Assessing the Influence of Feedback Strategies on Errors in Crowdsourced Annotation of Tumor Images
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Crowdsourcing for Supporting Artificial Intelligence (AI)
2.2. Crowdsourcing for Supporting Medical Imaging and Media
2.3. Reliable Answers in Evaluation of Medical Images
2.4. Quality of Crowdsourcing Results
2.5. The Way the Crowdworkers Are Trained
3. Materials and Methods
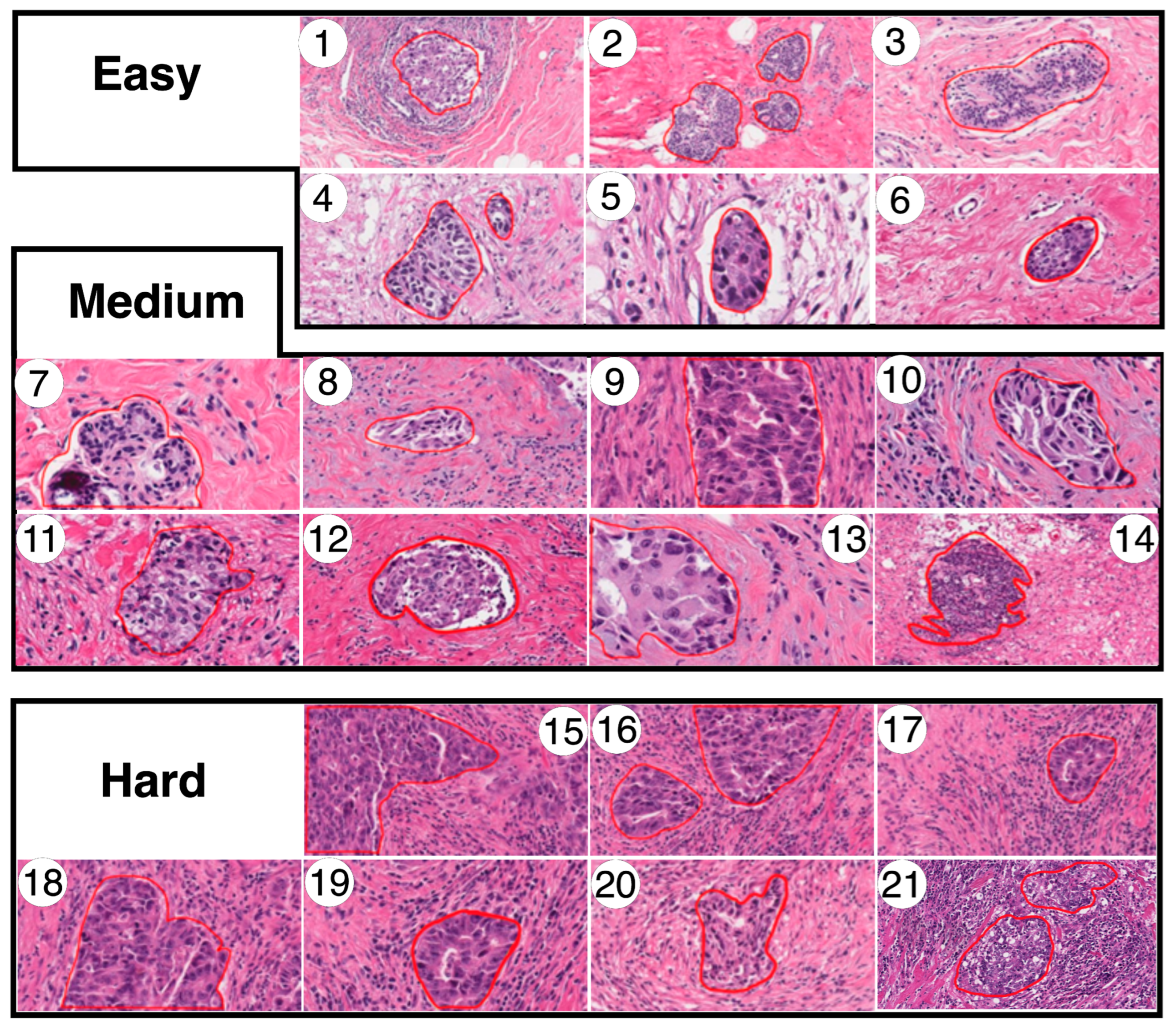
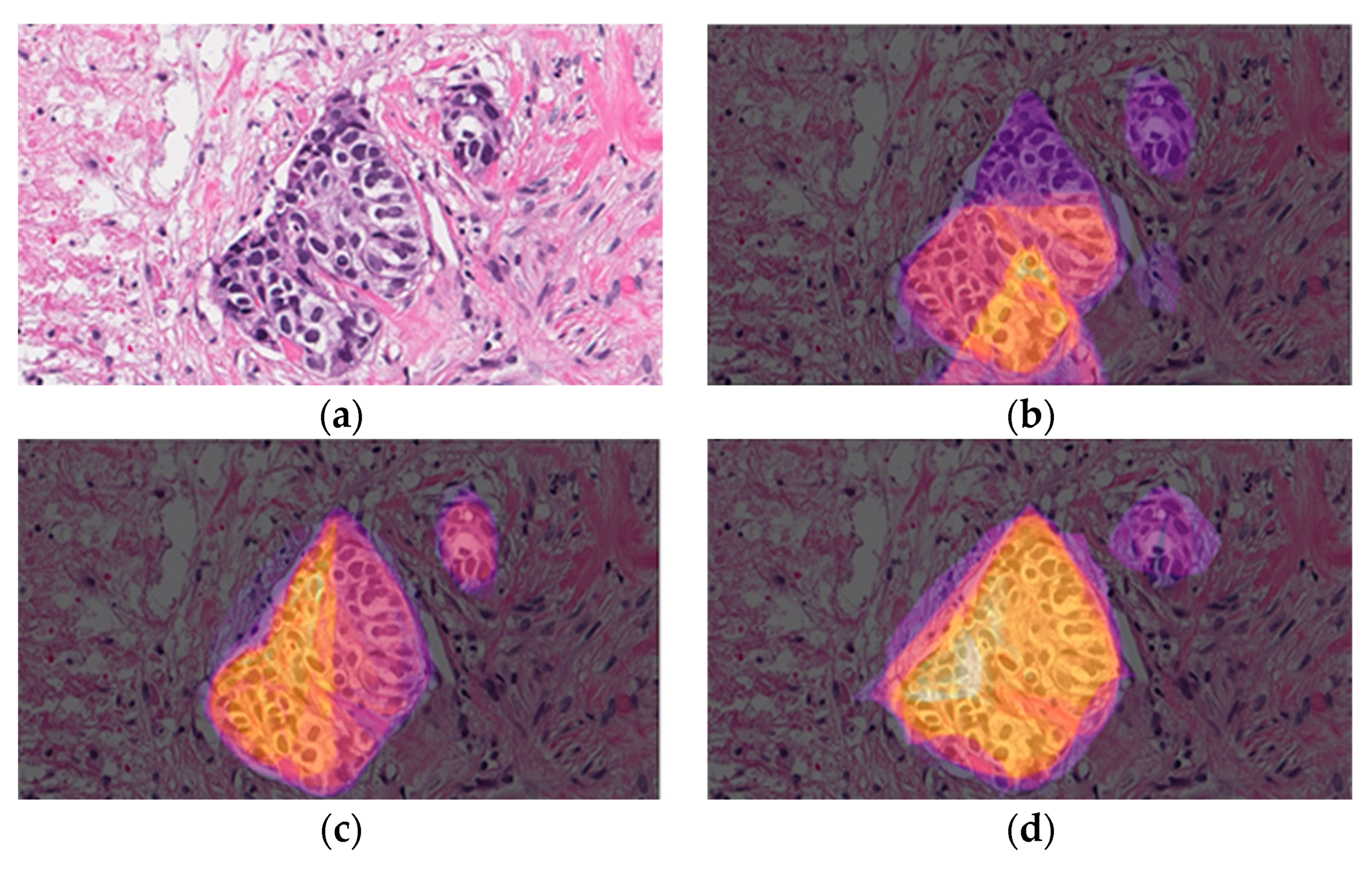
3.1. Dataset
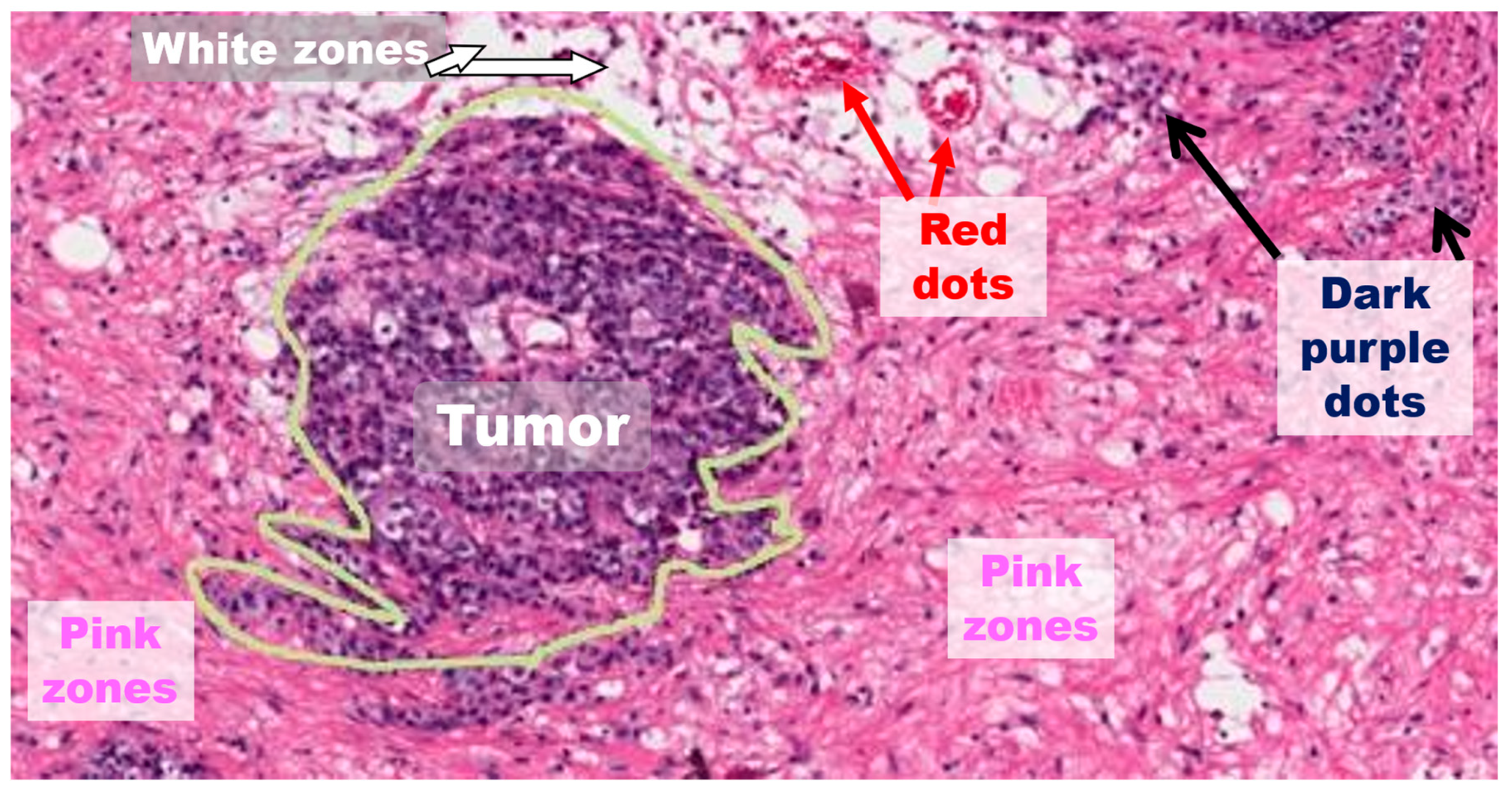
- Easy: The tumor is enhanced over all the structures around it. Typically, white zones are near and delimit the specific tumor zone.
- Medium: The tumor could be dispersed over all the structures around it. Nevertheless, there are other related structures which appear to be like tumors in other locations of the image, but the actual measurement has not classified them.
