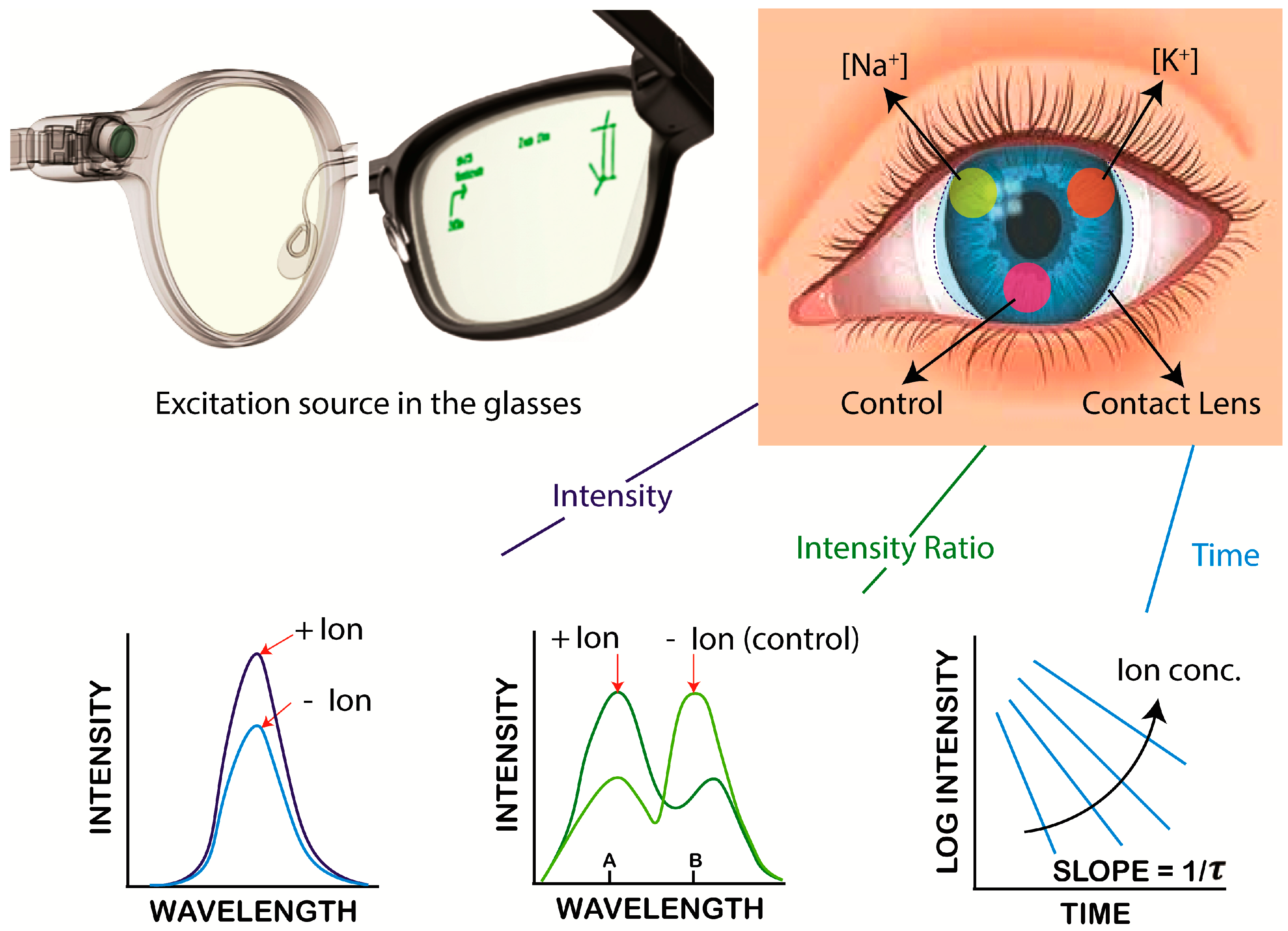
First Design of a Contact Lens for Diagnosis of Dehydration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection