Bifunctional TiO2@AgNP Superstructures as a SERS-Sensing Platform for Identifying Flavonoids in Chinese Herbal Medicine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Characterization Methods
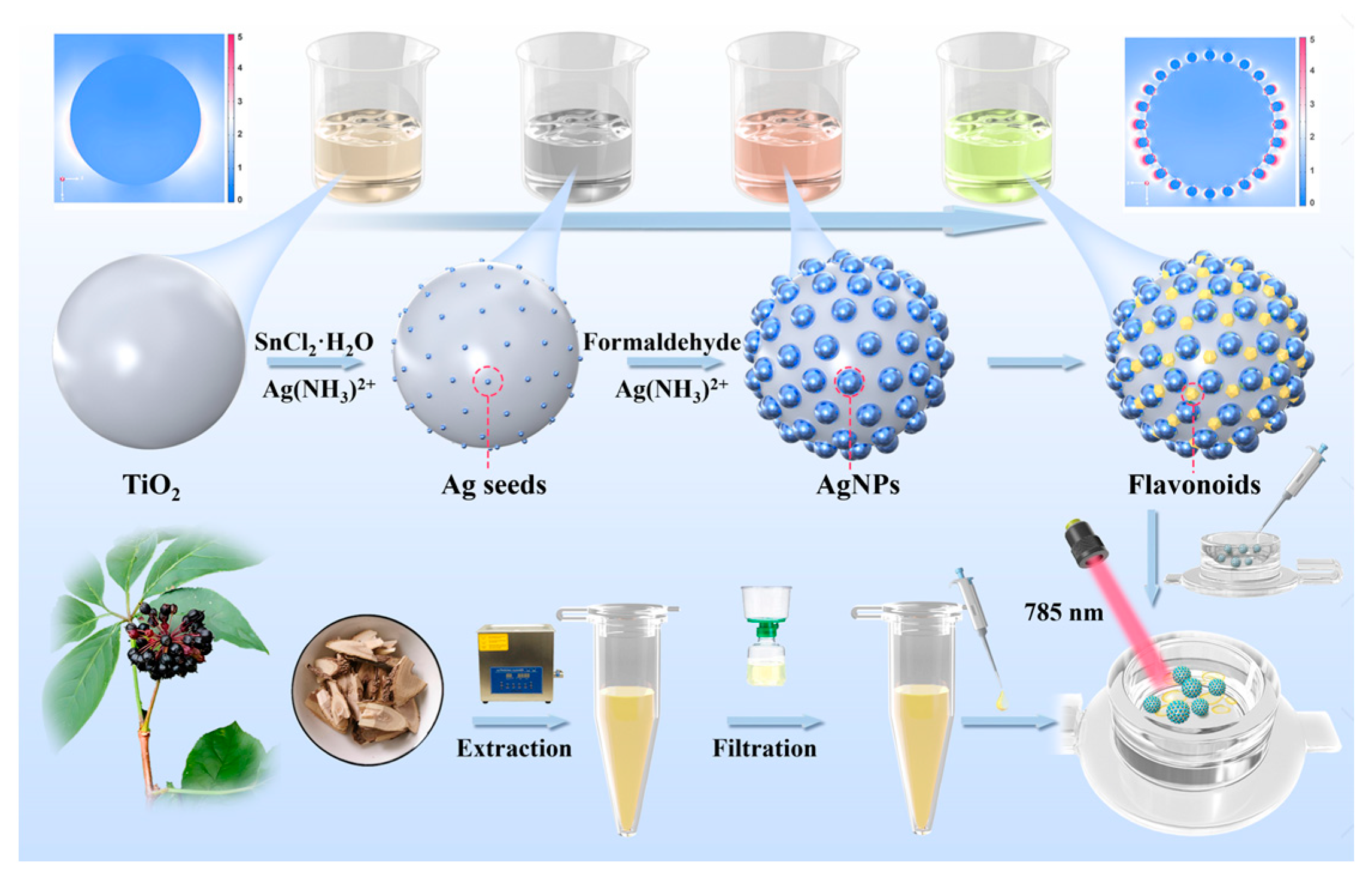
2.3. Synthesis of TiO2 Nanoparticles
2.4. Synthesis of TiO2@AgNP Nanocomposites
2.5. Preparation of AS Extracts
2.6. SERS Measurement Protocol
3. Results
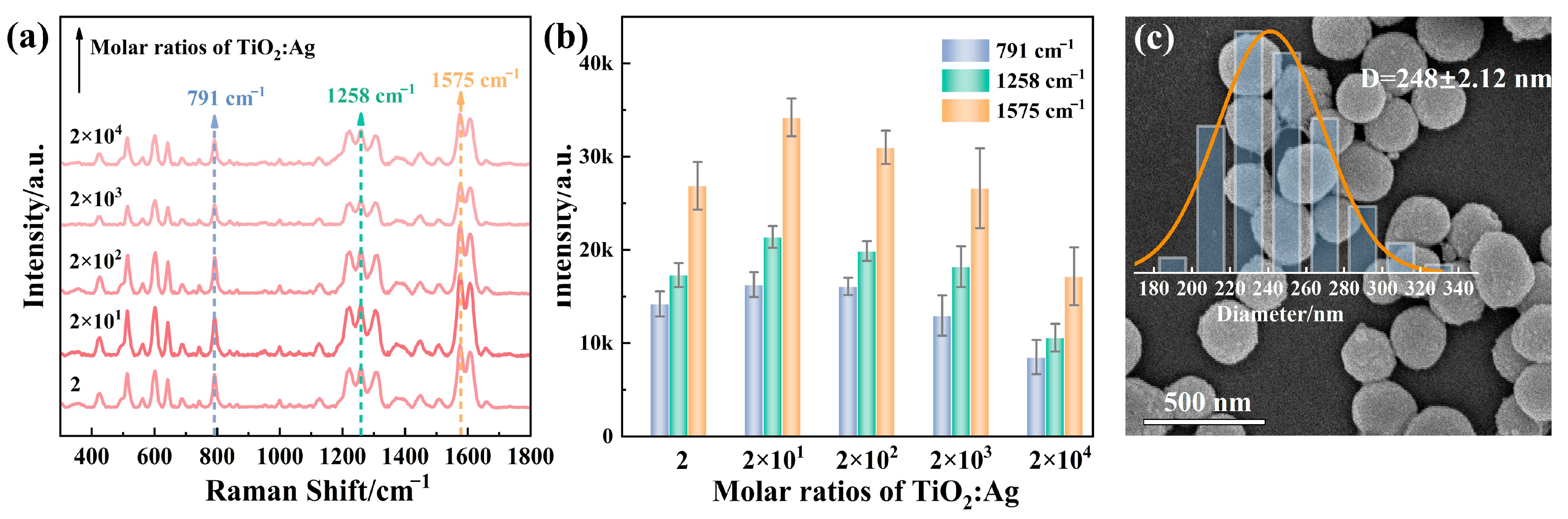
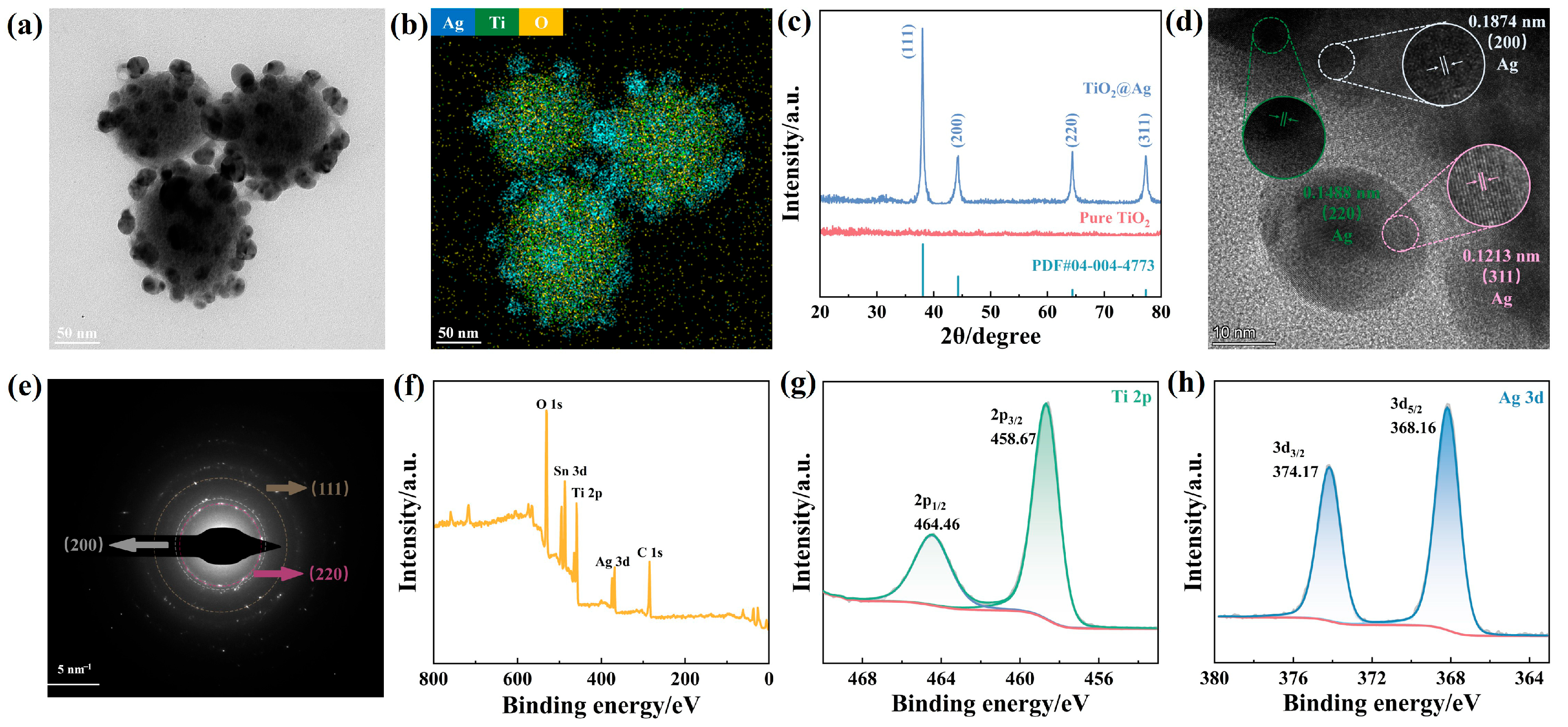
3.1. Optimization and Structural Characterization of TiO2@AgNPs
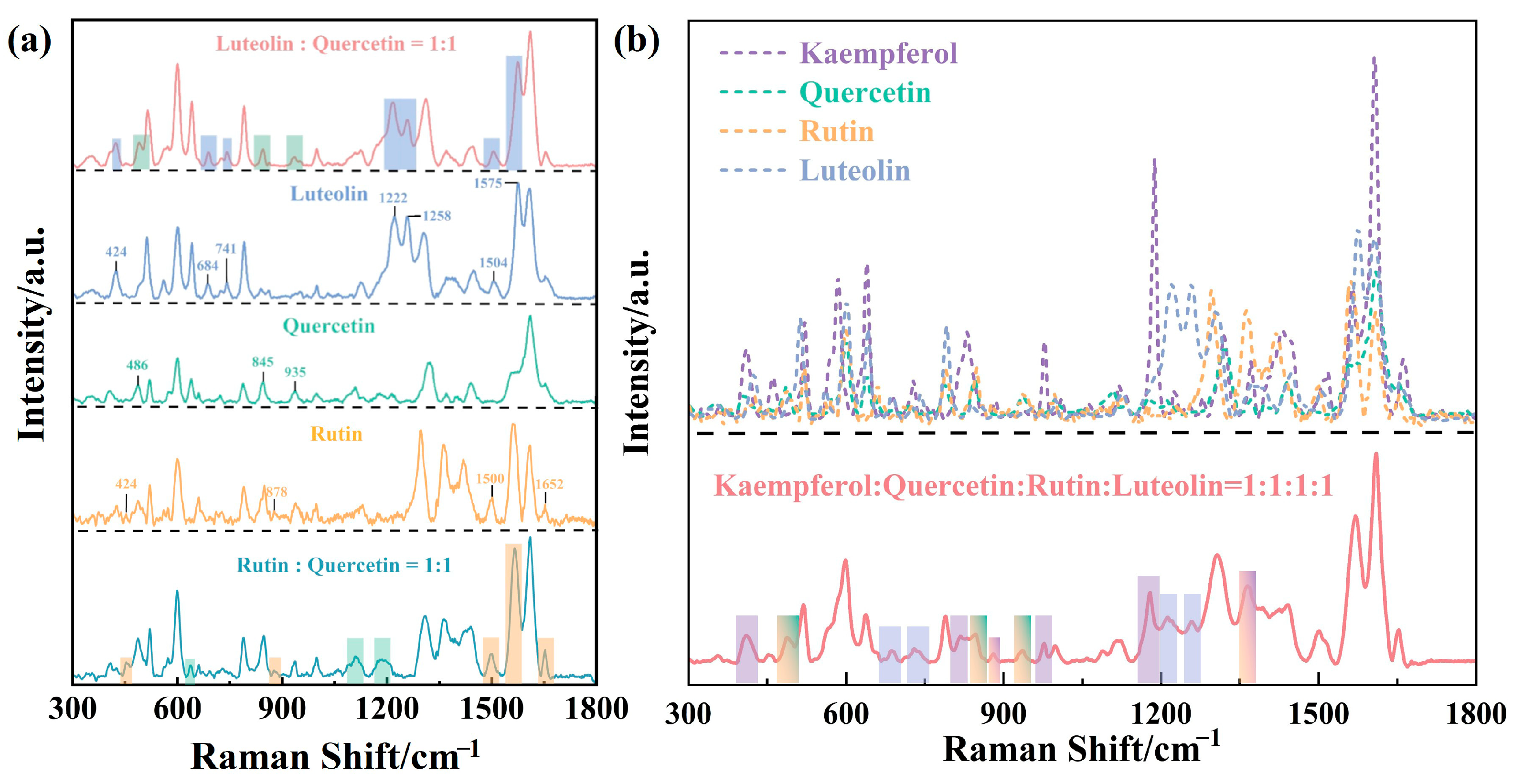
3.2. Establishment of the SERS Sensor for Flavonoid Detection and Quantitative Analysis
3.3. Practical Feasibility of Rapid Multiplex Analysis of Flavonoids
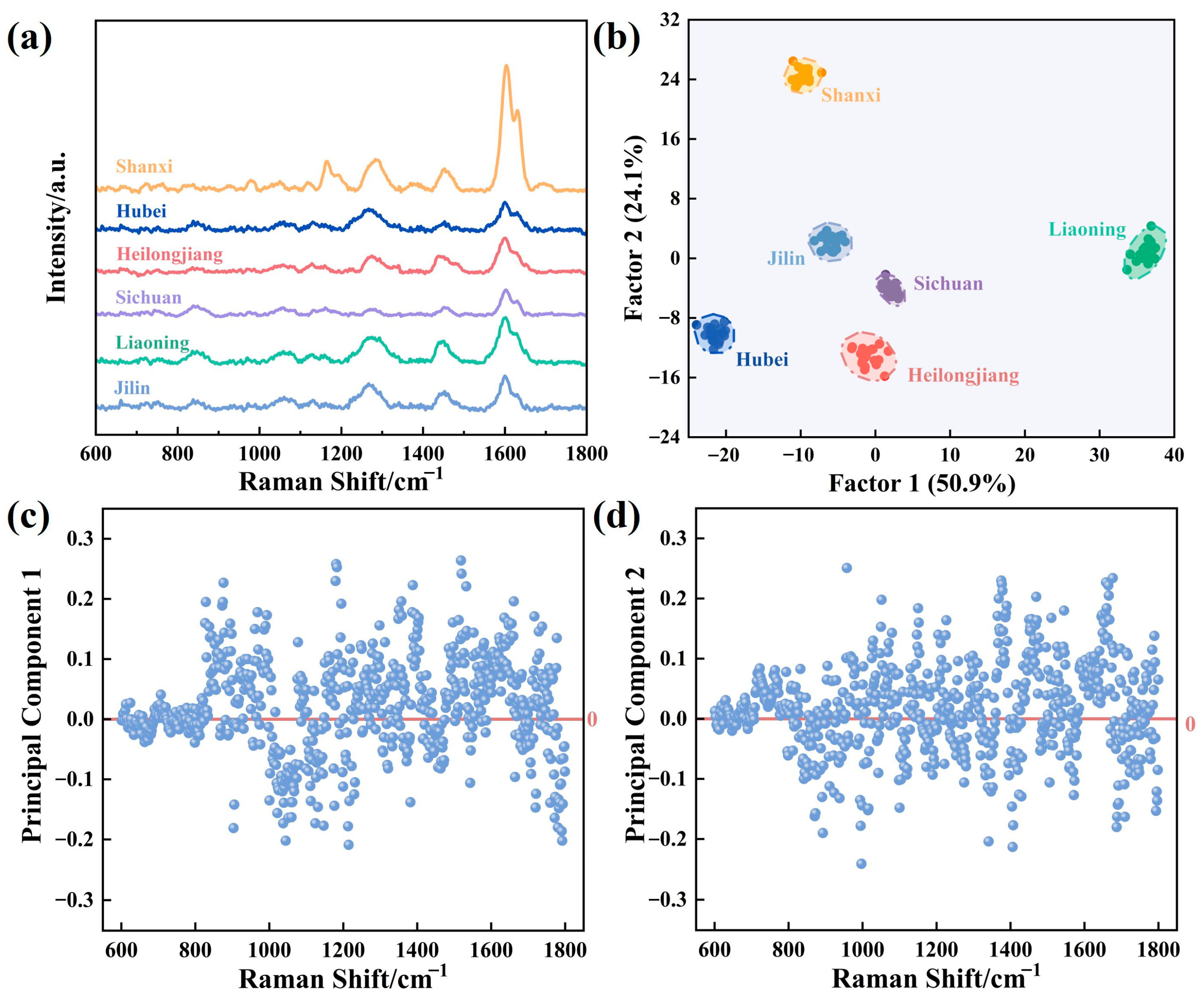
3.4. SERS Discrimination of AS from Different Origins
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jia, A.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Deng, B.; Qiu, Z.; Fu, C. A review of Acanthopanax senticosus (Rupr and Maxim.) harms: From ethnopharmacological use to modern application. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 268, 113586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Ren, Y.-S.; Li, X.-T.; Cai, M.T.; Li, H.-L.; Ding, W.L.; Wu, Y.-H.; Guo, H.-B.; Tang, Z.H.; Sun, F.; et al. MS/MS molecular networking-guided in-depth profiling of triterpenoid saponins from the fruit of Eleutherococcus senticosus and their neuroprotectivity evaluation. Phytochem. Anal. 2023, 34, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.-G.; Huang, Y.X.; Liang, J.; Kuang, H.-X. Comparable studies of two polysaccharides from leaves of Acanthopanax senticosus: Structure and antioxidation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 147, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Wang, H.S.; Lee, M.W. Anti-inflammatory effects of fermented bark of Acanthopanax sessiliflorus and its isolated compounds on lipopolysaccharide-treated RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. Evid. Based Compl. Alt. 2020, 2020, 6749425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, M.