- Hard: The tumor is very difficult to discern over all the structures around it. Frequently, there are thick or even no white zones delimiting the tumor zone. For instance, there are numerous lymphocytic structures visible in the image.
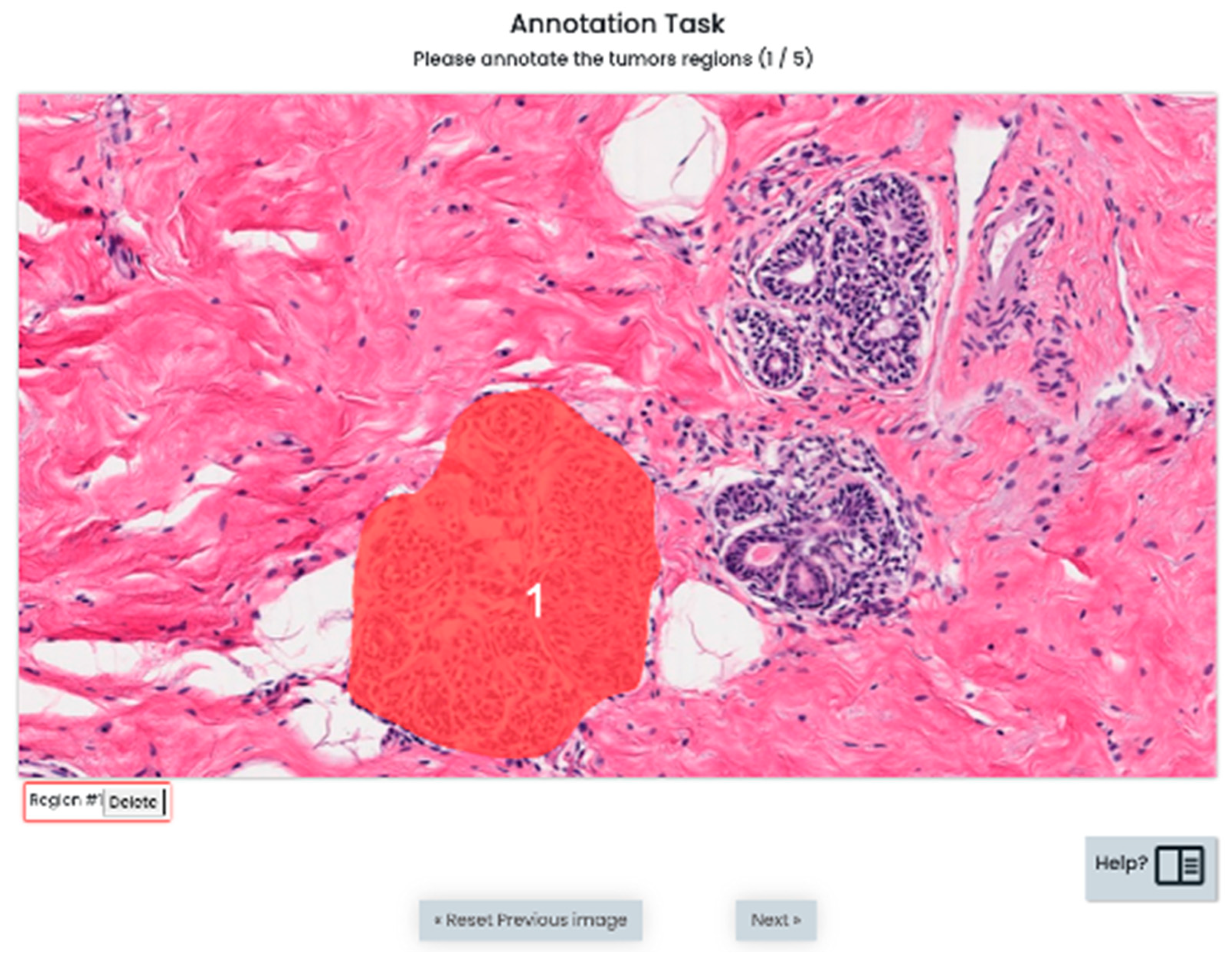
3.2. S1: Initial Version Training Strategy
3.3. S2: Optimized Training Strategy (OSTRAGY)
3.4. S3: Optimized Training Strategy with Instant Feedback (INSTRAGY)
Preliminary Preprocessing of Dataset
3.5. Evaluation Metrics and Statistical Analysis
3.5.1. Differences Between Training Strategies: Overall Perspective Using Blocked Designs
- All three vectors follow the normal distribution: ANOVA test [44,45] was applied to check if the groups are statistically different. Welch ANOVA test [46] was applied to the groups which did not have equal variances. To determine which of the groups presents the statistically lowest error (and statistically best performance), a Post Hoc Tukey HSD test [47] was also applied.