of SiHG Contact Lens
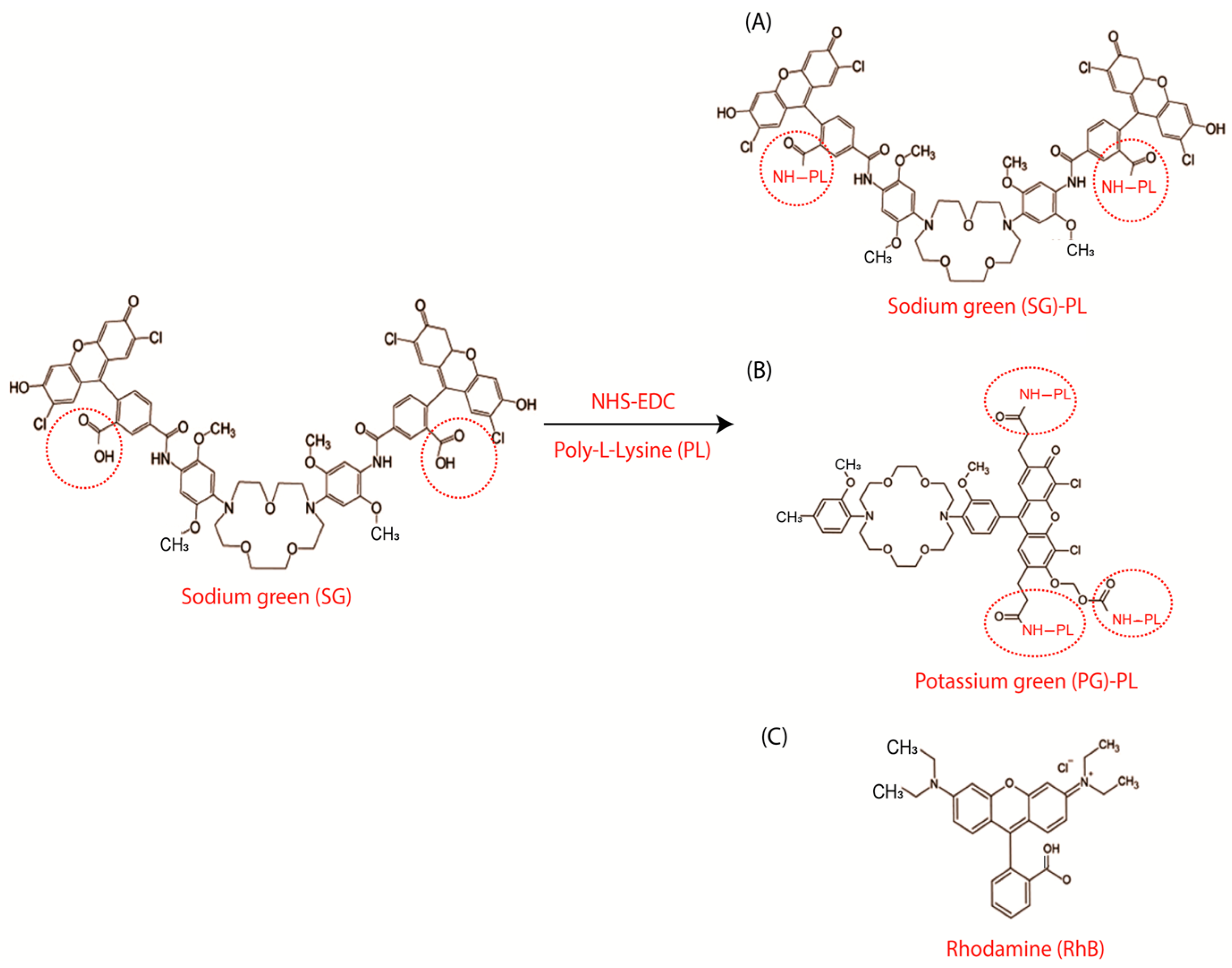
2.2. Synthesis of the Sodium-Sensitive and Potassium-Sensitive Fluorophores
