Journal Description
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal of electronic commerce, published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SSCI (Web of Science), dblp, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q1 (Business) / CiteScore - Q1 (General Business, Management and Accounting )
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 34 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 5.1 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2024).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
Impact Factor:
5.1 (2023);
5-Year Impact Factor:
5.1 (2023)
Latest Articles
Transparency as a Trust Catalyst: How Self-Disclosure Strategies Reshape Consumer Perceptions of Unhealthy Food Brands on Digital Platforms
J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2025, 20(2), 133; https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer20020133 - 6 Jun 2025
Abstract
Digital food-ordering apps make it simple to buy indulgent drinks yet hard to judge their health risks. We conducted five online experiments (N = 1048) to compare two messages for sugary beverages: self-promotion that stresses taste and self-disclosure that plainly warns “high sugar/high
[...] Read more.
Digital food-ordering apps make it simple to buy indulgent drinks yet hard to judge their health risks. We conducted five online experiments (N = 1048) to compare two messages for sugary beverages: self-promotion that stresses taste and self-disclosure that plainly warns “high sugar/high calories”. Brands that chose self-disclosure were seen as more socially responsible and transparent, which in turn raised trust and lifted purchase intent. These gains were strongest for users who care deeply about the category or the brand and remained robust even among highly health-conscious shoppers. The results show that, for “vice” foods, honest warnings can outperform glossy claims. Our study extends signaling and attribution theories to digital food markets and offers managers a straightforward playbook for complying with new labeling rules while still driving sales.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Digital Marketing Dynamics: From Browsing to Buying)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Modeling Mobile Game Design Features Through Grounded Theory: Key Factors Influencing User Behavior
by
Chang Ma and Jingbo Shao
J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2025, 20(2), 132; https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer20020132 - 5 Jun 2025
Abstract
The mobile gaming industry has undergone remarkable expansion alongside advancements in mobile and information technologies. Facing intensified market competition due to user number saturation and product homogeneity, industry practitioners require actionable insights into design features that drive user engagement and in-game payments. This
[...] Read more.
The mobile gaming industry has undergone remarkable expansion alongside advancements in mobile and information technologies. Facing intensified market competition due to user number saturation and product homogeneity, industry practitioners require actionable insights into design features that drive user engagement and in-game payments. This study employs a qualitative research approach based on grounded theory, focusing on role-playing mobile games as the research subject. Primary data were collected through in-depth interviews and focus groups with gaming industry professionals and users, supplemented by online textual data collection. Utilizing the three-stage coding paradigm of grounded theory and drawing upon emotional design theory, this study constructs a dimensional model of mobile game design features comprising 4 major categories, 16 primary design characteristics, and 41 specific design elements. The findings provide theoretical support for understanding how mobile game design features influence user behaviors while offering practical insights for optimizing mobile game products. This research contributes to both academic discourse and industrial practice by systematically identifying and categorizing critical design elements that affect user engagement in mobile games.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Digital Marketing and the Connected Consumer)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Enterprise Digital Transformation Drivers: Market or Government? A Case Study from China
by
Tinghui Li, Linteng Ni and Yanting Xu
J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2025, 20(2), 131; https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer20020131 - 3 Jun 2025
Abstract
The relative dominance of government and market forces in enterprise digital transformation remains underexplored. This paper aims to provide new insights into this topic. Using data from China’s A-share-listed companies (2007–2023), we test the short- and long-term impacts of government subsidies and market
[...] Read more.
The relative dominance of government and market forces in enterprise digital transformation remains underexplored. This paper aims to provide new insights into this topic. Using data from China’s A-share-listed companies (2007–2023), we test the short- and long-term impacts of government subsidies and market strength on enterprise digital transformation, quantify their relative contributions, explore substitution effects, investigate synergistic interactions, and examine heterogeneous impacts across different enterprise ownership types and life cycle stages, using the fixed effects regression model, exponential smoothing, interaction term, coupling coordination model, and group regression. The results indicate that both government subsidies and market forces drive digital transformation in enterprises, with government subsidies having a slightly stronger effect. There is a substitutive relationship between the two, and their synergy significantly promotes digital transformation. However, their impact varies across different types of enterprises. Stronger market forces do not always lead to greater transformation; in fact, for non-state-owned enterprises, market strength can hinder digital transformation. Similarly, government subsidies do not consistently promote digital transformation. Their effect is less pronounced for growth and maturity-stage enterprises, while declining enterprises are more motivated to pursue digital transformation to benefit from subsidies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Digital Business Organization)
Open AccessArticle
Concrete or Abstract? The Impact of Green Advertising Appeals and Information Framing on Consumer Responses
by
Jiahong Yu, Xixiang Sun, Ying Huang and Yige Jia
J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2025, 20(2), 130; https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer20020130 - 3 Jun 2025
Abstract
Green advertising messages often face challenges of abstraction and outcome ambiguity. To address this, we apply the framing effect theory to explore how concrete versus abstract expressions in green advertising interact with consumer perceptions. Drawing on the Stereotype Content Model (SCM), we propose
[...] Read more.