- All three vectors did not follow the normal distribution: The Friedman test [48,49] was applied to check if the groups are statistically different. To determine which of the groups presents the statistically lowest error (and statistically best performance), a Post Hoc HSD test [50] was also applied.
- All statistical evaluations were performed in Python version 3.9, using the libraries Statsmodels.api, statsmodels.formula.api, OLS (the three come from Statsmodels package version 0.14.0), and scikit_posthocs version 0.8.1.
3.5.2. Analysis of Significant Association Between the Training Strategy and Performance Metrics
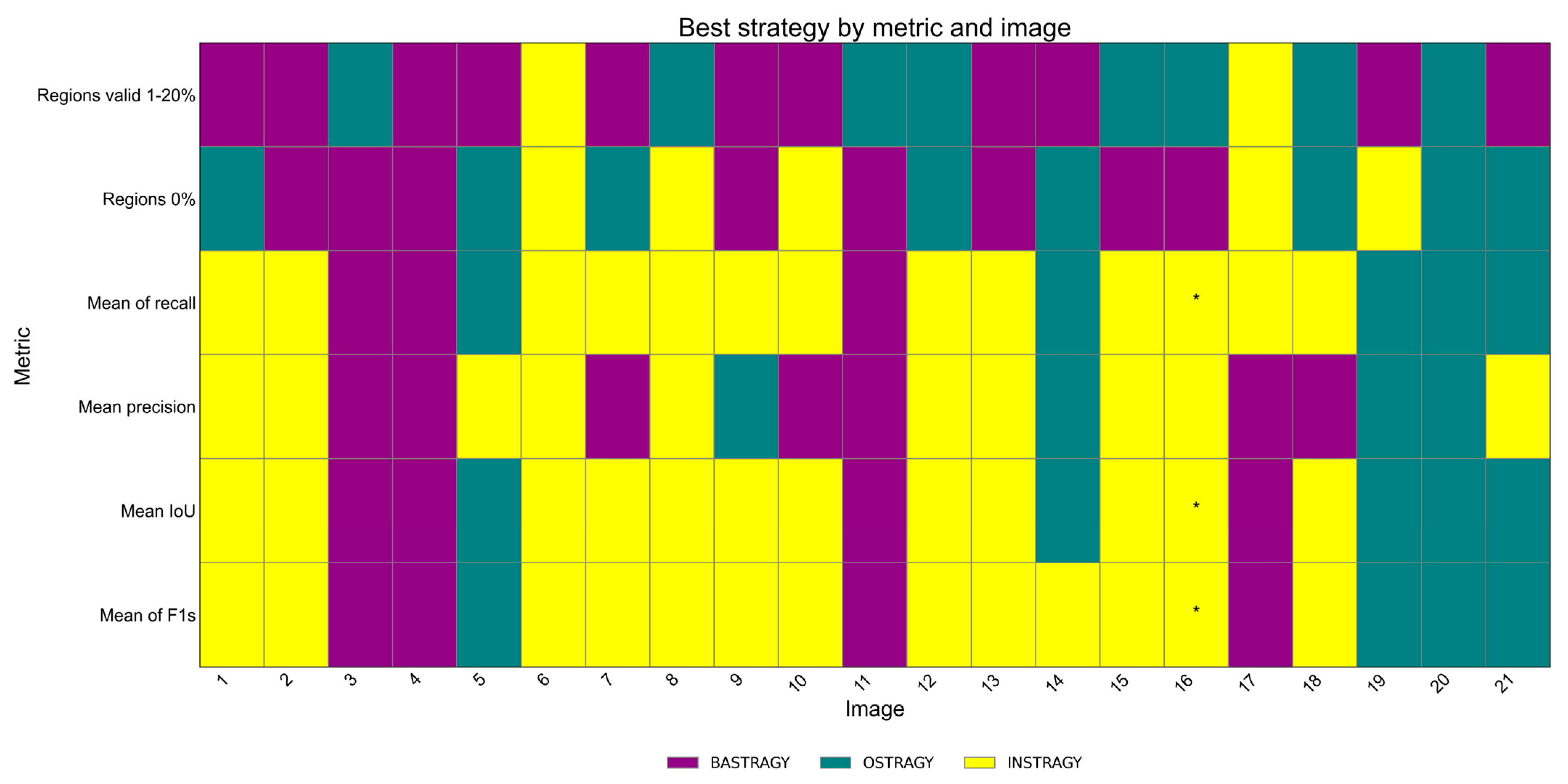
3.5.3. Differences Between Training Strategies: Perspective per Image
- All three vectors follow the normal distribution: ANOVA test [52] was applied to check if the groups are statistically different. Welch ANOVA test [46] was applied to groups which do not have equal variances. To determine which of the groups presents the statistically lowest error (and statistically best performance), the Nemenyi Post Hoc test for multiple pairwise comparisons [53,54] was also applied.
- All three vectors did not follow the normal distribution: The Kruskal–Wallis H-test [55,56] was applied to check if the groups are statistically different. To determine which of the groups presents the statistically lowest error (and statistically best performance), a Post Hoc Dunn test with a Bonferroni correction test [57,58] was also applied.