2.3. Probe Labeling of SiHG Lenses
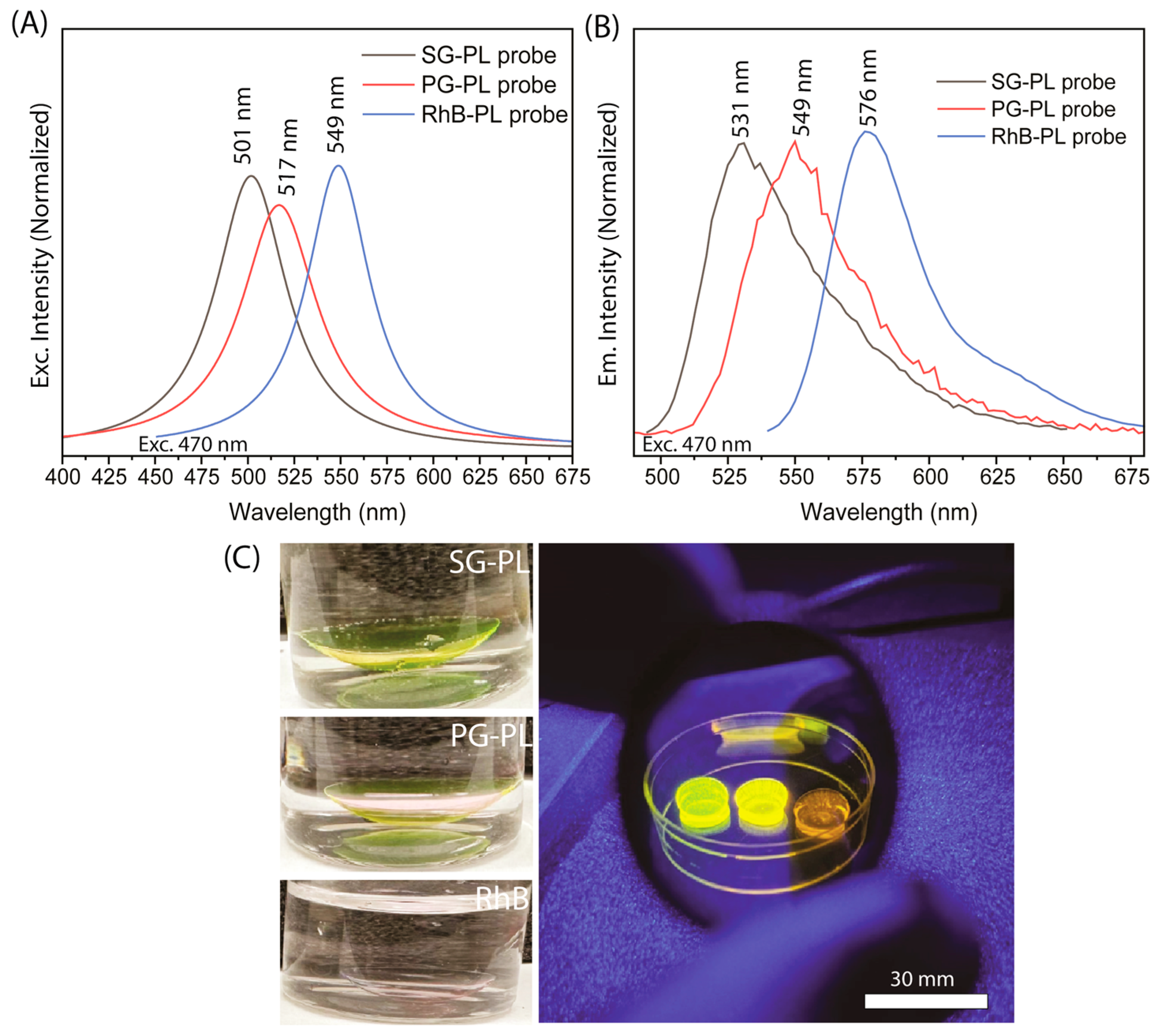
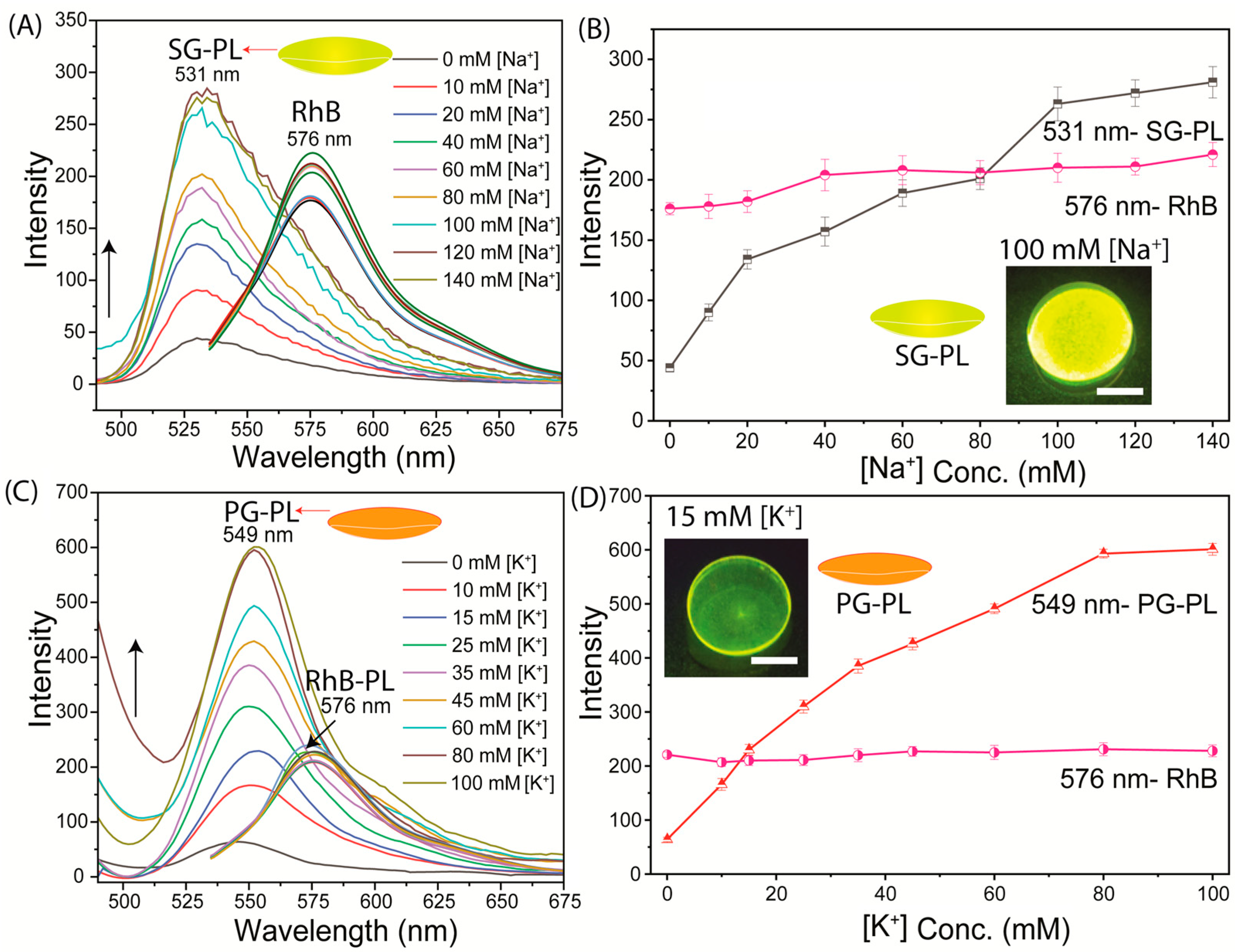
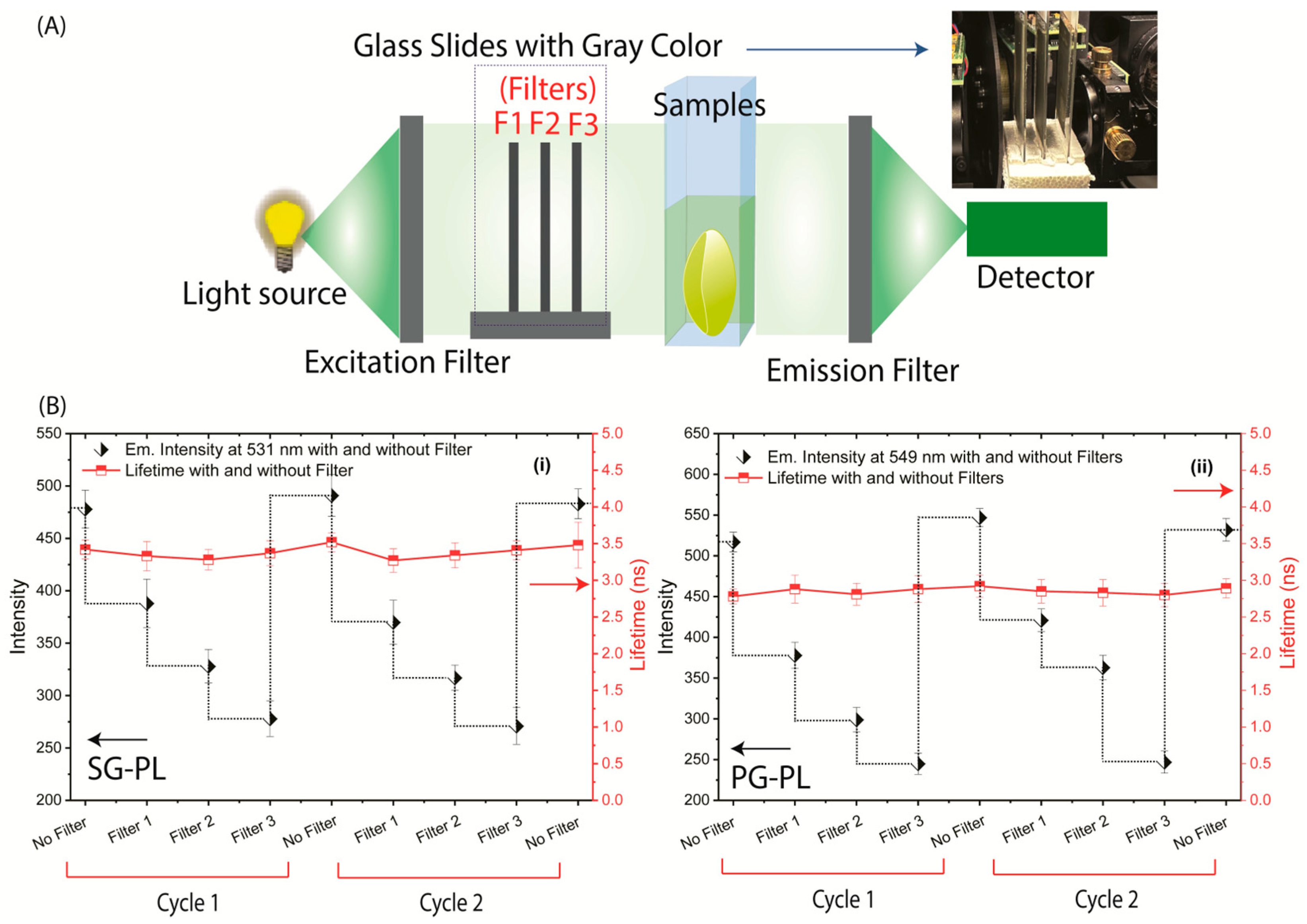