Green advertising messages often face challenges of abstraction and outcome ambiguity. To address this, we apply the framing effect theory to explore how concrete versus abstract expressions in green advertising interact with consumer perceptions. Drawing on the Stereotype Content Model (SCM), we propose a congruence framework: concrete messages align with competence appeals, while abstract messages align with warmth appeals. Through two experiments, we demonstrate that such congruence significantly enhances green purchase intention. Experiment 1 establishes the interaction effect between message framing (concrete vs. abstract) and appeal type (competence vs. warmth), revealing that concrete–competence and abstract–warmth pairings outperform mismatched conditions. Experiment 2 further validates advertising attitudes as a mediator and product involvement as a moderator, clarifying boundary conditions. These findings advance the theoretical understanding of framing effects in sustainability communication and offer actionable strategies for marketers: aligning message specificity (concrete/abstract) with appeal dimensions (competence/warmth) can amplify consumer engagement, particularly when tailored to product contexts.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Digital Marketing and the Connected Consumer)
►▼
Show Figures
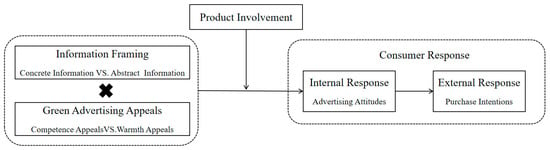
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Customer-Centric Decision-Making with XAI and Counterfactual Explanations for Churn Mitigation
by
Simona-Vasilica Oprea and Adela Bâra
J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2025, 20(2), 129; https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer20020129 - 3 Jun 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In this paper, we propose a methodology designed to deliver actionable insights that help businesses retain customers. While Machine Learning (ML) techniques predict whether a customer is likely to churn, this alone is not enough. Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) methods, such as SHapley
[...] Read more.
In this paper, we propose a methodology designed to deliver actionable insights that help businesses retain customers. While Machine Learning (ML) techniques predict whether a customer is likely to churn, this alone is not enough. Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) methods, such as SHapley Additive Explanations (SHAP) and Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations (LIME), highlight the features influencing the prediction, but businesses need strategies to prevent churn. Counterfactual (CF) explanations bridge this gap by identifying the minimal changes in the business–customer relationship that could shift an outcome from churn to retention, offering steps to enhance customer loyalty and reduce losses to competitors. These explanations might not fully align with business constraints; however, alternative scenarios can be developed to achieve the same objective. Among the six classifiers used to detect churn cases, the Balanced Random Forest classifier was selected for its superior performance, achieving the highest recall score of 0.72. After classification, Diverse Counterfactual Explanations with ML (DiCEML) through Mixed-Integer Linear Programming (MILP) is applied to obtain the required changes in the features, as well as in the range permitted by the business itself. We further apply DiCEML to uncover potential biases within the model, calculating the disparate impact of some features.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Measuring Consumer Experience in Community Unmanned Stores: Development of the ECUS-Scale for Omnichannel Digital Retail
by
Weizhuan Hu, Linghao Zhang, Yilin Wang and Jianbin Wu
J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2025, 20(2), 128; https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer20020128 - 3 Jun 2025
Abstract
As consumer behavior increasingly shifts toward hyperlocal, digitally mediated retail journeys, community unmanned stores have emerged as a transformative model that integrates smart technologies with community proximity services. These fully automated stores offer convenient, contactless shopping and hybrid digital–physical interactions, playing an increasingly
[...] Read more.
As consumer behavior increasingly shifts toward hyperlocal, digitally mediated retail journeys, community unmanned stores have emerged as a transformative model that integrates smart technologies with community proximity services. These fully automated stores offer convenient, contactless shopping and hybrid digital–physical interactions, playing an increasingly important role within broader omnichannel digital retail ecosystems. However, there remains a lack of validated instruments to assess customer experience in such autonomous and locally embedded retail formats. This study develops and validates an ECUS-scale (an experience in community unmanned store scale), a multidimensional measurement tool grounded in qualitative research and refined through exploratory and confirmatory factor analysis. The scale identifies nine key dimensions—convenient service, smooth transaction, preferential price, good quality, safe environment, secure payment, comfortable space, comfortable interaction, and friendly image—across 36 items. These dimensions reflect the technological, spatial, and emotional–social aspects of customer experience in unmanned retail settings. The findings demonstrate that the ECUS-scale offers a robust framework for evaluating consumer experience in low-staffed, tech-enabled community stores, with strong relevance to omnichannel digital retail strategies. Theoretically, it advances the literature on smart retail experience by capturing underexplored dimensions such as emotional engagement with technology and perceptions of safety in staff-free environments. Practically, it serves as a diagnostic tool for businesses to enhance experience design and optimize customer engagement across digital and physical touchpoints.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Digital Marketing Dynamics: From Browsing to Buying)
Open AccessArticle
Quality Information Disclosure and Blockchain Technology Adoption of Competitive Suppliers on the Third-Party E-Commerce Platform
by
Shengming Zhang, Xumei Zhang, Bo Wang and Bin Dan
J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2025, 20(2), 127; https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer20020127 - 3 Jun 2025
Abstract
This study investigates the quality information disclosure and blockchain technology adoption strategies of suppliers on a third-party e-commerce platform. Based on a Stackelberg game model, the impacts of blockchain technology adoption on the quality information disclosure decision and profit of the third-party e-commerce
[...] Read more.