4. Results
4.1. Overall Trends
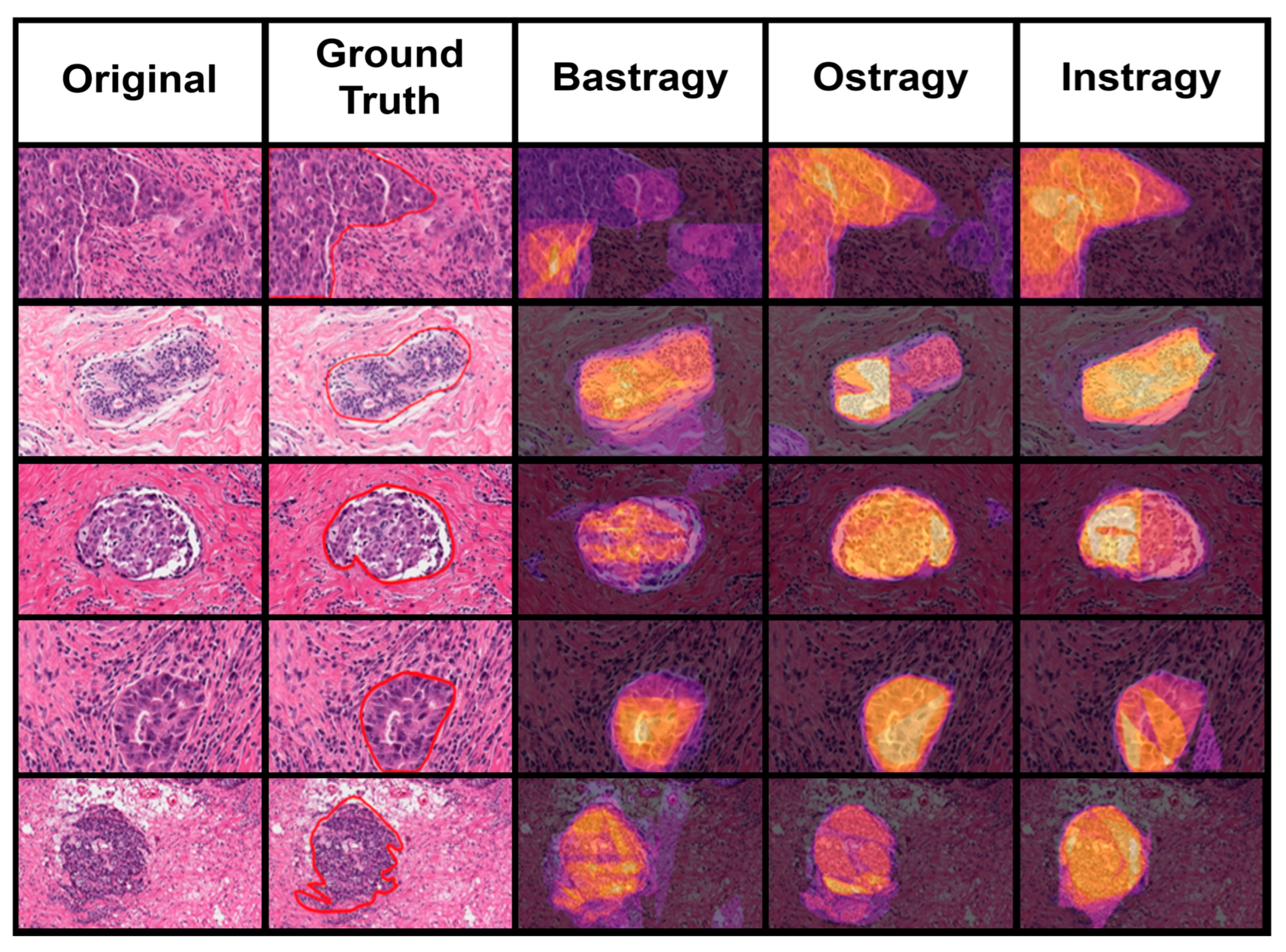
4.2. Analysis of Results per Image
4.2.1. Delimitation of Tumor Zones
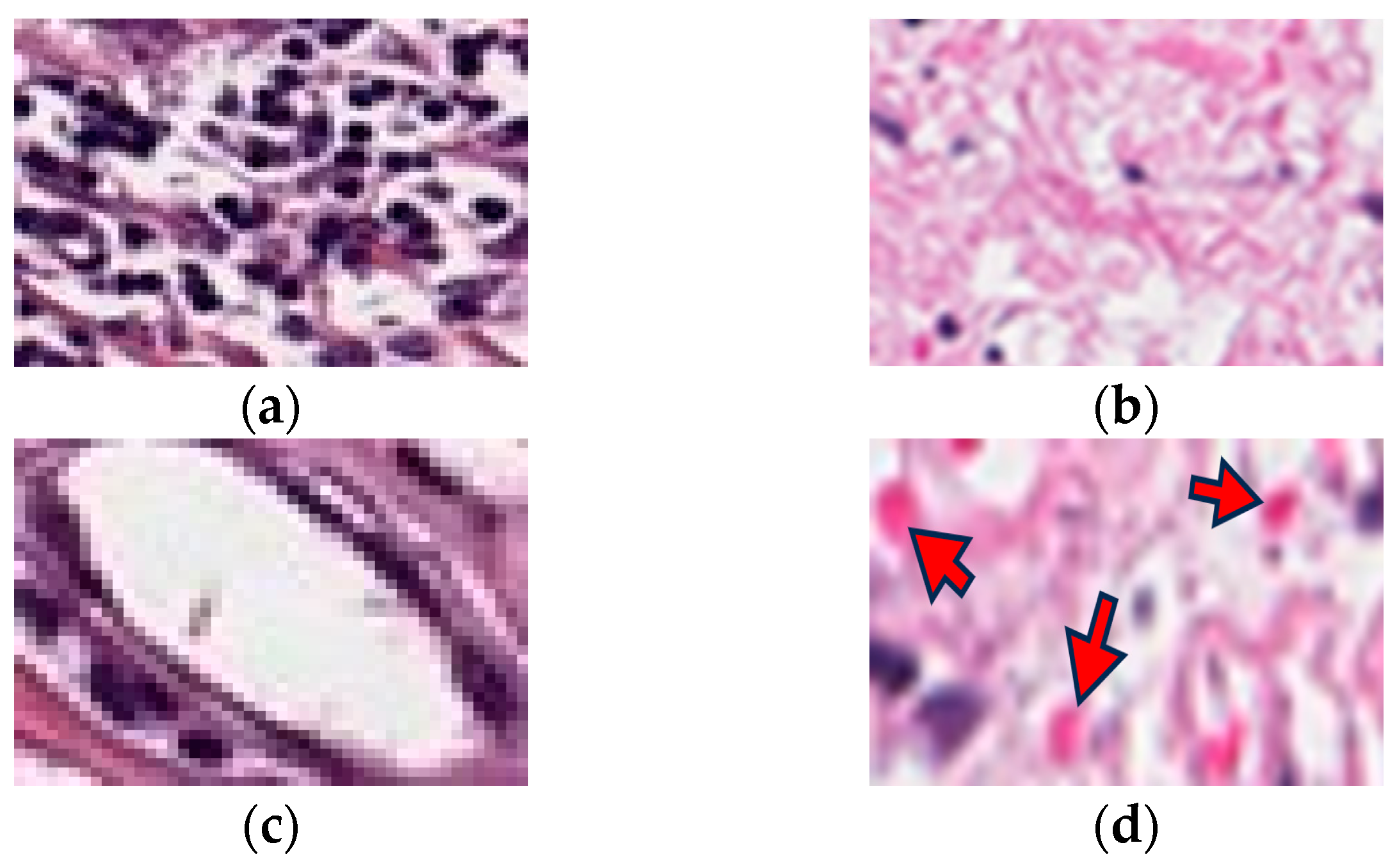
4.2.2. Pink Regions (Other Non-Tumor Tissues)
4.2.3. Red Regions
4.2.4. Dark Dot Regions
4.2.5. White Regions
4.3. Untypical Results
5. Discussion
5.1. Summary of the Findings
5.2. Comparison of Training Strategies
5.3. Crowdsourced Definition of Error Pattern
6. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Estellés-Arolas, E.; Navarro-Giner, R.; González-Ladrón-de-Guevara, F. Crowdsourcing Fundamentals: Definition and Typology. In Advances in Crowdsourcing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 33–48. [Google Scholar]
- Estellés-Arolas, E.; González-Ladrón-De-Guevara, F. Towards an Integrated Crowdsourcing Definition. J. Inf. Sci. 2012, 38, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatsu, R.T.; Grossman, E.B.; Iacovou, C.L. A Taxonomy of Crowdsourcing Based on Task Complexity. J. Inf. Sci. 2014, 40, 823–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, J. Income Security in the On-Demand Economy: Findings and Policy Lessons from a Survey of Crowdworkers 2016. Comp. Labor Law Policy J. 2015, 37, 543. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, X.; Sheng, V.S. Learning from Crowdsourced Labeled Data: A Survey. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2016, 46, 543–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, J.W. Making Better Use of the Crowd: How Crowdsourcing Can Advance Machine Learning Research. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2018, 18, 1–46. [Google Scholar]
- Gutman, D.A.; Khalilia, M.; Lee, S.; Nalisnik, M.; Mullen, Z.; Beezley, J.; Chittajallu, D.R.; Manthey, D.; Cooper, L.A.D. The Digital Slide Archive: A Software Platform for Management, Integration, and Analysis of Histology for Cancer Research. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, e75–e78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, P.K.-Y.; Luo, H.; Wang, M.; Leung, P.H.; Cheng, J.C.P. Recognition of Pedestrian Trajectories and Attributes with Computer Vision and Deep Learning Techniques. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2021, 49, 101356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, C.M.; Johansen, T.S.D.; Sørensen, E.N.; Westermann, C.E.; Wittrock, S. Applications of Machine Learning in Tabular Document Digitisation. Hist. Methods J. Quant. Interdiscip. Hist. 2023, 56, 34–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubna; Mufti, N.; Shah, S.A.A. Automatic Number Plate Recognition:A Detailed Survey of Relevant Algorithms. Sensors 2021, 21, 3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, S.; Barbosa-Silva, A.; Blagec, K.; Brauner, J.; Samwald, M. Mapping Global Dynamics of Benchmark Creation and Saturation in Artificial Intelligence. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León-Gómez, B.B.; Moreno-Gabriel, E.; Carrasco-Ribelles, L.A.; Fors, C.V.; Liutsko, L. Retos y desafíos de la inteligencia artificial en la investigación en salud. Gac. Sanit. 2022, 37, 102315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, D.M. Retos de la inteligencia artificial y sus posibles soluciones desde la perspectiva de un editorialista humano. Biomédica 2023, 43, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libreros, J.A.; Gamboa, E.; Hirth, M. Mistakes Hold the Key: Reducing Errors in a Crowdsourced Tumor Annotation Task by Optimizing the Training Strategy. In Human-Computer Interaction; Ruiz, P.H., Agredo-Delgado, V., Mon, A., Eds.; Communications in Computer and Information Science; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; Volume 1877, pp. 210–224. ISBN 978-3-031-57981-3. [Google Scholar]
- Pedraza, A.; Bueno, G.; Deniz, O.; Cristóbal, G.; Blanco, S.; Borrego-Ramos, M. Automated Diatom Classification (Part B): A Deep Learning Approach. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libreros, J.A.; Shafiq, M.H.; Gamboa, E.; Cleven, M.; Hirth, M. Visual Transformers Meet Convolutional Neural Networks: Providing Context for Convolution Layers in Semantic Segmentation of Remote Sensing Photovoltaic Imaging. In Big Data Analytics and Knowledge Discovery; Wrembel, R., Chiusano, S., Kotsis, G., Tjoa, A.M., Khalil, I., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; Volume 14912, pp. 359–366. ISBN 978-3-031-68322-0. [Google Scholar]
- Gamboa, E.; Libreros, A.; Hirth, M.; Dubiner, D. Human-AI Collaboration for Improving the Identification of Cars for Autonomous Driving. In Proceedings of the CIKM Workshops, Atlanta, GA, USA, 17–21 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Molina, H.; Joglekar, M.; Marcus, A.; Parameswaran, A.; Verroios, V. Challenges in Data Crowdsourcing. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2016, 28, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, J. The Role of Collective Intelligence in Crowdsourcing Innovation; LUT University: Lappeenranta, Finland, 2015; ISBN 978-952-265-876-0. [Google Scholar]
