Journal Description
Multimodal Technologies and Interaction
Multimodal Technologies and Interaction
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on multimodal technologies and interaction published monthly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, ESCI (Web of Science), Inspec, dblp Computer Science Bibliography, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Computer Science, Cybernetics) / CiteScore - Q1 (Neuroscience (miscellaneous))
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 21.7 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 4.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Journal Cluster of Artificial Intelligence: AI, AI in Medicine, Algorithms, BDCC, MAKE, MTI, Stats, Virtual Worlds and Computers.
Impact Factor:
2.4 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.7 (2024)
Latest Articles
APAR: A Structural Design and Guidance Framework for Gamification in Education Based on Motivation Theories
Multimodal Technol. Interact. 2026, 10(1), 10; https://doi.org/10.3390/mti10010010 - 10 Jan 2026
Abstract
►
Show Figures
Gamification is widely used to enhance student motivation, yet many educational design proposals remain conceptual and provide limited operational guidance for digital learning environments. This paper introduces APAR (Activities, Points, Achievements and Rewards), a content-independent structural framework for designing and implementing educational gamification
[...] Read more.
Gamification is widely used to enhance student motivation, yet many educational design proposals remain conceptual and provide limited operational guidance for digital learning environments. This paper introduces APAR (Activities, Points, Achievements and Rewards), a content-independent structural framework for designing and implementing educational gamification in learning platforms. Grounded in motivation theories (including Self-Determination Theory and Relatedness–Autonomy–Mastery–Purpose) and reward taxonomies (Status, Access, Power and Stuff), APAR distinguishes high-level design constructs from concrete game elements (e.g., points, badges and leaderboards) and provides a systematic design loop linking learning activities, feedback, intermediate goals and reinforcement. The contribution includes (i) a mapping table relating each APAR construct to motivation models, supported dynamics and typical learning-platform implementations; (ii) an actionable design guide; and (iii) an empirical illustration implemented in Moodle in a higher-education Computer Networks course. In this setting, the proportion of enrolled students taking the final exam increased from 58% to 72% in the first year, and the proportion of enrolled students passing increased from 17% to 38%; in 2022–2023 these values were 70% and 39%, respectively (56% of exam takers passed). While the use case relies on quantitative course-level indicators and is observational, the findings support the potential of structural gamification as an integrated methodological tool and motivate further mixed-method validations.
Full article
Open AccessSystematic Review
AI-Powered Procedural Haptics for Narrative VR: A Systematic Literature Review
by
Vimala Perumal and Zeeshan Jawed Shah
Multimodal Technol. Interact. 2026, 10(1), 9; https://doi.org/10.3390/mti10010009 - 9 Jan 2026
Abstract
Haptic feedback is important for narrative virtual reality (VR), yet authoring remains costly and difficult to scale due to device-specific tuning, placement constraints, and the need for semantically congruent timing. We systematically reviewed user studies on haptics in narrative VR to establish an
[...] Read more.
Haptic feedback is important for narrative virtual reality (VR), yet authoring remains costly and difficult to scale due to device-specific tuning, placement constraints, and the need for semantically congruent timing. We systematically reviewed user studies on haptics in narrative VR to establish an empirical baseline and identify gaps for AI-powered procedural haptics. Following PRISMA 2020, we searched IEEE Xplore, ACM Digital Library, Scopus, Web of Science, PubMed, and PsycINFO (English; human participants; haptics synchronized to narrative events) and performed backward/forward citation chasing (final search: 31 July 2025). We also conducted a parallel scoping scan of grey literature (arXiv and CHI/SIGGRAPH workshops/demos), finalized on 7 September 2025; these records are summarized separately and were not included in the evidence synthesis. Of 493 records screened, 26 full texts were assessed, and 10 studies were included. Quantitatively, presence improved in 6/8 studies that measured it and immersion improved in 3/3; sample sizes ranged 8–108. Across varied modalities and placements, haptics improved presence and immersion and often enhanced affect; validated measures of narrative comprehension were rare. None of the included studies evaluated AI-generated procedural haptics in user studies. We conclude by proposing a structured, three-phase research roadmap designed to bridge this critical gap, moving the field from theoretical promise to the empirical validation of intelligent systems capable of making rich, adaptive, and scalable haptic narratives a reality.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Multimodal User Interfaces and Experiences: Challenges, Applications, and Perspectives—2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
From Cues to Engagement: A Comprehensive Survey and Holistic Architecture for Computer Vision-Based Audience Analysis in Live Events
by
Marco Lemos, Pedro J. S. Cardoso and João M. F. Rodrigues
Multimodal Technol. Interact. 2026, 10(1), 8; https://doi.org/10.3390/mti10010008 - 8 Jan 2026
Abstract
The accurate measurement of audience engagement in real-world live events remains a significant challenge, with the majority of existing research confined to controlled environments like classrooms. This paper presents a comprehensive survey of Computer Vision AI-driven methods for real-time audience engagement monitoring and
[...] Read more.