This study investigates the quality information disclosure and blockchain technology adoption strategies of suppliers on a third-party e-commerce platform. Based on a Stackelberg game model, the impacts of blockchain technology adoption on the quality information disclosure decision and profit of the third-party e-commerce platform and suppliers are explored. The results indicate that whether blockchain adoption benefits suppliers depends on the unit blockchain cost and the reliability of quality information. Counterintuitively, higher information reliability may disadvantage suppliers under certain conditions. With the increase in unit blockchain cost, the incentive of suppliers to adopt blockchain is weakened, and suppliers need to adjust their strategies of quality information disclosure according to the adoption situation and the cost of blockchain. Adopting blockchain technology may be unfavorable to the suppliers but beneficial to the third-party e-commerce platform; the platform can incentivize suppliers to adopt blockchain and achieve a win-win situation. These findings provide some valuable managerial implications for the quality information disclosure decision of suppliers and blockchain adoption in the e-commerce platform supply chain.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Blockchain Business Applications and the Metaverse)
►▼
Show Figures
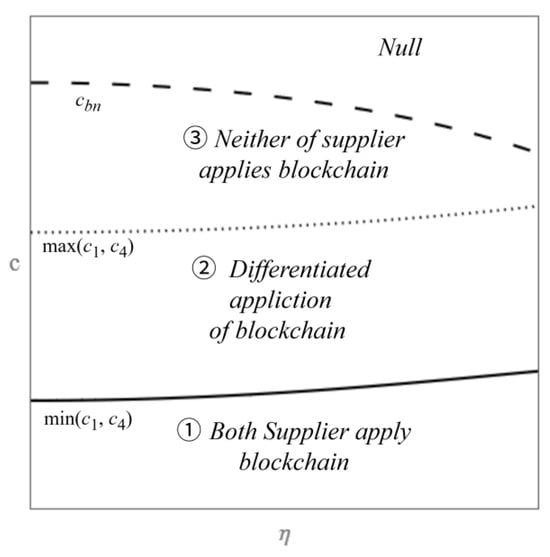
Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Creating Value in Metaverse-Driven Global Value Chains: Blockchain Integration and the Evolution of International Business
by
Sina Mirzaye Shirkoohi and Muhammad Mohiuddin
J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2025, 20(2), 126; https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer20020126 - 2 Jun 2025
Abstract
The convergence of blockchain and metaverse technologies is poised to redefine how Global Value Chains (GVCs) create, capture, and distribute value, yet scholarly insight into their joint impact remains scattered. Addressing this gap, the present study aims to clarify where, how, and under
[...] Read more.
The convergence of blockchain and metaverse technologies is poised to redefine how Global Value Chains (GVCs) create, capture, and distribute value, yet scholarly insight into their joint impact remains scattered. Addressing this gap, the present study aims to clarify where, how, and under what conditions blockchain-enabled transparency and metaverse-enabled immersion enhance GVC performance. A systematic literature review (SLR), conducted according to PRISMA 2020 guidelines, screened 300 articles from ABI Global, Business Source Premier, and Web of Science records, yielding 65 peer-reviewed articles for in-depth analysis. The corpus was coded thematically and mapped against three theoretical lenses: transaction cost theory, resource-based view, and network/ecosystem perspectives. Key findings reveal the following: 1. digital twins anchored in immersive platforms reduce planning cycles by up to 30% and enable real-time, cross-border supply chain reconfiguration; 2. tokenized assets, micro-transactions, and decentralized finance (DeFi) are spawning new revenue models but simultaneously shift tax triggers and compliance burdens; 3. cross-chain protocols are critical for scalable trust, yet regulatory fragmentation—exemplified by divergent EU, U.S., and APAC rules—creates non-trivial coordination costs; and 4. traditional IB theories require extension to account for digital-capability orchestration, emerging cost centers (licensing, reserve backing, data audits), and metaverse-driven network effects. Based on these insights, this study recommends that managers adopt phased licensing and geo-aware tax engines, embed region-specific compliance flags in smart-contract metadata, and pilot digital-twin initiatives in sandbox-friendly jurisdictions. Policymakers are urged to accelerate work on interoperability and reporting standards to prevent systemic bottlenecks. Finally, researchers should pursue multi-case and longitudinal studies measuring the financial and ESG outcomes of integrated blockchain–metaverse deployments. By synthesizing disparate streams and articulating a forward agenda, this review provides a conceptual bridge for international business scholarship and a practical roadmap for firms navigating the next wave of digital GVC transformation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Entrepreneurship, Innovation, FinTech Accounting and Industry 4.0)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Text Mining for Consumers’ Sentiment Tendency and Strategies for Promoting Cross-Border E-Commerce Marketing Using Consumers’ Online Review Data
by
Changting Liu, Tao Chen, Qiang Pu and Ying Jin
J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2025, 20(2), 125; https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer20020125 - 2 Jun 2025
Abstract
With the rapid advancement of information technology and the increasing maturity of online shopping platforms, cross-border shopping has experienced rapid growth. Online consumer reviews, as an essential part of the online shopping process, have become a vital way for merchants to obtain user
[...] Read more.
With the rapid advancement of information technology and the increasing maturity of online shopping platforms, cross-border shopping has experienced rapid growth. Online consumer reviews, as an essential part of the online shopping process, have become a vital way for merchants to obtain user feedback and gain insights into market demands. The research employs Python tools (Jupyter Notebook 7.0.8) to analyze the 14,078 pieces of review text data from the top four best-selling products in a certain product category on a certain cross-border e-commerce platform. By applying social network analysis, constructing LDA (Latent Dirichlet Allocation) topic models, and establishing LSTM (Long Short-Term Memory) sentiment classification models, the topics and sentiment distribution of the review set are obtained, and the evolution trends of topics and sentiments are analyzed according to different periods. The research finds that in the overall review set, consumers’ focus is concentrated on five aspects: functional features, quality and cost-effectiveness, usage effectiveness, post-purchase support, and design and assembly. In terms of changes in review sentiments, the negative proportion of the topics of functional features and usage effects is still relatively high. Given the above, this study integrates the 4P and 4C theories to propose strategies for enhancing the marketing capabilities of cross-border e-commerce in the context of digital cross-border operations, providing theoretical and practical marketing insights for cross-border e-commerce enterprises.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Human–Technology Synergies in AI-Driven E-Commerce Environments)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Prediction and Optimization for Multi-Product Marketing Resource Allocation in Cross-Border E-Commerce
by
Yi Xie, Heng-Qing Ye and Wenbin Zhu
J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2025, 20(2), 124; https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer20020124 - 2 Jun 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In cross-border e-commerce, effective marketing resource allocation is crucial due to the complexity introduced by diverse product categories, regional differences, and competition among category managers. Current methods either overlook these constraints or fail to enforce them efficiently due to computational challenges. We propose
[...] Read more.