- Tondello, G.F.; Wehbe, R.R.; Diamond, L.; Busch, M.; Marczewski, A.; Nacke, L.E. The Gamification User Types Hexad Scale. In Proceedings of the 2016 Annual Symposium on Computer-Human Interaction in Play, Austin, TX, USA, 16–19 October 2016; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 229–243. [Google Scholar]
- Vroom, V.H. Work and Motivation; Wiley: Oxford, UK, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, N.; Yin, C.; Zhang, J.X. Understanding the Relationships between Motivators and Effort in Crowdsourcing Marketplaces: A Nonlinear Analysis. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2015, 35, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Zhu, K.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, H. Motivating Participation in Crowdsourcing Contests: The Role of Instruction-Writing Strategy. Inf. Manag. 2022, 59, 103616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Pérez, M.; Amgad, M.; Morales-Álvarez, P.; Ruiz, P.; Cooper, L.A.D.; Molina, R.; Katsaggelos, A.K. Learning from Crowds in Digital Pathology Using Scalable Variational Gaussian Processes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, P.; Sandfort, V.; Gheysens, D.; Braeckevelt, G.-J.; Berte, J.; Summers, R.M. Segmenting the Kidney on CT Scans Via Crowdsourcing. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 16th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2019), Venice, Italy, 8–11 April 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 829–832. [Google Scholar]
- Rice, M.K.; Zenati, M.S.; Novak, S.M.; Al Abbas, A.I.; Zureikat, A.H.; Zeh, H.J.; Hogg, M.E. Crowdsourced Assessment of Inanimate Biotissue Drills: A Valid and Cost-Effective Way to Evaluate Surgical Trainees. J. Surg. Educ. 2019, 76, 814–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldenberg, M.; Ordon, M.; Honey, J.R.D.; Andonian, S.; Lee, J.Y. Objective Assessment and Standard Setting for Basic Flexible Ureterorenoscopy Skills Among Urology Trainees Using Simulation-Based Methods. J. Endourol. 2020, 34, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amgad, M.; Elfandy, H.; Hussein, H.; Atteya, L.A.; Elsebaie, M.A.T.; Abo Elnasr, L.S.; Sakr, R.A.; Salem, H.S.E.; Ismail, A.F.; Saad, A.M.; et al. Structured Crowdsourcing Enables Convolutional Segmentation of Histology Images. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 3461–3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, M.; Bourier, F.; Baur, C.; Milletari, F.; Navab, N.; Demirci, S. Robust Navigation Support in Lowest Dose Image Setting. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2019, 14, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandala, P.A.; Sivaswamy, J. Crowdsourced Annotations as an Additional Form of Data Augmentation for CAD Development. In Proceedings of the 2017 4th IAPR Asian Conference on Pattern Recognition (ACPR), Nanjing, China, 26–29 November 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 753–758. [Google Scholar]
- Conti, S.L.; Brubaker, W.; Chung, B.I.; Sofer, M.; Hsi, R.S.; Shinghal, R.; Elliott, C.S.; Caruso, T.; Leppert, J.T. Crowdsourced Assessment of Ureteroscopy with Laser Lithotripsy Video Feed Does Not Correlate with Trainee Experience. J. Endourol. 2019, 33, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozov, S.P.; Gombolevskiy, V.A.; Elizarov, A.B.; Gusev, M.A.; Novik, V.P.; Prokudaylo, S.B.; Bardin, A.S.; Popov, E.V.; Ledikhova, N.V.; Chernina, V.Y.; et al. A Simplified Cluster Model and a Tool Adapted for Collaborative Labeling of Lung Cancer CT Scans. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 206, 106111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzahl, C.; Aubreville, M.; Bertram, C.A.; Gerlach, S.; Maier, J.; Voigt, J.; Hill, J.; Klopfleisch, R.; Maier, A. Is Crowd-Algorithm Collaboration an Advanced Alternative to Crowd-Sourcing on Cytology Slides? In Bildverarbeitung für die Medizin 2020; Tolxdorff, T., Deserno, T.M., Handels, H., Maier, A., Maier-Hein, K.H., Palm, C., Eds.; Springer Fachmedien: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2020; pp. 26–31. ISBN 978-3-658-29266-9. [Google Scholar]
- Ascheid, D.; Baumann, M.; Pinnecker, J.; Friedrich, M.; Szi-Marton, D.; Medved, C.; Bundalo, M.; Ortmann, V.; Öztürk, A.; Nandigama, R.; et al. A Vascularized Breast Cancer Spheroid Platform for the Ranked Evaluation of Tumor Microenvironment-Targeted Drugs by Light Sheet Fluorescence Microscopy. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paley, G.L.; Grove, R.; Sekhar, T.C.; Pruett, J.; Stock, M.V.; Pira, T.N.; Shields, S.M.; Waxman, E.L.; Wilson, B.S.; Gordon, M.O.; et al. Crowdsourced Assessment of Surgical Skill Proficiency in Cataract Surgery. J. Surg. Educ. 2021, 78, 1077–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grote, A.; Schaadt, N.S.; Forestier, G.; Wemmert, C.; Feuerhake, F. Crowdsourcing of Histological Image Labeling and Object Delineation by Medical Students. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2019, 38, 1284–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.; Carpendale, S.; Gupta, N.; Hoßfeld, T.; Naderi, B.; Redi, J.; Siahaan, E.; Wechsung, I. Understanding the Crowd: Ethical and Practical Matters in the Academic Use of Crowdsourcing. In Proceedings of the Evaluation in the Crowd. Crowdsourcing and Human-Centered Experiments, Dagstuhl Castle, Germany, 22–27 November 2015; Archambault, D., Purchase, H., Hoßfeld, T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 27–69. [Google Scholar]