The accurate measurement of audience engagement in real-world live events remains a significant challenge, with the majority of existing research confined to controlled environments like classrooms. This paper presents a comprehensive survey of Computer Vision AI-driven methods for real-time audience engagement monitoring and proposes a novel, holistic architecture to address this gap, with this architecture being the main contribution of the paper. The paper identifies and defines five core constructs essential for a robust analysis: Attention, Emotion and Sentiment, Body Language, Scene Dynamics, and Behaviours. Through a selective review of state-of-the-art techniques for each construct, the necessity of a multimodal approach that surpasses the limitations of isolated indicators is highlighted. The work synthesises a fragmented field into a unified taxonomy and introduces a modular architecture that integrates these constructs with practical, business-oriented metrics such as Commitment, Conversion, and Retention. Finally, by integrating cognitive, affective, and behavioural signals, this work provides a roadmap for developing operational systems that can transform live event experience and management through data-driven, real-time analytics.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Human-AI Collaborative Interaction Design: Rethinking Human-Computer Symbiosis in the Age of Intelligent Systems)
►▼
Show Figures
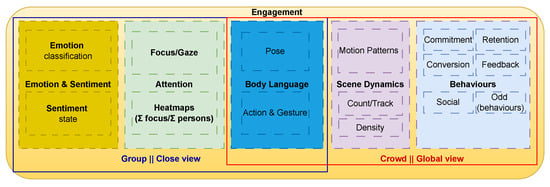
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Eye-Tracking and Emotion-Based Evaluation of Wardrobe Front Colors and Textures in Bedroom Interiors
by
Yushu Chen, Wangyu Xu and Xinyu Ma
Multimodal Technol. Interact. 2026, 10(1), 7; https://doi.org/10.3390/mti10010007 - 6 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Wardrobe fronts form a major visual element in bedroom interiors, yet material selection for their colors and textures often relies on intuition rather than evidence. This study develops a data-driven framework that links gaze behavior and affective responses to occupants’ preferences for wardrobe
[...] Read more.
Wardrobe fronts form a major visual element in bedroom interiors, yet material selection for their colors and textures often relies on intuition rather than evidence. This study develops a data-driven framework that links gaze behavior and affective responses to occupants’ preferences for wardrobe front materials. Forty adults evaluated color and texture swatches and rendered bedroom scenes while eye-tracking data capturing attraction, retention, and exploration were collected. Pairwise choices were modeled using a Bradley–Terry approach, and visual-attention features were integrated with emotion ratings to construct an interpretable attention index for predicting preferences. Results show that neutral light colors and structured wood-like textures consistently rank highest, with scene context reducing preference differences but not altering the order. Shorter time to first fixation and longer fixation duration were the strongest predictors of desirability, demonstrating the combined influence of rapid visual capture and sustained attention. Within the tested stimulus set and viewing conditions, the proposed pipeline yields consistent preference rankings and an interpretable attention-based score that supports evidence-informed shortlisting of wardrobe-front materials. The reported relationships between gaze, affect, and choice are associative and are intended to guide design decisions within the scope of the present experimental settings.
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
HISF: Hierarchical Interactive Semantic Fusion for Multimodal Prompt Learning
by
Haohan Feng and Chen Li
Multimodal Technol. Interact. 2026, 10(1), 6; https://doi.org/10.3390/mti10010006 - 6 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Recent vision-language pre-training models, like CLIP, have been shown to generalize well across a variety of multitask modalities. Nonetheless, their generalization for downstream tasks is limited. As a lightweight adaptation approach, prompt learning could allow task transfer by optimizing only several learnable vectors
[...] Read more.
Recent vision-language pre-training models, like CLIP, have been shown to generalize well across a variety of multitask modalities. Nonetheless, their generalization for downstream tasks is limited. As a lightweight adaptation approach, prompt learning could allow task transfer by optimizing only several learnable vectors and thus is more flexible for pre-trained models. However, current methods mainly concentrate on the design of unimodal prompts and ignore effective means for multimodal semantic fusion and label alignment, which limits their representation power. To tackle these problems, this paper designs a Hierarchical Interactive Semantic Fusion (HISF) framework for multimodal prompt learning. On top of frozen CLIP backbones, HISF injects visual and textual signals simultaneously in intermediate layers of a Transformer through a cross-attention mechanism as well as fitting category embeddings. This architecture realizes the hierarchical semantic fusion at the modality level with structural consistency kept at each layer. In addition, a Label Embedding Constraint and a Semantic Alignment Loss are proposed to promote category consistency while alleviating semantic drift in training. Extensive experiments across 11 few-shot image classification benchmarks show that HISF improves the average accuracy by around 0.7% compared to state-of-the-art methods and has remarkable robustness in cross-domain transfer tasks. Ablation studies also verify the effectiveness of each proposed part and their combination: hierarchical structure, cross-modal attention, and semantic alignment collaborate to enrich representational capacity. In conclusion, the proposed HISF is a new hierarchical view for multimodal prompt learning and provides a more lightweight and generalizable paradigm for adapting vision-language pre-trained models.