In cross-border e-commerce, effective marketing resource allocation is crucial due to the complexity introduced by diverse product categories, regional differences, and competition among category managers. Current methods either overlook these constraints or fail to enforce them efficiently due to computational challenges. We propose a two-stage optimization framework that integrates predictive models with constrained optimization. In the first stage, predictive models estimate user purchase probabilities and determine upper bounds on product-specific sending volumes. In the second stage, the resource allocation problem is formulated as a large-scale integer programming model, which is then transformed into a minimum-cost flow problem to ensure computational efficiency while preserving solution optimality. Experiments on real-world data show that our framework significantly outperforms baseline strategies, achieving a 14.48% increase in order volume and revenue improvements ranging from 0.19% to 43.91%. The minimum-cost flow algorithm consistently outperforms the greedy approach, especially in large-scale instances. The proposed framework enables scalable and constraint-compliant marketing resource allocation in cross-border e-commerce. It not only improves sales performance but also ensures strict adherence to operational constraints, making it well-suited for large-scale commercial deployment.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Locational Drivers of China’s Digital Creative Industries: Unveiling Regional Concentration and Sectoral Differences
by
Xiaoyi Luo, Ni Gao and Xiaoming Yuan
J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2025, 20(2), 123; https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer20020123 - 1 Jun 2025
Abstract
The digital creative industry (DCI) has become an integral part of China’s strategic emerging industries. This paper, utilizing county-level data from Chinese digital creative enterprises in 2022, examines the locational factors influencing the spatial distribution of China’s DCI through Principal Component Analysis and
[...] Read more.
The digital creative industry (DCI) has become an integral part of China’s strategic emerging industries. This paper, utilizing county-level data from Chinese digital creative enterprises in 2022, examines the locational factors influencing the spatial distribution of China’s DCI through Principal Component Analysis and Multiple Linear Regression Analysis. The findings indicate that technological innovation and the level of economic development universally and dominantly influence the agglomeration of all DCI sub-sectors. Service-oriented digital creative enterprises are more likely to cluster in areas with abundant cultural resources and public facilities, with government policies and financial subsidies playing a significant role. In contrast, digital creative equipment manufacturing companies are more likely to locate in proximity to market demand and related industries.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Exploring the Future of Creative Economy: Transforming Creative Industries through Innovation, Technology and Enhanced Consumer Engagement)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Reducing the Hypothetical Bias in Measuring Willingness to Pay for Mobile Communication Products
by
Jasmin Ebert, Peter Winzer and Carina Müller
J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2025, 20(2), 122; https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer20020122 - 1 Jun 2025
Abstract
Willingness to pay (WTP) measurements often contain a hypothetical bias (HB) when participants’ responses result from ‘fictitious’ survey scenarios rather than actual purchasing behavior or field studies. This discrepancy usually leads to inaccurate WTP values, which affect pricing strategies. Our quantitative online survey
[...] Read more.
Willingness to pay (WTP) measurements often contain a hypothetical bias (HB) when participants’ responses result from ‘fictitious’ survey scenarios rather than actual purchasing behavior or field studies. This discrepancy usually leads to inaccurate WTP values, which affect pricing strategies. Our quantitative online survey with German consumers (N = 215) examines the HB of WTP for different mobile phone plans as an example of a widespread consumer good. The aim is to focus on the correlation between hypothetical and actual WTP and the influence of socio-demographic factors on the HB. We used the Certainty Approach to correct hypothetical WTP data to reflect actual payment behavior. The findings show that hypothetical WTP values are generally higher than current expenditure, which demonstrates that HB significantly affects WTP measurements in the context of mobile communications products. The applied Certainty Approach successfully reduced this discrepancy. We found a moderate negative correlation between actual WTP and the extent of the HB, indicating that higher actual WTP is associated with lower bias. Moreover, socio-demographic factors such as age and income do not significantly influence the HB. This study suggests pricing strategies should consider HB-adjusted WTP values to avoid management decisions based on inflated hypothetical data.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Emerging Trends and Innovations in Electronic and Mobile Business: Navigating New Frontiers in E-commerce and Beyond)
►▼
Show Figures
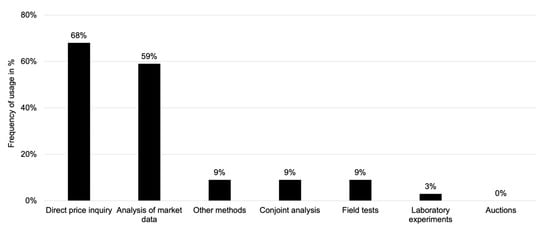
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Robust AI for Financial Fraud Detection in the GCC: A Hybrid Framework for Imbalance, Drift, and Adversarial Threats
by
Khaleel Ibrahim Al-Daoud and Ibrahim A. Abu-AlSondos
J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2025, 20(2), 121; https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer20020121 - 1 Jun 2025
Abstract
The rising complexity of financial fraud in highly digitalized regions such as the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) poses challenging issues owing to class imbalance, adversarial attacks, concept drift, and explainability requirements. This paper suggests a hybrid machine-learning framework (HMLF) that incorporates SMOTEBoost and
[...] Read more.