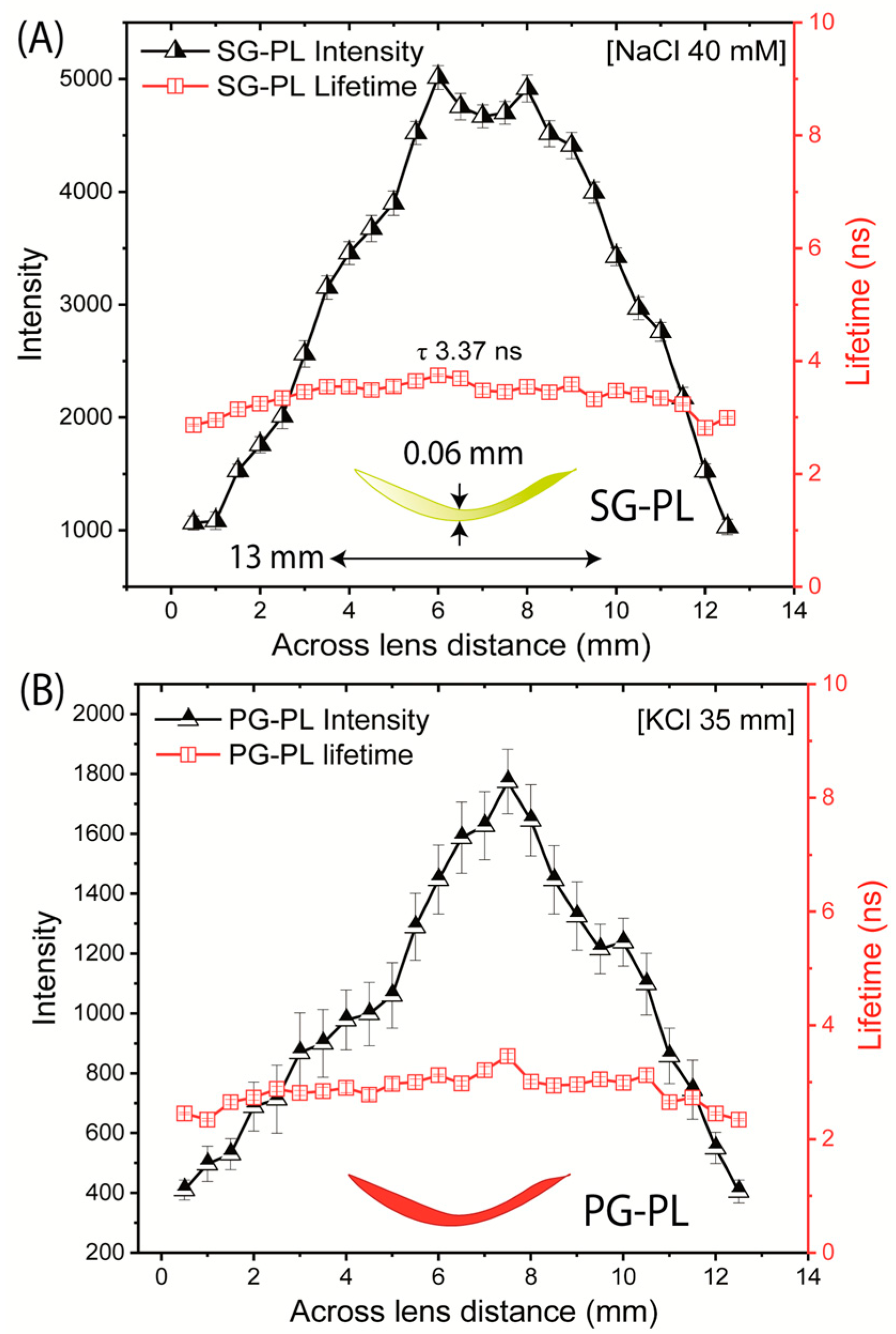
2.4. SiHG Lenses Fluorescence Measurements
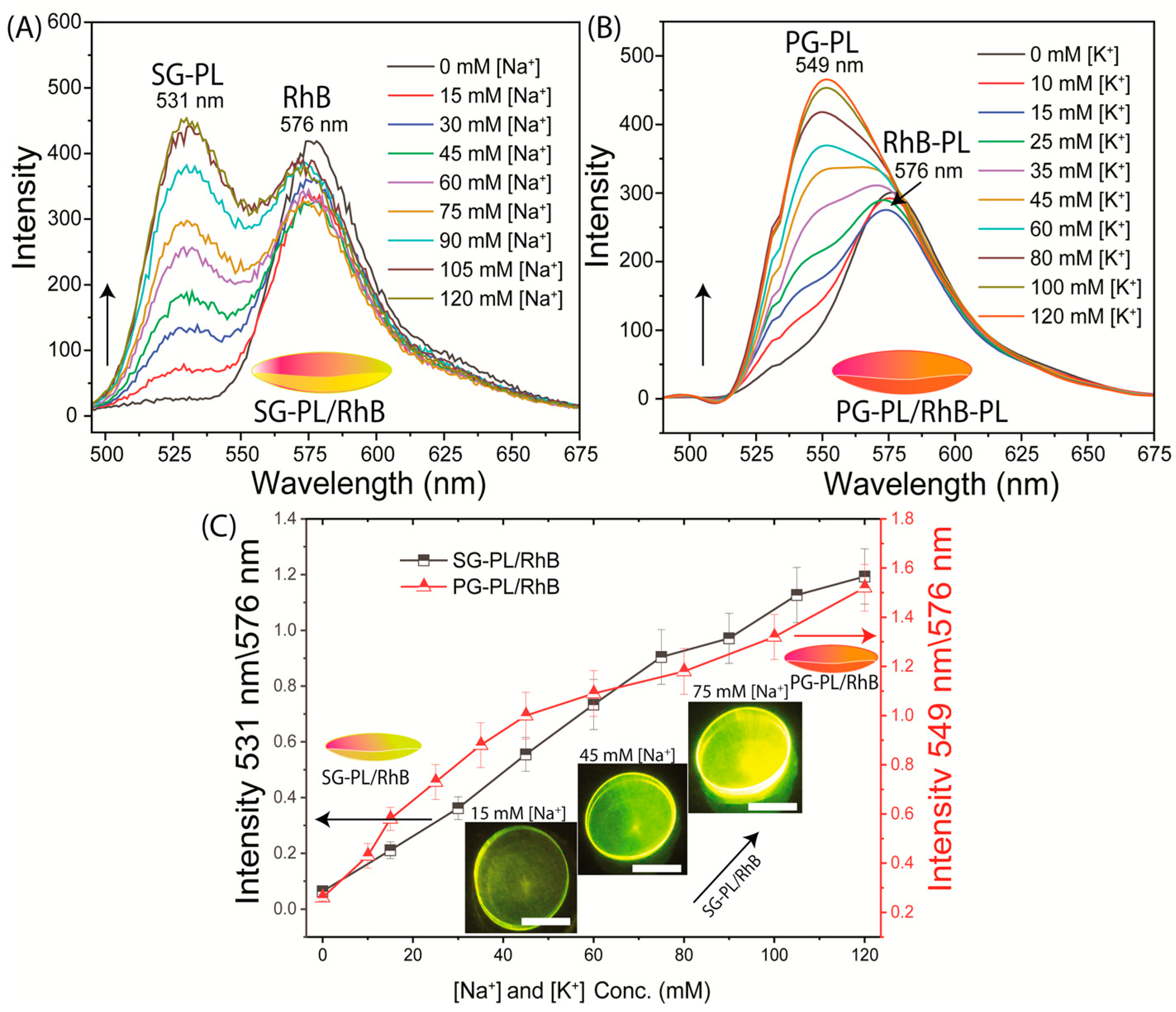
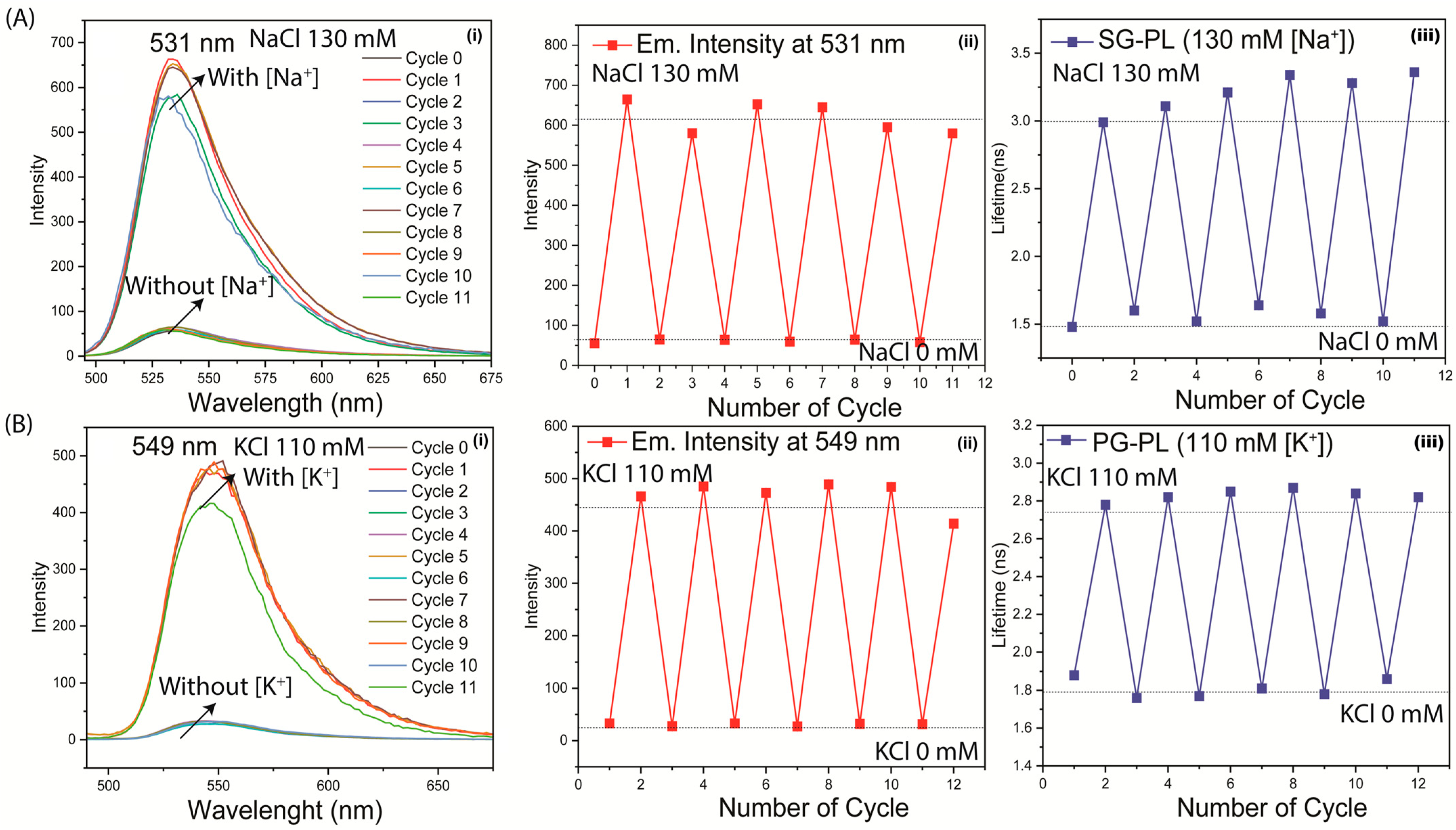