Full article
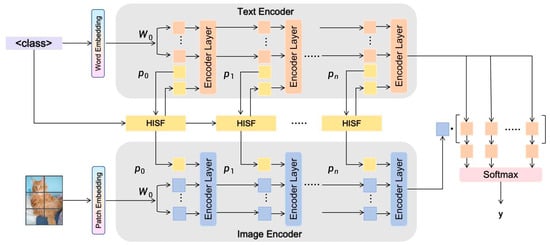
Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Neuroplasticity-Informed Learning Under Cognitive Load: A Systematic Review of Functional Imaging, Brain Stimulation, and Educational Technology Applications
by
Evgenia Gkintoni, Andrew Sortwell, Stephanos P. Vassilopoulos and Georgios Nikolaou
Multimodal Technol. Interact. 2026, 10(1), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/mti10010005 - 31 Dec 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
Background/Objectives: This systematic review examines neuroplasticity-informed approaches to learning under cognitive load, synthesizing evidence from functional imaging, brain stimulation, and educational technology research. As digital learning environments increasingly challenge learners with complex cognitive demands, understanding how neuroplasticity principles can inform adaptive educational design
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: This systematic review examines neuroplasticity-informed approaches to learning under cognitive load, synthesizing evidence from functional imaging, brain stimulation, and educational technology research. As digital learning environments increasingly challenge learners with complex cognitive demands, understanding how neuroplasticity principles can inform adaptive educational design becomes critical. This review examines how neural mechanisms underlying learning under cognitive load can inform the development of evidence-based educational technologies that optimize neuroplastic potential while mitigating cognitive overload. Methods: Following PRISMA guidelines, we synthesized 94 empirical studies published between 2005 and 2025 across PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and PsycINFO. Studies were selected based on rigorous inclusion criteria that emphasized functional neuroimaging (fMRI, EEG), non-invasive brain stimulation (tDCS, TMS), and educational technology applications, which examined learning outcomes under varying cognitive load conditions. Priority was given to research with translational implications for adaptive learning systems and personalized educational interventions. Results: Functional imaging studies reveal an inverted-U relationship between cognitive load and neuroplasticity, with a moderate challenge in optimizing prefrontal-parietal network activation and learning-related neural adaptations. Brain stimulation research demonstrates that tDCS and TMS can enhance neuroplastic responses under cognitive load, particularly benefiting learners with lower baseline abilities. Educational technology applications demonstrate that neuroplasticity-informed adaptive systems, which incorporate real-time cognitive load monitoring and dynamic difficulty adjustment, significantly enhance learning outcomes compared to traditional approaches. Individual differences in cognitive capacity, neurodiversity, and baseline brain states substantially moderate these effects, necessitating the development of personalized intervention strategies. Conclusions: Neuroplasticity-informed learning approaches offer a robust framework for educational technology design that respects cognitive load limitations while maximizing adaptive neural changes. Integration of functional imaging insights, brain stimulation protocols, and adaptive algorithms enables the development of inclusive educational technologies that support diverse learners under cognitive stress. Future research should focus on scalable implementations of real-time neuroplasticity monitoring in authentic educational settings, as well as on developing ethical frameworks for deploying neurotechnology-enhanced learning systems across diverse populations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Innovative Theories and Practices for Designing and Evaluating Inclusive Educational Technology and Online Learning)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Neuroception of Psychological Safety and Attitude Towards General AI in uHealth Context
by
Anca-Livia Panfil, Simona C. Tamasan, Claudia C. Vasilian, Raluca Horhat and Diana Lungeanu
Multimodal Technol. Interact. 2026, 10(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/mti10010004 - 30 Dec 2025
Abstract
Interest in general AI is widespread, and much is expected from its large-scale adoption in the healthcare sector. However, the success of uHealth implementations relies on genuine trust, beyond technical performance. Neuroception of psychological safety (NPS), grounded in polyvagal theory, encompasses the human
[...] Read more.
Interest in general AI is widespread, and much is expected from its large-scale adoption in the healthcare sector. However, the success of uHealth implementations relies on genuine trust, beyond technical performance. Neuroception of psychological safety (NPS), grounded in polyvagal theory, encompasses the human subconscious and automatic processes of safety and risk detection. We conducted a cross-sectional survey to explore a hypothetical connection between NPS and the perception of general AI in the uHealth context, by an anonymous online questionnaire comprising the following: Neuroception of Psychological Safety Scale (NPSS), four-item AI Attitude Scale (AIAS-4), and questions on AI threat, age, gender, and level of education. Multivariate analysis was performed using covariance-based structural equation modeling. We received 201 responses: 73 (36.3%) males vs. 128 (63.7%) females, all adults with varying levels of education (from 0 = basic formal education to 4 = master’s degree). Respondents belonged to four demographic cohorts: from Baby boomers to Generation Z. SEM results indicated that attitudes towards AI-driven health interventions are significantly impacted by social engagement and compassion (NPSS factors). Gender, education, and demographic cohort were confirmed as significant covariates. NPS-related attitudes towards AI should be considered and analyzed by healthcare providers, application developers, and policy or regulatory authorities.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue uHealth Interventions and Digital Therapeutics for Better Diseases Prevention and Patient Care)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Mixed Reality Game Design for the Effectiveness and Application Research of Integrating Sustainable Concepts into Blended Learning
by
Zhengqing Wang, Chenxi Xiao and Pengwei Hsiao
Multimodal Technol. Interact. 2026, 10(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/mti10010003 - 30 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study explores how mixed reality (MR) game environments, enabled by sensor-based motion tracking and interactive visualization technologies, can be effectively integrated into blended learning to promote sustainability education. Using eight Macau bakeries as empirical cases, field investigations collected and categorized surplus bread
[...] Read more.
