Diagnostic Accuracy of Diffusion-Weighted MRI for Differentiating Benign and Malignant Thyroid Nodules: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
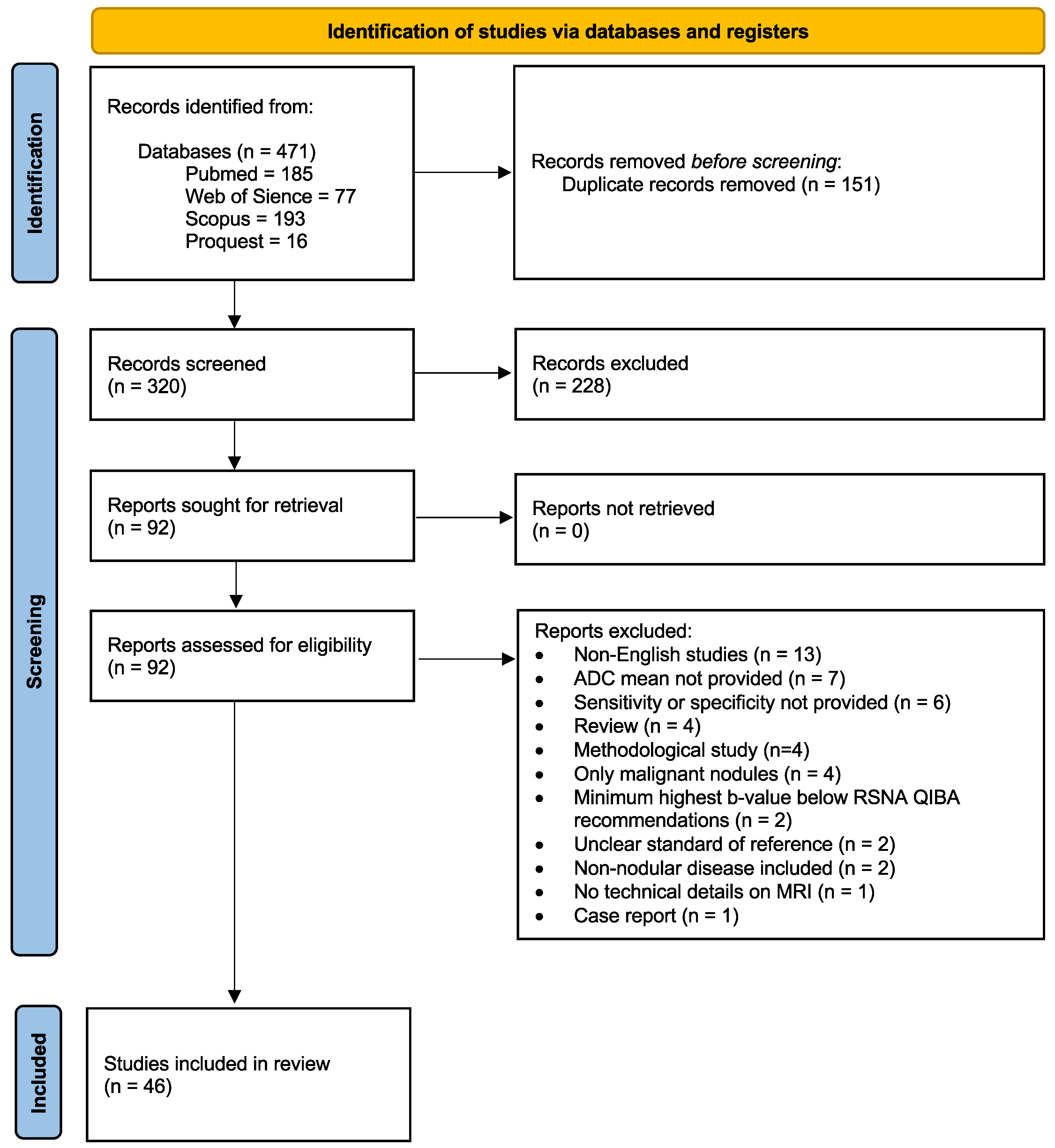
3.1. Literature Search
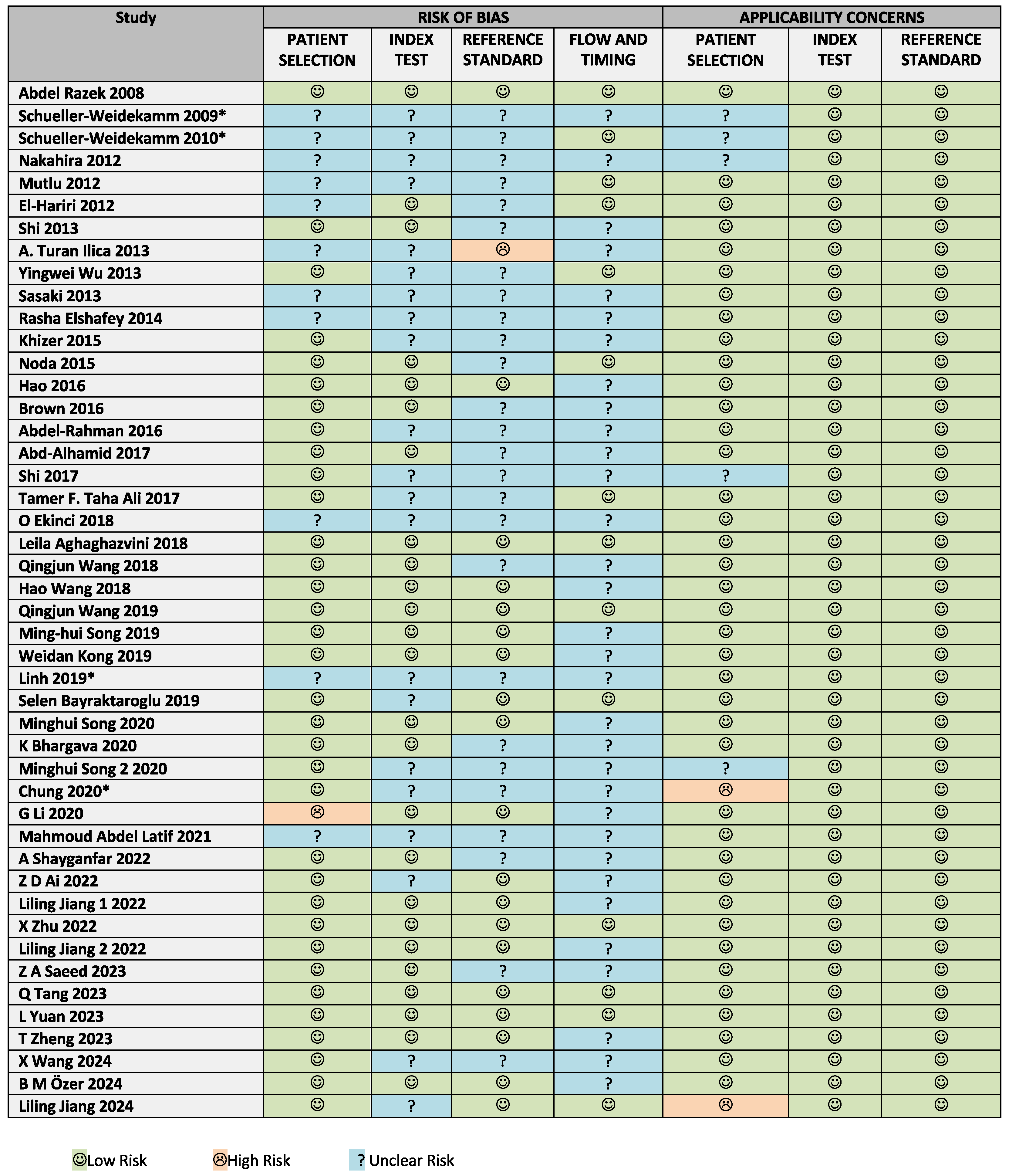
3.2. Risk of Bias and Applicability Assessment
3.3. Study Characteristics
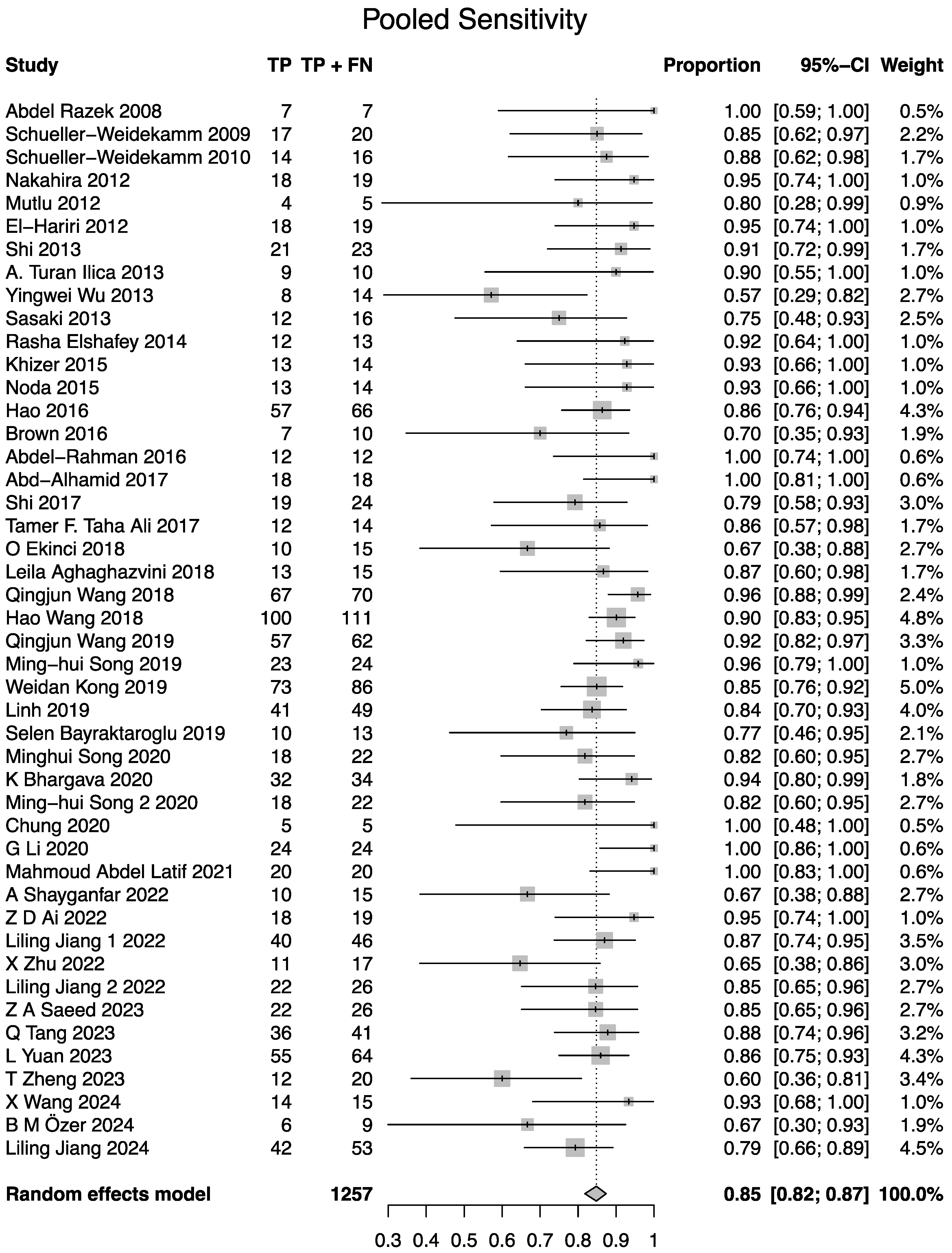
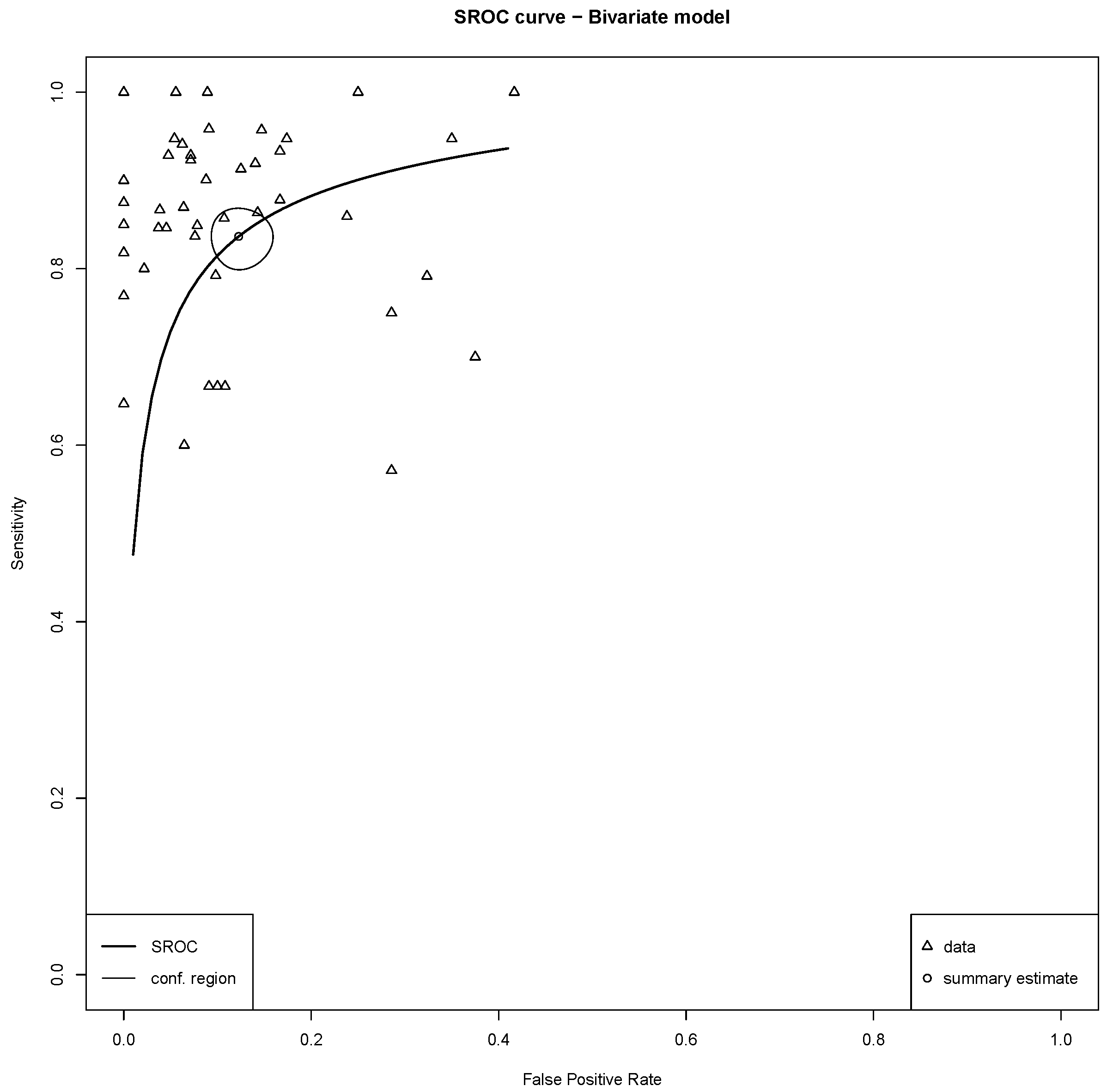
3.4. Meta-Analysis of Diagnostic Performance
3.5. Studies Reporting Lower ADC Values for Benign than for Malignant Nodules
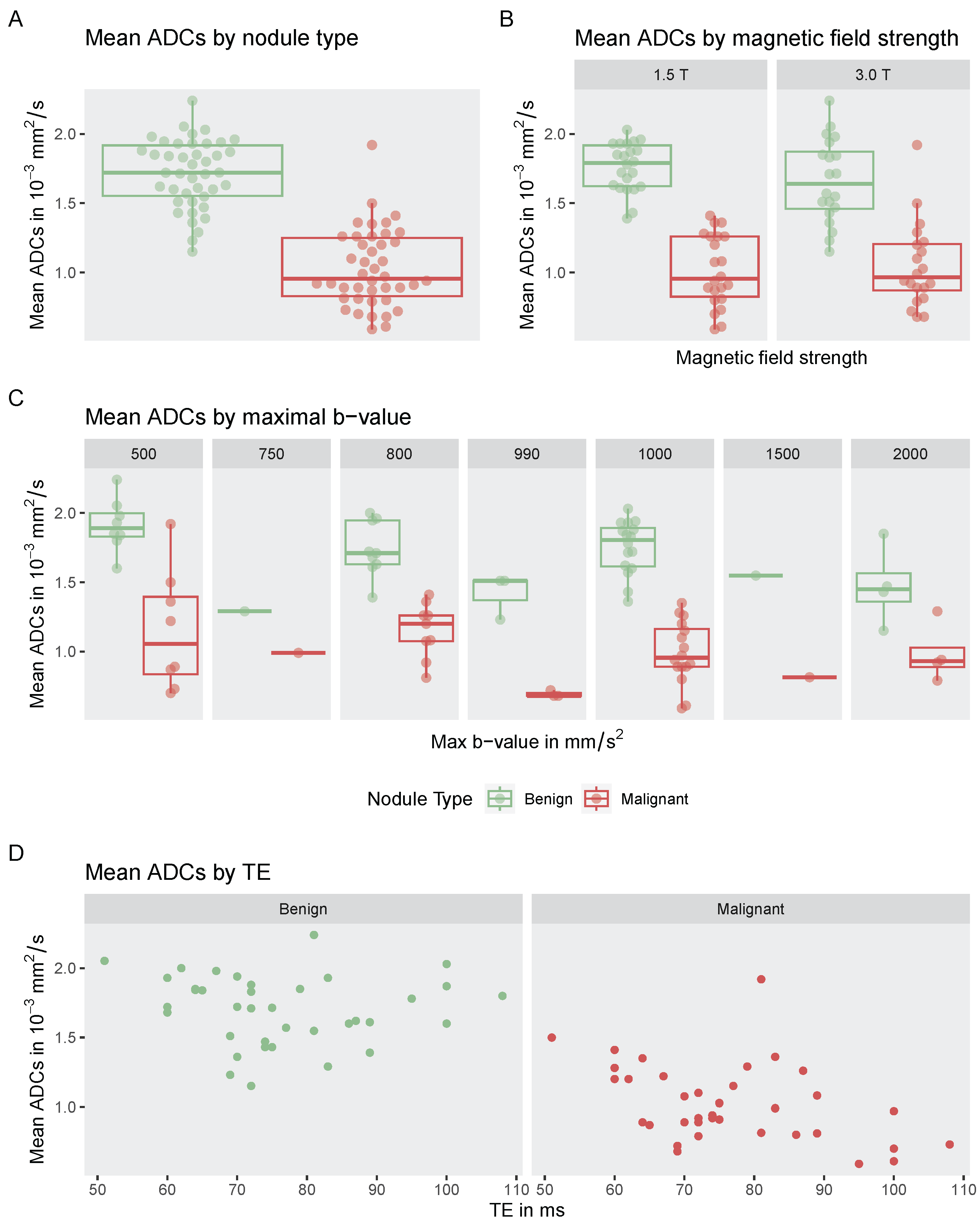
3.6. Influence on Highest b-Value, Magnetic Field Strength, and Echo Time on Reported ADC Values
3.7. Studies Reporting on Multimodal Analysis
- T1 Mapping: Yuan et al. (2023) assessed the feasibility of combining T1 mapping with ADC measurements. They reported an AUC of 0.837 for ADC and 0.845 for T1 mapping, with a combined AUC of 0.956. Notably, the acquisition time for T1 mapping was only 36 s [32].