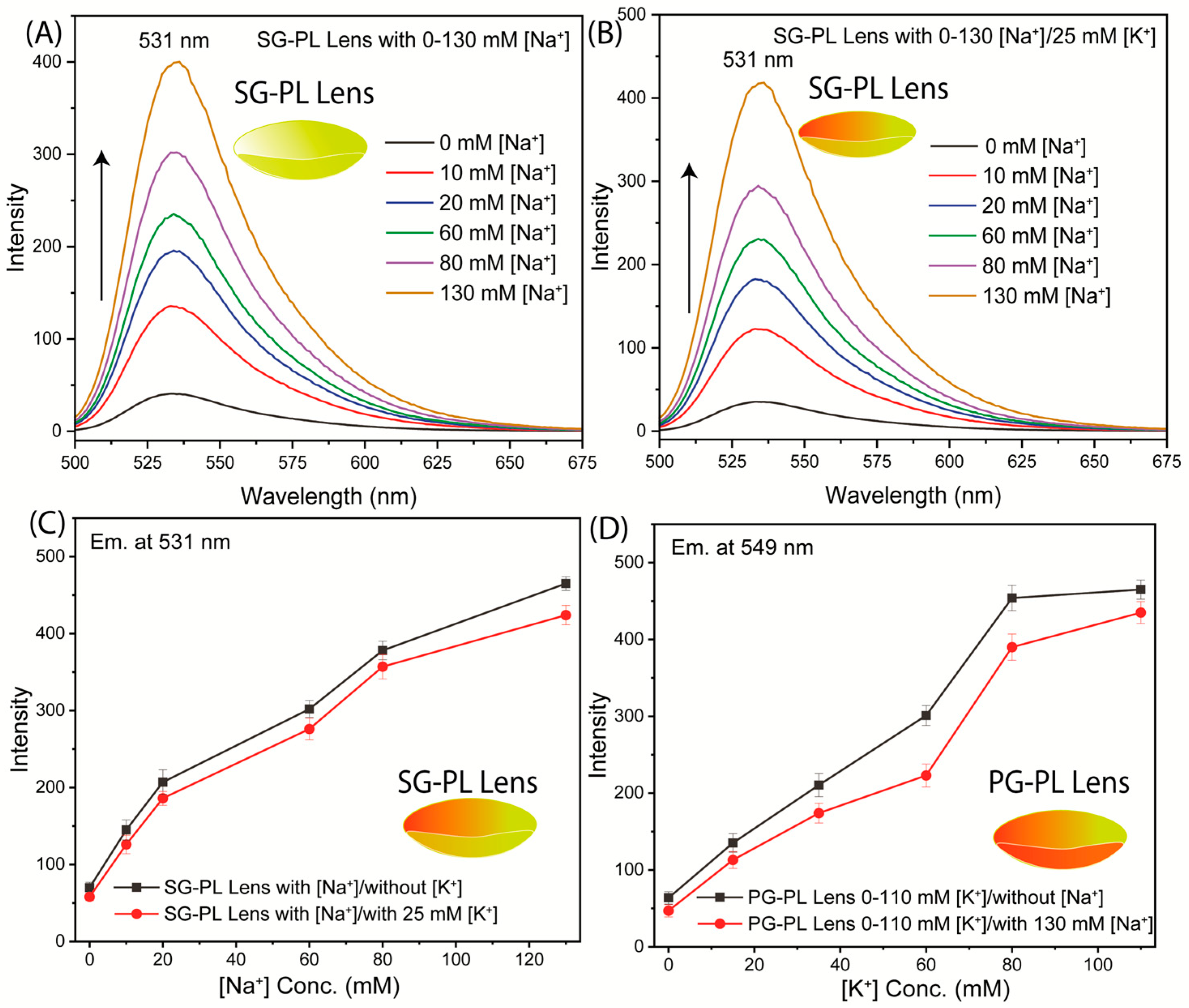
3. Results
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Costillo, L. The most surprising dehydration statistics in 2023. Gitnux Marketing Report. 9 May 2023, p. 13. Available online: https://blog.gitnux.com/topics/statistics/health-fitness/ (accessed on 15 October 2023).