This study explores how mixed reality (MR) game environments, enabled by sensor-based motion tracking and interactive visualization technologies, can be effectively integrated into blended learning to promote sustainability education. Using eight Macau bakeries as empirical cases, field investigations collected and categorized surplus bread samples, while carbon emission frameworks informed pedagogical design. Employing a multidimensional research methodology combining questionnaires and semi-structured interviews, the study delved into the intrinsic link between bread waste and carbon emissions. Through perceptual interaction design and task-oriented challenge modes within the MR environment, users were immersed in experiencing the pathway of sustainable behavioral impact. Post-instructional engagement with the MR game revealed that >90% of participants expressed strong affinity for the system design, and >85% perceived it as intuitively operable. Analysis of user feedback and performance data demonstrates the system’s potential to deliver solutions for reducing bread waste and carbon emissions. By establishing a replicable MR game framework and technical mechanisms, this research offers novel perspectives for future sustainability education studies in the field of behavioral mixed reality design.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Human–AI Feedback Loop for Pronunciation Training: A Mobile Application with Phoneme-Level Error Highlighting
by
Aleksei Demin, Georgii Vorontsov and Dmitrii Chaikovskii
Multimodal Technol. Interact. 2026, 10(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/mti10010002 - 26 Dec 2025
Abstract
This paper presents an AI-augmented pronunciation training approach for Russian language learners through a mobile application that supports an interactive learner–system feedback loop. The system combines a pre-trained Wav2Vec2Phoneme neural network with Needleman–Wunsch global sequence alignment to convert reference and learner speech into
[...] Read more.
This paper presents an AI-augmented pronunciation training approach for Russian language learners through a mobile application that supports an interactive learner–system feedback loop. The system combines a pre-trained Wav2Vec2Phoneme neural network with Needleman–Wunsch global sequence alignment to convert reference and learner speech into aligned phoneme sequences. Rather than producing an overall pronunciation score, the application provides localized, interpretable feedback by highlighting phoneme-level matches and mismatches in a red/green transcription, enabling learners to see where sounds were substituted, omitted, or added. Implemented as a WeChat Mini Program with a WebSocket-based backend, the design illustrates how speech-to-phoneme models and alignment procedures can be integrated into a lightweight mobile interface for autonomous pronunciation practice. We further provide a feature-level comparison with widely used commercial applications (Duolingo, HelloChinese, Babbel), emphasizing differences in feedback granularity and interpretability rather than unvalidated accuracy claims. Overall, the work demonstrates the feasibility of alignment-based phoneme-level feedback for mobile pronunciation training and motivates future evaluation of recognition reliability, latency, and learning outcomes on representative learner data.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Human-AI Collaborative Interaction Design: Rethinking Human-Computer Symbiosis in the Age of Intelligent Systems)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Motion Capture as an Immersive Learning Technology: A Systematic Review of Its Applications in Computer Animation Training
by
Xinyi Jiang, Zainuddin Ibrahim, Jing Jiang and Gang Liu
Multimodal Technol. Interact. 2026, 10(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/mti10010001 - 23 Dec 2025
Abstract
Motion capture (MoCap) is increasingly recognized as a powerful multimodal immersive learning technology, providing embodied interaction and real-time motion visualization that enrich educational experiences. Although MoCap is gaining prominence within educational research, its pedagogical value and integration into computer animation training environments have
[...] Read more.
Motion capture (MoCap) is increasingly recognized as a powerful multimodal immersive learning technology, providing embodied interaction and real-time motion visualization that enrich educational experiences. Although MoCap is gaining prominence within educational research, its pedagogical value and integration into computer animation training environments have received relatively limited systematic investigation. This review synthesizes findings from 17 studies to analyze how MoCap supports instructional design, creative development, and workflow efficiency in animation education. Results show that MoCap enables a multimodal learning process by combining visual, kinesthetic, and performative modalities, strengthening learners’ sense of presence, agency, and perceptual–motor understanding. Furthermore, we identified five key technical affordances of MoCap, including precision and fidelity, multi-actor and creative control, interactivity and immersion, perceptual–motor learning, and emotional expressiveness, which together shape both cognitive and creative learning outcomes. Emerging trends highlight MoCap’s growing convergence with VR/AR, XR, real-time rendering engines, and AI-augmented motion analysis, expanding its role in the design of immersive and interactive educational systems. This review offers insights into the use of MoCap in animation education research and provides a springboard for future work on more immersive and industry-relevant training.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Educational Virtual/Augmented Reality)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Mapping Blended Learning Activities to Students’ Digital Competence in VET
by
Marko Radovan and Danijela Makovec Radovan
Multimodal Technol. Interact. 2025, 9(12), 118; https://doi.org/10.3390/mti9120118 - 15 Dec 2025
Abstract
While blended learning facilitates digital literacy development, the specific design models and student factors contributing to this process remain underexplored. This study examined the relationship between various blended learning design models and digital literacy skill acquisition among 106 upper-secondary Vocational Education and Training
[...] Read more.
