- Article
From Click to Regret: Investigating Impulsive Buying and Post-Purchase Cognitive Dissonance Through the S-O-R Lens
- Afruza Haque,
- Rasheda Akter Rupa and
- Nahida Sultana
- + 2 authors
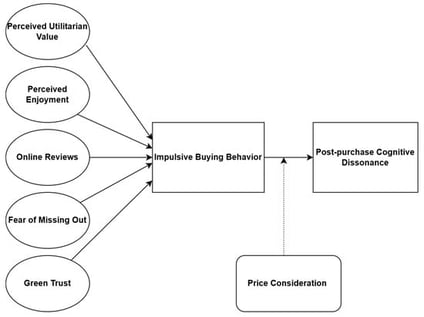
In the online shopping context, the proliferation of digital platforms has contributed to an increase in impulsive buying behavior (IBB), which can sometimes lead to regret. This study aims to explore the intrinsic and extrinsic stimuli that influence consumers’ online impulsive buying behavior, which subsequently affects their post-purchase cognitive dissonance, with the moderating role of price consideration (PC). The conceptual framework was formulated using the Stimulus–Organism–Response (S-O-R) model. A total of 813 responses were collected and analyzed using Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM). The findings revealed that perceived utilitarian value (PUV), perceived enjoyment (PE), fear of missing out (FOM), and green trust (GT) positively impact online impulsive buying behavior (IBB), which, in turn, positively impacts post-purchase cognitive dissonance (PCD). Moreover, a significant moderating role of PC is found in the relationship between IBB and PCD, suggesting that consumers with low price consideration tend to regret their impulsive buying more. The findings provide insights that guide online retail sellers and digital marketers to develop or implement customized strategies based on the intrinsic and extrinsic stimuli that influence customers’ impulsive buying and subsequent post-purchase cognitive dissonance.
13 March 2026