-H. Different solvent fractions of Acanthopanax senticosus harms exert antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities and inhibit the human Kv1.3 channel. J. Med. Food. 2015, 18, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liu, T.; Qi, S.; Gu, H.; Li, J.; Yang, L. Tea saponin additive to extract eleutheroside B and E from Eleutherococcus senticosus by ultrasonic mediation and its application in a semi-pilot scale. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2022, 86, 106039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, J.; Li, G.; Zhang, S.; Wen, L.; Li, W. Strategies for identifying adulterated Acanthopanax senticosus using portable mass spectrometry and chemometrics. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 136, 106827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Zhang, X.; Kan, Q.; Chu, X. Antioxidant Activity of Acanthopanax senticosus Flavonoids in H2O2-Induced RAW 264.7 Cells and DSS-Induced Colitis in Mice. Molecules 2022, 27, 2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amelia, V.; Aversano, R.; Chiaiese, P.; Carputo, D. The antioxidant properties of plant flavonoids: Their exploitation by molecular plant breeding. Phytochem. Rev. 2018, 17, 611–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Ferns, K.; Yan, Z.-Q.; Yin, S.-Y.; Kou, J.-J.; Li, D.; Zeng, Z.; Yin, L.; Wang, X.; Bao, H.-X.; et al. Acanthopanax senticosus: Photochemistry and Anticancer Potential. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2016, 44, 1543–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luna, S.L.R.D.; Ramírez-Garza, R.E.; Saldívar, S.O.S. Environmentally Friendly Methods for Flavonoid Extraction from Plant Material: Impact of Their Operating Conditions on Yield and Antioxidant Properties. Sci. World J. 2020, 2020, 6792069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, Z.; Zeng, F.; Zhu, Z.; Qian, D.; Guo, S.; Wang, H.; Duan, J. Comparative analysis of sixteen flavonoids from different parts of Sophora flavescens Ait. by ultra high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharmaceut. Biomed. 