The rising complexity of financial fraud in highly digitalized regions such as the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) poses challenging issues owing to class imbalance, adversarial attacks, concept drift, and explainability requirements. This paper suggests a hybrid machine-learning framework (HMLF) that incorporates SMOTEBoost and cost-sensitive learning to address imbalances, adversarial training and FraudGAN to ensure robustness, DDM and ADWIN to achieve adaptive learning, and SHAP, LIME, and human-in-the-loop (HITL) analysis to ensure explainability. Employing real transaction data from the GCC banks, the framework is tested through a design science research approach. Experiments illustrate significant gains in fraud recall (from 35% to 85%), adversarial robustness (attack success rate decreased from 35% to 5%), and drift recovery (within 24 h), while retaining operational latency below 150 milliseconds. This paper substantiates that incorporating technical resilience with institutional constraints offers an auditable, scalable, and regulation-compliant solution for detecting fraud in high-risk financial contexts.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Artificial Intelligence Applications in Financial Technology, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures
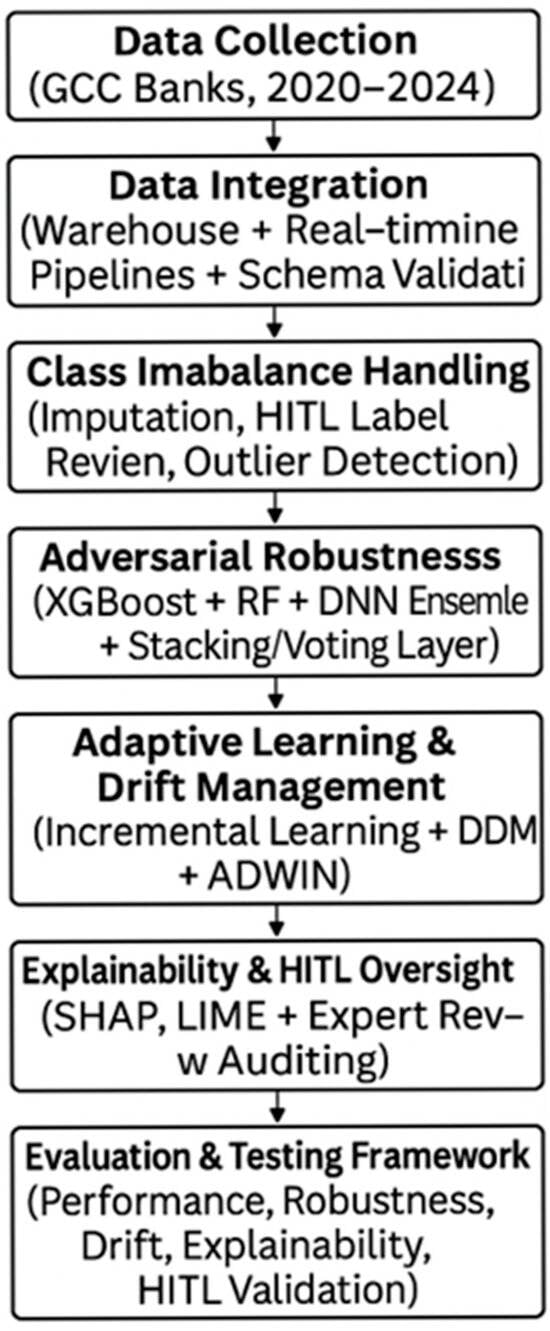
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Risk Assessment of Live-Streaming Marketing Based on Hesitant Fuzzy Multi-Attribute Group Decision-Making Method
by
Changlu Zhang, Yuchen Wang and Jian Zhang
J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2025, 20(2), 120; https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer20020120 - 1 Jun 2025
Abstract
(1) Background: With the deep integration of e-commerce and video technology, live-streaming marketing has emerged globally and maintained rapid growth. However, most of the current research on live-streaming e-commerce marketing focuses on merchants’ sales strategies and consumers’ purchase intentions, and there is relatively
[...] Read more.
(1) Background: With the deep integration of e-commerce and video technology, live-streaming marketing has emerged globally and maintained rapid growth. However, most of the current research on live-streaming e-commerce marketing focuses on merchants’ sales strategies and consumers’ purchase intentions, and there is relatively little research related to the risks of live-streaming e-commerce marketing. Nevertheless, with the development of live-streaming e-commerce marketing and its integration with technologies such as artificial intelligence and virtual reality (VR), live-streaming e-commerce marketing still faces challenges such as unclear subject responsibility, difficulty in verifying the authenticity of marketing information, and uneven product quality. It also harbors problems such as the ethical misbehavior of AI anchors and the excessive beautification of products by VR technology. (2) Methods: This study systematically analyzes the scenarios of live-streaming marketing to elucidate the mechanisms of risk formation. Utilizing fault tree analysis (FTA) and risk checklist methods, risks are identified based on the three core elements of live-streaming marketing: “people–products–scenes”. Subsequently, the Delphi method is employed to refine the initial risk indicator system, resulting in the construction of a comprehensive risk indicator system comprising three first-level indicators, six second-level indicators, and 16 third-level indicators. A hesitant fuzzy multi-attribute group decision-making method (HFMGDM) is then applied to calculate the weights of the risk indicators and comprehensively assess the live-streaming marketing risks in live broadcast rooms of three prominent celebrity anchors in China. Furthermore, a detailed analysis is conducted on the risks associated with the six secondary indicators. Based on the risk evaluation results, targeted recommendations are proposed. This study aims to enhance consumers’ awareness of risk prevention when conducting live-streaming transactions and pay attention to related risks, thereby safeguarding consumer rights and fostering the healthy and sustainable development of the live-streaming marketing industry. (3) Conclusions: The results show that the top five risk indicators in terms of weight ranking are: Ethical Risk of the AI Anchor (A4), VR Technology Promotion Risk (F3), Anchor Reputation (A1), Product Quality (D1), and Logistics Distribution Service Quality (D2). The comprehensive live-streaming marketing risk of each live broadcast room is Y > L > D. Based on the analysis results, targeted recommendations are provided for anchors, MCN institutions, merchants, supply chains, and live-streaming platforms to improve consumer satisfaction and promote sustainable development of the live-streaming marketing industry.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Emerging Technologies and Marketing Innovation)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Examining Readiness to Buy Fashion Products Authenticated with Blockchain
by
Danica Sovtić, Aleksandra Trpkov, Miloš Radenković, Snežana Popović and Aleksandra Labus
J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2025, 20(2), 119; https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer20020119 - 1 Jun 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The fashion industry is undergoing significant transformation through blockchain technology, which enhances product traceability, authenticity, and transactional transparency. This study explores blockchain’s potential to revolutionize the fashion supply chain by enabling detailed monitoring from design and manufacturing to certification, quality control, storage, transportation,
[...] Read more.
