- Article
Emotion Recognition Using Multi-View EEG-fNIRS and Cross-Attention Feature Fusion
- Ni Yan,
- Guijun Chen and
- Xueying Zhang
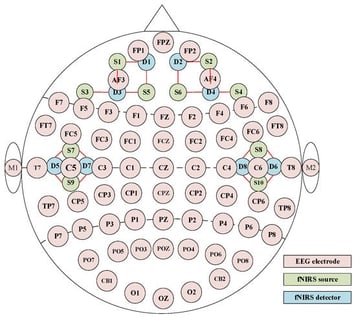
To improve the accuracy of emotion recognition, this paper proposes a multi-view EEG-fNIRS and cross-attention fusion module named FGCN-TCNN-CAF, which employs a differentiated modeling strategy for the frequency, spatial, and temporal features of EEG-fNIRS signals. First, frequency-domain and time-domain features are extracted from EEG, and time-domain features are obtained from fNIRS signals. Then, a frequency-domain graph convolutional network (FGCN) and a time-domain convolutional network (TCNN) are deployed in parallel. The EEG feature views from different frequency bands are modeled using an FGCN module to capture graph-structured relationships, while the time-domain views of EEG and fNIRS are processed by a TCNN module to extract spatial and temporal features. Finally, a cross-attention fusion network (CAF) is applied to achieve interactive fusion of multimodal features. Experiments demonstrate that the proposed multi-view EEG approach achieves higher recognition accuracy compared to using only the EEG view. Additionally, the mmultimodalrecognition results outperform single-modal EEG and single-modal fNIRS by 1.73% and 6.65%, respectively. When compared with other emotion recognition models, the proposed method achieves the highest accuracy of 96.09%, proving its superior performance.
2 March 2026