2018, 156, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuutila, A.M.; Kammiovirta, K.K.; Oksman-Caldentey, M. Comparison of methods for the hydrolysis of flavonoids and phenolic acids from onion and spinach for HPLC analysis. Food Chem. 2002, 76, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesquita, E.; Monteiro, M. Simultaneous HPLC determination of flavonoids and phenolic acids profile in Pêra-Rio orange juice. Food Res. Int. 2018, 106, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xie, Q.; Li, J.; Sun, L.; Xie, Y.; Ozaki, Y.; Ji, W. Macroscale TiO2 Microspherical Arrays with Multiple Synergistic Effect for Highly Sensitive Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2400523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, S.E.J.; Sirimuthu, N.M.S. Quantitative surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 1012–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, T.; Procházka, M.; Dong, Z.-C.; Ji, W.; Yamamoto, Y.S.; Zhang, Y.; Ozaki, Y. Toward a New Era of SERS and TERS at the Nanometer Scale: From Fundamentals to Innovative Applications. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 1552–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, S.; Emory, S.R. Probing Single Molecules and Single Nanoparticles by Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. Science 1997, 275, 1102–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlucker, S. Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy: Concepts and Chemical Applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2014, 53, 4756–4795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cialla-May, D.; Zheng, X.S.; Weber, K.; Popp, J. Recent progress in surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for biological and biomedical applications: From cells to clinics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 3945–3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Xu, K.; Jiang, S.; Luo, D.; Chen, R.; Xu, C.; Shum, P.; Liu, Y.J. Recent