- Manz, F.; Wentz, A. The importance of good hydration for the prevention of chronic diseases. Nutr. Rev. 2005, 63, S2–S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sharkawy, A.M.; Virdee, A.; Wahab, A.; Humes, D.J.; Sahota, O.; Devonald, M.A.J.; Lobo, D.N. Dehydration and clinical outcome in hospitalised older adults: Cohort study. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2017, 8, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelis, M.F. Disorders of Serum Sodium Concentration in the Elderly Patient, Chapter 16; American Society of Nephrology: Washington, DC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds, C.J.; Foglia, E.; Booth, P.; Fu, C.H.Y.; Gardner, M. Dehydration in older people: A systematic review of the effects of dehydration on health outcomes, healthcare costs and cognitive performance. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2021, 95, 104380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woff, A.; Stuckler, D.; McKee, M. Are patients admitted to hospitals from care homes dehydrated? J. Roc. Soc. Med. 2015, 108, 259–265. [Google Scholar]
- Paulis, S.J.C.; Everink, I.H.J.; Halfens, R.J.G.; Lohrmann, C.; Schols, J.M.G.A. Prevalence and risk factors of dehydration among nursing home residents: A systematic review. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2018, 19, 646–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, A.M.; Seemer, J.; Knudsen, A.W.; Munk, T. Narrative review of low-intake dehydration in older adults. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pross, N. Effects of dehydration on brain functioning: A life span perspective. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 70, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benelam, B.; Wyness, L. Hydration and health: A review. Nutr. Bull. 2010, 35, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, M.N.; Johnson, C.S. A review of the literature on dehydration in the institutionized elderly. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. Metab. 2010, 5, e47–e53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavzzo-Mourey, R. Dehydration in the elderly: A short review. J. Natl. Med. Assoc. 1987, 79, 1033–1038. [Google Scholar]
- Hooper, L.; Abdelhamid, A.; Attreed, N.J.; Campbell, W.W.; Channell, A.M.; Chassagne, P.; Culp, K.R.; Fletcher, S.J.; Fortes, M.B.; Fuller, N.; et al. Clinical symptoms, signs and tests for identification of impending and current water-loss dehydration in older people. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 2015, CD009647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladey, J.; Corbett, J.; Forni, L.; Hooper, L.; Hughes, F.; Minto, G.; Moss, C.; Price, S.; Whyte, G.; Woodcock, T.; et al. A multidisciplinary consensus on dehydration: Definition, diagnostic methods and clinical implications. Ann. Med. 2019, 51, 232–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.R.; Cote, T.R.; Lawhorne, L.; Levenson, S.A.; Rubenstein, L.Z.; Smith, D.A.; Stefanacci, R.G.; Tangalos, E.G.; Morley, J.E.; Dehydration Council. Understanding clinical dehydration and its treatment. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2008, 9, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, M.H.; Barstow, C.H.; Pyzocha, N.J. Diagnosis and management of sodium disorders: Hyponatremia and hypernatremia. Am. Fam. Physician 2015, 91, 299–307. [Google Scholar]
- Lombardi, G.; Ferraro, P.M.; Calvaruso, L.; Naticchia, A.; D’Alonzo, S.; Gambaro, G. Sodium fluctuations and mortality in a general hospital population. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2019, 44, 604–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolini, E.A.; Nunes, R.S.; Santos, G.V.; da Silva, S.L.; Carreira, M.M.; Pellison, F.G.; Menegueti, M.G.; Auxiliadora-Martins, M.; Bellissimo-Rodrigues, F.; Feres, M.A.; et al. Could dysnatremias play a role as independent factors to predict mortality in surgical critically ill patients? Medicine 2017, 96, e6182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pringle, K.; Shah, S.P.; Umulisa, I.; Munyaneza, R.B.M.; Dushimiyimana, J.M.; Stegmann, K.; Musavuli, J.; Ngabitsinze, P.; Stulac, S.; Levine, A.C. Comparing the accuracy of the three popular clinical dehydration scales in children with diarrhea. Int. J. Emerg. Med. 2011, 4, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunn, D.K.; Hooper, L. Signs and symptooms of low-intake dehydration do not work in older care home residents, DRIE diagnostic study. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2019, 20, 963–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.S.; Wong, H.L.; Ip, Y.L.; Peng, Z.; Yiu, R.; Yuan, H.; Wong, J.K.W.; Chan, Y.K. Current and future perspectives on microfluidic tear analytic devices. ACS Sens. 2022, 7, 1300–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Jiang, N.; Bikkannavar, P.; Cordeiro, M.F.; Yetisen, A.K. Ophthalmic sensing technologies for ocular disease diagnostics. Analyst 2021, 146, 6416–6444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, M.; Birkenfeld, J.S.; Butterworth, I. Noninvasive monitoring to detect dehydration: Are we there yet? Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2023, 25, 23–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherz, W.; Doane, M.G.; Dohlman, C.H. Tear volume in normal eyes and keratoconjunctivitis sicca. Albrecht Von Graefes Arch. Klin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 1974, 192, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Haeringen, N.J. Clinical biochemistry of tears. Surv. Ophthalmol. 1981, 26, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishihara, K.; Shi, X.; Fukazawa, K.; Yamaoka, T.; Yao, G.; Wu, J.Y. Biomimetic-Engineered Silicone Hydrogel Contact Lens Materials. ACS Appl. Bio. Mater. 2023, 6, 3600–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tranoudis, L.; Efron, N. Tensile properties of soft contact lens materials. Contact Lens Anterior Eye 2004, 27, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vhamra, T.S.; Tighe, B.J. Mechanical properties of contact lenses: The contribution of measurement techniques and clinical feedback to 50 years of materials development. Contact Lens Anterior Eye 2016, 40, 70–81. [Google Scholar]
- Klimant, I.; Wolfbeis, O.S. Oxygen-sensitive luminescent materials based on silicone-soluble ruthenium diimine complexes. Anal. Chem. 1995, 67, 3160–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trettnak, W.; Gruber, W.; Reininger, F.; Klimant, I. Recent progress in optical oxygen sensor instrumentation. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1995, 29, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bambrick, I.L.; Kostov, Y.; Rao, G. In vitro cell culture pO2 is significantly different from incubator pO2. Am. J. Chem. Eng. 2011, 27, 1185–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano, F.N.; Lakowicz, J.R. A water-soluble luminescence oxygen sensor. Photochem. Photobiol. 1998, 67, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savariraj, A.D.; Salih, A.; Alam, F.; Elsherif, M.; Al Qattan, B.; Khan, A.K.; Yetisen, A.K.; Butt, H. Ophthalmic sensors and drug delivery. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 2046–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badugu, R.; Reece, E.A.; Lakowicz, J.R. Glucose-sensitive silicone hydrogel contact lens toward tear glucose monitoring. J. Biomed. Opt. 2018, 23, 057006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badugu, R.; Jeng, B.H.; Reece, E.A.; Lakowicz, J.R. Contact lens to measure individual ion concentrations in tears and applications to dry eye disease. Anal. Biochem. 2018, 542, 84–94. [Google Scholar]
- Badugu, R.; Szmacinski Reece, E.A.; Jeng, B.H.; Lakowicz, J.R. Fluorescent contact lens for continuous non-invasive measurements of sodium and chloride ion concentrations in tears. Anal. Biochem. 2020, 608, 113902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badugu, R.; Szmacinski, H.; Reece, E.A.; Jeng, B.H.; Lakowicz, J.R. Sodium-sensitive contact lens for diagnostics of ocular pathologies. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 331, 129434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivashanmugan, K.; Reece, E.A.; Lakowicz, J.R. On the Possibility of Fluorescent Capture Immunoassays on a Contact Lens. Biosensors 2025, 15, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gromacki, S.J. Caring for Soft Prosthetic Contact Lenses. Contact Lens Spectrum/Special Edition. 1 May 2013, p. 13. Available online: https://www.clspectrum.com/issues/2013/may/contact-lens-care-compliance/ (accessed on 1 May 2013).