- Morphologic Parameters: Tang et al. (2023) integrated DWI metrics with morphological features commonly assessed in TIRADS. A combined model incorporating mean diffusivity from diffusion kurtosis imaging, maximum diameter, and margin irregularity achieved an AUC of 0.996, with a sensitivity of 95.1% and specificity of 100.0% [29].Wang et al. (2018) explored a multivariable model combining DWI with post-contrast and morphologic parameters. Independent predictors included ADC, irregular shape, a ring sign in the delayed phase, and cystic degeneration. An ADC-only model achieved an AUC of 0.95, while a combined model reached an AUC of 0.99 [45].
- Amide Proton Transfer-Weighted Imaging (APT): Li et al. (2020) examined APT imaging in combination with DWI (44 nodules; 22 malignant and 22 benign). APT alone yielded an AUC of 0.835. While ADC alone achieved an AUC of 0.95, the addition of APT did not further improve diagnostic performance (combined AUC: 0.95) [18].
- Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Imaging (DCE): Song et al. (2020) evaluated the incremental value of DCE imaging alongside IVIM-derived diffusion parameters. Pharmacokinetic modeling of DCE parameters produced modest diagnostic performance (AUC = 0.668 for , and 0.682 for ). In contrast, the IVIM-derived diffusion coefficient D alone achieved an AUC of 0.969. A combined model () improved the AUC to 0.991, although it was not significantly different from the AUC of D alone [21].Similarly, Sasaki et al. (2013) proposed a stepwise diagnostic approach combining ADC and DCE time intensity curves. While the combined model showed an accuracy of 91%, ADC alone achieved the same accuracy, suggesting limited added value of DCE [51].
- Spectroscopy: Three studies, all conducted in Egypt, evaluated the diagnostic performance of MR spectroscopy (MRS) in addition to DWI [46,50,52]. All reported improved sensitivity and specificity when combining ADC with MRS, although none described how the combined models were constructed, and none tested whether the improvements were statistically significant. Two of the studies originated from the same institution [50,52]. El-Hariri et al. (2012) reported sensitivities and specificities of 94% and 95% for DWI, 94.7% and 89.2% for MRS, and 96% and 100% for the combined approach, respectively [52]. Elshafey et al. (2014) reported 96% sensitivity and 85% specificity for DWI, 96% and 92% for MRS, and 100% and 93% for the combination [46]. Taha Ali (2017), in a cohort of 42 nodules (28 benign, 14 malignant), used MRS to assess the presence of a choline peak. Reported sensitivity and specificity were 100% and 89.3% for MRS, 85.7% and 89.2% for DWI, and 100% and 96% for the combined method [50].
