- Article
Task-Adaptive and Multi-Level Contextual Understanding for Emotion Recognition in Conversations
- Xiaomeng Yao,
- Wei Cao and
- Xiaochao Fan
- + 2 authors
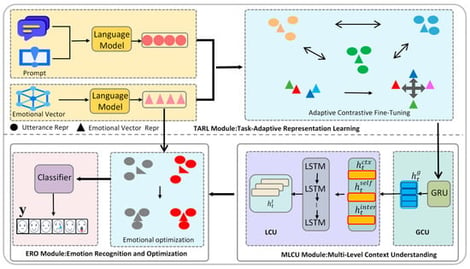
Emotion recognition in conversations (ERC) is a significant task in natural language processing, aimed at identifying the emotion of each utterance within a conversation. Current research predominantly relies on pre-trained language models, often incorporating sophisticated network architectures to capture complex contextual semantics in conversations. However, existing approaches have not successfully combined effective task-specific adaptation with adequate modeling of conversational context complexity. To address this, we propose a model named TAMC-ERC (Task-Adaptive and Multi-level Contextual Understanding for Emotion Recognition in Conversations). The model adopts a progressive recognition framework that sequentially builds on foundational utterance representations, integrates conversation-level contexts, and leads to a task-adaptive classification decision. First, the Task-Adaptive Representation Learning module produces highly discriminative utterance representations. It achieves this by integrating emotion space information into prompts and employing contrastive learning. Subsequently, the Multi-Level Contextual Understanding module performs in-depth modeling of the conversational context. It synergistically integrates both macroscopic narratives and microscopic interactions to construct a comprehensive emotional context. Finally, the classifier is directly parameterized by the emotion concept vectors from the task-adaptive stage. This creates a coherent task adaptation process, maintaining task-specific awareness from representation learning through to the final decision. Experiments on three benchmark datasets demonstrate that TAMC-ERC achieves highly competitive performance: it attains weighted average F1 scores of 71.04% on IEMOCAP, 66.95% on MELD, and 40.99% on EmoryNLP. These results set a new state of the art and demonstrate that the model outperforms most existing baselines. This work validates that integrating task adaptation with multi-level contextual modeling is key to addressing conversational complexity and improving recognition accuracy.
9 February 2026