- Dart, J.K.G.; Radford, C.F.; Minassian, D.; Verma, S.; Stapleton, F. Risk factors for microbial keratitis with contemporary contact lenses. Ophthalmology 2008, 115, 1647–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaduto, R.C.; Grotyohann, L.W. Measurement of mitochondrial potential using fluorescent rhodamine derivatives. Biophys. J. 1999, 76, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reungpatthanaphong, P.; Dechsupa, S.; Meesungnoen, J.; Loetchutiant, C.; Mankhetkorn, S. Rhodamine B as a mitochondrial probe for measurement and monitoring of mitochondrial membrane potential in drug sensitive and resistant cells. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2003, 57, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szmacinski, H.; Lakowicz, J.R. Frequency-domain lifetime measurements and sensing In highly scattering media. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1996, 30, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szmacinski, H.; Lakowicz, J.R. Optical measurements of pH using fluorescence lifetimes and phase-modulation fluorometry. Anal. Chem. 1993, 85, 1668–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakowicz, J.R.; Szmacinski, H.; Nowaczyk, K.; Berndt, K.W.; Johnson, M.L. Fluorescence lifetime imaging. Anal. Biochem. 1992, 202, 316–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhling, K.; Hirvonen, L.M.; Levitt, J.A.; Chung, P.-H.; Tregidgo, C.; Le Marois, A.; Rusakov, D.A.; Zheng, K.; Ameer-Beg, S.; Poland, S.; et al. Fluorescence lifetime imaging (FLIM): Basic concepts and some recent developments. Med. Photonics 2014, 27, 3–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhaes, N.; Simoes, G.M.; Ramos, C.; Samelo, J.; Oliveira, A.C.; Filipe, H.A.L.; Moreno, M.J.; Loura, L.M.S. Interactions between Rhodamine dyes and model membrane systems—Insights from Molecular Dynamics simulations. Molecules 2022, 27, 1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Du, W.; Hu, Z.; Uvdal, K.; Li, L.; Huang, W. Hybrid rhodamine fluorophores in the visible NIR region for biological imaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 14026–14043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Xiao, Y.; Qian, X.; Zhao, D.; Xu, Y. A design concept of long wavelength fluorescent analogs of rhodamine dyes: Replacement of oxygen with silicon atom. Chem. Commun. 2008, 15, 1780–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Fang, X.; Qiao, Q.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z. Quantitative assessment of rhodamine spectra. Chin. Chem. Letts. 2021, 32, 943–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueyama, H.; Takagi, M.; Takenaka, S. A novel potassium sensing in aqueous media with a synthetic oligonucleotide derivative, fluorescence resonance energy transfer associated with guanine quartet potassium ion complex formation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 14286–14287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CoroNa Red as a Potential Probe for Intracellular Sodium Imaging. FDSS Appl. Note No. 2. 10 March 2013. Hamamatsu Photonics. Available online: https://www.hamamatsu.com/content/dam/hamamatsu-photonics/sites/documents/99_SALES_LIBRARY/sys/SBIS0006E_FDSS_ap02.pdf (accessed on 9 June 2025).
- Boens, N.; Leen, V.; Dehaen, W. Fluorescent indicators based on BODIPY. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 1130–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, T.; Terai, T.; Komatsu, T.; Hanaoka, K.; Nagano, T. Development of a potassium ion-selective fluorescent sensor based on 3-styrylated BODIPY. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Letts. 2011, 21, 6090–6093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakowicz, J.R.; Badugu, R.; Sivashanmugan, K.; Reece, E.A. Remote measurements of tear electrolyte concentrations on both sides of an inserted contact lens. Chemosenors 2023, 11, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, T.A.; Papayassiliou, D.V.; Lee, L.L.; Striolo, A. Liquid water can slip on a hydrophilic surface. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 16170–16175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Zhang, L.; Monga, D.; Stone, H.A.; Dai, X. Hydrophilic slippery surface enabled coarsening effect for rapid water harvesting. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2021, 4, 100387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanduc, M.; Schlaich, A.; Schneck, E.; Netz, R.R. Water mediated interactions between hydrophilic and hydrophobic surfaces. Langmuir 2016, 32, 8767–8782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webber, W.R.S.; Jones, D.P.; Wright, P. Fluorophotometric measurements of tear turnover rate in normal healthy persons: Evidence for a circadian rhythm. Eye 1987, 1, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, M.; Lee, M.-S.; Kim, K.; Ji, S.; Kim, Y.-T.; Park, J.; Na, K.; Bae, K.-H.; Kim, H.K.; et al. Wearable smart sensor systems integrated on soft contact lenses for wireless ocular diagnostics. Nat. Comm. 2017, 8, 14997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsherif, M.; Moreddu, R.; Alam, F.; Salih, A.E.; Ahmed, I.; Butt, H. Wearable smart contact lenses for continual glucose monitoring: A review. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 858784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, K.H.; Desai, D.T.; Patel, H.P.; Shah, D.O.; Willcox, M.D.P.; Maulvi, F.A. Contact lens as an emerging platform for non-invasive bio-sensing: A Review. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2024, 376, 115617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sivashanmugan, K.; Albert, R.E.; Lakowicz, J.R. First Design of a Contact Lens for Diagnosis of Dehydration. Biosensors 2025, 15, 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15080532
Sivashanmugan K, Albert RE, Lakowicz JR. First Design of a Contact Lens for Diagnosis of Dehydration. Biosensors. 2025; 15(8):532. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15080532
Chicago/Turabian StyleSivashanmugan, Kundan, Reece E. Albert, and Joseph R. Lakowicz. 2025. "First Design of a Contact Lens for Diagnosis of Dehydration" Biosensors 15, no. 8: 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15080532
APA StyleSivashanmugan, K., Albert, R. E., & Lakowicz, J. R. (2025). First Design of a Contact Lens for Diagnosis of Dehydration. Biosensors, 15(8), 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15080532





