- Systematic Review
Digital Forest Bathing: A Systematic Review
- Lilith Tersch,
- Dennis Anheyer and
- Thomas Ostermann
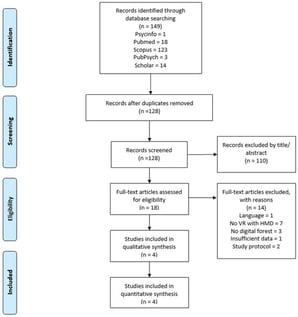
In recent years, forest bathing has gained popularity worldwide due to its many positive effects on health. In the face of increasing urbanization and limited access to natural forests, digital forest bathing is a promising alternative. Digital forest bathing could also be an option for people with restricted mobility, which could be a way to make the health-promoting effects of forests more accessible. This systematic review examines the current state of research on digital forest bathing, considers the associated effects, and highlights the technical possibilities and thereby consolidates the currently limited evidence base in this emerging field. For literature identification, the databases APA, PsycInfo, PubMed, PubPsych, Scopus, and Google Scholar were searched. A total of four studies were included. The results indicate that digital forest bathing could have positive effects on relaxation and well-being that could be comparable to real-life forest bathing, and summarize how interventions were technically implemented across the included studies. As there are still a few studies on digital forest bathing, the implementation of the research varies greatly, and some studies have risks of bias; the results presented here should be interpreted with caution. In addition to a critical examination of the study designs and quality, suggestions for further research in this area are given, and key methodological constraints relevant for interpreting early effects are outlined.
6 February 2026