3.8. Studies Investigating Advanced DWI Techniques
3.9. Studies Investigating Advanced Diffusion Models
Studies Investigating the Influence of b-Value Choice on Diagnostic Performance
4. Discussion
4.1. Beyond Previous Meta-Analyses: Analysis of Technical Parameters
4.2. Combination with Other Imaging Techniques
4.3. Limitations
4.4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACR | American College of Radiology |
| ADC | Apparent diffusion coefficient |
| ATA | American Thyroid Association |
| AUC | Area under the receiver operating curve |
| cDWI | Conventional single-shot spin echo echo-planar imaging |
| DCE | Dynamic contrast-enhanced MR perfusion |
| DKI | Diffusion kurtosis imaging |
| DWI | Diffusion-weighted MRI |
| EPI DWI | Echo-Planar Imaging DWI |
| FNA | Fine needle aspiration (cytology) |
| IVIM | Intravoxel incoherent motion |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| MRS | Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy |
| MUSE-DWI | Multiplexed sensitivity-encoding diffusion-weighted imaging |
| NIFTP | Neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features |
| PRISMA-DTA | Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses of Diagnostic Test Accuracy |
| QIBA | Quantitative Imaging Biomarkers Alliance |
| rFOV | Reduced field-of-view DWI |
| SIR | Signal intensity ratios |
| SMS-RESOLVE-DWI | Simultaneous Multi-Slice Readout Segmentation of Long Variable |
| Echo-Trains DWI | |
| sROC | Summary receiver operating characteristic |
| TE | Echo time |
| TIRADS | Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System |
Appendix A
| Database | Search Query |
|---|---|
| PubMed | ((“Thyroid nodule”[Mesh]) OR (Thyroid[Title/Abstract])) AND (“Diffusion Magnetic Resonance Imaging”[Mesh] OR (diffusion-weighted[Title/Abstract]) OR (DWI[Title/Abstract])) |
| Web of Science | ((TS=(DWI)) OR TS=(diffusion-weighted)) AND TS=(Thyroid nodule) |
| Scopus | TITLE-ABS-KEY (thyroid) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY (nodule) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY (diffusion) AND (LIMIT-TO (DOCTYPE, “ar”) OR LIMIT-TO (DOCTYPE, “re”) OR LIMIT-TO (DOCTYPE, “cp”)) |
| ProQuest | noft(thyroid) AND noft(diffusion) AND noft(Magnetic resonance imaging) AND noft(nodule) |

| This Meta-Analysis | Lian-Ming Wu et al. (2014) [10] | Lihua Chen et al. (2016) [11] | Meyer et al. (2021) [12] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of included studies | 46 | 7 | 15 | 24 |
| Number of Nodules | 3003 | 358 | 765 | 1714 |
| Studies exluded from our review and reasons | [65]: Only available in Chinese. [66]: Could not be found based on the citation in the review. | [66]: Could not be found based on the citation in the review. [65,67,68]: Only available in Chinese. | [69]: Also included lymph nodes besides thyroid nodules. [70,71]: Insufficient maximum b-value. [71,72,73,74]: Reported only ADC values but not sensitivity and specificity. [75,76]: Included only malignant nodules. [77]: Unclear standard of reference. | |
| Pooled sensitivity | 0.84 (95 % CI: 0.81–0.86) | 0.91 (95 % CI: 0.87–0.94) | 0.90 (95 % CI: 0.85–0.93) | - |
| Pooled specificity | 0.88 (95 % CI: 0.85–0.90) | 0.93 (95 % CI: 0.86–0.96) | 0.95 (95% CI: 0.88–0.98) | - |
| AUC | 0.91 | 0.94 | 0.95 | - |
References
- Fisher, S.B.; Perrier, N.D. The incidental thyroid nodule. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guth, S.; Theune, U.; Aberle, J.; Galach, A.; Bamberger, C. Very high prevalence of thyroid nodules detected by high frequency (13 MHz) ultrasound examination. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 39, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haugen, B.R. 2015 American Thyroid Association management guidelines for adult patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer: What is new and what has changed? Cancer 2017, 123, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sollmann, L.; Eveslage, M.; Danzer, M.F.; Schäfers, M.; Heitplatz, B.; Conrad, E.; Hescheler, D.; Riemann, B.; Noto, B. Additional Value of Pertechnetate Scintigraphy to American College of Radiology Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data Systems and European Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data Systems for Thyroid Nodule Classification in Euthyroid Patients. Cancers 2024, 16, 4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Wen, J.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Y. Diagnostic performance of American College of Radiology TI-RADS: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2021, 216, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, V.; Massoud, E.; Jensen, C.; Zhang, Y.; Hanlon, B.M.; Hitchcock, M.; Arroyo, N.; Chiu, A.S.; Fernandes-Taylor, S.; Alagoz, O.; et al. Diagnostic accuracy of fine-needle biopsy in the detection of thyroid malignancy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Surg. 2022, 157, 1105–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaleontiou, M.; Haymart, M.R. Too much of a good thing? A cautionary tale of thyroid cancer overdiagnosis and overtreatment. Thyroid 2020, 30, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.F.; Feng, Q.; Qiang, J.W.; Li, R.K.; Wang, L.; Yu, J.P. Utility of diffusion-weighted imaging in differentiating malignant from benign thyroid nodules with magnetic resonance imaging and pathologic correlation. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2013, 37, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.y.; Yao, Q.y.; Zhou, Q.y.; Lu, Q.; Suo, S.t.; Chen, J.; Zheng, W.j.; Dai, Y.m.; Wu, L.m.; Xu, J.r. Preliminary study of diffusion kurtosis imaging in thyroid nodules and its histopathologic correlation. Eur. Radiol. 2017, 27, 4710–4720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.M.; Chen, X.X.; Li, Y.L.; Hua, J.; Chen, J.; Hu, J.; Xu, J.R. On the utility of quantitative diffusion-weighted MR imaging as a tool in differentiation between malignant and benign thyroid nodules. Acad. Radiol. 2014, 21, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xu, J.; Bao, J.; Huang, X.; Hu, X.; Xia, Y.; Wang, J. Diffusion-weighted MRI in differentiating malignant from benign thyroid nodules: A meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e008413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, H.J.; Wienke, A.; Surov, A. Discrimination between malignant and benign thyroid tumors by diffusion-weighted imaging–A systematic review and meta analysis. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2021, 84, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salameh, J.P.; Bossuyt, P.M.; McGrath, T.A.; Thombs, B.D.; Hyde, C.J.; Macaskill, P.; Deeks, J.J.; Leeflang, M.; Korevaar, D.A.; Whiting, P.; et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis of diagnostic test accuracy studies (PRISMA-DTA): Explanation, elaboration, and checklist. BMJ 2020, 370, m2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- RSNA Quantitative Imaging Biomarkers Alliance: QIBA Profile: Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging (DWI). 2019. Available online: https://qibawiki.rsna.org/images/6/63/QIBA_DWIProfile_Consensus_Dec2019_Final.pdf (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- Whiting, P.F.; Rutjes, A.W.; Westwood, M.E.; Mallett, S.; Deeks, J.J.; Reitsma, J.B.; Leeflang, M.M.; Sterne, J.A.; Bossuyt, P.M.; QUADAS-2 Group. QUADAS-2: A revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann. Intern. Med. 2011, 155, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balduzzi, S.; Rücker, G.; Schwarzer, G. How to perform a meta-analysis with R: A practical tutorial. Evidence-Based Mental Health 2019, 22, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doebler, P.; Sousa-Pinto, B. mada: Meta-Analysis of Diagnostic Accuracy. In R Package, Version 0.5.11; The R Foundation: Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Jiang, G.; Mei, Y.; Gao, P.; Liu, R.; Jiang, M.; Zhao, Y.; Li, M.; Wu, Y.; Fu, S.; et al. Applying Amide Proton Transfer-Weighted Imaging (APTWI) to Distinguish Papillary Thyroid Carcinomas and Predominantly Solid Adenomatous Nodules: Comparison With Diffusion-Weighted Imaging. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilica, A.T.; Artaş, H.; Ayan, A.; Günal, A.; Emer, O.; Kilbas, Z.; Meric, C.; Atasoy, M.M.; Uzuner, O. Initial experience of 3 Tesla apparent diffusion coefficient values in differentiating benign and malignant thyroid nodules. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2013, 37, 1077–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khizer, A.T.; Raza, S.; Slehria, A.U.R. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging and ADC mapping in differentiating benign from malignant thyroid nodules. J. Coll. Physicians Surg.-JCPSP 2015, 25, 785–788. [Google Scholar]
- Song, M.; Yue, Y.; Guo, J.; Zuo, L.; Peng, H.; Chan, Q.; Jin, Y. Quantitative analyses of the correlation between dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI and intravoxel incoherent motion DWI in thyroid nodules. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2020, 12, 3984–3992. [Google Scholar]
- Saeed, Z.A.; Arooj, S.; Rashid, N.; Masood, M.; Asghar, A. Role of Diffusion-Weighted MRI ( DWI) in Differentiating Between Benign and Malignant Nodules of Thyroid Taking Histopathology as Gold Standard. Ann. King Edw. Med. Univ. Lahore Pak. 2023, 29, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Z.D.; Yu, X.P.; Hou, L.; Liu, J.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Chen, J. The value of intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in the differential diagnosis of thyroid carcinoma and nodular goiter. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2022, 15, 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Bhargava, K.; Narula, H.; Mittal, A.; Sharma, D.; Goel, K.; Nijhawan, D. Role of Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Differentiating Benign From Malignant Thyroid Lesions: A Prospective Study. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2020, 14, TC1–TC4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, P.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Shi, J.; Hu, S. Multiplexed sensitivity-encoding versus single-shot echo-planar imaging: A comparative study for diffusion-weighted imaging of the thyroid lesions. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2024, 42, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Chen, J.; Huang, H.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J.; Lan, X.; Liu, D.; Zhang, J. Comparison of the Differential Diagnostic Performance of Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Imaging and Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging in Malignant and Benign Thyroid Nodules. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 895972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Li, Q.; Liu, W.; Wu, J.; Liu, D.; Zhang, J. rFOV-DWI and SMS-RESLOVE-DWI in patients with thyroid nodules: Comparison of image quality and apparent diffusion coefficient measurements. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2022, 91, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ning, H.; Zhang, X.; Lu, Y.; Shi, Q. Diagnostic value of high b-value (2000s/mm2) DWI for thyroid micronodules. Medicine 2019, 98, e14298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Liu, X.; Jiang, Q.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, J.; Wu, P.Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, J. Unenhanced magnetic resonance imaging of papillary thyroid carcinoma with emphasis on diffusion kurtosis imaging. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2023, 13, 2697–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.H.; Jin, Y.F.; Guo, J.S.; Zuo, L.; Xie, H.; Shi, K.; Yue, Y.L. Application of whole-lesion intravoxel incoherent motion analysis using iZOOM DWI to differentiate malignant from benign thyroid nodules. Acta Radiol. 2019, 60, 1127–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, M.A.; Rakhawy, M.M.E.; Saleh, M.F. Diagnostic accuracy of B-mode ultrasound, ultrasound elastography and diffusion weighted MRI in differentiation of thyroid nodules (prospective study). Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 2021, 52, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Zhao, P.; Lin, X.; Yu, T.; Diao, R.; Ning, G. T1 mapping and reduced field-of-view DWI at 3.0 T MRI for differentiation of thyroid papillary carcinoma from nodular goiter. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2023, 43, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.C.; Zhu, Z.F.; Tang, J.; Wen, X.W.; Fang, Y.; Han, J. Quantitative differentiation of malignant and benign thyroid nodules with multi-parameter diffusion-weighted imaging. World J. Clin. Cases 2022, 10, 8587–8598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Yue, X.; Ren, J.; Tao, X. A comparative analysis of diffusion-weighted imaging and ultrasound in thyroid nodules. BMC Med Imaging 2019, 19, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, T.; Xie, X.; Ni, Z.; Tang, L.; Wu, P.Y.; Song, B. Quantitative evaluation of diffusion-weighted MRI for differentiating benign and malignant thyroid nodules larger than 4 cm. BMC Med Imaging 2023, 23, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayraktaroglu, S.; Öztürk, P.K.; Ceylan, N.; Makay, O.; Icöz, G.; Ertan, Y. 3 tesla apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values of thyroid nodules: Prediction of benignancy and malignancy. Iran. J. Radiol. 