progress on two-dimensional layered materials for surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy and their applications. Mater. Today Phys. 2021, 18, 100378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Xie, Q.; Jiang, B.; Li, J.; Xie, Y.; Ji, W. Evaluating the Kinetics and Molecular Mechanism for Biomimetic Metabolic Activation of PAHs by Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 10365–10372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, L.; Li, J.; Xie, Q.; Hu, J.; Liu, J.; Xu, C.; Peng, J.; Chen, C.; Ji, W. Plasmonic Coacervate as a Droplet-Based SERS Platform for Rapid Enrichment and Microanalysis of Hydrophobic Payloads. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 18772–18780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Yu, J.; Liu, S.; Cai, L.; Han, X.X. In situ surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for membrane protein analysis and sensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2025, 267, 116819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, Y.; Fales, A.M.; Register, J.; Yuan, H.; Vo-Dinh, T. Direct analysis of traditional Chinese medicines using surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS). Drug Test. Anal. 2014, 6, 1063–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Sun, Z.; Xie, M.; Gu, S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Q. A new method for rapid identification of traditional Chinese medicine based on a new silver sol: Using the SERS spectrum for quality control of flavonoids and flavonoid glycosides in Potentilla discolor Bge. J. Mater. Chem. C 2023, 11, 15138–15148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Li, C.; Wu, P. Afterglow Nanoprobes for In-vitro Background-free Biomarker Analysis. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2024, 40, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Xing, X.; Shen, X.; Ouyang, J.; Na, N. A Review on Nanomaterial-based Strategies for Manipulating Tumor Microenvironment to Enhance Chemodynamic Therapy. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2024, 40, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Ma, Y.; Wang, X.; Xie, Y.; Chen, C.; Ji, W. Rapid Construction of Interfacial Plasmonic Nanoarray for SERS Sensing of Flavonoids. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2025, 271, 117044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samriti; Rajput, V.R.; Gupta, K.; Prakash, J. Engineering metal oxide semiconductor nanostructures for enhanced charge transfer: Fundamentals and emerging SERS applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 10, 73–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Sun, L.; Dong, Y.; Chang, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Li, J.; Xie, Y.; Ji, W. Semiconductor Superstructures with Multiple Synergistic Resonances for SERS Exploring Multiplex Noncovalent Interactions. Nano Lett. 2025, 25, 6645–6653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musumeci, A.; Gosztola, D.; Schiller, T.; Dimitrijevic, N.M.; Mujica, V.; Martin, D.; Rajh, T. SERS of Semiconducting Nanoparticles (TiO2 Hybrid Composites). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 6040–6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavarz, M.; Kassanos, P.; Tan, B.; Venkatakrishnan, K. Metal-oxide surface-enhanced Raman biosensor template towards point-of-care EGFR detection and cancer diagnostics. Nanoscale Horiz. 2020, 5, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, D.; Lu, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J. Improved SERS Sensitivity on Plasmon-Free TiO2 Photonic Microarray by Enhancing Light-Matter Coupling. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 9886–9889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.M.; Xie, Q.H.; Wu, S.; Li, J.B.; Sun, L.; Ji, W. Revealing Adsorption Mechanism of p-Mercaptobenzoic Acid with TiO2 Surfaces Using Electric Field-Enhanced Semiconductor SERS. J. Phys. Chem. C 2023, 127, 9418–9424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Wang, Y.X.; Zhao, B. Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering of 4-Mercaptopyridine on the Surface of TiO2 Nanofibers Coated with Ag Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 12786–12791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corredor, C.; Teslova, T.; Cañamares, M.V.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, J.; Lombardi, J.R.; Leona, M. Raman and surface-enhanced Raman spectra of chrysin, apigenin and luteolin. Vib. Spectrosc. 2009, 49, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Song, G.; Zhou, L.; Wang, X.; You, L.; Li, J. Highly sensitively detecting tetramethylthiuram disulfide based on synergistic contribution of metal and semiconductor in stable Ag/TiO2 core-shell SERS substrates. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 539, 147744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Sang, Q.; Du, J.; Yang, M.; Li, X.; Shen, Y.; Han, X.X.; Jiang, X.; Zhao, B. A Ag synchronously deposited and doped TiO2 hybrid as ultrasensitive SERS substrate: A multi-function platform for SERS detection and photocatalytic degradation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 15149–15157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Ma, J.; Gu, C.; Xiong, W.; Jiang, T. Synchronous enhancement of electromagnetic and chemical effects-induced quantitative adsorptive detection of quercetin based on flexible polymer-silver-ZIF-67 SERS substrate. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2023, 378, 133176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teslova, T.; Corredor, C.; Livingstone, R.; Spataru, T.; Birke, R.L.; Lombardi, J.R.; Cañamares, M.V.; Leona, M. Raman and surface-enhanced Raman spectra of flavone and several hydroxy derivatives. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2007, 38, 802–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Bai, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, B.; Zhao, D.; Zhao, Y. SERS spectroscopy of kaempferol and galangin under the interaction of human serum albumin with adsorbed silver