The fashion industry is undergoing significant transformation through blockchain technology, which enhances product traceability, authenticity, and transactional transparency. This study explores blockchain’s potential to revolutionize the fashion supply chain by enabling detailed monitoring from design and manufacturing to certification, quality control, storage, transportation, and delivery. To assess customers’ readiness to adopt these authenticated products, an innovative model for fashion product traceability and authenticity based on blockchain was proposed. Since the adoption of blockchain models relies on widespread user involvement, it is crucial to examine the factors that motivate individuals to take part. To this end, an acceptance study was conducted using the modified UTAUT2 (Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology) framework, with data analyzed using SMART PLS software. The results indicate that the proposed blockchain model can improve transparency, authenticity, and customer trust in fashion products. Furthermore, the findings identify expected effort, perceived efficiency, and social influence as key factors influencing blockchain adoption in the fashion industry. These insights show the importance of targeted education and customer engagement strategies for successful implementations of blockchain technology in the fashion industry.
Full article
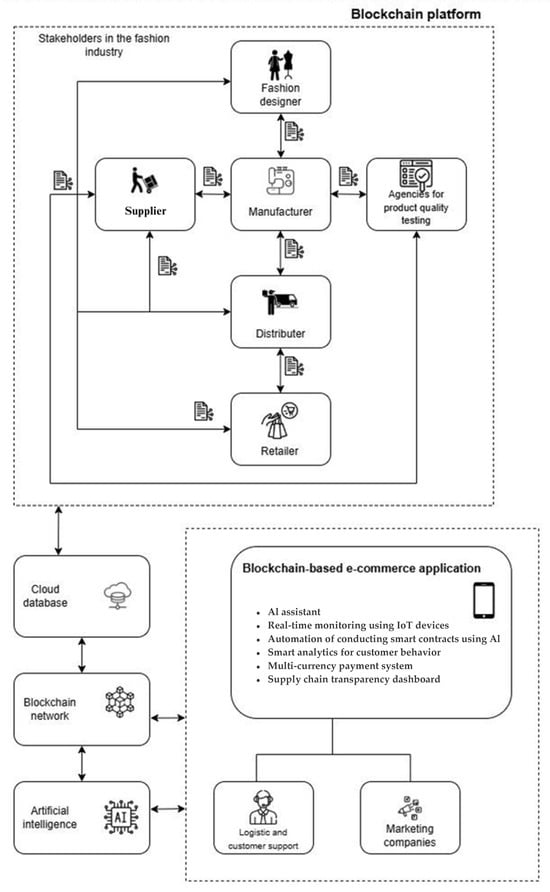
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Navigating the Future: Envisioning Metaverse Adoption in Indonesian Tourism Through the Technological–Organizational–Environmental (TOE) Framework
by
Afrizal Firman, Ka Yin Chau, Ankita Manohar Walawalkar and Massoud Moslehpour
J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2025, 20(2), 118; https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer20020118 - 30 May 2025
Abstract
This study explores the factors influencing the adoption of Metaverse technology in the Indonesian tourism sector through the lens of the Technological–Organizational–Environmental (TOE) framework. Data collected from 303 respondents representing academia, government, and industry were analyzed using Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) with SmartPLS
[...] Read more.
This study explores the factors influencing the adoption of Metaverse technology in the Indonesian tourism sector through the lens of the Technological–Organizational–Environmental (TOE) framework. Data collected from 303 respondents representing academia, government, and industry were analyzed using Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) with SmartPLS 4. The findings reveal that relative advantage, compatibility, top management support, government policy and regulation, and competitive pressure significantly influence the intention to adopt Metaverse technology, while complexity does not. Notably, competitive pressure emerged as the most critical factor, especially among university and government respondents. The study provides theoretical insights into technology adoption and practical recommendations for fostering Metaverse integration in tourism. Despite its contributions, limitations such as sample composition and excluded TOE variables suggest avenues for future research. This work underscores the importance of strategic collaboration among academia, government, and industry to enhance Metaverse adoption in the tourism industry, paving the way for innovation and competitive advantage.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Blockchain Business Applications and the Metaverse)
►▼
Show Figures
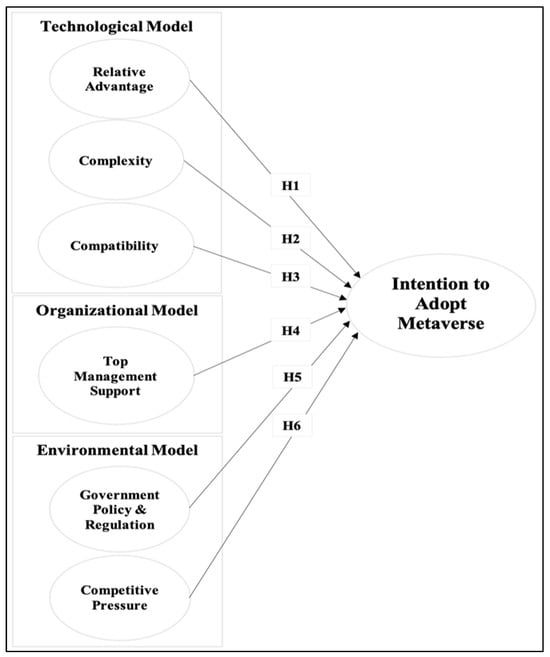
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Predicting Mobile Payment Behavior Through Explainable Machine Learning and Application Usage Analysis
by
Myounggu Lee, Insu Choi and Woo-Chang Kim
J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2025, 20(2), 117; https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer20020117 - 30 May 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In the increasingly competitive mobile ecosystem, understanding user behavior is essential to improve targeted sales and the effectiveness of advertising. With the widespread adoption of smartphones and the increasing variety of mobile applications, predicting user behavior has become more complex. This study presents
[...] Read more.
