the removal of microplastics from wastewater, promoting research and innovation, and ensuring sustainable practices for sustainable management of water resources.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Land Use and Rainfall as Drivers of Microplastic Transport in Canal Systems: A Case Study from Upstate New York
by
Md Nayeem Khan Shahariar, Addrita Haque, Thomas M. Holsen and Abul B. M. Baki
Microplastics 2025, 4(4), 106; https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4040106 - 15 Dec 2025
Abstract
Microplastic pollution in freshwater systems represents a growing environmental concern, yet the dynamics of microplastic distributions in smaller tributaries like canals/creeks remain understudied. This case study presents an investigation of microplastic contamination in a canal system in upstate New York, USA, examining land
[...] Read more.
Microplastic pollution in freshwater systems represents a growing environmental concern, yet the dynamics of microplastic distributions in smaller tributaries like canals/creeks remain understudied. This case study presents an investigation of microplastic contamination in a canal system in upstate New York, USA, examining land use and rainfall that influence microplastic abundance, distribution, and characteristics. Water and sediment samples were collected bi-weekly (June–August 2023) from sites representing runoff from diverse land-use types: agricultural areas, residential zones, academic buildings, and parking lots. The study reveals significant land-use dependent variations in contamination, with mean concentrations of 17 ± 7 items/L in the water column, while suspended sediment and bedload reached 540 ± 230 items/kg and 370 ± 80 items/kg, respectively. Upstream water column exhibited the highest loads (27 ± 2 items/L), driven by cumulative agricultural and commercial inputs, while downstream declines highlighted vegetation-mediated sedimentation. Land-use patterns strongly influenced contamination profiles, with parking lots exhibiting tire-wear fragments, artificial turf contributing polyethylene particles, and residential areas contributing 43% textile fibers. Rainfall intensity and antecedent dry days differentially influenced transport mechanisms. Antecedent dry days strongly predicted parking lot runoff fluxes surpassing rainfall intensity effects and underscored impervious surfaces as transient microplastic reservoirs.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Microplastics in Freshwater Ecosystems)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Citizen Science for Assessment of Microplastics on Beaches: A Case Study in Mexico
by
Ana Isabel Hernández-Soriano, Arely Areanely Cruz-Salas, Natalia Paulina Martínez-Toledo, Mariana Elizabeth Ballesteros-López, Alethia Vázquez-Morillas and Juan Carlos Alvarez-Zeferino
Microplastics 2025, 4(4), 105; https://doi.org/10.3390/microplastics4040105 - 11 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Microplastic pollution is a global environmental problem that affects marine and coastal ecosystems, and whose traditional monitoring is often expensive and limited in coverage. In this citizen science project, through the active participation of 26 local volunteers, data were gathered on the abundance
[...] Read more.
Microplastic pollution is a global environmental problem that affects marine and coastal ecosystems, and whose traditional monitoring is often expensive and limited in coverage. In this citizen science project, through the active participation of 26 local volunteers, data were gathered on the abundance and types of microplastics present on various Mexican beaches, while also promoting public awareness. Participants received materials and basic training to identify and collect microplastics using a standardized methodology, which enabled the creation of a broad and representative database consisting of 63 samples from 42 different beaches. A total of 1500 particles were collected, of which 75.13% were microplastics. The average success rate in collecting microplastics among the volunteers was 63.7 ± 34.7%. The results revealed a considerable diversity of microplastics in the studied areas, with a mean concentration of 3.5 MP/m ± 3.4 MP/m, fragments as the most common type identified (45% of the total), white as the predominant color (43%) and polyethylene as the polymer with the highest proportion (31%). This citizen science approach proved to be an effective tool for environmental monitoring, as the median value of correct identification of microplastics in this study was 80%. This method facilitates large-scale data collection and contributes to community engagement in marine conservation. Moreover, although it needs improvement, the advantages of this methodology are evident in its ability to complement traditional scientific studies and support more informed and participatory public policies in plastic waste management.
Full article
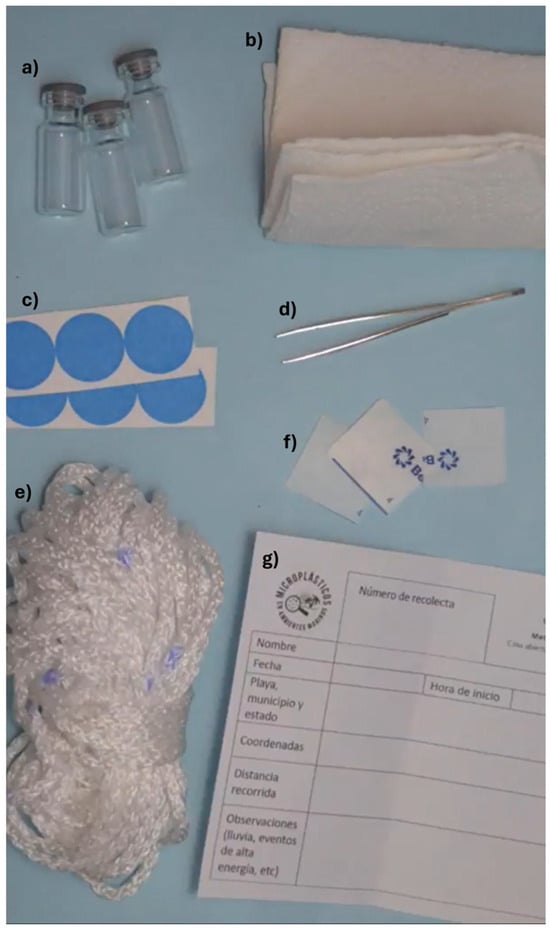
Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
IJERPH, Microplastics, Polymers, Toxics
Plastic Contamination (Plastamination): An Environmental and Public Health-Related Concern
Topic Editors: Rosaria Meccariello, Antonino Testa, Francesco Cappello, Antonietta SantoroDeadline: 30 June 2026
Topic in
Microplastics, Polymers, Sustainability, Toxics, Water
Microplastics Across Ecosystems: Multidisciplinary Approaches to Sources, Sinks and Health Sustainable Solutions
Topic Editors: Caio Rodrigues Nobre, Camilo Dias Seabra PereiraDeadline: 30 November 2026
Topic in
Fishes, Foods, Microplastics, Veterinary Sciences, Poultry, Animals, Ruminants
Micro- and Nanoplastics in Animals and Livestock Production
Topic Editors: Sonia Tassone, Beniamino T. Cenci-Goga, Samia Ben Said, Khalil AbidDeadline: 31 December 2026

Special Issues
Special Issue in
Microplastics
Microplastics and Human Health: Impact, Challenges and Interaction Mechanisms
Guest Editor: Javier BayoDeadline: 31 March 2026
Special Issue in
Microplastics
Microplastics in Freshwater Ecosystems
Guest Editor: Piotr ZielińskiDeadline: 31 August 2026
Special Issue in
Microplastics
Micro- and Nanoplastics Beyond the Mainstream: Understudied Dimensions and Emerging Approaches
Guest Editors: Manuela Piccardo, Antonio TerlizziDeadline: 30 September 2026
Special Issue in
Microplastics
The Role of Recycling in Reducing Microplastic Pollution in Textile Industry
Guest Editors: Maria Râpă, Carmen GaidauDeadline: 30 September 2026
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Microplastics
Feature Papers in Microplastics
Collection Editor: Nicolas Kalogerakis