nanoparticles. Spectrochim. Acta A 2012, 92, 234–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paczkowska, M.; Lewandowska, K.; Bednarski, W.; Mizera, M.; Podborska, A.; Krause, A.; Cielecka-Piontek, J. Application of spectroscopic methods for identification (FT-IR, Raman spectroscopy) and determination (UV, EPR) of quercetin-3-O-rutinoside. Experimental and DFT based approach. Spectrochim. Acta A 2015, 140, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Matosa, Y.M.L.S.; Vasconcelosb, D.L.M.; Barretob, A.C.H.; Rochac, J.E.; Netoc, J.B.; Campinac, F.F.; de A. M. Guedesd, T.T.; Sousac, A.K.; Teixeirac, R.N.P.; Alvarez-Pizarroe, J.C.; et al. Reduction of the phytotoxic effect of mercury chloride by rutin and evaluation of interactions by vibrational spectroscopy (Raman and FTIR). Vib. Spectrosc. 2020, 109, 103084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Qi, S.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ji, W. Bifunctional TiO2@AgNP Superstructures as a SERS-Sensing Platform for Identifying Flavonoids in Chinese Herbal Medicine. Biosensors 2025, 15, 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15080536
Li Y, Li J, Wang H, Qi S, Zhang Z, Wang Y, Wang Y, Ji W. Bifunctional TiO2@AgNP Superstructures as a SERS-Sensing Platform for Identifying Flavonoids in Chinese Herbal Medicine. Biosensors. 2025; 15(8):536. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15080536
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yulin, Junbo Li, Haisu Wang, Shaorui Qi, Zhehao Zhang, Yaqiu Wang, Ying Wang, and Wei Ji. 2025. "Bifunctional TiO2@AgNP Superstructures as a SERS-Sensing Platform for Identifying Flavonoids in Chinese Herbal Medicine" Biosensors 15, no. 8: 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15080536
APA StyleLi, Y., Li, J., Wang, H., Qi, S., Zhang, Z., Wang, Y., Wang, Y., & Ji, W. (2025). Bifunctional TiO2@AgNP Superstructures as a SERS-Sensing Platform for Identifying Flavonoids in Chinese Herbal Medicine. Biosensors, 15(8), 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15080536