In the increasingly competitive mobile ecosystem, understanding user behavior is essential to improve targeted sales and the effectiveness of advertising. With the widespread adoption of smartphones and the increasing variety of mobile applications, predicting user behavior has become more complex. This study presents a comprehensive framework for predicting mobile payment behavior by integrating demographic, situational, and behavioral factors, focusing on patterns in mobile application usage. To address the complexity of the data, we use a combination of machine-learning models, including extreme gradient boosting, light gradient boosting machine, and CatBoost, along with Shapley additive explanations (SHAP) to improve interpretability. An analysis of extensive panel data from Korean Android users reveals that incorporating application usage behavior in such models considerably improves the accuracy of mobile payment predictions. The study identifies key predictors of payment behavior, indicated by high Shapley values, such as using social networking services (e.g., KakaoTalk and Instagram), media applications (e.g., YouTube), and financial and membership applications (e.g., Toss and OK Cashbag). Moreover, the results of the SHAP force analysis reveal the individual session-level drivers of mobile purchases. These findings advance the literature on mobile payment prediction and offer practical insights for improving targeted marketing strategies by identifying key behavioral drivers of mobile transactions.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Enjoying the Festivalscape: The Effect of Festival Cues in Live-Streaming Studios on Consumers’ Intention to Stay
by
Ruijuan Wu and Huizhen Jin
J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2025, 20(2), 116; https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer20020116 - 28 May 2025
Abstract
Live-streaming e-commerce has attracted the attention of e-retailers and consumers in recent years. However, there is a lack of evidence in understanding the influence of atmospheric stimuli of live stream on consumer engagement. This paper seeks to examine the effect of festival cues
[...] Read more.
Live-streaming e-commerce has attracted the attention of e-retailers and consumers in recent years. However, there is a lack of evidence in understanding the influence of atmospheric stimuli of live stream on consumer engagement. This paper seeks to examine the effect of festival cues in live-streaming studios on consumers’ intention to stay in the live-streaming context. Results of four laboratory experiments indicated that presenting festival cues enhanced consumers’ intention to stay. In the relationship between festival cues and consumers’ intention to stay, festivalscape perception and pleasure–arousal played serial mediating roles. Product category moderated the effect of festival cues on consumers’ intention to stay. For non-festival products, presenting festival cues led to a stronger intention to stay. The moderating role of involvement was significant in the relationship between festival cues and intention to stay. Regarding less involved consumers, presenting festival cues significantly enhanced their intention to stay. Our work contributes to the existing knowledge of e-commerce live-streaming, festivalscape, and festival shopping, and offers relevant managerial implications for live-streaming e-retailers.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Digital Marketing and the Connected Consumer)
►▼
Show Figures
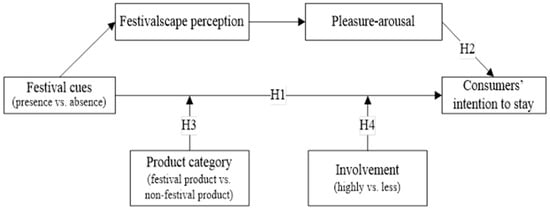
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Interactive Viral Marketing Through Big Data Analytics, Influencer Networks, AI Integration, and Ethical Dimensions
by
Leonidas Theodorakopoulos, Alexandra Theodoropoulou and Christos Klavdianos
J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2025, 20(2), 115; https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer20020115 - 26 May 2025
Abstract
The rapid growth of digital platforms has fundamentally reshaped network and viral marketing, profoundly transforming how information spreads across social networks and influences consumer behavior. This comprehensive review synthesizes theoretical, computational, and ethical perspectives into an integrated narrative, providing novel insights into the
[...] Read more.
The rapid growth of digital platforms has fundamentally reshaped network and viral marketing, profoundly transforming how information spreads across social networks and influences consumer behavior. This comprehensive review synthesizes theoretical, computational, and ethical perspectives into an integrated narrative, providing novel insights into the mechanisms driving information diffusion within contemporary interactive marketing. By integrating foundational concepts from social network theory, advanced graph models, and behavioral dynamics, the paper demonstrates how the interplay between network structures, influencer behaviors, and AI-driven algorithms significantly redefines traditional marketing paradigms. A distinctive theoretical contribution of this study lies in its innovative combination of Big Data analytics with AI-based predictive modeling, explicitly revealing how real-time algorithmic personalization not only enhances marketing effectiveness but also creates new ethical tensions surrounding misinformation, algorithmic bias, and consumer vulnerability. Addressing recent calls for greater theoretical originality and narrative coherence in interactive marketing research, this review explicitly highlights how these insights resolve critical theoretical puzzles and clarify contemporary ethical dilemmas. Additionally, the paper identifies emerging trends—including Web3 marketing, decentralized platforms, and neuroscience-driven targeting—offering clear future research directions. Through its integrative, narrative-driven framework, this study significantly advances interactive marketing theory, providing essential guidance for scholars and practitioners navigating the evolving complexities of digital influence.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Interactive Marketing in the Digital Era)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Development and Validation of a Framework on Consumer Satisfaction in Fresh Food E-Shopping: The Integration of Theory and Data
by
Yingxue Ren, Yitong Qu, Junbin Liang and Fangfang Zhao
J. Theor. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res. 2025, 20(2), 114; https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer20020114 - 26 May 2025
Abstract
Consumer satisfaction critically determines the operational sustainability of fresh food e-commerce platforms, yet integrated investigations combining multi-source data remain scarce. This study develops a theory–data fusion framework to identify key satisfaction drivers in China’s fresh e-commerce sector. Utilizing Python-based crawlers, we extracted 1252
[...] Read more.