While blended learning facilitates digital literacy development, the specific design models and student factors contributing to this process remain underexplored. This study examined the relationship between various blended learning design models and digital literacy skill acquisition among 106 upper-secondary Vocational Education and Training (VET) students. Relationships among student activities, digital competencies, and prior blended learning experience were analyzed. Engagement in collaborative, task-based instructional designs—specifically collaborative projects and regular quizzing supported by digital tools—was positively associated with digital competence. Conversely, passive participation in live sessions or viewing pre-recorded videos exhibited a comparatively weaker association with competence development. While the use of virtual/augmented reality and interactive video correlated positively with digital tool usage, it did not significantly predict perceptions of online safety or content creation skills. Students with prior blended learning experience reported higher proficiency in developmental competencies, such as content creation and research, compared to their inexperienced peers. Cluster analysis identified three distinct student profiles based on technical specialization and blended learning experience. Overall, these findings suggest that blended learning implementation should prioritize structured collaboration and formative assessment.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Online Learning to Multimodal Era: Interfaces, Analytics and User Experiences)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Augmented Reality in Biology Education: A Literature Review
by
Katja Stanič and Andreja Špernjak
Multimodal Technol. Interact. 2025, 9(12), 117; https://doi.org/10.3390/mti9120117 - 25 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This systematic review summarises the latest research on the use of augmented reality (AR) in biology education at primary, secondary and tertiary levels. Searching Web of Science, Scopus and Google Scholar, we found 40 empirical studies published up until early 2024. For each
[...] Read more.
This systematic review summarises the latest research on the use of augmented reality (AR) in biology education at primary, secondary and tertiary levels. Searching Web of Science, Scopus and Google Scholar, we found 40 empirical studies published up until early 2024. For each study, we analysed biological content, technical features, learning practices and pedagogical impact. AR is most used in human anatomy, particularly in the circulatory and respiratory systems, but also in genetics, cell biology, virology, botany, ecology and molecular processes. Mobile devices dominate as a mediation platform, with marker-based tracking and either commercial apps or self-developed Unity/Vuforia solutions. Almost all studies embed AR in constructivist or inquiry-based pedagogies, and report improved motivation, engagement and conceptual understanding. Nevertheless, reporting on the technical details is inconsistent and the long-term effects are not yet sufficiently researched. AR should therefore be viewed as a pedagogical tool rather than a technological goal that requires careful instructional design and equitable access to ensure meaningful and sustainable learning.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Cross-Modal Attention Fusion: A Deep Learning and Affective Computing Model for Emotion Recognition
by
Himanshu Kumar, Martin Aruldoss and Martin Wynn
Multimodal Technol. Interact. 2025, 9(12), 116; https://doi.org/10.3390/mti9120116 - 24 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Artificial emotional intelligence is a sub-domain of human–computer interaction research that aims to develop deep learning models capable of detecting and interpreting human emotional states through various modalities. A major challenge in this domain is identifying meaningful correlations between heterogeneous modalities—for example, between
[...] Read more.
Artificial emotional intelligence is a sub-domain of human–computer interaction research that aims to develop deep learning models capable of detecting and interpreting human emotional states through various modalities. A major challenge in this domain is identifying meaningful correlations between heterogeneous modalities—for example, between audio and visual data—due to their distinct temporal and spatial properties. Traditional fusion techniques used in multimodal learning to combine data from different sources often fail to adequately capture meaningful and less computational cross-modal interactions, and struggle to adapt to varying modality reliability. Following a review of the relevant literature, this study adopts an experimental research method to develop and evaluate a mathematical cross-modal fusion model, thereby addressing a gap in the extant research literature. The framework uses the Tucker tensor decomposition to analyse the multi-dimensional array of data into a set of matrices to support the integration of temporal features from audio and spatiotemporal features from visual modalities. A cross-attention mechanism is incorporated to enhance cross-modal interaction, enabling each modality to attend to the relevant information from the other. The efficacy of the model is rigorously evaluated on three publicly available datasets and the results conclusively demonstrate that the proposed fusion technique outperforms conventional fusion methods and several more recent approaches. The findings break new ground in this field of study and will be of interest to researchers and developers in artificial emotional intelligence.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Reducing Periprocedural Pain and Anxiety of Child Patients with Guided Relaxation Exercises in a Virtual Natural Environment: A Clinical Research Study
by
Ilmari Jyskä, Markku Turunen, Kaija Puura, Elina Karppa, Sauli Palmu and Jari Viik
Multimodal Technol. Interact. 2025, 9(12), 115; https://doi.org/10.3390/mti9120115 - 24 Nov 2025
Abstract
Fear of needles is common among child patients. It causes stress and can lead to difficulty in procedures and future treatment avoidance. Virtual reality (VR) has emerged as a promising tool to reduce pain and anxiety non-pharmacologically. However, a research gap exists regarding
[...] Read more.