- Difallah, D.; Filatova, E.; Ipeirotis, P. Demographics and Dynamics of Mechanical Turk Workers. In Proceedings of the Eleventh ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, Marina Del Rey, CA, USA, 5–9 February 2018; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA; pp. 135–143. [Google Scholar]
- Na, K.; Han, K. How Leaderboard Positions Shape Our Motivation: The Impact of Competence Satisfaction and Competence Frustration on Motivation in a Gamified Crowdsourcing Task. Internet Res. 2023, 33, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashikawa, M.; Kawamura, T.; Ohsuga, A. Proposal of Grade Training Method for Quality Improvement in Microtask Crowdsourcing. Web Intell. 2019, 17, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyal, P.; Ye, S. An Examination of the Dynamics of Crowdsourcing Contests: Role of Feedback Type. Inf. Syst. Res. 2024, 35, 394–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Han, L.; Stein, G.; Day, S.; Bien-Gund, C.; Mathews, A.; Ong, J.J.; Zhao, P.-Z.; Wei, S.-F.; Walker, J.; et al. Crowdsourcing in Health and Medical Research: A Systematic Review. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2020, 9, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamboa, E.; Galda, R.; Mayas, C.; Hirth, M. The Crowd Thinks Aloud: Crowdsourcing Usability Testing with the Thinking Aloud Method. In Proceedings of the HCI International 2021—Late Breaking Papers: Design and User Experience, Virtual Event, 24–29 July 2021; Stephanidis, C., Soares, M.M., Rosenzweig, E., Marcus, A., Yamamoto, S., Mori, H., Rau, P.-L.P., Meiselwitz, G., Fang, X., Moallem, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 24–39. [Google Scholar]
- Fractional Factorial Experiments. In Design and Analysis of Experiments; Dean, A., Voss, D., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 483–545. ISBN 978-0-387-22634-7. [Google Scholar]
- Design and Analysis of Experiments; Dean, A., Voss, D., Eds.; Springer Texts in Statistics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1999; ISBN 978-0-387-98561-9. [Google Scholar]
- Welch, B.L. On the Comparison of Several Mean Values: An Alternative Approach. Biometrika 1951, 38, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tukey, J.W. The Problem of Multiple Comparisons; Princeton University: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1953. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, D.G.; Afonso, A.; Medeiros, F.M. Overview of Friedman’s Test and Post-Hoc Analysis. Commun. Stat.—Simul. Comput. 2015, 44, 2636–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Shan, G.; Amei, A.; Zhao, J.; Young, D.; Clark, S. A Modified Friedman Test for Randomized Complete Block Designs. Commun. Stat.—Simul. Comput. 2017, 46, 1508–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, H.; Williams, L.J. Tukey’s Honestly Significant Difference (HSD) Test. Encycl. Res. Des. 2010, 3, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro, S.S.; Wilk, M.B. An Analysis of Variance Test for Normality (Complete Samples). Biometrika 1965, 52, 591–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.L.; Acton, C.; Fullerton, D.A.; Maltby, J.; Campling, J. Analysis of Variance (ANOVA). In SPSS for Social Scientists; Campling, J., Ed.; Macmillan Education UK: London, UK, 2002; pp. 145–154. ISBN 978-0-333-92286-6. [Google Scholar]
- Nemenyi, P.B. Distribution-Free Multiple Comparisons; Princeton University: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Hollander, M.; Wolfe, D.A.; Chicken, E. Nonparametric Statistical Methods; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- McKight, P.E.; Najab, J. Kruskal-Wallis Test. In The Corsini Encyclopedia of Psychology; Weiner, I.B., Craighead, W.E., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; p. 1. ISBN 978-0-470-17024-3. [Google Scholar]
- Kruskal, W.H.; Wallis, W.A. Use of Ranks in One-Criterion Variance Analysis. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1952, 47, 583–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, O.J. Multiple Comparisons among Means. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1961, 56, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, R.A.; Davies, L.N.; Dunne, M.C.M.; Gilmartin, B. Statistical Guidelines for Clinical Studies of Human Vision. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2011, 31, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirth, M.; Libreros, J.; Gamboa, E.; Henke, E. Mistakes Hold the Key: Providing Instant Feedback Based on Errors to Crowdworkers in Tumor Annotation Imaging. Zenodo 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, N. Learning through Errors in Training. In Errors in Organizations; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2011; ISBN 978-0-203-81782-7. [Google Scholar]
