- Article
Selection of High-Yielding Genotypes of Coffea canephora at Transitional Altitude: Adaptability and Stability and Impacts of Water Management
- Tafarel Victor Colodetti,
- Wagner Nunes Rodrigues and
- Marcelo Antonio Tomaz
- + 4 authors
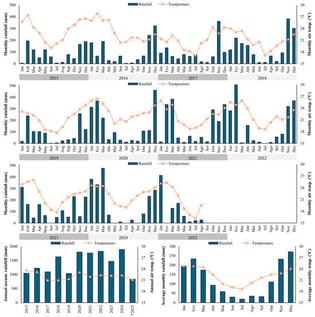
Expanding Coffea canephora cultivation to transitional altitudes offers a promising strategy to sustain coffee production under climate change. This study evaluated 27 genotypes cultivated under two water management regimes (fully and minimally irrigated) at 650 m altitude in Espírito Santo, Brazil, over eight harvests (2018–2025). A split-plot design was analyzed using a three-way mixed model (REML/BLUP) to estimate genetic parameters and predicted genotypic values. Adaptability and stability were assessed using the harmonic mean of relative performance of genotypic values (HMRPGV) and weighted average of absolute scores (WAASB) and integrated into a multi-trait selection index. Significant genotypic and temporal effects were detected, while the interaction between genotypes and water management regimes was non-significant, indicating consistent performance under different water regimes. Broad-sense heritability was moderate, with high selective accuracy. Genotypes 108 and 203 achieved the highest predicted yields (91.4 and 86.8 bags ha−1) and superior adaptability. The multi-trait index identified six outstanding genotypes—108, 203, 201, 306, 303, and 302—combining high yield, broad adaptability, and temporal stability, resulting in an expected genetic gain of 8.17% in relation to the original population. These findings demonstrate that selected C. canephora genotypes are well adapted to transitional altitudes, supporting breeding programs for climate-resilient and high-yielding crops.
7 February 2026