Fear of needles is common among child patients. It causes stress and can lead to difficulty in procedures and future treatment avoidance. Virtual reality (VR) has emerged as a promising tool to reduce pain and anxiety non-pharmacologically. However, a research gap exists regarding what VR content is most effective in decreasing periprocedural stress. This article reports a VR feasibility study conducted with 83 child patients aged 8–12 years during a cannulation procedure. It has a between-subjects design with four groups, comparing deep breathing and mindfulness-based relaxation in a virtual nature environment (VNE) to passive VNE and standard care. The results from both relaxation exercise groups have been previously reported. This follow-up article adds findings from passive VNE and control groups, comparing all four for effectiveness and patient experience. The key findings highlight that deep breathing was highly effective according to heart rate variability (HRV) data, but less enjoyable than the mindfulness-based relaxation, which achieved higher patient satisfaction but was less effective according to HRV. Passive VNEs were pleasant but did not cause measurable stress reduction. All VR interventions improved patient experience over standard care. Relaxation exercises in a VNE reduce periprocedural stress more efficiently than passive VNEs or standard care in pediatrics.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue uHealth Interventions and Digital Therapeutics for Better Diseases Prevention and Patient Care)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Evaluating Rich Visual Feedback on Head-Up Displays for In-Vehicle Voice Assistants: A User Study
by
Mahmoud Baghdadi, Dilara Samad-Zada and Achim Ebert
Multimodal Technol. Interact. 2025, 9(11), 114; https://doi.org/10.3390/mti9110114 - 16 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In-vehicle voice assistants face usability challenges due to limitations in delivering feedback within the constraints of the driving environment. The presented study explores the potential of Rich Visual Feedback (RVF) on Head-Up Displays (HUDs) as a multimodal solution to enhance system usability. A
[...] Read more.
In-vehicle voice assistants face usability challenges due to limitations in delivering feedback within the constraints of the driving environment. The presented study explores the potential of Rich Visual Feedback (RVF) on Head-Up Displays (HUDs) as a multimodal solution to enhance system usability. A user study with 32 participants evaluated three HUD User Interface (UI) designs: the AR Fusion UI, which integrates augmented reality elements for layered, dynamic information presentation; the Baseline UI, which displays only essential keywords; and the Flat Fusion UI, which uses conventional vertical scrolling. To explore HUD interface principles and inform future HUD design without relying on specific hardware, a simulated near-field overlay was used. Usability was measured using the System Usability Scale (SUS), and distraction was assessed with a penalty point method. Results show that RVF on the HUD significantly influences usability, with both content quantity and presentation style affecting outcomes. The minimal Baseline UI achieved the highest overall usability. However, among the two Fusion designs, the AR-based layered information mechanism outperformed the flat scrolling method. Distraction effects were not statistically significant, indicating the need for further research. These findings suggest RVF-enabled HUDs can enhance in-vehicle voice assistant usability, potentially contributing to safer, more efficient driving.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Multi-Institution Mixed Methods Analysis of a Novel Acid-Base Mnemonic Algorithm
by
Camille Massaad, Harrison Howe, Meize Guo and Tyler Bland
Multimodal Technol. Interact. 2025, 9(11), 113; https://doi.org/10.3390/mti9110113 - 11 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Acid-base analysis is a high-load diagnostic skill that many medical students struggle to master when taught using traditional text-based flowcharts. This multi-institution mixed-methods study evaluated a novel visual mnemonic algorithm that integrated Medimon characters, symbolic imagery, and pop-culture references into the standard acid-base
[...] Read more.