Consumer satisfaction critically determines the operational sustainability of fresh food e-commerce platforms, yet integrated investigations combining multi-source data remain scarce. This study develops a theory–data fusion framework to identify key satisfaction drivers in China’s fresh e-commerce sector. Utilizing Python-based crawlers, we extracted 1252 online reviews of Aksu apples from a certain fresh produce e-commerce platform alongside 509 validated questionnaires. Through systematic literature synthesis, three core dimensions—perceived value (price–performance balance), platform experience (interface usability), and perceived quality (freshness assurance)—were operationalized into measurable indicators. The final structural equation model reveals that perceived value, platform experience, and perceived quality all have significant positive impacts on consumer satisfaction. This study pioneers a methodological paradigm integrating computational text mining (Octopus Collector + SPSS Pro) with traditional psychometric scales, achieving superior model fit (RMSEA = 0.023, CFI = 0.981). These findings empower platforms to implement a precision strategy. The validated framework provides a theoretical basis for omnichannel consumer research while addressing the data-source bias prevalent in prior studies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Electronic Commerce and Information Management Towards the Digital Era)
►▼
Show Figures
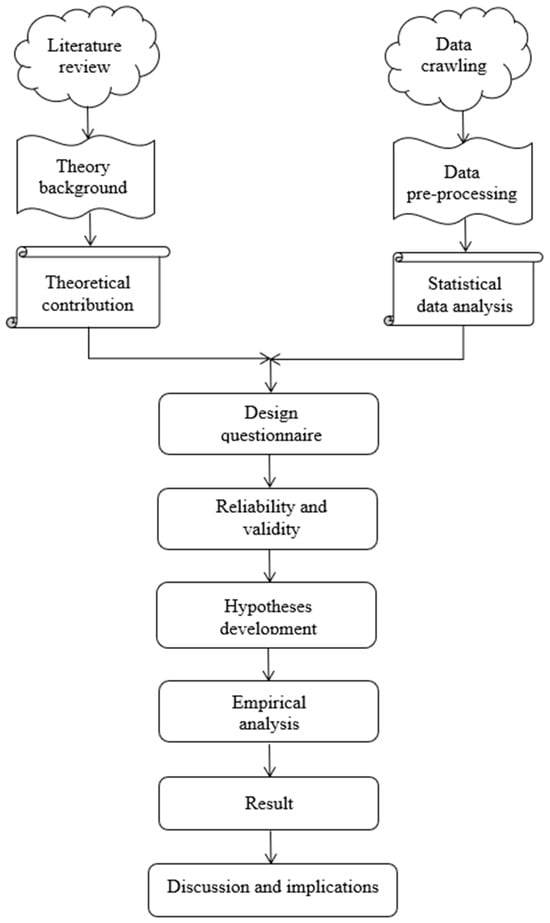
Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal MenuJournal Browser
► ▼ Journal Browser-
arrow_forward_ios
Forthcoming issue
arrow_forward_ios Current issue - Volumes not published by MDPI
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Businesses, Sustainability, JTAER
Digital Marketing Dynamics: From Browsing to Buying
Topic Editors: José Luís Mendes Loureiro Abrantes, Natália de Lima Figueiredo, Bruno Morgado Ferreira, Luís F. MartinezDeadline: 15 June 2025
Topic in
Administrative Sciences, Businesses, Behavioral Sciences, JTAER
Interactive Marketing in the Digital Era
Topic Editors: Chenglu Wang, Jiaxun He, Fue Zeng, Rui Guo, Morgan Yang, Andy Hao, Hongfei LiuDeadline: 26 June 2025
Topic in
AI, BDCC, FinTech, IJFS, JTAER, Risks
Artificial Intelligence Applications in Financial Technology, 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Albert Y.S. Lam, Andy ChunDeadline: 31 December 2025
Topic in
Administrative Sciences, Businesses, Informatics, JTAER
Innovations in New Media: Shaping the Future of Interactive Marketing
Topic Editors: Chenglu Wang, Hongfei Liu, Morgan Yang, Qing Ye, Yunjia ChiDeadline: 28 February 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
JTAER
ICEC 2025: Transforming E-Commerce with AI: Navigating Innovation, Personalization, and Ethical Challenges
Guest Editors: Kai Li, Xiaofei Zhang, Yi Wu, Sai Liang, Mengli YuDeadline: 10 June 2025
Special Issue in
JTAER
Digitalization and Sustainable Supply Chain
Guest Editors: Qiang Lu, Tiantong XuDeadline: 31 August 2025
Special Issue in
JTAER
AI-Based Disruption, Innovations, and New Business Models in E-Commerce: Empirical Research, Case Studies and Current Trends
Guest Editors: Stephan Böhm, Sid Suntrayuth, Müge Klein, Ela Sibel Bayrak MeydanoğluDeadline: 1 December 2025
Special Issue in
JTAER
Blockchain Business Applications and the Metaverse
Guest Editor: Rand LowDeadline: 20 December 2025
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
JTAER
The New Era of Digital Marketing
Collection Editors: Shib Sankar Sana, Sweety Sadhukhan
Topical Collection in
JTAER
Customer Relationships in Electronic Commerce
Collection Editor: Yung-Shen Yen
Topical Collection in
JTAER
The Connected Consumer
Collection Editors: Inma Rodríguez-Ardura, Gisela Ammetller
Topical Collection in
JTAER
Emerging Topics in Omni-Channel Operations
Collection Editors: Gang Li, T. C. Edwin Cheng, Tao Zhang