- Frese, M.; Altmann, A. The Treatment of Errors in Learning and Training. Dev. Ski. Inf. Technol. 1989, 65. [Google Scholar]

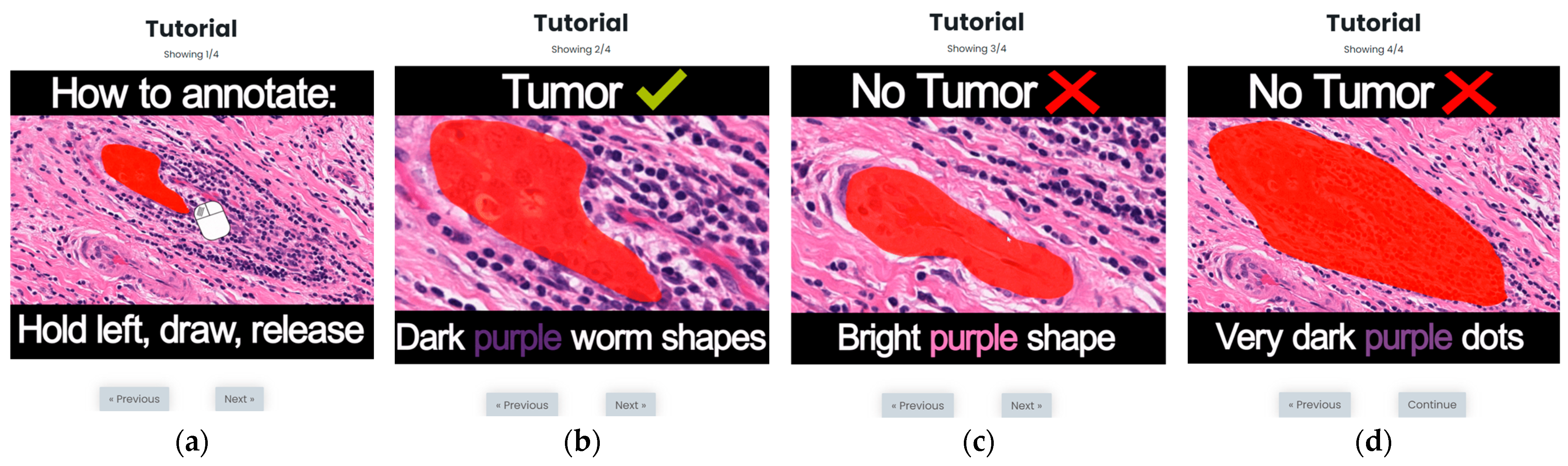
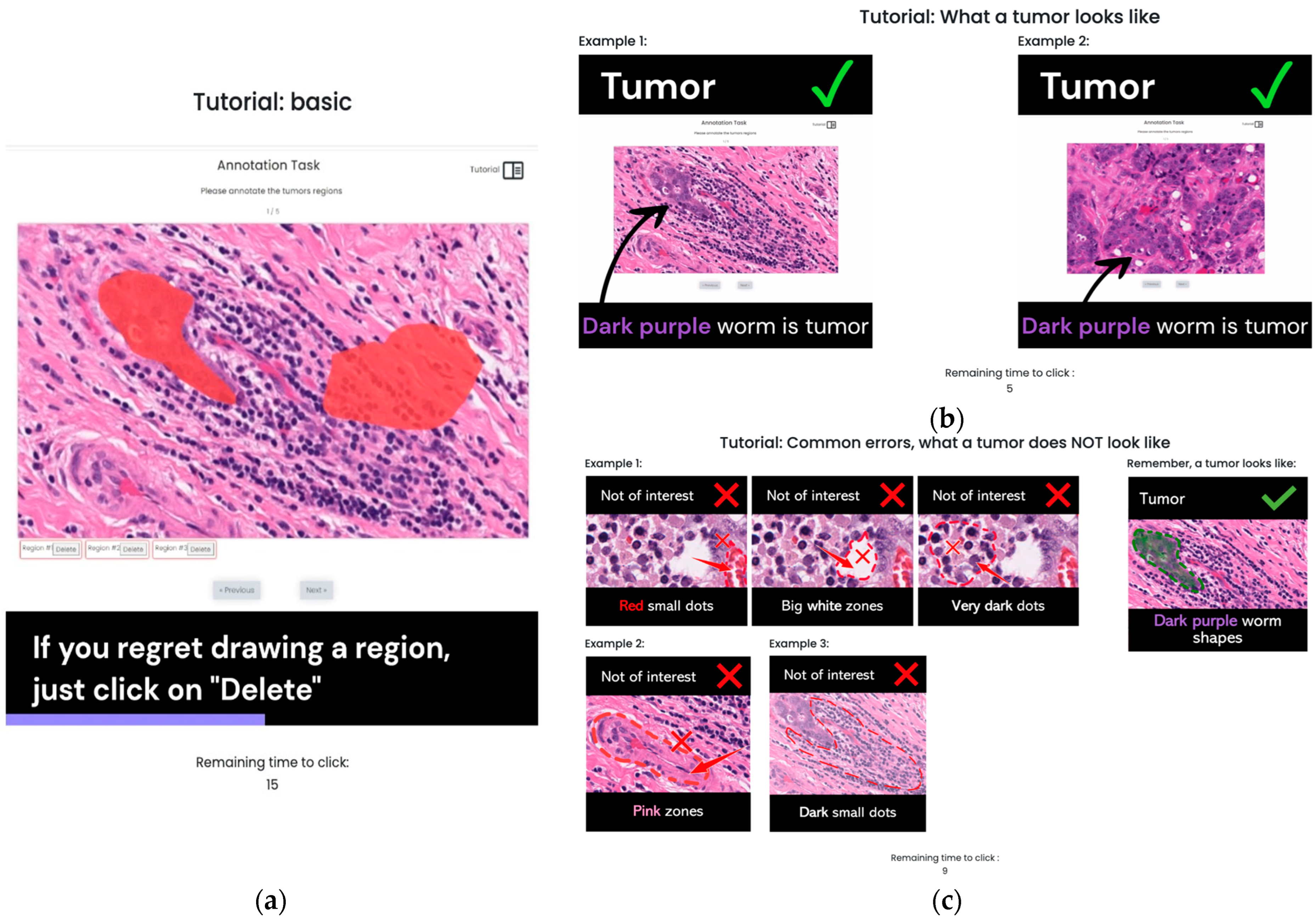
| Type of Error | Error Message |
|---|---|
| Region’s shape | It looks like you are drawing a region more related to a line. We are pretty sure that the tumors do not have this shape. Please review them again and take another look at the help button. You can undo this region. Please click on “delete”. |
| Non-tumor region (pink region, dark dot region, white or red region identified) | It looks like you are drawing over a non-tumor region. We are pretty sure the tumors do not have this color. Please review again and take another look at the help button. If it is not a tumor, please click on “delete”. |
| Region’s size | It looks like you are making the regions too small. We are pretty sure the tumors are not so small. Please click on “delete” and take another look at the tutorial button. |
| Type of Region | IQR | Median |
|---|---|---|
| Tumor | 198–221 | 216 |
| Black dots (lymphocytes) | 188–197 | 189 |
| Pink (other tissues) | 213–229 | 215 |
| White | 195–231 | 221 |
| Red | 230–243 | 235 |
| Type of Error/Tumor Zone | Performance Metric | p-Value | Normality p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tumor-zone annotation | mrecall_img_worker | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** |
| mf1_img_worker | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** | |
| miou_img_worker | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** | |
| regions_0p | 0.008 ** | 0.000 *** | |
| regions_valid_81_100p | 0.009 ** | 0.000 *** | |
| regions_valid_61_80p | 0.055 | 0.000 *** | |
| regions_valid_21_40p | 0.103 | 0.000 *** | |
| regions_valid_1_20p | 0.110 | 0.000 *** | |
| mprecision_img_worker | 0.263 | 0.000 *** | |
| unable_to_reconstruct | 0.331 | 0.000 *** | |
| regions_valid_41_60p | 0.895 | 0.000 *** | |
| Dark dot errors | regions_0p | 0.002 ** | 0.000 *** |
| miou_img_worker | 0.073 | 0.000 *** | |
| mf1_img_worker | 0.073 | 0.000 *** | |
| mprecision_img_worker | 0.105 | 0.000 *** | |
| regions_valid_21_40p | 0.264 | 0.000 *** | |
| regions_valid_41_60p | 0.267 | 0.000 *** | |
| mrecall_img_worker | 0.302 | 0.000 *** | |
| regions_valid_61_80p | 0.307 | 0.000 *** | |
| unable_to_reconstruct | 0.331 | 0.000 *** | |
| regions_valid_1_20p | 0.481 | 0.000 *** | |
| regions_valid_81_100p | 0.895 | 0.000 *** | |
| Pink tissue error | mprecision_img_worker | 0.001 *** | 0.000 *** |
| mrecall_img_worker | 0.010 ** | 0.000 *** | |
| mf1_img_worker | 0.022 * | 0.000 *** | |
| miou_img_worker | 0.043 * | 0.000 *** | |
| regions_0p | 0.097 | 0.000 *** | |
| regions_valid_21_40p | 0.212 | 0.000 *** | |
| regions_valid_81_100p | 0.304 | 0.000 *** | |
| regions_valid_1_20p | 0.308 | 0.000 *** | |
| unable_to_reconstruct | 0.331 | 0.000 *** | |
| regions_valid_41_60p | 0.368 | 0.000 *** | |
| regions_valid_61_80p | 0.961 | 0.000 *** | |
| Red tissue error | regions_0p | 0.043 * | 0.000 *** |
| miou_img_worker | 0.047 * | 0.000 *** | |
| mprecision_img_worker | 0.047 * | 0.000 *** | |
| mf1_img_worker | 0.047 * | 0.000 *** | |
| regions_valid_41_60p | 0.050 * | 0.000 *** | |
| regions_valid_61_80p | 0.074 | 0.000 *** | |
| regions_valid_1_20p | 0.309 | 0.000 *** | |
| unable_to_reconstruct | 0.331 | 0.000 *** | |
| regions_valid_81_100p | 0.597 | 0.000 *** | |
| mrecall_img_worker | 0.633 | 0.000 *** | |
| regions_valid_21_40p | 0.670 | 0.000 *** | |
| White zone error | regions_0p | 0.010 * | 0.000 *** |
| regions_valid_41_60p | 0.057 | 0.000 *** | |
| regions_valid_81_100p | 0.109 | 0.000 *** | |
| mprecision_img_worker | 0.126 | 0.000 *** | |
| mrecall_img_worker | 0.167 | 0.000 *** | |
| miou_img_worker | 0.215 | 0.000 *** | |
| mf1_img_worker | 0.215 | 0.000 *** | |
| regions_valid_21_40p | 0.239 | 0.000 *** | |
| unable_to_reconstruct | 0.331 | 0.000 *** | |
| regions_valid_61_80p | 0.368 | 0.000 *** | |
| regions_valid_1_20p | 0.775 | 0.000 *** | |
| All types combined | regions_valid_1_20p | 0.010 ** | 0.000 *** |
| regions_0p | 0.050 * | 0.000 *** | |
| regions_valid_61_80p | 0.071 | 0.000 *** | |
| mprecision_img_worker | 0.084 | 0.000 *** | |
| regions_valid_41_60p | 0.287 | 0.000 *** | |
| unable_to_reconstruct | 0.331 | 0.000 *** | |
| regions_valid_21_40p | 0.359 | 0.000 *** | |
| miou_img_worker | 0.368 | 0.000 *** | |
| regions_valid_81_100p | 0.402 | 0.000 *** | |
| mrecall_img_worker | 0.405 | 0.000 *** | |
| mf1_img_worker | 0.467 | 0.000 *** |
| Type of Error/Tumor Zone | Performance Metric | Group 1 | Group 2 | p-Value | Higher Value | Lower Value | Difference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tumor-zone annotation | miou_img_worker | BAS | INS | 0.001 *** | INS | BAS | 0.090 |