Acid-base analysis is a high-load diagnostic skill that many medical students struggle to master when taught using traditional text-based flowcharts. This multi-institution mixed-methods study evaluated a novel visual mnemonic algorithm that integrated Medimon characters, symbolic imagery, and pop-culture references into the standard acid-base diagnostic framework. First-year medical students (n = 273) at six distributed WWAMI campuses attended an identical lecture on acid-base physiology. Students at five control campuses received the original text-based algorithm, while students at one experimental campus received the Medimon algorithm in addition. Achievement was measured with a unit exam (nine focal items, day 7) and a final exam (four focal items, day 11). A Differences-in-Differences approach compared performance on focal items versus baseline items across sites. Students at the experimental campus showed no significant advantage on the unit exam (DiD = +1.2%, g = 0.12) but demonstrated a larger, but still non-significant, medium-to-large effect on the final exam (DiD = +11.0%, g = 0.85). At the experimental site, 39 students completed the Situational Interest Survey for Multimedia (SIS-M), revealing significantly higher triggered, maintained-feeling, maintained-value, and overall situational interest scores for the Medimon algorithm (all p < 0.001). Thematic analysis of open-ended responses identified four themes: enhanced clarity, improved memorability, increased engagement, and barriers to interpretation. Collectively, the findings suggest that embedding visual mnemonics and serious-game characters into diagnostic algorithms can enhance learner interest and may improve long-term retention in preclinical medical education.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
A Scoping Review of AI-Driven mHealth Systems for Precision Hydration: Integrating Food and Beverage Water Content for Personalized Recommendations
by
Kyriaki Apergi, Georgios D. Styliaras, George Tsirogiannis, Grigorios N. Beligiannis and Olga Malisova
Multimodal Technol. Interact. 2025, 9(11), 112; https://doi.org/10.3390/mti9110112 - 8 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Precision nutrition increasingly integrates mobile health (mHealth) and artificial intelligence (AI) tools. However, personalized hydration remains underdeveloped, particularly in accounting for both food- and beverage-derived water intake. Objective: This scoping review maps the existing literature on mHealth applications that incorporate machine learning
[...] Read more.
Background: Precision nutrition increasingly integrates mobile health (mHealth) and artificial intelligence (AI) tools. However, personalized hydration remains underdeveloped, particularly in accounting for both food- and beverage-derived water intake. Objective: This scoping review maps the existing literature on mHealth applications that incorporate machine learning (ML) or AI for personalized hydration. The focus is on systems that combine dietary (food-based) and fluid (beverage-based) water sources to generate individualized hydration assessments and recommendations. Methods: Following the PRISMA-ScR guidelines, we conducted a structured literature search across three databases (PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science) through March 2025. Studies were included if they addressed AI or ML within mHealth platforms for personalized hydration or nutrition, with an emphasis on systems using both beverage and food intake data. Results: Of the 43 included studies, most examined dietary recommender systems or hydration-focused apps. Few studies used hydration assessments focusing on both food and beverages or employed AI for integrated guidance. Emerging trends include wearable sensors, AR tools, and behavioral modeling. Conclusions: While numerous digital health tools address hydration or nutrition separately, there is a lack of comprehensive systems leveraging AI to guide hydration from both food and beverage sources. Bridging this gap is essential for effective, equitable, and precise hydration interventions. In this direction, we propose a hydration diet recommender system that integrates demographic, anthropometric, psychological, and socioeconomic data to create a truly personalized diet and hydration plan with a holistic approach.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Digital Model-Based Serious Game for PID-Controller Education: One-Axis Drone Model, Analytics, and Student Study
by
Raul Brumar, Stelian Nicola and Horia Ciocârlie
Multimodal Technol. Interact. 2025, 9(11), 111; https://doi.org/10.3390/mti9110111 - 24 Oct 2025
Abstract
This paper presents a serious game designed to support the teaching of PID controllers. The game couples a visually clear Unity scene with a physics-accurate digital model of a drone with a single degree of freedom (called a one-axis drone) and helps prepare
[...] Read more.
This paper presents a serious game designed to support the teaching of PID controllers. The game couples a visually clear Unity scene with a physics-accurate digital model of a drone with a single degree of freedom (called a one-axis drone) and helps prepare students to meet the demands of Industry 4.0 and 5.0. An analytics back-end logs system error at 10 Hz and interaction metrics, enabling instructors to diagnose common tuning issues from a plot and to provide actionable hints to students. The design process that led to choosing the one-axis drone and turbulence application via “turbulence balls” is explained, after which the implementation is described. The proposed solution is evaluated in a within-subjects study performed with 21 students from mixed technical backgrounds across two short, unsupervised tinkering sessions of up to 10 min framed by four quizzes of both general and theoretical content. Three questions shaped the analysis: (i) whether error traces can be visualized by instructors to generate actionable hints for students; (ii) whether brief, unsupervised play sessions yield measurable gains in knowledge or stability; and (iii) whether efficiency of tuning improves without measurable changes in tune performance. Results show that analysis of plotted error values exposes recognizable issues with PID tunes that map to concrete hints provided by the instructor. When it comes to unsupervised play sessions, no systematic pre/post improvement in quiz scores or normalized area under absolute error was observed. However, it required significantly less effort from students in the second session to reach the same tune performance, indicating improved tuning efficiency. Overall, the proposed serious game with the digital twin-inspired one-axis drone and custom analytics back-end has emerged as a practical, safe, and low-cost auxiliary tool for teaching PID controllers, helping bridge the gap between theory and practice.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Video Games: Learning, Emotions, and Motivation)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
From Consumption to Co-Creation: A Systematic Review of Six Levels of AI-Enhanced Creative Engagement in Education
by
Margarida Romero
Multimodal Technol. Interact. 2025, 9(10), 110; https://doi.org/10.3390/mti9100110 - 21 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
As AI systems become more integrated into society, the relationship between humans and AI is shifting from simple automation to co-creative collaboration. This evolution is particularly important in education, where human intuition and imagination can combine with AI’s computational power to enable innovative
[...] Read more.
