- Article
Nondestructive Detection of Early Subsurface Bruises in Fragrant Pears Using Structured-Illumination Reflectance Imaging and Mask R-CNN
- Baishao Zhan,
- Zhangwei Guo and
- Hailiang Zhang
- + 3 authors
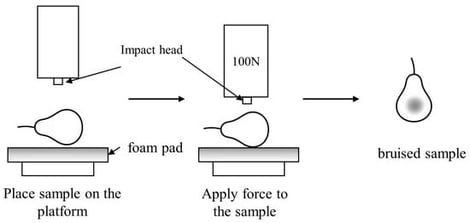
To achieve accurate identification of early subcutaneous bruising regions in fragrant pears, this study developed a detection system based on Structured-Illumination Reflectance Imaging (SIRI) and integrated it with both machine learning and deep learning models. Structured-illumination images were acquired at six spatial frequencies (50, 100, 150, 200, 250, and 300 cycle·m−1) and evaluated after demodulation through both visual assessment and contrast index (CI) analysis. The optimal spatial frequency of 150 cycle·m−1 was selected for subsequent analysis. Texture features were extracted from AC, DC, and RT images based on the gray-level co-occurrence matrix (GLCM), and classification was performed using three machine learning models KNN, PLS-DA, LightGBM and the deep learning Mask R-CNN model. The results showed that the classification performance of RT images was superior to that of AC and DC images. Among them, the PLS-DA model achieved an accuracy of 95.00% on the test set for RT images. The Mask R-CNN model achieved a recognition accuracy of 99.17% on the RT image test set. These results demonstrate that the combination of SIRI and deep learning enables highly sensitive and nondestructive detection of early subcutaneous bruising in Korla pears, providing an efficient and reliable technical approach for fruit quality grading and postharvest intelligent inspection.
6 February 2026