- Article
Bias Correction and Explainability Framework for Large Language Models: A Knowledge-Driven Approach
- Xianming Yang,
- Qi Li and
- Wei Wang
- + 3 authors
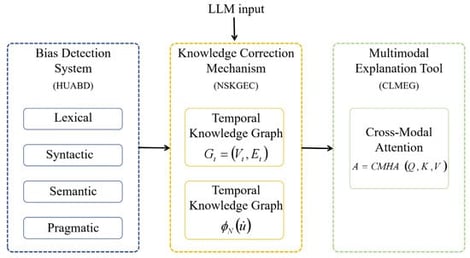
Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated extraordinary capabilities in natural language generation; however, their real-world deployment is frequently hindered by the generation of factually incorrect or biased content, along with an inherent deficiency in transparency. To address these critical limitations and thereby enhance the reliability and explainability of LLM outputs, this study proposes a novel integrated framework, namely the Adaptive Knowledge-Driven Correction Network (AKDC-Net), which incorporates three core algorithmic innovations. Firstly, the Hierarchical Uncertainty-Aware Bias Detector (HUABD) performs multi-level linguistic analysis (lexical, syntactic, semantic, and pragmatic) and, for the first time, decomposes predictive uncertainty into epistemic and aleatoric components. This decomposition enables principled, interpretable bias detection with clear theoretical underpinnings. Secondly, the Neural-Symbolic Knowledge Graph Enhanced Corrector (NSKGEC) integrates a temporal graph neural network with a differentiable symbolic reasoning module, facilitating logically consistent and factually grounded corrections based on dynamically updated knowledge sources. Thirdly, the Contrastive Learning-driven Multimodal Explanation Generator (CLMEG) leverages a cross-modal attention mechanism within a contrastive learning paradigm to generate coherent, high-quality textual and visual explanations that enhance the interpretability of LLM outputs. Extensive evaluations were conducted on a challenging medical domain dataset to validate the effectiveness of the proposed AKDC-Net framework. Experimental results demonstrate significant improvements over state-of-the-art baselines: specifically, a 14.1% increase in the F1-score for bias detection, a 19.4% enhancement in correction quality, and a 31.4% rise in user trust scores. These findings establish a new benchmark for the development of more trustworthy and transparent artificial intelligence (AI) systems, laying a solid foundation for the broader and more reliable application of LLMs in high-stakes domains.
10 February 2026