As AI systems become more integrated into society, the relationship between humans and AI is shifting from simple automation to co-creative collaboration. This evolution is particularly important in education, where human intuition and imagination can combine with AI’s computational power to enable innovative forms of learning and teaching. This study is grounded in the #ppAI6 model, a framework that describes six levels of creative engagement with AI in educational contexts, ranging from passive consumption to active, participatory co-creation of knowledge. The model highlights progression from initial interactions with AI tools to transformative educational experiences that involve deep collaboration between humans and AI. In this study, we explore how educators and learners can engage in deeper, more transformative interactions with AI technologies. The #ppAI6 model categorizes these levels of engagement as follows: level 1 involves passive consumption of AI-generated content, while level 6 represents expansive, participatory co-creation of knowledge. This model provides a lens through which we investigate how educational tools and practices can move beyond basic interactions to foster higher-order creativity. We conducted a systematic literature review following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines for reporting the levels of creative engagement with AI tools in education. This review synthesizes existing literature on various levels of engagement, such as interactive consumption through Intelligent Tutoring Systems (ITS), and shifts focus to the exploration and design of higher-order forms of creative engagement. The findings highlight varied levels of engagement across both learners and educators. For learners, a total of four studies were found at level 2 (interactive consumption). Two studies were found that looked at level 3 (individual content creation). Four studies focused on collaborative content creation at level 4. No studies were observed at level 5, and only one study was found at level 6. These findings show a lack of development in AI tools for more creative involvement. For teachers, AI tools mainly support levels two and three, facilitating personalized content creation and performance analysis with limited examples of higher-level creative engagement and indicating areas for improvement in supportive collaborative teaching practices. The review found that two studies focused on level 2 (interactive consumption) for teachers. In addition, four studies were identified at level 3 (individual content creation). Only one study was found at level 5 (participatory co-creation), and no studies were found at level 6. In practical terms, the review suggests that educators need professional development focused on building AI literacy, enabling them to recognize and leverage the different levels of creative engagement that AI tools offer.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Testing a New Approach to Monitor Mild Cognitive Impairment and Cognition in Older Adults at the Community Level
by
Isabel Paniak, Ethan Cohen, Christa Studzinski and Lia Tsotsos
Multimodal Technol. Interact. 2025, 9(10), 109; https://doi.org/10.3390/mti9100109 - 21 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Dementia and mild cognitive impairment (MCI) are growing health concerns in Canada’s aging population. Over 700,000 Canadians currently live with dementia, and this number is expected to rise. As the older adult population increases, coupled with an already strained healthcare system, there is
[...] Read more.
Dementia and mild cognitive impairment (MCI) are growing health concerns in Canada’s aging population. Over 700,000 Canadians currently live with dementia, and this number is expected to rise. As the older adult population increases, coupled with an already strained healthcare system, there is a pressing need for innovative tools that support aging in place. This study explored the feasibility and acceptability of using a Digital Human (DH) conversational agent, combined with AI-driven speech analysis, to monitor cognitive function, anxiety, and depression in cognitively healthy community-dwelling older adults (CDOA) aged 65 and older. Sixty older adults participated in up to three in-person sessions over six months, interacting with the DH through journaling and picture description tasks. Afterward, 51 of the participants completed structured interviews about their experiences and perceptions of the DH and AI more generally. Findings showed that 84% enjoyed interacting with the DH, and 96% expressed interest in learning more about AI in healthcare. While participants were open and curious about AI, 67% voiced concerns about AI replacing human interaction in healthcare. Most found the DH friendly, though reactions to its appearance varied. Overall, participants viewed AI as a promising tool, provided it complements, rather than replaces, human interactions.
Full article

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Electronics, MTI, BDCC, AI, Virtual Worlds, Applied Sciences
AI-Based Interactive and Immersive Systems
Topic Editors: Sotiris Diplaris, Nefeli Georgakopoulou, Stefanos Vrochidis, Giuseppe Amato, Maurice Benayoun, Beatrice De GelderDeadline: 31 December 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
MTI
Multimodal Interaction Design in Immersive Learning and Training Environments
Guest Editors: Qian Li, Yunfei Long, Lei ShiDeadline: 20 February 2026
Special Issue in
MTI
Artificial Intelligence in Medical Radiation Science, Radiology and Radiation Oncology
Guest Editor: Curtise K. C. NgDeadline: 28 February 2026
Special Issue in
MTI
Human-AI Collaborative Interaction Design: Rethinking Human-Computer Symbiosis in the Age of Intelligent Systems
Guest Editor: Qianling JiangDeadline: 20 April 2026
Special Issue in
MTI
Educational Virtual/Augmented Reality
Guest Editor: Arun KulshreshthDeadline: 30 April 2026