2019, 16, e63974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özer, B.M.; Pabuscu, Y.; Tarhan, S.; Oval, G.Y.; Aydede, H.; Demireli, P.; Karadeniz, T. Effectiveness of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DW-MRI) in the differentiation of thyroid nodules. Thyroid Res. 2024, 17, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Alhamid, T.; Khafagy, A.G.; Sersy, H.A.; Askora, A.; Rabie, T.M.; Taha, M.S.; Ebrahim, A.; Sayed, H.M.E. Certainty of pretreatment apparent diffusion coefficient in the characterization of thyroid gland pathologies. Egypt. J. Otolaryngol. 2017, 33, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakahira, M.; Saito, N.; Murata, S.I.; Sugasawa, M.; Shimamura, Y.; Morita, K.; Takajyo, F.; Omura, G.; Matsumura, S. Quantitative diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging as a powerful adjunct to fine needle aspiration cytology for assessment of thyroid nodules. Am. J. Otolaryngol.—Head Neck Med. Surg. 2012, 33, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Pan, C.; Chen, W.W.; Li, T.; Zhu, W.Z.; Qi, J.P. Differentiation between malignant and benign thyroid nodules and stratification of papillary thyroid cancer with aggressive histological features: Whole-lesion diffusion-weighted imaging histogram analysis. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2016, 44, 1546–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, Y.; Kanematsu, M.; Goshima, S.; Kondo, H.; Watanabe, H.; Kawada, H.; Bae, K.T. MRI of the thyroid for differential diagnosis of benign thyroid nodules and papillary carcinomas. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2015, 204, W332–W335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghaghazvini, L.; Sharifian, H.; Yazdani, N.; Hosseiny, M.; Kooraki, S.; Pirouzi, P.; Ghadiri, A.; Shakiba, M.; Kooraki, S. Differentiation between benign and malignant thyroid nodules using diffusion-weighted imaging, a 3-T MRI study. Indian J. Radiol. Imaging 2018, 28, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.M.; Nagala, S.; McLean, M.A.; Lu, Y.; Scoffings, D.; Apte, A.; Gonen, M.; Stambuk, H.E.; Shaha, A.R.; Tuttle, R.M.; et al. Multi-institutional validation of a novel textural analysis tool for preoperative stratification of suspected thyroid tumors on diffusion-weighted MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2016, 75, 1708–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shi, L.; Ning, H.; Zhang, X.; Lu, Y. Utility of high b-value (2000 sec/mm2) DWI with RESOLVE in differentiating papillary thyroid carcinomas and papillary thyroid microcarcinomas from benign thyroid nodules. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wei, R.; Liu, W.; Chen, Y.; Song, B. Diagnostic efficacy of multiple MRI parameters in differentiating benign vs. malignant thyroid nodules. BMC Med. Imaging 2018, 18, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elshafey, R.; Elattar, A.; Mlees, M.; Esheba, N. Role of quantitative diffusion-weighted MRI and 1H MR spectroscopy in distinguishing between benign and malignant thyroid nodules. Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 2014, 45, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu, H.; Sivrioglu, A.K.; Sonmez, G.; Velioglu, M.; Sildiroglu, H.O.; Basekim, C.C.; Kizilkaya, E. Role of apparent diffusion coefficient values and diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in differentiation between benign and malignant thyroid nodules. Clin. Imaging 2012, 36, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razek, A.A.K.A.; Sadek, A.G.; Kombar, O.R.; Elmahdy, T.E.; Nada, N. Role of apparent diffusion coefficient values in differentiation between malignant and benign solitary thyroid nodules. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2008, 29, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Rahman, H.M.; Abowarda, M.H.; Abdel-Aal, S.M. Diffusion-weighted MRI and apparent diffusion coefficient in differentiation of benign from malignant solitary thyroid nodule. Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 2016, 47, 1385–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, T.F.T. Solitary thyroid nodule: Diagnostic yield of combined diffusion weighted imaging and magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 2017, 48, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, M.; Sumi, M.; Kaneko, K.I.; Ishimaru, K.; Takahashi, H.; Nakamura, T. Multiparametric MR imaging for differentiating between benign and malignant thyroid nodules: Initial experience in 23 patients. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2013, 38, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hariri, M.A.; Gouhar, G.K.; Said, N.S.; Riad, M.M. Role of diffusion-weighted imaging with ADC mapping and in vivo 1H-MR spectroscopy in thyroid nodules. Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 2012, 43, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Chen, J.; Tan, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, D.; Zhang, J. Comparative analysis of the image quality and diagnostic performance of the zooming technique with diffusion-weighted imaging using different b-values for thyroid papillary carcinomas and benign nodules. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1241776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yue, X.; Shen, W.; Du, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Tao, X.; Tang, C.Y. Diagnostic value of diffusion-weighted MR imaging in thyroid disease: Application in differentiating benign from malignant disease. BMC Med. Imaging 2013, 13, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekinci, O.; Boluk, S.E.; Eren, T.; Ozemir, I.A.; Boluk, S.; Salmaslioglu, A.; Leblebici, M.; Alimoglu, O. Utilidad de la resonancia magnética ponderada por difusión cervical en la detección del cáncer tiroideo. Cirugía Espa Nola 2018, 96, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.; Yue, Y.; Jin, Y.; Guo, J.; Zuo, L.; Peng, H.; Chan, Q. Intravoxel incoherent motion and ADC measurements for differentiating benign from malignant thyroid nodules: Utilizing the most repeatable region of interest delineation at 3.0 T. Cancer Imaging 2020, 20, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schueller-Weidekamm, C.; Kaserer, K.; Schueller, G.; Scheuba, C.; Ringl, H.; Weber, M.; Czerny, C.; Herneth, A. Can quantitative diffusion-weighted MR imaging differentiate benign and malignant cold thyroid nodules? Initial results in 25 patients. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2009, 30, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schueller-Weidekamm, C.; Schueller, G.; Kaserer, K.; Scheuba, C.; Ringl, H.; Weber, M.; Czerny, C.; Herneth, A.M. Diagnostic value of sonography, ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration cytology, and diffusion-weighted MRI in the characterization of cold thyroid nodules. Eur. J. Radiol. 2010, 73, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linh, L.T.; Cuong, N.N.; Hung, T.V.; Hieu, N.V.; Lenh, B.V.; Hue, N.D.; Pham, V.H.; Nga, V.T.; Chu, D.T. Value of diffusion weighted MRI with quantitative ADC map in diagnosis of malignant thyroid disease. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.; Lee, J.; Yoon, R.; Sung, T.Y.; Song, D.; Pfeuffer, J.; Kim, I. Differentiation of follicular carcinomas from adenomas using histogram obtained from diffusion-weighted MRI. Clin. Radiol. 2020, 75, 878.e13–878.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shayganfar, A.; Azin, N.; Hashemi, P.; Ghanei, A.M.; Hajiahmadi, S. Diagnostic accuracy of multiple MRI parameters in dealing with incidental thyroid nodules. SN Compr. Clin. Med. 2022, 4, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Dendukuri, N. Statistics for quantifying heterogeneity in univariate and bivariate meta-analyses of binary data: The case of meta-analyses of diagnostic accuracy. Stat. Med. 2014, 33, 2701–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iima, M.; Partridge, S.C.; Le Bihan, D. Six DWI questions you always wanted to know but were afraid to ask: Clinical relevance for breast diffusion MRI. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 2561–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikiforov, Y.E.; Seethala, R.R.; Tallini, G.; Baloch, Z.W.; Basolo, F.; Thompson, L.D.; Barletta, J.A.; Wenig, B.M.; Al Ghuzlan, A.; Kakudo, K.; et al. Nomenclature revision for encapsulated follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma: A paradigm shift to reduce overtreatment of indolent tumors. JAMA Oncol. 2016, 2, 1023–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, S.; Liu, C.H.; Bai, R.J. Value of diffusion weighted imaging in diagnosis of nodular lesions of thyroid: A preliminary study. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2010, 90, 3351–3354. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; QJ, L.W.; Liu, W. Application of MR diffusion weighted imaging in the differentiation of malignant from benign thyroid focal lesions. Radiol Pract. (China) 2009, 24, 719–722. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, B.; Liu, H.J.; Wang, C.B.; Li, M.; Min, Z.G.; Ma, S.H. ADC values in differentiation of benign and malignant thyroid nodules. Chin. J. Med. Imaging Technol. 2011, 27, 510–514. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, X.; Tao, X.; Gao, X. Application of diffusion-weighted MR imaging in the diagnosis of thyroid disease. Chin. J. Radiol. 2012, 12, 500–504. [Google Scholar]
- Aydın, H.; Kızılgöz, V.; Tatar, İ.; Damar, Ç.; Güzel, H.; Hekimoğlu, B.; Delibaşı, T. The role of proton MR spectroscopy and apparent diffusion coefficient values in the diagnosis of malignant thyroid nodules: Preliminary results. Clin. Imaging 2012, 36, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozgeyik, Z.; Coskun, S.; Dagli, A.F.; Ozkan, Y.; Sahpaz, F.; Ogur, E. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of thyroid nodules. Neuroradiology 2009, 51, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, G.; Erdem, T.; Muammer, H.; Mutlu, D.Y.; Fırat, A.K.; Sahin, I.; Alkan, A. Diffusion-weighted images differentiate benign from malignant thyroid nodules. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2010, 31, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilli, A.; Ayaz, U.Y.; Cakir, E.; Cakal, E.; Gultekin, S.S.; Hekimoglu, B. The efficacy of apparent diffusion coefficient value calculation in differentiation between malignant and benign thyroid nodules. Clin. Imaging 2012, 36, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Jiang, G.; Gao, P.; Li, G.; Nie, L.; Yan, J.; Jiang, M.; Duan, R.; Zhao, Y.; Luo, J.; et al. Non-invasive amide proton transfer imaging and ZOOM diffusion-weighted imaging in differentiating benign and malignant thyroid micronodules. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Chen, J.; Zhao, Y.L.; Liu, J.H.; Zhang, L.; Liu, C.S.; Huang, D. Feasibility of intravoxel incoherent motion for differentiating benign and malignant thyroid nodules. Acad. Radiol. 2019, 26, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Sun, Z.; Ge, Y.; Li, J.; Dou, W. Can diffusion-weighted MR imaging be used as a tool to predict extrathyroidal extension in papillary thyroid carcinoma? Acad. Radiol. 2021, 28, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schob, S.; Voigt, P.; Bure, L.; Meyer, H.J.; Wickenhauser, C.; Behrmann, C.; Höhn, A.; Kachel, P.; Dralle, H.; Hoffmann, K.T.; et al. Diffusion-weighted imaging using a readout-segmented, multishot EPI sequence at 3 T distinguishes between morphologically differentiated and undifferentiated subtypes of thyroid carcinoma—a preliminary study. Transl. Oncol. 2016, 9, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Yuan, Z.; Yang, C.; Zhang, J.; Liu, C.; Sun, J.; Ye, X. Role of multi-modality functional imaging in differentiation between benign and malignant thyroid 18 F-fluorodeoxyglucose incidentaloma. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2019, 21, 1561–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Noto, B.; Bobe, C.; Brandt, J.; Raum, H.N.; Nacul, N.G.; Riemann, B.; Helfen, A. Diagnostic Accuracy of Diffusion-Weighted MRI for Differentiating Benign and Malignant Thyroid Nodules: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2025, 17, 2677. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17162677
Noto B, Bobe C, Brandt J, Raum HN, Nacul NG, Riemann B, Helfen A. Diagnostic Accuracy of Diffusion-Weighted MRI for Differentiating Benign and Malignant Thyroid Nodules: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers. 2025; 17(16):2677. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17162677
Chicago/Turabian StyleNoto, Benjamin, Carolin Bobe, Jonas Brandt, Heiner N. Raum, Nabila Gala Nacul, Burkhard Riemann, and Anne Helfen. 2025. "Diagnostic Accuracy of Diffusion-Weighted MRI for Differentiating Benign and Malignant Thyroid Nodules: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Cancers 17, no. 16: 2677. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17162677
APA StyleNoto, B., Bobe, C., Brandt, J., Raum, H. N., Nacul, N. G., Riemann, B., & Helfen, A. (2025). Diagnostic Accuracy of Diffusion-Weighted MRI for Differentiating Benign and Malignant Thyroid Nodules: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers, 17(16), 2677. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17162677






