- Review
CNS-Specific and Coagulation Biomarkers in Traumatic Brain Injury: Beyond the Reach of the Scalpel—A Scoping Review
- Serban Iancu Papacocea,
- Ioana Anca Bădărău and
- Toma Marius Papacocea
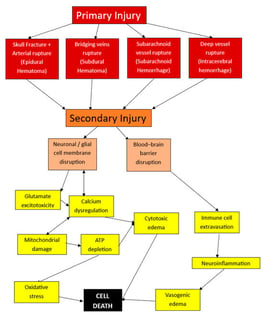
Despite significant advances in neurosurgical and critical care, traumatic brain injury (TBI) remains a major cause of morbidity and mortality. Surgical treatment of intracranial hemorrhagic lesions can only target the primary mechanical injuries and their immediate consequences but fails to address the biochemical pathological cascade that unfolds during the second injury. This review synthesizes current knowledge regarding the use of several biomarkers in diagnosis and prognosis assessment. A structured literature search was conducted by querying the PubMed database. Articles evaluating diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in adult TBI were screened according to Prisma guidelines, and data regarding biomarkers type, cut-off values, and correlations with the outcome were extracted and summarized. Among Central Nervous System (CNS)-Specific markers, S100 calcium-binding protein (S100B) emerged as a remarkably strong negative predictor for Computed Tomography (CT)-visible intracranial lesions (NPV = 97.3–100%), whereas glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) yielded both high NPV and brain specificity. Coagulation parameters such as the international normalized ratio (INR) and fibrinogen were independently correlated with mortality and unfavorable outcomes. Fibrinogen displayed a bidirectional relationship with increased mortality risk at both low (<2 g/L) and high (>4.5 g/L) values. In conclusion, biomarkers quantify the otherwise invisible progression of secondary traumatic brain injury that persists even after successful surgery.
5 February 2026



![Sample processing. (1) Specimen selection, (2) root length measurement, (3) working groups, (4,5) sample processing (hydrochloric acid, aceto-orcine + acetic acid [45%]), (6) squash, and (7) microscopic analysis. Created in BioRender. Delgado, D. (2025) https://BioRender.com/6m8c9ch (accessed on 9 January 2026).](https://mdpi-res.com/cdn-cgi/image/w=281,h=192/https://mdpi-res.com/applbiosci/applbiosci-05-00009/article_deploy/html/images/applbiosci-05-00009-g001-550.jpg)