| miou_img_worker | OST | INS | 0.019 * | INS | OST | 0.033 | |
| mrecall_img_worker | BAS | INS | 0.001 *** | INS | BAS | 0.098 | |
| mrecall_img_worker | OST | INS | 0.004 ** | INS | OST | 0.040 | |
| mrecall_img_worker | INS | OST | 0.004 ** | INS | OST | 0.040 | |
| mf1_img_worker | BAS | INS | 0.001 *** | INS | BAS | 0.106 | |
| mf1_img_worker | OST | INS | 0.004 ** | INS | OST | 0.051 | |
| mf1_img_worker | INS | OST | 0.004 ** | INS | OST | 0.051 | |
| regions_0p | BAS | INS | 0.024 * | BAS | INS | 0.365 | |
| regions_0p | OST | INS | 0.019 * | OST | INS | 0.439 | |
| Dark dots error | regions_0p | BAS | INS | 0.015 * | BAS | INS | 0.794 |
| regions_0p | OST | INS | 0.003 ** | OST | INS | 0.923 | |
| Pink tissue error | mprecision_img_worker | BAS | OST | 0.036 * | BAS | OST | 0.083 |
| mprecision_img_worker | BAS | INS | 0.001 *** | BAS | INS | 0.092 | |
| mprecision_img_worker | INS | BAS | 0.001 *** | BAS | INS | 0.092 | |
| mrecall_img_worker | OST | BAS | 0.015 * | BAS | OST | 0.024 | |
| mf1_img_worker | OST | BAS | 0.036 * | BAS | OST | 0.021 | |
| White zone error | regions_0p | INS | OST | 0.015 * | OST | INS | 1.035 |
| Type of Error/Tumor Zone | Performance Metric | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tumor annotation zones | mrecall_img_worker | 27.471 | 0.000 *** |
| regions_valid_81_100p | 16.554 | 0.000 *** | |
| mf1_img_worker | 25.013 | 0.000 *** | |
| miou_img_worker | 23.752 | 0.001 *** | |
| mprecision_img_worker | 14.092 | 0.029 * | |
| regions_valid_61_80p | 4.779 | 0.092 | |
| regions_0p | 6.207 | 0.184 | |
| regions_valid_41_60p | 5.540 | 0.236 | |
| regions_valid_21_40p | 4.325 | 0.364 | |
| unable_to_reconstruct | 4.020 | 0.403 | |
| regions_valid_1_20p | 3.009 | 0.556 | |
| Dark dots error | regions_valid_1_20p | 6.518 | 0.164 |
| regions_valid_61_80p | 4.881 | 0.300 | |
| regions_valid_41_60p | 2.038 | 0.361 | |
| unable_to_reconstruct | 4.020 | 0.403 | |
| regions_valid_81_100p | 4.020 | 0.403 | |
| regions_0p | 4.011 | 0.404 | |
| regions_valid_21_40p | 3.009 | 0.556 | |
| Pink tissue error | mprecision_img_worker | 31.909 | 0.000 *** |
| miou_img_worker | 25.458 | 0.000 *** | |
| mf1_img_worker | 25.458 | 0.000 *** | |
| mrecall_img_worker | 11.464 | 0.003 ** | |
| regions_valid_21_40p | 9.061 | 0.060 | |
| unable_to_reconstruct | 4.020 | 0.403 | |
| regions_0p | 4.011 | 0.404 | |
| regions_valid_41_60p | 4.011 | 0.404 | |
| regions_valid_81_100p | 3.307 | 0.508 | |
| regions_valid_61_80p | 2.670 | 0.615 | |
| regions_valid_1_20p | 2.511 | 0.643 | |
| Red tissue error | regions_valid_41_60p | 6.026 | 0.049 * |
| regions_0p | 8.011 | 0.091 | |
| regions_valid_61_80p | 5.537 | 0.236 | |
| regions_valid_1_20p | 5.515 | 0.238 | |
| unable_to_reconstruct | 4.020 | 0.403 | |
| regions_valid_81_100p | 4.003 | 0.406 | |
| regions_valid_21_40p | 1.611 | 0.447 | |
| White zone error | sum_union_img_worker | 8.420 | 0.015 * |
| regions_valid_81_100p | 9.282 | 0.054 | |
| regions_valid_41_60p | 8.605 | 0.072 | |
| regions_0p | 8.011 | 0.091 | |
| regions_valid_1_20p | 4.175 | 0.383 | |
| miou_img_worker | 1.885 | 0.390 | |
| mf1_img_worker | 1.885 | 0.390 | |
| unable_to_reconstruct | 4.020 | 0.403 | |
| mprecision_img_worker | 1.475 | 0.478 | |
| regions_valid_61_80p | 0.989 | 0.610 | |
| mrecall_img_worker | 0.379 | 0.828 | |
| regions_valid_21_40p | 1.262 | 0.868 | |
| All types combined | regions_0p | 22.436 | 0.000 *** |
| unable_to_reconstruct | 20.100 | 0.000 *** | |
| mprecision_img_worker | 8.138 | 0.017 * | |
| mrecall_img_worker | 2.309 | 0.315 | |
| regions_valid_81_100p | 4.679 | 0.322 | |
| miou_img_worker | 2.038 | 0.361 | |
| mf1_img_worker | 2.038 | 0.361 | |
| regions_valid_1_20p | 4.004 | 0.405 | |
| regions_valid_41_60p | 4.004 | 0.405 | |
| regions_valid_61_80p | 3.432 | 0.488 | |
| regions_valid_21_40p | 3.414 | 0.491 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Libreros, J.A.; Gamboa, E.; Henke, E.; Hirth, M. Assessing the Influence of Feedback Strategies on Errors in Crowdsourced Annotation of Tumor Images. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2025, 9, 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc9090220
Libreros JA, Gamboa E, Henke E, Hirth M. Assessing the Influence of Feedback Strategies on Errors in Crowdsourced Annotation of Tumor Images. Big Data and Cognitive Computing. 2025; 9(9):220. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc9090220
Chicago/Turabian StyleLibreros, Jose Alejandro, Edwin Gamboa, Erik Henke, and Matthias Hirth. 2025. "Assessing the Influence of Feedback Strategies on Errors in Crowdsourced Annotation of Tumor Images" Big Data and Cognitive Computing 9, no. 9: 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc9090220
APA StyleLibreros, J. A., Gamboa, E., Henke, E., & Hirth, M. (2025). Assessing the Influence of Feedback Strategies on Errors in Crowdsourced Annotation of Tumor Images. Big Data and Cognitive Computing, 9(9), 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc9090220







